概要
选择率是指:根据数据库统计信息,计算出一个约束条件过滤掉的数据,过滤出的数据量占总数据量的占比就是选择率。
-
选择率的计算依赖于数据库统计信息,如果没有统计信息时,则会给出一些默认值;
-
如果有相关统计信息,则会根据统计信息进行计算。
统计信息
create table t1 (id int, c2 text);
alter table t1 add constraint pk_t1_id primary key (id);
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION generate_data()
RETURNS int AS $$
DECLARE
i INT;
start INT;
row_count INT := 20000;
val INT;
BEGIN
SELECT COUNT(*) INTO start FROM t1;
FOR i IN SELECT generate_series(1, row_count) LOOP
INSERT INTO t1 VALUES (start + i, left(pg_catalog.random()::text, 7));
END LOOP;
-- set null value
val := abs(right(pg_catalog.random(), 2)::int - right(pg_catalog.random(), 2)::int);
i := 1;
FOR i IN SELECT generate_series(1, val) LOOP
start := start * (right(pg_catalog.random(), 1)::int);
UPDATE t1 SET c2 = NULL WHERE id = start;
END LOOP;
RETURN row_count;
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
select generate_data();
analyze t1;
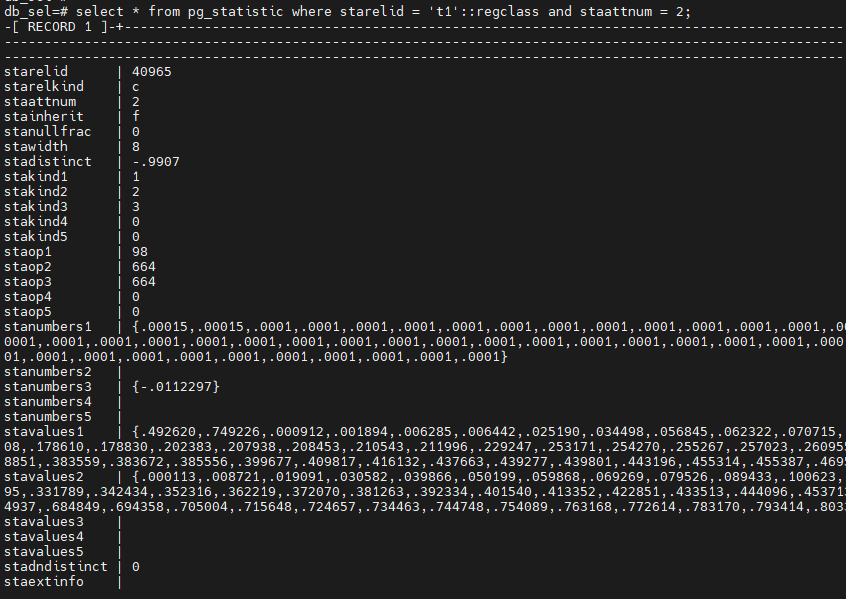
表的统计信息存储在系统表 pg_statistic中,可以通过 ANALYZE table 来生成表的统计信息:
| 名称 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| starelid | oid | 所描述的字段所属的表或者索引。 |
| starelkind | “char” | 所属对象的类型。 |
| staattnum | smallint | 所描述的字段在表中的编号,从1开始。 |
| stainherit | boolean | 是否统计有继承关系的对象。 |
| stanullfrac | real | 该字段中为NULL的记录的比率。 |
| stawidth | integer | 非NULL记录的平均存储宽度,以字节计。 |
| stadistinct | real | 标识全局统计信息中数据库节点上字段里唯一的非NULL数据值的数目。一个大于零的数值是独立数值的实际数目。一个小于零的数值是表中行数的分数的负数(比如,一个字段的数值平均出现概率为两次,则可以表示为stadistinct=-0.5)。零值表示独立数值的数目未知。 |
| stakindN | smallint | 一个编码,表示这种类型的统计存储在pg_statistic行的第n个“槽位”。n的取值范围:1~5 |
| staopN | oid | 一个用于生成这些存储在第n个“槽位”的统计信息的操作符。比如,一个柱面图槽位会显示<操作符,该操作符定义了该数据的排序顺序。n的取值范围:1~5 |
| stanumbersN | real[] | 第n个“槽位”的相关类型的数值类型统计,如果该槽位和数值类型没有关系,则就是NULL。n的取值范围:1~5 |
| stavaluesN | anyarray | 第n个“槽位”类型的字段数据值,如果该槽位类型不存储任何数据值,则就是NULL。每个数组的元素值实际上都是指定字段的数据类型,因此,除了把这些字段的类型定义成anyarray之外,没有更好地办法。n的取值范围:1~5 |
| stadndistinct | real | 标识dn1上字段里唯一的非NULL数据值的数目。一个大于零的数值是独立数值的实际数目。一个小于零的数值是表中行数的分数的负数(比如,一个字段的数值平均出现概率为两次,则可以表示为stadistinct=-0.5)。零值表示独立数值的数目未知。 |
| staextinfo | text | 统计信息的扩展信息。预留字段。 |
其中stakindN表示统计信息的类型,常见的类型如下:
| 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| STATISTIC_KIND_MVC | 高频值,在一个列里出现最频繁的值,按照出现频率进行排序,并且生成一个一一对应的频率数组。 |
| STATISTIC_KIND_HISTOGRAM | 直方图,openGuass用等频率直方图来描述一个列中分布数据的分布,高频值不会出现在直方图中。 |
| STATISTIC_KIND_CORRELATION | 相关系数,相关系数记录的是当前列未排序的数据分布和排序后数据分布的相关性,这个用于索引扫描时来进行代价估算。如排序和未排序后的相关性为0,则索引扫描的代价就会高一些。 |
stakindN、stanumbersN与stavaluesN一起构成一个卡槽,例如如下数据:stakind1=1表示STATISTIC_KIND_MVC为高频率值,stavalues1则表示高频值的数组,stanumbers1则表示每个高频值对应的频率值的数组;stakind2=3表示STATISTIC_KIND_HISTOGRAM为直方图,则stavalues2表示直方图的数据
select * from pg_statistic where starelid = 't1'::regclass and staattnum = 2;
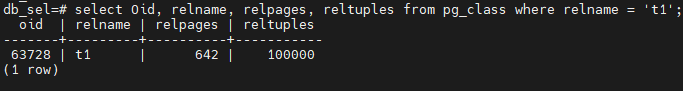
此外,在ANALYZE之后,还会在pg_class中使用reltuples存储表中的行数,使用relpages存储磁盘使用的页。
select Oid, relname, relpages, reltuples from pg_class where relname = 't1';
选择率计算
前面介绍过选择率的计算依赖于统计信息,例如高频值、直方图、NULL值率等来计算选择率。
选择率计算代码入口函数为clause_selectivity。
这里介绍比较常用的OpExpr对应的选择率计算,不同的操作符有不同的计算方式,以下是一些常用操作符对应的执行函数:
| 操作符 | 函数 |
|---|---|
= |
eqsel |
<> |
neqsel |
<、<= |
scalarltsel_internal |
>、>= |
scalargtsel |
like |
likesel |
用以下SQL作为示例:
-- 非高频值
select * from t1 where c2 = '.734463';
- 如果不是
Var = Const这种情形,则返回默认值DEFAULT_EQ_SEL,以下是一些默认值
/* default selectivity estimate for equalities such as "A = b" */
#define DEFAULT_EQ_SEL 0.005
/* default selectivity estimate for inequalities such as "A < b" */
#define DEFAULT_INEQ_SEL 0.3333333333333333
/* default selectivity estimate for range inequalities "A > b AND A < c" */
#define DEFAULT_RANGE_INEQ_SEL 0.005
/* default selectivity estimate for pattern-match operators such as LIKE */
#define DEFAULT_MATCH_SEL 0.005
/* default number of distinct values in a table */
#define DEFAULT_NUM_DISTINCT 200
/* default number of rows */
#define DEFAULT_NUM_ROWS 10
/* default number of distinct values and biase for the special expression */
#define DEFAULT_SPECIAL_EXPR_DISTINCT 10
#define DEFAULT_SPECIAL_EXPR_BIASE (pow(u_sess->pgxc_cxt.NumDataNodes, (double)1 / 2) / u_sess->pgxc_cxt.NumDataNodes)
/* default selectivity estimate for boolean、null、nan、infinite test nodes */
#define DEFAULT_UNK_SEL 0.005
#define DEFAULT_NOT_UNK_SEL (1.0 - DEFAULT_UNK_SEL)
/* default selectivity estimate for neq anti join */
#define MIN_NEQ_ANTI_SEL 0.05
#define MAX_NEQ_SEMI_SEL (1.0 - MIN_NEQ_ANTI_SEL)
/*
* If expression is not variable = something or something = variable, then
* punt and return a default estimate.
*/
if (!get_restriction_variable(root, args, varRelid, &vardata, &other, &varonleft)) {
/*
* For Var=Var cases, return non-null frac instead of DEFAULT_EQ_SEL.
* This is to avoid selectivity underestimate.
*/
if (is_var_eq_var_expr(args)) {
Node* left = (Node*)linitial(args);
selec = nulltestsel(root, IS_NOT_NULL, left, varRelid, JOIN_INNER, NULL);
PG_RETURN_FLOAT8((float8)selec);
}
PG_RETURN_FLOAT8(DEFAULT_EQ_SEL);
}
- 如果查询列正好具有唯一性约束,则直接返回
1 / tuples;
/*
* If we matched the var to a unique index or DISTINCT clause, assume
* there is exactly one match regardless of anything else. (This is
* slightly bogus, since the index or clause's equality operator might be
* different from ours, but it's much more likely to be right than
* ignoring the information.)
*/
if (vardata->isunique && vardata->rel && vardata->rel->tuples >= 1.0)
return 1.0 / vardata->rel->tuples;
- 如果该列统计信息存在高频值,并且查询常量直接存在于高频值数组中,则直接返回对应频率即可;
/*
* Is the constant "=" to any of the column's most common values?
* (Although the given operator may not really be "=", we will assume
* that seeing whether it returns TRUE is an appropriate test. If you
* don't like this, maybe you shouldn't be using eqsel for your
* operator...)
*/
if (get_attstatsslot(vardata->statsTuple,
vardata->atttype,
vardata->atttypmod,
STATISTIC_KIND_MCV,
InvalidOid,
NULL,
&values,
&nvalues,
&numbers,
&nnumbers)) {
FmgrInfo eqproc;
fmgr_info(opfuncoid, &eqproc);
for (i = 0; i < nvalues; i++) {
/* be careful to apply operator right way 'round */
if (varonleft)
match = DatumGetBool(FunctionCall2Coll(&eqproc, DEFAULT_COLLATION_OID, values[i], constval));
else
match = DatumGetBool(FunctionCall2Coll(&eqproc, DEFAULT_COLLATION_OID, constval, values[i]));
if (match)
break;
}
} else {
/* no most-common-value info available */
values = NULL;
numbers = NULL;
i = nvalues = nnumbers = 0;
}
if (match) {
selec = numbers[i];
- 高频值中没有出现,则首先会减去
1.0 - (sum(mvc) + stanullfrac)的值selec;
/*
* Comparison is against a constant that is neither NULL nor any
* of the common values. Its selectivity cannot be more than
* this:
*/
double sumcommon = 0.0;
double otherdistinct;
double extrapolationselec = 0.0;
for (i = 0; i < nnumbers; i++)
sumcommon += numbers[i];
selec = 1.0 - sumcommon - stats->stanullfrac;
- 获取去重后的除了NULL和高频值之外的其它剩余元组数量
distinctTuple;
otherdistinct = get_variable_numdistinct(vardata, &isdefault, false, 1.0, NULL, STATS_TYPE_GLOBAL) - nnumbers;
- 如果开启了参数
var_eq_const_selectivity并且是整数类型,则直接使用直方图计算整型常量的选择率;
static double var_eq_const_selectivity(VariableStatData *vardata, double selec, double otherdistinct, Datum constval) { if (u_sess->attr.attr_sql.var_eq_const_selectivity == true && IsIntType(vardata->atttype)) { double hist_selec = var_eq_const_histogram(vardata, selec, otherdistinct, constval); ...... } return selec; }
- 再用
selec / distincTuple得到最终选择率;
if (otherdistinct > 1)
selec /= otherdistinct;
- 最后进行选择率的修正,既然该值没有出现在高频值中,那么其选择率就不能大于高频值中数据的选择率。
if (nnumbers > 0 && selec > numbers[nnumbers - 1])
selec = numbers[nnumbers - 1];
「喜欢这篇文章,您的关注和赞赏是给作者最好的鼓励」
关注作者
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文章的来源(墨天轮),文章链接,文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






