探究问题
本篇笔记文章主要记录 citus 分片表在涉及分片键的查询/写入,可下推情况下的优化器执行步骤。
通过本篇笔记,可以回答如下的四个问题:
- citus 复用了哪些 hook,执行复用的路径是怎么样的?
- 优化器层面如何确定 id 所在分片位置,查询了哪些元数据表?
- 优化器发送了哪些 query,确认执行计划?
执行例子
-- 创建分片表
CREATE TABLE t1(c1 int primary key,c2 int);
INSERT INTO t1 SELECT generate_series(1,1000),generate_series(1,1000);
SELECT create_distributed_table('t1','c1');
-- 执行简单查询
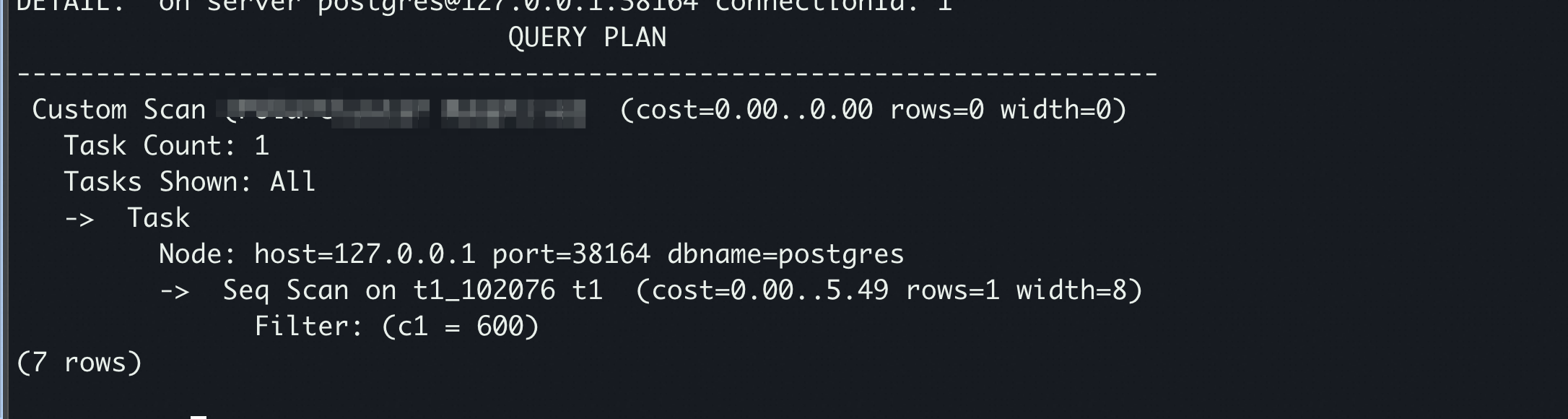
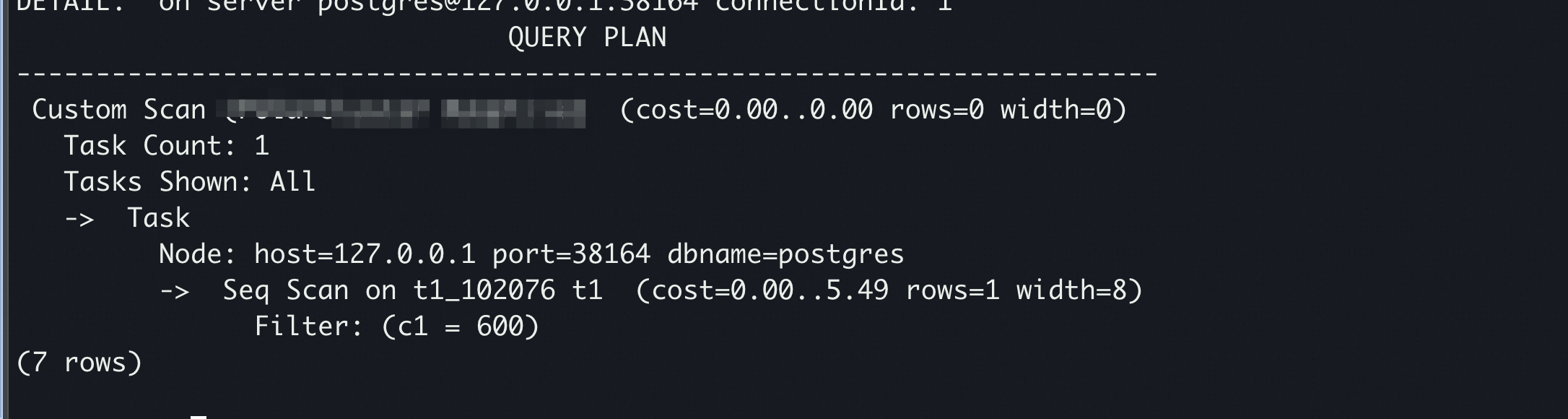
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE c1=6666;
执行步骤
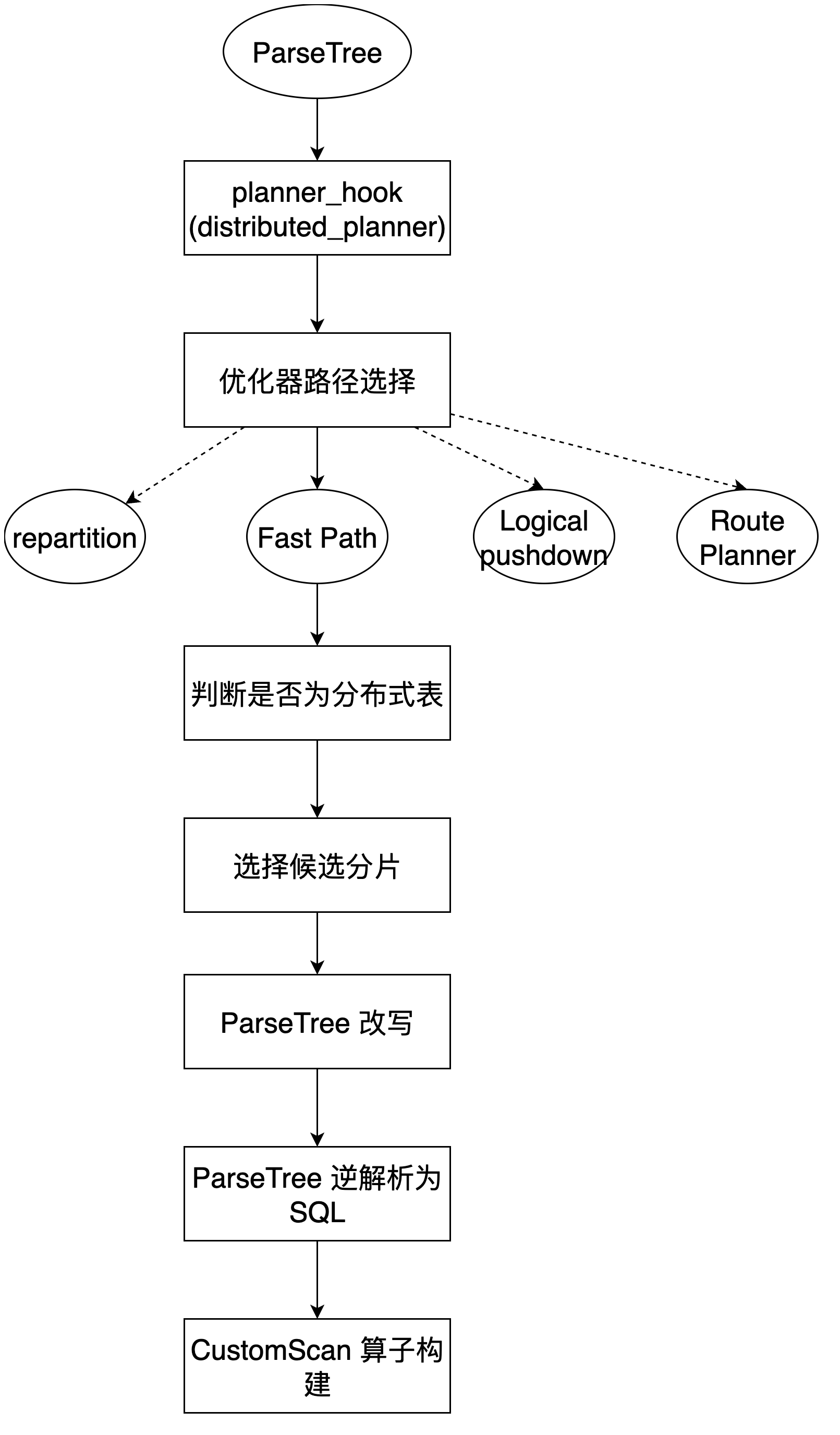
步骤流程图
执行流程
- citus 并没有入侵 SQL 生成 parseTree 的阶段,仍然按照原生 PG 的逻辑生成 parseTree。
- citus 重载了 ,将 parseTree 构建为分布式计划。
distributed_planner 函数的基本逻辑可以用下面代码进行说明:
PlannedStmt *
distributed_planner(Query *parse,
const char *query_string,
int cursorOptions,
ParamListInfo boundParams)
{
if (cursorOptions & CURSOR_OPT_FORCE_DISTRIBUTED)
{
/*
* 仅针对 CTE 这种递归查询的情况,会将 cursorOptions 设置上
* CURSOR_OPT_FORCE_DISTRIBUTED
*/
}
else if (CitusHasBeenLoaded())
{
// 在 load Citus 的情况下,才会生成分布式计划
bool maybeHasForeignDistributedTable = false;
needsDistributedPlanning =
ListContainsDistributedTableRTE(rangeTableList,
&maybeHasForeignDistributedTable);
// 仅在 ParseTree 中含有分布式表的情况下会生成分布式计划(分片表/复制表/添加元数据的本地表)
if (needsDistributedPlanning)
{
// 判断是否能够生成 FastPath 计划
fastPathRouterQuery = FastPathRouterQuery(parse, &distributionKeyValue);
if (maybeHasForeignDistributedTable)
{
WarnIfListHasForeignDistributedTable(rangeTableList);
}
}
// 由于需要从 parseTree 反解析成 SQL,需要将 rewrite 的 relation 进行重新映射
if (needsDistributedPlanning)
{
/*
* standard_planner scribbles on its input, but for deparsing we need the
* unmodified form. Before copying we call AssignRTEIdentities to be able
* to match RTEs in the rewritten query tree with those in the original
* tree.
*/
rteIdCounter = AssignRTEIdentities(rangeTableList, rteIdCounter);
planContext.originalQuery = copyObject(parse);
if (!fastPathRouterQuery)
{
/*
* When there are partitioned tables (not applicable to fast path),
* pretend that they are regular tables to avoid unnecessary work
* in standard_planner.
*/
bool setPartitionedTablesInherited = false;
AdjustPartitioningForDistributedPlanning(rangeTableList,
setPartitionedTablesInherited);
}
}
// 构建分布式计划上下文
DistributedPlanningContext planContext = {
.query = parse,
.cursorOptions = cursorOptions,
.boundParams = boundParams,
};
// 对分片物理表进行隐藏
...
// 生成分布式计划
PlannedStmt *result = NULL;
PG_TRY();
{
if (fastPathRouterQuery)
{
// 如果是 fast_path,则会直接生成 fast path 的执行计划
result = PlanFastPathDistributedStmt(&planContext, distributionKeyValue);
}
else
{
/*
* Call into standard_planner because the Citus planner relies on both the
* restriction information per table and parse tree transformations made by
* postgres' planner.
*/
planContext.plan = standard_planner(planContext.query, NULL,
planContext.cursorOptions,
planContext.boundParams);
if (needsDistributedPlanning)
{
result = PlanDistributedStmt(&planContext, rteIdCounter);
}
else if ((result = TryToDelegateFunctionCall(&planContext)) == NULL)
{
result = planContext.plan;
}
}
}
PG_CATCH();
{
PopPlannerRestrictionContext();
PlannerLevel--;
PG_RE_THROW();
}
PG_END_TRY();
// ... 尾部处理
}
}
下面分别就 中的关键函数进行说明:
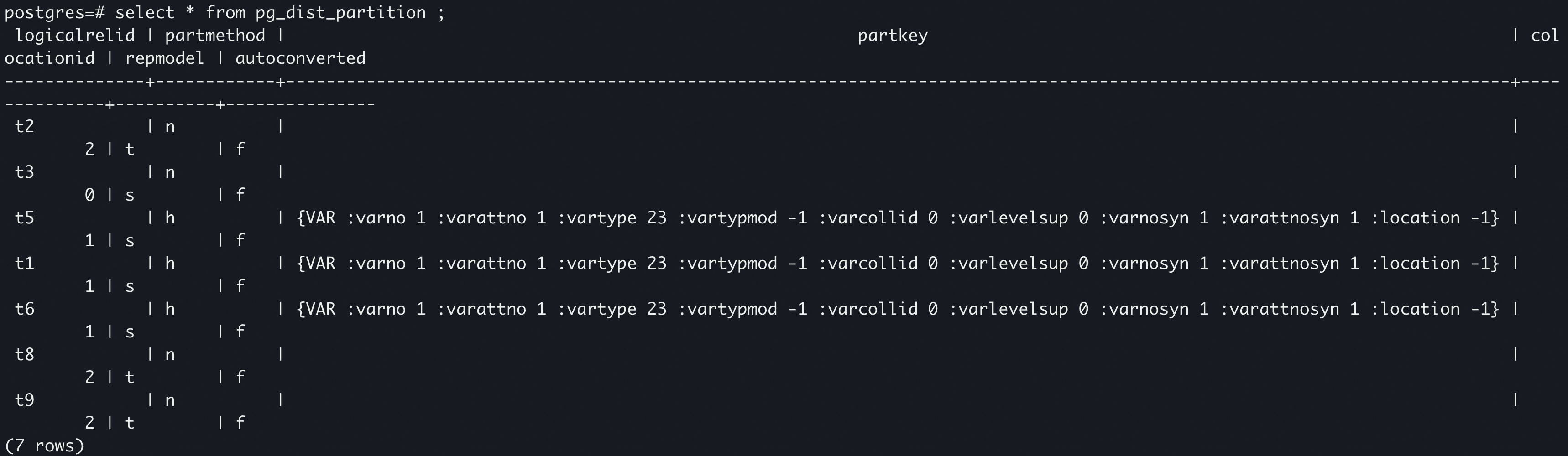
- 该函数用来判断 Query 中是否含有分布式表(分片表/复制表/添加元数据的本地表)
只要在元数据表 中出现过的表就认为是分布式表
- 用于判断是否符合 FastPath query 的生成条件,具体的条件如下所示:
- 查询中不存在任何的 CTE,子查询,set 操作;
- 该条 query 只设计单一 hash 分布式 table 或者复制表;
- WHERE 子句中带有分布键的等值操作符,可以用 in/and/or 相连;
- 不含有 sublinks/CTEs 的 insert 语句
- 函数用于生成分布式计划,下面会进行详细说明
下面就关键函数 FastPath 分布式计划生成进行解析:
执行路径 : -> ->
-> 判断 query 执行类型:
switch (routerPlan)
{
case INSERT_SELECT_INTO_CITUS_TABLE:
{
distributedPlan =
CreateInsertSelectPlan(planId,
originalQuery,
plannerRestrictionContext,
boundParams);
break;
}
case INSERT_SELECT_INTO_LOCAL_TABLE:
{
distributedPlan =
CreateInsertSelectIntoLocalTablePlan(planId,
originalQuery,
boundParams,
hasUnresolvedParams,
plannerRestrictionContext);
break;
}
case DML_QUERY:
{
/* modifications are always routed through the same planner/executor */
distributedPlan =
CreateModifyPlan(originalQuery, query, plannerRestrictionContext);
break;
}
case MERGE_QUERY:
{
distributedPlan =
CreateMergePlan(planId, originalQuery, query, plannerRestrictionContext,
boundParams);
break;
}
case REPLAN_WITH_BOUND_PARAMETERS:
{
/*
* Unresolved parameters can cause performance regressions in
* INSERT...SELECT when the partition column is a parameter
* because we don't perform any additional pruning in the executor.
*/
return NULL;
}
case SELECT_QUERY:
{
/*
* For select queries we, if router executor is enabled, first try to
* plan the query as a router query. If not supported, otherwise try
* the full blown plan/optimize/physical planning process needed to
* produce distributed query plans.
*/
distributedPlan =
CreateRouterPlan(originalQuery, query, plannerRestrictionContext);
break;
}
}
如果是 则先尝试路由计划生成,
->->
是构建路由计划的核心函数,下面以注释的方式解释每一步的执行细节
/*
* RouterJob builds a Job to represent a single shard select/update/delete and
* multiple shard update/delete queries.
*/
/*
* RouterJob 构建一个单一分片的 select/update/delete 和
* 多分片 update/detele queries
*/
Job *
RouterJob(Query *originalQuery, PlannerRestrictionContext *plannerRestrictionContext,
DeferredErrorMessage **planningError)
{
uint64 shardId = INVALID_SHARD_ID;
List *placementList = NIL;
List *relationShardList = NIL;
List *prunedShardIntervalListList = NIL;
bool isMultiShardModifyQuery = false;
Const *partitionKeyValue = NULL;
/* router planner should create task even if it doesn't hit a shard at all */
bool replacePrunedQueryWithDummy = true;
bool isLocalTableModification = false;
/* check if this query requires coordinator evaluation */
/* 检查 query 是否需要协调节点评估 */
bool requiresCoordinatorEvaluation = RequiresCoordinatorEvaluation(originalQuery);
FastPathRestrictionContext *fastPathRestrictionContext =
plannerRestrictionContext->fastPathRestrictionContext;
/*
* We prefer to defer shard pruning/task generation to the
* execution when the parameter on the distribution key
* cannot be resolved.
*/
if (fastPathRestrictionContext->fastPathRouterQuery &&
fastPathRestrictionContext->distributionKeyHasParam)
{
/*
* 根据 originalQuery 生成一个 job
*/
Job *job = CreateJob(originalQuery);
job->deferredPruning = true;
ereport(DEBUG2, (errmsg("Deferred pruning for a fast-path router "
"query")));
return job;
}
else
{
(*planningError) = PlanRouterQuery(originalQuery, plannerRestrictionContext,
&placementList, &shardId, &relationShardList,
&prunedShardIntervalListList,
replacePrunedQueryWithDummy,
&isMultiShardModifyQuery,
&partitionKeyValue,
&isLocalTableModification);
}
if (*planningError)
{
return NULL;
}
/* 设置 job 的 partitionKeyValue */
Job *job = CreateJob(originalQuery);
job->partitionKeyValue = partitionKeyValue;
if (originalQuery->resultRelation > 0)
{
RangeTblEntry *updateOrDeleteOrMergeRTE = ExtractResultRelationRTE(originalQuery);
if (updateOrDeleteOrMergeRTE->rtekind == RTE_SUBQUERY)
{
/*
* Not generating tasks for MERGE target relation might
* result in incorrect behavior as source rows with NOT
* MATCHED clause might qualify for insertion.
*/
if (IsMergeQuery(originalQuery))
{
ereport(ERROR, (errcode(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED),
errmsg("Merge command is currently "
"unsupported with filters that "
"prunes down to zero shards"),
errhint("Avoid `WHERE false` clause or "
"any equivalent filters that "
"could prune down to zero shards")));
}
else
{
/*
* If all of the shards are pruned, we replace the
* relation RTE into subquery RTE that returns no
* results. However, this is not useful for UPDATE
* and DELETE queries. Therefore, if we detect a
* UPDATE or DELETE RTE with subquery type, we just
* set task list to empty and return the job.
*/
job->taskList = NIL;
return job;
}
}
}
if (isMultiShardModifyQuery)
{
job->taskList = QueryPushdownSqlTaskList(originalQuery, job->jobId,
plannerRestrictionContext->
relationRestrictionContext,
prunedShardIntervalListList,
MODIFY_TASK,
requiresCoordinatorEvaluation,
planningError);
if (*planningError)
{
return NULL;
}
}
else
{
GenerateSingleShardRouterTaskList(job, relationShardList,
placementList, shardId,
isLocalTableModification);
}
job->requiresCoordinatorEvaluation = requiresCoordinatorEvaluation;
return job;
}
这里的 Job 为代表物理计划中的一个基本逻辑单元,表示一组数据传输的任务,如下计划中的一个 一个 Job,一个 Job 中又可以多个 Tasks 组成,每个 Tasks 表示发往一个节点的任务。
Job 结构体的构成如下所示:
/*
* Job represents a logical unit of work that contains one set of data transfers
* in our physical plan. The physical planner maps each SQL query into one or
* more jobs depending on the query's complexity, and sets dependencies between
* these jobs. Each job consists of multiple executable tasks; and these tasks
* either operate on base shards, or repartitioned tables.
*/
typedef struct Job
{
CitusNode type;
uint64 jobId;
Query *jobQuery;
List *taskList;
List *dependentJobList;
bool subqueryPushdown;
bool requiresCoordinatorEvaluation; /* only applies to modify jobs */
bool deferredPruning;
Const *partitionKeyValue;
/* for local shard queries, we may save the local plan here */
List *localPlannedStatements;
/*
* When we evaluate functions and parameters in jobQuery then we
* should no longer send the list of parameters along with the
* query.
*/
bool parametersInJobQueryResolved;
uint32 colocationId; /* common colocation group ID of the relations */
} Job;
- 函数用于构建路由 Query 计划
/*
* PlanRouterQuery runs router pruning logic for SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, and
* MERGE queries. If there are shards present and query is routable, all RTEs
* have been updated to point to the relevant shards in the originalQuery. Also,
* placementList is filled with the list of worker nodes that has all the
* required shard placements for the query execution. anchorShardId is set to
* the first pruned shardId of the given query. Finally, relationShardList is
* filled with the list of relation-to-shard mappings for the query.
*
* If the given query is not routable, it fills planningError with the related
* DeferredErrorMessage. The caller can check this error message to see if query
* is routable or not.
*
* Note: If the query prunes down to 0 shards due to filters (e.g. WHERE false),
* or the query has only read_intermediate_result calls (no relations left after
* recursively planning CTEs and subqueries), then it will be assigned to an
* arbitrary worker node in a round-robin fashion.
*
* Relations that prune down to 0 shards are replaced by subqueries returning
* 0 values in UpdateRelationToShardNames.
*/
DeferredErrorMessage *
PlanRouterQuery(Query *originalQuery,
PlannerRestrictionContext *plannerRestrictionContext,
List **placementList, uint64 *anchorShardId, List **relationShardList,
List **prunedShardIntervalListList,
bool replacePrunedQueryWithDummy, bool *multiShardModifyQuery,
Const **partitionValueConst,
bool *isLocalTableModification)
{
bool isMultiShardQuery = false;
DeferredErrorMessage *planningError = NULL;
bool shardsPresent = false;
CmdType commandType = originalQuery->commandType;
Oid targetRelationId = InvalidOid;
bool fastPathRouterQuery =
plannerRestrictionContext->fastPathRestrictionContext->fastPathRouterQuery;
*placementList = NIL;
/*
* When FastPathRouterQuery() returns true, we know that standard_planner() has
* not been called. Thus, restriction information is not avaliable and we do the
* shard pruning based on the distribution column in the quals of the query.
*/
if (fastPathRouterQuery)
{
/* 获取常量的分布键 KeyValue 值, */
Const *distributionKeyValue =
plannerRestrictionContext->fastPathRestrictionContext->distributionKeyValue;
List *shardIntervalList =
TargetShardIntervalForFastPathQuery(originalQuery, &isMultiShardQuery,
distributionKeyValue,
partitionValueConst);
Assert(!isMultiShardQuery);
*prunedShardIntervalListList = shardIntervalList;
ereport(DEBUG2, (errmsg("Distributed planning for a fast-path router "
"query")));
}
else
{
*prunedShardIntervalListList =
TargetShardIntervalsForRestrictInfo(plannerRestrictionContext->
relationRestrictionContext,
&isMultiShardQuery,
partitionValueConst);
}
if (isMultiShardQuery)
{
/*
* If multiShardQuery is true and it is a type of SELECT query, then
* return deferred error. We do not support multi-shard SELECT queries
* with this code path.
*/
if (commandType == CMD_SELECT)
{
return DeferredError(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED,
"Router planner cannot handle multi-shard select queries",
NULL, NULL);
}
Assert(UpdateOrDeleteOrMergeQuery(originalQuery));
if (!IsMergeQuery(originalQuery))
{
planningError = ModifyQuerySupported(originalQuery, originalQuery,
isMultiShardQuery,
plannerRestrictionContext);
}
if (planningError != NULL)
{
return planningError;
}
else
{
*multiShardModifyQuery = true;
return planningError;
}
}
*relationShardList =
RelationShardListForShardIntervalList(*prunedShardIntervalListList,
&shardsPresent);
if (!EnableNonColocatedRouterQueryPushdown &&
!AllShardsColocated(*relationShardList))
{
return DeferredError(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED,
"router planner does not support queries that "
"reference non-colocated distributed tables",
NULL, NULL);
}
if (!shardsPresent && !replacePrunedQueryWithDummy)
{
/*
* For INSERT ... SELECT, this query could be still a valid for some other target
* shard intervals. Thus, we should return empty list if there aren't any matching
* workers, so that the caller can decide what to do with this task.
*/
return NULL;
}
/*
* We bail out if there are RTEs that prune multiple shards above, but
* there can also be multiple RTEs that reference the same relation.
*/
if (RelationPrunesToMultipleShards(*relationShardList))
{
planningError = DeferredError(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED,
"cannot run command which targets "
"multiple shards", NULL, NULL);
return planningError;
}
/* we need anchor shard id for select queries with router planner */
uint64 shardId = GetAnchorShardId(*prunedShardIntervalListList);
/* both Postgres tables and materialized tables are locally avaliable */
RTEListProperties *rteProperties = GetRTEListPropertiesForQuery(originalQuery);
if (isLocalTableModification)
{
*isLocalTableModification =
IsLocalTableModification(targetRelationId, originalQuery, shardId,
rteProperties);
}
bool hasPostgresLocalRelation =
rteProperties->hasPostgresLocalTable || rteProperties->hasMaterializedView;
List *taskPlacementList =
CreateTaskPlacementListForShardIntervals(*prunedShardIntervalListList,
shardsPresent,
replacePrunedQueryWithDummy,
hasPostgresLocalRelation);
if (taskPlacementList == NIL)
{
planningError = DeferredError(ERRCODE_FEATURE_NOT_SUPPORTED,
"found no worker with all shard placements",
NULL, NULL);
return planningError;
}
/*
* If this is an UPDATE or DELETE query which requires coordinator evaluation,
* don't try update shard names, and postpone that to execution phase.
*/
bool isUpdateOrDelete = UpdateOrDeleteOrMergeQuery(originalQuery);
if (!(isUpdateOrDelete && RequiresCoordinatorEvaluation(originalQuery)))
{
UpdateRelationToShardNames((Node *) originalQuery, *relationShardList);
}
*multiShardModifyQuery = false;
*placementList = taskPlacementList;
*anchorShardId = shardId;
return planningError;
}
执行过程如下:
- 如果符合的条件,则直接通过函数获取目标 ShardId。
- 中通过来获取对应的 shardid 区间。citus 中所有根据 value 值计算所在分片都是通过该函数计算。例如,函数也是通过来查询数据对应分片。实现步骤如下:
- 根据 hash 函数计算分片键的 hash 值,假设该值为 a
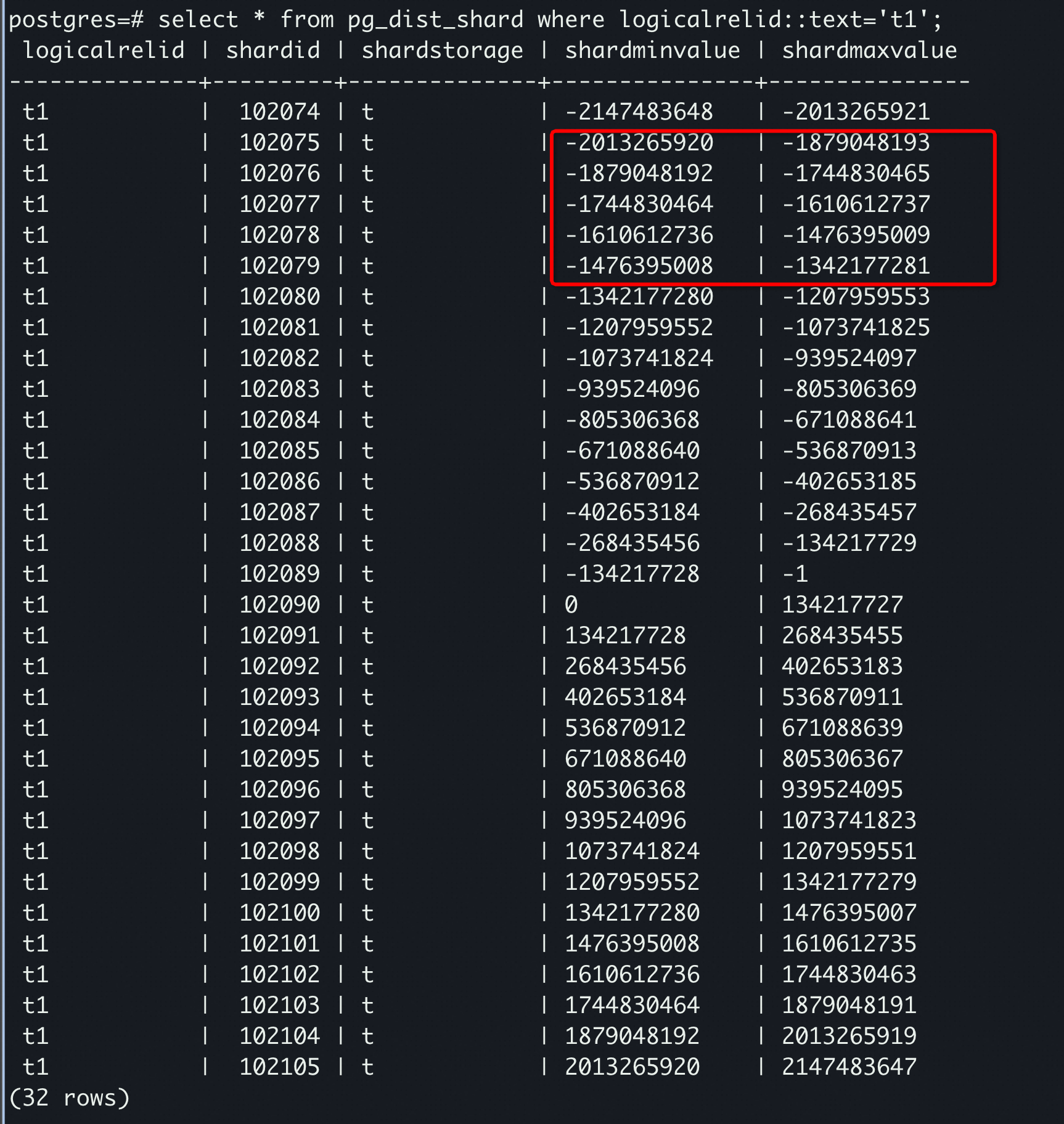
- 通过hash 值 a 去 中二分查询,a 所在 shard 区间,返回对应的 shardid。元数据表结构如下所示,这里保存着每个 shardid 对应的
- 通过 shardid 转换到
- 通过 元数据表找到 shardid->placementid 的映射关系,通过 placementid 可以路由找到 ,也就是 placement 所在的 node。
- 进行 shardid 替换,如果是非 UpdateOrDelete 并且不需要 CN 节点评估的情况下,对 中的 RTE 进行替换。
/*
* If this is an UPDATE or DELETE query which requires coordinator evaluation,
* don't try update shard names, and postpone that to execution phase.
*/
bool isUpdateOrDelete = UpdateOrDeleteOrMergeQuery(originalQuery);
if (!(isUpdateOrDelete && RequiresCoordinatorEvaluation(originalQuery)))
{
UpdateRelationToShardNames((Node *) originalQuery, *relationShardList);
}
- 实现的方式是遍历整棵 ,对逻辑表的 RTE 进行替换。
- 构建完 后,会更新 Job。
- 最后,通过->-> -> 路径从 反解析成 。自此,一个带有分布式 SQL 的分布式计划生成完毕
上面 4 个问题的回答
- citus 复用了哪些 hook,执行复用的路径是怎么样的?
- 优化器层面主要复用了,单独增加了一个 节点来作数据路由和广播
- 优化器层面如何确定 id 所在分片位置,查询了哪些元数据表?
- 通过 表确定是否是分布式表,判断是否筛选条件所在 shardid,来确定分片所在节点。
- 优化器发送了哪些 query,确认执行计划?
- 例如会被替换成 并放入 算子,形成 Job。