Cache Lab
cache lab 缓存实验
代码下载
从CSAPP上面下载对应的lab代码
http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/3e/labs.html
环境准备
需要安装 valgrind
。可以参考文章Valgrind centos。
安装好以后执行valgrind --version
可以看到版本号。
Cache simulator
• cache simulator not a cache
。我们不是实现一个真正的缓存,只是实现一个模拟器。• 不存储内容 • 不使用block offset • 只计算命中数,不命中数和驱逐数(hit count, miss count,eviction count) • 缓存模拟器需要在不同的s,b,E下运行。 • 使用LRU替换策略
Hints
• 使用二维数组 struct cache_line cache[S][E]; • S = 2^s • cache_line 上面说了不需要block offset,所以可以忽略block的内容 • Valid bit • Tag • LRU counter • 通过getopt获取命令行输入 • 返回-1表示没有输入了 • 通常在循环里面接收参数 • 需要包含#include <unistd.h>,#include <getopt.h> • 通常使用switch来处理不同的输入 • 考虑如何处理无效输入 • 更多信息 man 3 getopt • fscanf可以指定要读的流(scanf只能读标准输入流),用来读取trace file • 一个流的指针 • 如何解析文件的信息的格式化字符串 • 其余部分是指向存储解析数据的变量的指针 • 参数 • 通常在循环里使用 • 当命中EOF或者没有匹配到格式化字符串的时候返回-1 • 更多信息 man fscanf • Malloc/free • malloc分配数据到heap • 记得 free 掉malloc的数据 • 不要 free 你没有分配的内存

要求我们实现csim.c
文件,给了一个示例csim-ref
文件。
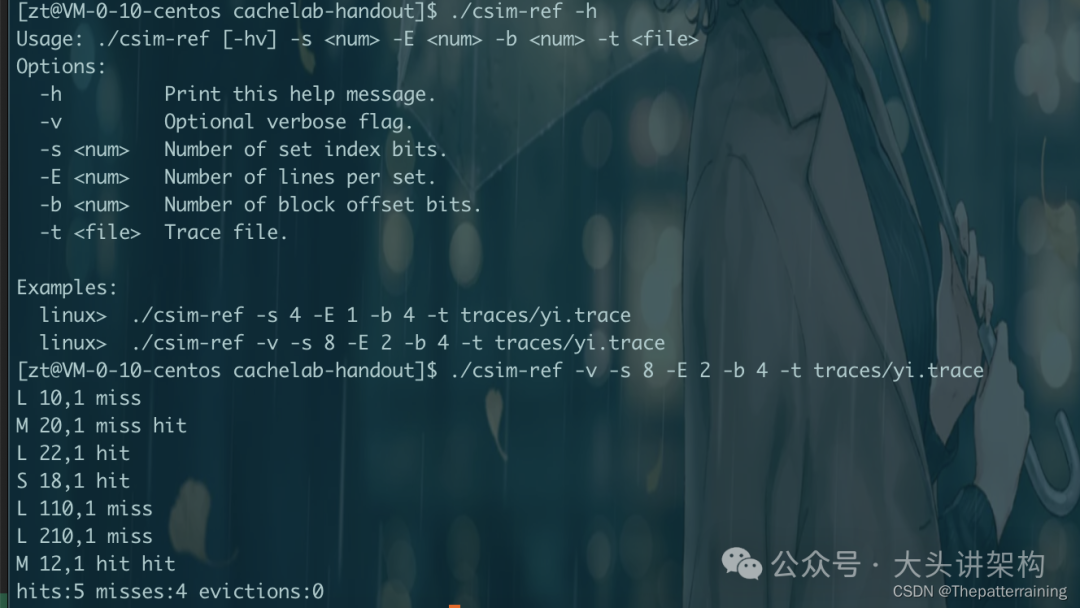
输入./csim-ref -h
可以看到我们要实现的东西。
首先需要接受参数,参数有
• -h 输出帮助信息 • -v 可选详细标志,根据示例程序来,就是输出 L 10,1 miss
这些信息• -s [num] set index bit 数 • -E [num] 每个set的行数 • -b [num] block offset bit数 • -t [file] Trace file文件路径
根据上面的提示可以知道,通过getopt
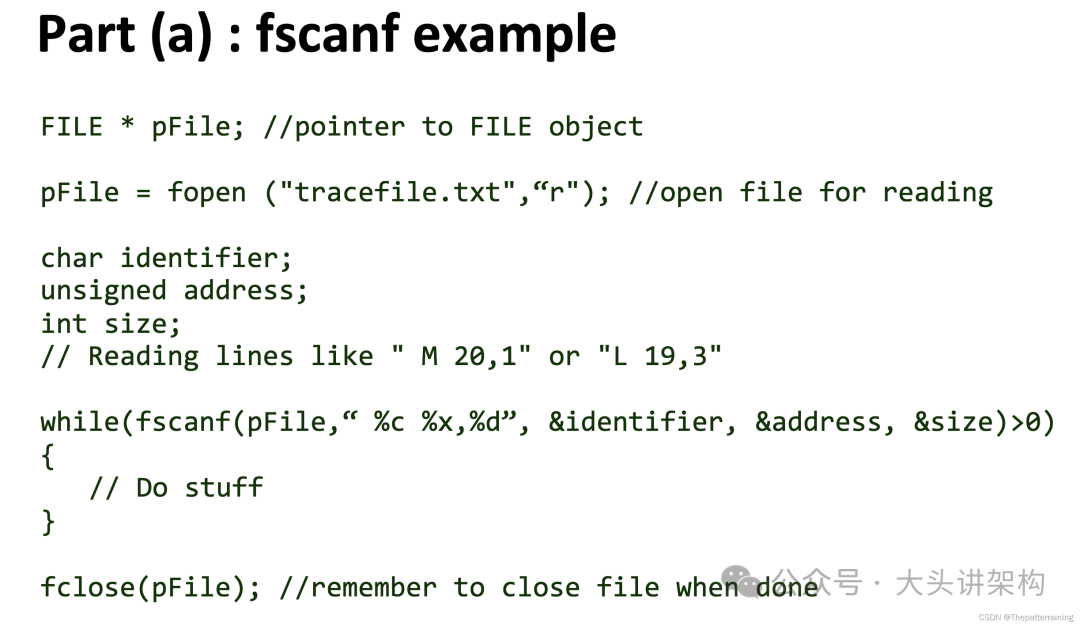
函数来接收参数,并通过switch来处理。读取文件则通过fscanf
函数,来读取-t传的文件。
下面是./traces/yi.trace
文件的内容
L 10,1
M 20,1
L 22,1
S 18,1
L 110,1
L 210,1
M 12,1
• L 代表数据载入 • S 代表数据存储 • M 代表数据修改,需要一次载入 + 一次存储 • 后面的10,20,22这些代表地址 • 最后的1代表操作内存访问的字节数
完整代码
#include "cachelab.h"
#include <unistd.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedefstruct{
int valid;
int tag;
int time_stamp;
} cache_line;
int timestamp =0;
// 开始匹配到合适的set 找到命中的cache,如果命中返回1,如果没有命中返回0
intfind_hit_cache(cache_line *cache_line,int E,int tag, int*hits){
int isHit =0;
// 循环set中的cache_line 找到是否有匹配tag && valid
for(int i =0; i < E; i++){
if(cache_line[i].valid ==1&& cache_line[i].tag == tag ){
//hit
printf("hit \n");
*hits =*hits +1;
isHit =1;
//刷新时间
cache_line[i].time_stamp = timestamp;
return isHit;
}
}
return isHit;
}
// 找到一个空的cache line放进去,找到了就返回1,没有找到就返回0
intfind_empty_cache(cache_line *cache_line,int E,int tag){
int have_empty_cache =0;
for(int i =0; i< E; i++){
if(cache_line[i].valid ==0){
// 空的
// 把当前内存放入cache
cache_line[i].valid =1;
cache_line[i].tag = tag;
cache_line[i].time_stamp = timestamp;
// 找到了就不需要替换了
have_empty_cache =1;
return have_empty_cache;
}
}
return have_empty_cache;
}
// 获取要替换的索引
intget_eviction_index(cache_line *cache_line, int E){
int max_time_stamp = timestamp;
int eviction_index =-1;
for(int i =0; i< E; i++){
if(cache_line[i].time_stamp < max_time_stamp){
//找到time_stamp最小的那个
max_time_stamp = cache_line[i].time_stamp;
eviction_index = i;
}
}
return eviction_index;
}
// LRU替换
voidLRU(cache_line *cache_line, int E,int tag){
// 获取要替换的索引
int eviction_index = get_eviction_index(cache_line, E);
// 替换
cache_line[eviction_index].valid =1;
cache_line[eviction_index].tag = tag;
cache_line[eviction_index].time_stamp = timestamp;
}
// L和S操作,M就调用两次这个
intload_and_store(unsigned address,int b,int s,int u_max,int E,cache_line **cache, int *hits,int *misses,int *evications){
// 获取set index block offset tag
int set_index,tag;
set_index =(address >> b)& u_max;
tag =(address >> b)>> s;
// 开始匹配到合适的set 找到命中的cache,如果命中返回1,如果没有命中返回0
int isHit = find_hit_cache(cache[set_index], E, tag, hits);
if(isHit ==0){
// miss
printf("miss \n");
*misses =*misses +1;
// 找到一个空的cache line放进去,找到了就返回1,没有找到就返回0
int have_empty_cache = find_empty_cache(cache[set_index], E, tag);
// 如果没有找到空的cache,就需要LRU替换
if(have_empty_cache ==0){
printf("evictions \n");
*evications =*evications +1;
//LRU替换
LRU(cache[set_index], E, tag);
}
}
// 更新全局时间戳
timestamp++;
return0;
}
intmain(int argc, char** argv)
{
// 接受参数 getopt
int opt,v,s,E,b,S,B;
// 文件
FILE* pFile;
while(-1!=(opt = getopt(argc, argv,"h?v?s:E:b:t:"))){
// opt is h,v,s,E,b,t的ASCII码值
// 通过switch对不同的参数进行不同的处理
switch(opt){
case'h':
printf("./csim: Missing required command line argument \n Usage: ./csim-ref [-hv] -s <num> -E <num> -b <num> -t <file> \n Options: \n -h Print this help message. \n -v Optional verbose flag. \n -s <num> Number of set index bits. \n -E <num> Number of lines per set. \n -b <num> Number of block offset bits. \n -t <file> Trace file. \n\n Examples: \n ./csim -s 4 -E 1 -b 4 -t traces/yi.trace \n ./csim -v -s 8 -E 2 -b 4 -t traces/yi.trace \n");
// h参数输出帮助内容
break;
case'v':
// v参数输出详细信息
v =1;
printf("v:%d \n",v);
break;
case's':
// S is set 2^s 的数量
// s is Number of set index bits
s = atoi(optarg);
S =1<< s;
printf("s:%d, S:%d \n",s,S);
break;
case'E':
// E is cache line 的数量
// Number of lines per set
E = atoi(optarg);
printf("E:%d \n",E);
break;
case'b':
// B is block data 的字节
// b is Number of block offset bits
b = atoi(optarg);
B =1<< b;
printf("b:%d, B:%d \n",b,B);
break;
case't':
// t is Trace file
// 读取文件
//t = atoi(optarg);
pFile = fopen(optarg,"r");
printf("t:%s, file:%p \n",optarg,pFile);
break;
default:
printf("非法参数 \n");
break;
}
}
if(s ==0|| E ==0|| b ==0){
return0;
}
// cache存储
cache_line **cache =(cache_line **)malloc(S *sizeof(cache_line *));
if(cache ==NULL){
printf("内存分配失败 \n");
}
for(int i =0; i < S; i++){
cache[i]=(cache_line *)malloc(E *sizeof(cache_line));
if(cache[i]==NULL){
printf("内存分配失败,开始回滚 \n");
// 在这里需要释放已分配的内存,然后退出
for(int j =0; j < i;++j){
free(cache[j]);
}
free(cache);
}
}
int u_max =1;
for(int i =0; i < s -1; i++){
u_max =(u_max <<1)|1;
}
// 读取文件
char identifier;
unsigned address;
int size;
int hits,misses,evictions;
// Reading lines like " M 20,1" or "L 19,3"
while(fscanf(pFile," %c %x,%d",&identifier,&address,&size)>0)
{
// Do stuff
// 开始计算 hits,misses,evictions, hits:0 misses:0 evictions:0
//printf("identifier %c, addr:%x, size:%d \n",identifier,address,size);
//根据identifier来判断动作L load S store M = 一次L 一次S
if(identifier =='L'|| identifier =='S'){
printf("identifier %c, addr:%x, size:%d \n",identifier,address,size);
load_and_store(address,b,s,u_max,E,cache,&hits,&misses,&evictions);
}elseif(identifier =='M'){
// 一次L 一次S
printf("identifier %c, addr:%x, size:%d \n",identifier,address,size);
load_and_store(address,b,s,u_max,E,cache,&hits,&misses,&evictions);
load_and_store(address,b,s,u_max,E,cache,&hits,&misses,&evictions);
}
}
fclose(pFile);//remember to close file when done
printSummary(hits, misses, evictions);
// 释放数组内存
for(int i =0; i< S; i++){
free(cache[i]);
}
free(cache);
return0;
}
文章转载自大头讲架构,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






