1. 背景介绍
2. 知识储备
2.1 HBase Snapshot
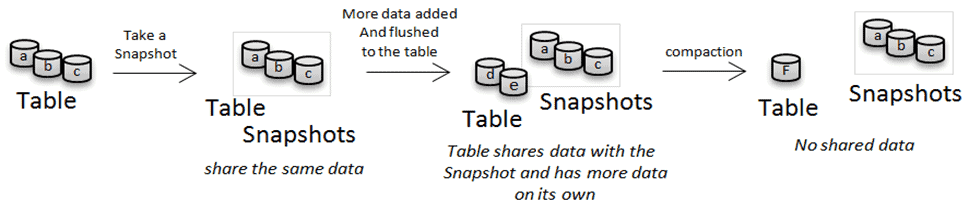 |
2.2 HBase Replication
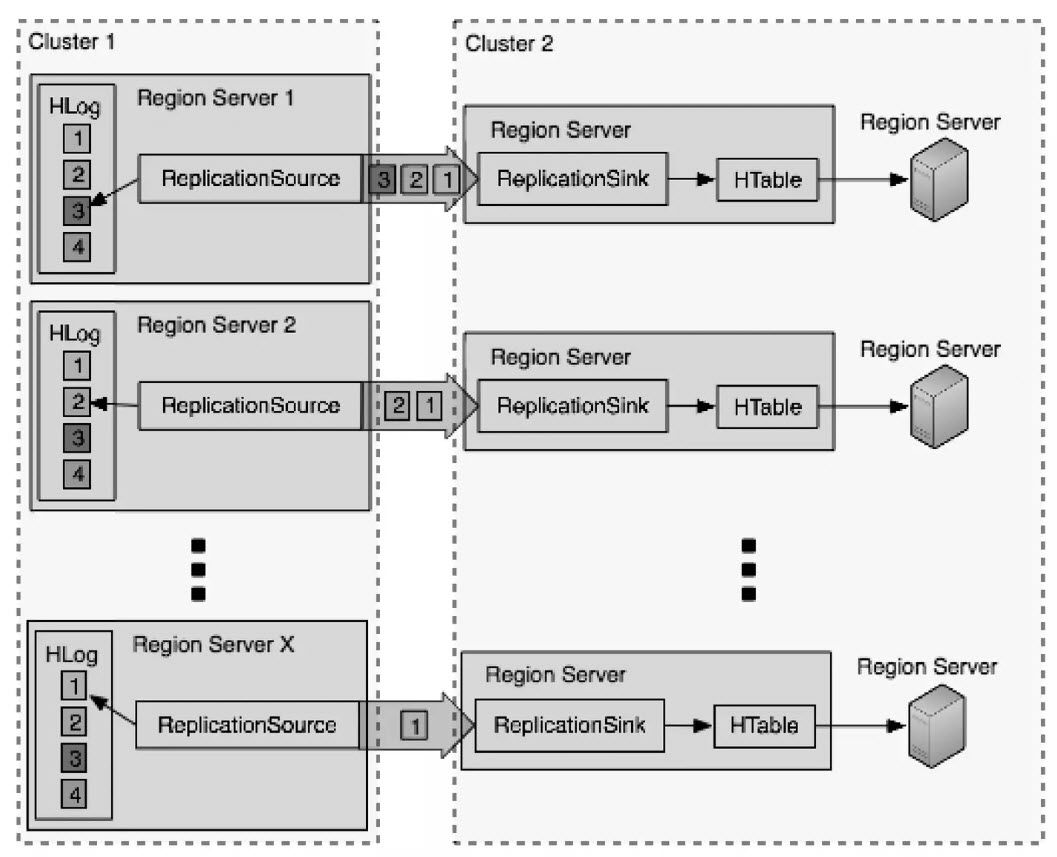 |
数据同步是 RegionServer 和 RegionServer 之间对拷的 (所以 Replication 有一个限速配置:set_peer_bandwidth,限制的也是单台 RegionServer 用于同步 WAL 日志的带宽) RegionServer 会启动独立的线程异步执行 WAL 日志推送和接收 为了保证Region Server 和 Region Server 之间对拷数据的有序性,WAL Log 的 edits 是以队列形式按顺序推送到目标端并进行回放的 在目标端 edits 是以批量方式写入目标表的
3. 方案介绍
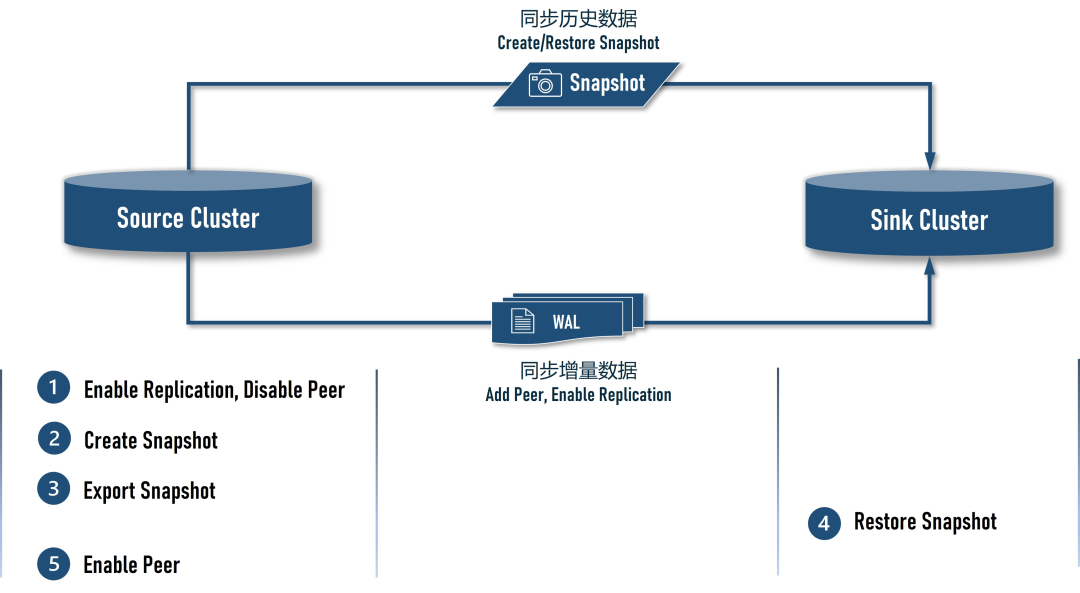 |
在 Source Cluster 上将 Sink Cluster 添加为 peer,但需先 disable peer,然后再 enable 目标表的 replication,目的是让 Source Cluster 在创建前快照前先积累 WAL 日志,避免迁移过程中丢失数据 在 Source Cluster 上创建快照 在 Source Cluster 上将创建好的快照导出到 S3 在 Sink Cluster 上还原快照 在 Source Cluster 上 enable peer,恢复数据同步,直至数据追平
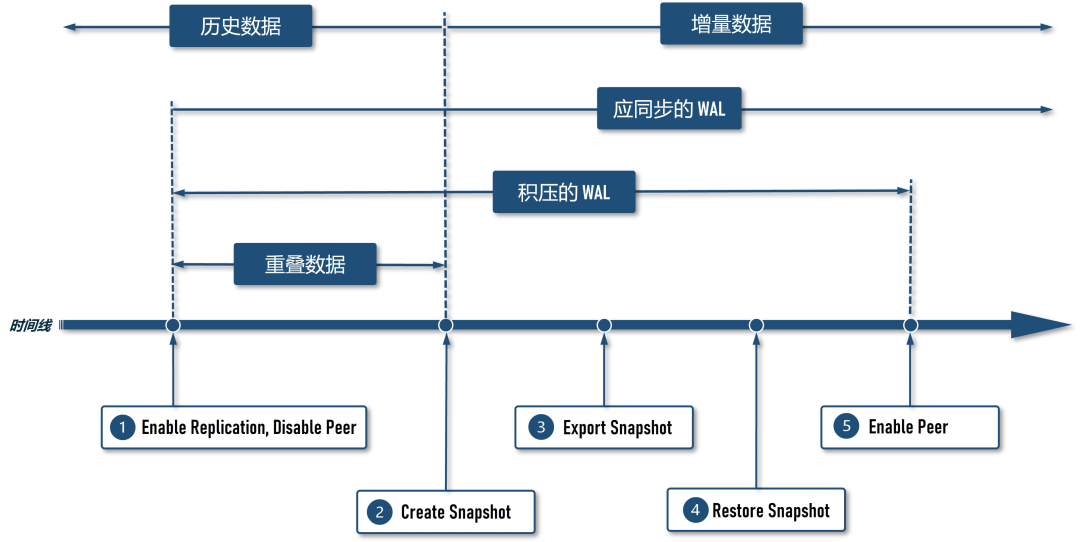 |
4. 环境说明
1.4.9(EMR版本:
5.23.0),集群节点配置是
R5.4xlarge(16 vCore,128 GB),集群规模是 3 个 Master Node + 25 个 Core Node,Source Cluster 和 Sink Cluster 保持一致配置,以下是两个集群的详细信息:
1.4.9 | 1.4.9 | |
5.23.0 | 5.23.0 | |
R5.4xlarge | R5.4xlarge | |
3Master Node + 25Core Node | 3Master Node + 25Core Node | |
50 TB | 50 TB | |
HDFS(EBS) | S3 | |
usertable | usertable | |
9870 | 9870 |
5. 演练操作
本演练的多数命令都需执行较长时间,因此,命令都使用了 nohup ... &
形式转为了后台运行,以防 Linux 终端 Session 超时导致命令意外终止;本演练的操作必须按顺序执行,不可在前一个命令转为后台运行后,立即执行下一条命令; 演练过程中需要在 Source Cluster、Sink Cluster 和 AWS Console 上来回切换,为了提醒操作者,本文特意使用 [ 执行环境 ] :: ...
形式的标题强调本节操作的执行环境
5.1 [ AWS Console ] :: 创建 Source Cluster
R5.4xlarge机型有
128 GB内存,根据 EMR 的 [ 官方建议 ],分配的大数据服务的总内存(Yarn + HBase)可以设置为
120 GB,剩余的
8 GB留给操作系统,考虑到迁移阶段 Source Cluster 需要执行快照导出和行数统计,这些都是 Map-Reduce 作业,因此,我们将一半的内存
60 GB分配给了 Yarn,另一半
60 GB内存分配给 HBase。以下是 Source Cluster 的 EMR 集群配置(请注意替换配置中出现的
<your_aws_access_key_id>和
<your_aws_secret_access_key>):
[
{
"Classification": "hdfs-site",
"Properties": {
"dfs.replication": "1"
}
},
{
"Classification": "core-site",
"Properties": {
"fs.s3.awsAccessKeyId": "<your_aws_access_key_id>",
"fs.s3.awsSecretAccessKey": "<your_aws_secret_access_key>"
}
},
{
"Classification": "yarn-site",
"Properties": {
"yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb": "61440",
"yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb": "61440"
}
},
{
"Classification": "hbase-env",
"Configurations": [
{
"Classification": "export",
"Properties": {
"HBASE_MASTER_OPTS": "\"$HBASE_MASTER_OPTS -Xmx60g\"",
"HBASE_REGIONSERVER_OPTS": "\"$HBASE_REGIONSERVER_OPTS -Xmx60g\""
}
}
],
"Properties": {}
},
{
"Classification": "hbase-site",
"Properties": {
"hbase.rpc.timeout": "86400000",
"hbase.client.operation.timeout": "86400000",
"hbase.client.scanner.timeout.period": "86400000",
"hbase.client.sync.wait.timeout.msec": "86400000",
"hbase.client.procedure.future.get.timeout.msec": "86400000"
}
}
]
hbase.client.scanner.timeout.period hbase.client.sync.wait.timeout.msec hbase.client.procedure.future.get.timeout.msec |
5.2 [ Source Cluster ] :: 全局变量
<your-hbase-sink-cluster-location>):
export SINK_CLUSTER_HBASE_ROOT_DIR="s3://<your-hbase-sink-cluster-location>"
export TABLE_NAME="usertable"
export SNAPSHOT_NAME="usertable-snapshot"
export YCSB_VERSION="0.17.0"
export HBASE_VERSION="hbase14"
export YCSB_HOME="/opt/ycsb-${HBASE_VERSION}-binding-${YCSB_VERSION}"
export YCSB_HISTORICAL_RECORD_COUNT=5242880 # history data volume: 50 TB
export YCSB_INCREMENTAL_RECORD_COUNT=524288 # incremental data volume: 5 TB
export YCSB_INCREMENTAL_RECORD_BATCH=0
export WORKER_NODES=25
export REGIN_SPLITS=$((9780-1))
export SNAPSHOT_EXPORT_MAPPERS=198
export YCSB_THREADS=$WORKER_NODES
s3://<your-hbase-sink-cluster-location> | ||
usertable | ||
usertable-snapshot | ||
0.17.0 | ||
hbase14 | ||
/opt/ycsb-${HBASE_VERSION}-binding-${YCSB_VERSION} | ||
5242880 | ||
524288 | ||
25 | ||
$((9780-1)) | ||
198 | ||
$WORKER_NODES |
5.3 [ Source Cluster ] :: 创建目标桶
aws s3 mb $SINK_CLUSTER_HBASE_ROOT_DIR
# clean up in case the bucket is already in used, especially when re-run
nohup aws s3 rm --recursive $SINK_CLUSTER_HBASE_ROOT_DIR &> rm-root-dir.out &
tail -f rm-root-dir.out
5.4 [ Source Cluster ] :: 监控数据表目录容量
pkill -f du-hdfs-s3
cat << EOF > /tmp/du-hdfs-s3.sh
for i in {1..1008};do
echo -ne "[ \$(date +'%F %R') ]\n\n"
hdfs dfs -du -h /user/hbase/
dataVolume=\$(aws s3 ls --summarize --human-readable --recursive $SINK_CLUSTER_HBASE_ROOT_DIR/data/default/ | \
sed -n "s/\s*Total Size:\s\(.*\)/\1/p")
echo "\$dataVolume $SINK_CLUSTER_HBASE_ROOT_DIR/data/default/"
archiveVolume=\$(aws s3 ls --summarize --human-readable --recursive $SINK_CLUSTER_HBASE_ROOT_DIR/archive/data/default/ | \
sed -n "s/\s*Total Size:\s\(.*\)/\1/p")
echo "\$archiveVolume $SINK_CLUSTER_HBASE_ROOT_DIR/archive/data/default/"
sleep 600
done
EOF
nohup sh /tmp/du-hdfs-s3.sh &> du-hdfs-s3.out &
tail -f du-hdfs-s3.out
5.5 [ Source Cluster ] :: 创建测试表
cat << EOF | sudo -u hbase hbase shell
create '${TABLE_NAME}', 'cf', {SPLITS => (1..${REGIN_SPLITS}).map {|i| "user#{10000+i*(99999-10000)/${REGIN_SPLITS}}"}}
describe '${TABLE_NAME}'
EOF
5.6 [ Source Cluster ] :: 安装 YCSB
YCSB_URL="https://github.com/brianfrankcooper/YCSB/releases/download/${YCSB_VERSION}/ycsb-${HBASE_VERSION}-binding-${YCSB_VERSION}.tar.gz"
wget -c $YCSB_URL -P /tmp/
sudo tar -xzf /tmp/$(basename $YCSB_URL) -C /opt
5.7 [ Source Cluster ] :: 压入全量数据
sudo pkill -f ycsb
nohup sudo -u hbase $YCSB_HOME/bin/ycsb load $HBASE_VERSION \
-cp /etc/hbase/conf/ \
-p table=$TABLE_NAME \
-p columnfamily=cf \
-p recordcount=$YCSB_HISTORICAL_RECORD_COUNT \
-p fieldcount=10 \
-p fieldlength=1048576 \
-p workload=site.ycsb.workloads.CoreWorkload \
-p clientSideBuffering=true \
-p writebuffersize=34359738368 \
-threads $YCSB_THREADS \
-s &> ycsb-historical-load.out &
tail -f ycsb-historical-load.out
5.8 ※ 等待 25 小时 ※
du-hdfs-s3.out中的统计数据,可以发现如下规律:
用于存储表数据的文件夹 /user/hbase/data/default/usertable
其数据量整体保持持续上涨态势,但在固定周期内会有一定的小幅缩减,这是因为在周期内发生了 Compaction,文件总体积会有一定的缩减;用于存储表归档文件的文件夹 /user/hbase/archive/data/default/usertable
其数据量维持在几百 GB 到 1TB 之间波动,原因是:周期性执行 Compaction 后,旧的 HFile 会被移动到该文件夹下,此时文件夹的总容量是上涨的,但是另一个周期性的清理线程又会定期删除该文件夹下的数据,所以该文件夹的总容量不会一直增长,而是在一个范围内波动。
5.9 [ Source Cluster ] :: 检查全量数据
ycsb-historical-load.out文件中会输出汇总信息,如果想核实一下写入数据的体量和条数,可以使用下面的命令:
hdfs dfs -du -h /user/hbase/data/default/ /user/hbase/archive/data/default/
nohup sudo -u hbase hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.RowCounter $TABLE_NAME &> rowcounter-$TABLE_NAME.out &
tail -f rowcounter-$TABLE_NAME.out
nohup sudo -u hbase hbase shell <<< "count '$TABLE_NAME', INTERVAL => 1000000" &> count.out &
tail -f count.out
5.10 [ Source Cluster ] :: 压入增量数据
# incremental insert, retry every 60 seconds if write failed, keep trying 6 hours.
cat << EOF > incremental.workload
recordcount=$YCSB_INCREMENTAL_RECORD_COUNT
insertstart=$((YCSB_HISTORICAL_RECORD_COUNT + (YCSB_INCREMENTAL_RECORD_BATCH++) * YCSB_INCREMENTAL_RECORD_COUNT))
fieldcount=10
fieldlength=1048576
workload=site.ycsb.workloads.CoreWorkload
clientSideBuffering=true
writebuffersize=1073741824
core_workload_insertion_retry_limit=360
core_workload_insertion_retry_interval=60
EOF
# downgrade concurrency, 1 thread only.
nohup sudo -u hbase $YCSB_HOME/bin/ycsb load $HBASE_VERSION \
-cp /etc/hbase/conf/ \
-p table=$TABLE_NAME \
-p columnfamily=cf \
-P incremental.workload \
-threads 1 \
-s &> ycsb-incremental-load-$YCSB_INCREMENTAL_RECORD_BATCH.out &
tail -f ycsb-incremental-load-$YCSB_INCREMENTAL_RECORD_BATCH.out
core_workload_insertion_retry_limit和
core_workload_insertion_retry_interval两个配置项不能通过-p 参数直接设置,但是配置在 workload 文件是可以的。这里我们需要调大这两个配置的默认值,特别是重试次数,以确保后续在 disable 数据表期间,增量数据的写入进程不会中断。
5.11 [ AWS Console ] :: 创建 Sink Cluster
hbase.master.cleaner.interval,如果不调大该配置项的值,在还原快照时就会遇到
can't find hfile错误,导致还原失败。产生这个问题的原因是:我们将快照导出到了 Sink Cluster 的
hbase.rootdir(具体是写到 archive 文件夹)下,因为这样 Sink Cluster 可以直接识别导出的快照并进行还原(与 Sink Cluster 自己创建快照类似),是效率最高的一种做法,但是,在 50 TB 数量级下,由于快照导出的时间过长,Sink Cluster 上负责定期清理旧文件的线程会将尚未导出完成的快照文件判定为 Sink Cluster 自己的旧文件而将其删除。解决这一问题的方法是调大旧文件的扫描周期或调大文件被判定为旧文件的时效,它们对应下面两项配置:
jq . << EOF | tee sink-cluster.json | jq
[
{
"Classification": "hdfs-site",
"Properties": {
"dfs.replication": "3"
}
},
{
"Classification": "yarn-site",
"Properties": {
"yarn.nodemanager.resource.memory-mb": "61440",
"yarn.scheduler.maximum-allocation-mb": "61440"
}
},
{
"Classification": "hbase-env",
"Configurations": [
{
"Classification": "export",
"Properties": {
"HBASE_MASTER_OPTS": "\"\$HBASE_MASTER_OPTS -Xmx60g\"",
"HBASE_REGIONSERVER_OPTS": "\"\$HBASE_REGIONSERVER_OPTS -Xmx60g\""
}
}
],
"Properties": {}
},
{
"Classification": "hbase",
"Properties": {
"hbase.emr.storageMode": "s3"
}
},
{
"Classification": "emrfs-site",
"Properties": {
"fs.s3.maxConnections": "50000"
}
},
{
"Classification": "hbase-site",
"Properties": {
"hbase.rootdir": "$SINK_CLUSTER_HBASE_ROOT_DIR/",
"hbase.hregion.majorcompaction": "0",
"hbase.master.cleaner.interval": "604800000",
"hbase.rpc.timeout": "86400000",
"hbase.client.sync.wait.timeout.msec": "86400000",
"hbase.client.operation.timeout": "86400000",
"hbase.client.scanner.timeout.period": "86400000",
"hbase.client.procedure.future.get.timeout.msec": "86400000",
"hbase.snapshot.master.timeoutMillis": "86400000",
"hbase.snapshot.master.timeout.millis": "86400000",
"hbase.snapshot.region.timeout": "86400000"
}
}
]
EOF
hbase.client.sync.wait.timeout.msec hbase.client.operation.timeout hbase.client.scanner.timeout.period hbase.client.procedure.future.get.timeout.msec hbase.snapshot.master.timeoutMillis hbase.snapshot.master.timeout.millis hbase.snapshot.region.timeout |
hbase.master.cleaner.interval的取值,这个时间必须大于快照导出+还原的操作总时长,如果设置的时间小于操作用时,就会出现
can't find hfile错误,也就是操作途中文件被自动删除了。此外,还要留心的是:这是一个周期时间 ,如果我们没有在启动集群后马上进行快照导出和还原操作,那么,之后再操作时将处于文件清理时间窗口的什么位置就不太容易确定了(HBase 没有关于文件清理的 Info 级别日志),遇上自动删除文件的概率会增大,这一点要始终保持清醒的认识。在本文的操作演示中,为了避免这些问题,我们特意将
hbase.master.cleaner.interval配置为了一个很大的值:7 天,操作完成后,需要将该项和其他超时相关的配置项都改回默认值。
sudo yum -y install xmlstarlet
xmlstarlet sel -t -v '/configuration/property[name = "hbase.zookeeper.quorum"]/value' -n /etc/hbase/conf/hbase-site.xml
<your-sink-cluster-hbase-master-host-list>):
# run on [ Source Cluster ] !
export SINK_CLUSTER_HBASE_MASTER_HOST="<your-sink-cluster-hbase-master-host-list>"
5.12 ※ 暂停写入 ※
5.13 [ Source Cluster ] :: 建立与 Sink Cluster 的同步
cat << EOF | nohup sudo -u hbase hbase shell &> enable-replication.out &
# disable table first...
disable '${TABLE_NAME}'
# replication config ops...
alter '${TABLE_NAME}',{NAME => 'cf', REPLICATION_SCOPE => '1'}
add_peer 'sink_cluster', CLUSTER_KEY => '$SINK_CLUSTER_HBASE_MASTER_HOST:2181:/hbase'
disable_peer 'sink_cluster'
list_peers
enable_table_replication '$TABLE_NAME'
list_replicated_tables
status 'replication'
# enable table
enable '${TABLE_NAME}'
EOF
tail -f enable-replication.out
5.14 [ Source Cluster ] :: 创建快照
# disble table
sudo -u hbase hbase shell <<< "disable '$TABLE_NAME'"
# create snapshot
sudo -u hbase hbase snapshot create -n $SNAPSHOT_NAME -t $TABLE_NAME
# sleep for a while, snapshot may be NOT available immediately.
sleep 120
# check if snapshot is available
sudo -u hbase hbase snapshot info -list-snapshots
# enable table
sudo -u hbase hbase shell <<< "enable '$TABLE_NAME'"
5.15 ※ 恢复写入 ※
5.16 [ Source Cluster ] :: 导出快照
# export snapshot to sink cluster hbase root dir
nohup sudo -u hbase hbase snapshot export \
-snapshot $SNAPSHOT_NAME \
-copy-to "$SINK_CLUSTER_HBASE_ROOT_DIR/" \
-mappers $SNAPSHOT_EXPORT_MAPPERS &> export-snapshot.out &
tail -f /var/log/hbase/hbase.log
--mappers控制的是导出作业的 map task 的数量,该值过大或过小都会影响导出性能,建议配置为可用容器(Yarn Container)数量的整数倍(例如 4 倍)。
5.17 ※ 等待 3 小时 ※
5.18 [ Sink Cluster ] :: 还原快照
确认快照已存在 sudo -u hbase hbase snapshot info -list-snapshots 还原快照 cat << EOF | nohup sudo -u hbase hbase shell &> restore-snapshot.out &
disable '$TABLE_NAME'
restore_snapshot '$SNAPSHOT_NAME'
enable '$TABLE_NAME'
EOF
tail -f restore-snapshot.out
5.19 ※ 等待 2 小时 ※
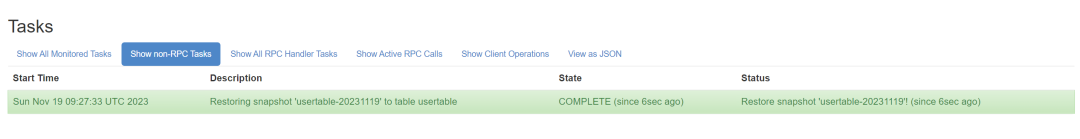 |
5.20 [ Sink Cluster ] :: 修改配置并重启
hbase.master.cleaner.interval的值,这会使得文件大量积压,虽然 HFile 存放于 S3 上,不存在磁盘写满的情况,但是 HBase on S3 的 WAL 文件却是存放在 HDFS 上的,如不能及时改回默认配置,磁盘会有被写满的危险。而重启 HBase 集群是有一定风险的,最好是在关停读写并 disable 所有数据表的前提下操作。在整个操作流程中,此时修改配置并重启 Sink Cluster 集群是最好的时机,因为此时集群尚未接入实时写入的数据,方便 disable table,重启集群会比较安全。
5.21 [ Source Cluster ] :: 放开与 Sink Cluster 的同步
pkill -f status-replication
cat << EOF > /tmp/status-replication.sh
for i in {1..1008};do
sudo -u hbase hbase shell <<< "status 'replication'"
sleep 60
done
EOF
nohup sh /tmp/status-replication.sh &> status-replication.out &
tail -f status-replication.out
sudo -u hbase hbase shell <<< "enable_peer 'sink_cluster'"
 |
 |
5.22 ※ 等待日志追平 ※
tail -f status-replication.out的输出,当 SizeOfLogQueue 降为 1 后,就表明 WAL 日志已经追平。
5.23 [ Sink Cluster ] :: 使用新配置创建新集群
暂停 Source Cluster 的写入 关停旧集群(具体操作请遵循此官方文档:[ HBase on Amazon S3 (Amazon S3 storage mode) ] 的 “Shutting down and restoring a cluster without data loss” 一节) 移除 Source Cluster 与 旧的 Sink Cluster 之间的 replication 关系 使用正常配置创建新的 Sink Cluster 配置 Source Cluster 与新的 Sink Cluster 之间的 replication 关系 恢复 Source Cluster 的写入
5.24 ※ 核对数据 ※
sudo pkill -f ycsb
nohup sudo -u hbase hbase org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.RowCounter $TABLE_NAME &> rowcounter-$TABLE_NAME.out &
tail -f /var/log/hbase/hbase.log
/var/log/hbase/hbase.log可以在文件末尾看到 RowCounter 输出的统计结果,如果 ROWS 数据一致,就表明数据一致,迁移过程中没有丢失数据:
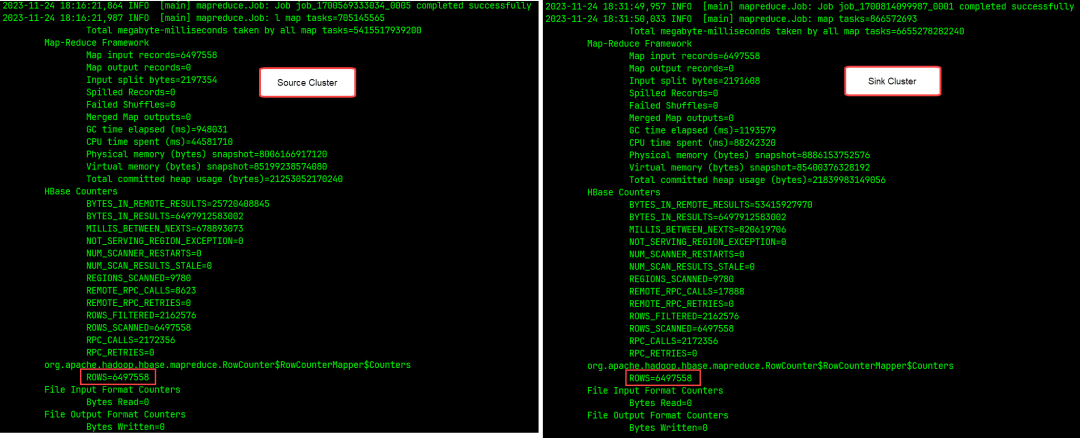 |
6. 资源清理
6.1 移除同步
cat << EOF | sudo -u hbase hbase shell &> remove-peer.out &
disable_table_replication '$TABLE_NAME'
alter '${TABLE_NAME}',{NAME => 'cf',REPLICATION_SCOPE => '0'}
disable_peer 'sink_cluster'
remove_peer 'sink_cluster'
status 'replication'
EOF
tail -f remove-peer.out
6.2 删除快照
sudo -u hbase hbase shell <<< "delete_snapshot '$SNAPSHOT_NAME'"
6.3 删除测试表
cat << EOF | sudo -u hbase hbase shell &> drop-table.out &
truncate '${TABLE_NAME}'
disable '${TABLE_NAME}'
drop '${TABLE_NAME}'
EOF
tail -f drop-table.out
7. 已知错误
7.1 导出快照时报:Unable to load AWS credentials 错误
ERROR [main] snapshot.ExportSnapshot: Snapshot export failed
....
Caused by: com.amazon.ws.emr.hadoop.fs.shaded.com.amazonaws.SdkClientException: Unable to load AWS credentials from any provider in the chain:
....
 |
 |
7.2 还原快照时报:can’t find hfile 错误
7.3 HDFS 空间耗尽
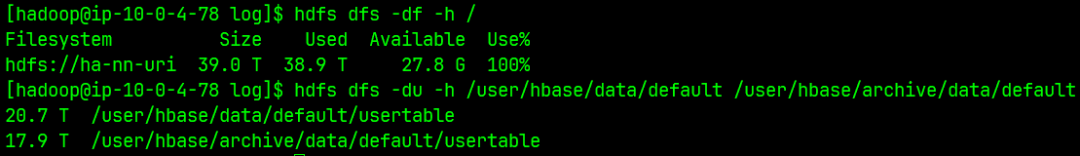 |
7.4 HBase Shell 报 ERROR:The procedure x is still running 或 Snapshot … wasn’t completed in expectedTime 错误
@shell.hbase.configuration.setInt("hbase.rpc.timeout", 86400000)
@shell.hbase.configuration.setInt("hbase.client.operation.timeout", 86400000)
@shell.hbase.configuration.setInt("hbase.client.sync.wait.timeout.msec", 86400000)
7.5 导出快照时报错:IllegalStateException: Reached max limit of upload attempts for part 错误
fs.s3.maxConnections。此外,如果在作业执行过程中偶有几次这样的报错,并不会导致整个导出作业失败,因为 Hadoop 会自动重试失败的 map 任务。以下是 MR 作业重试的截图:
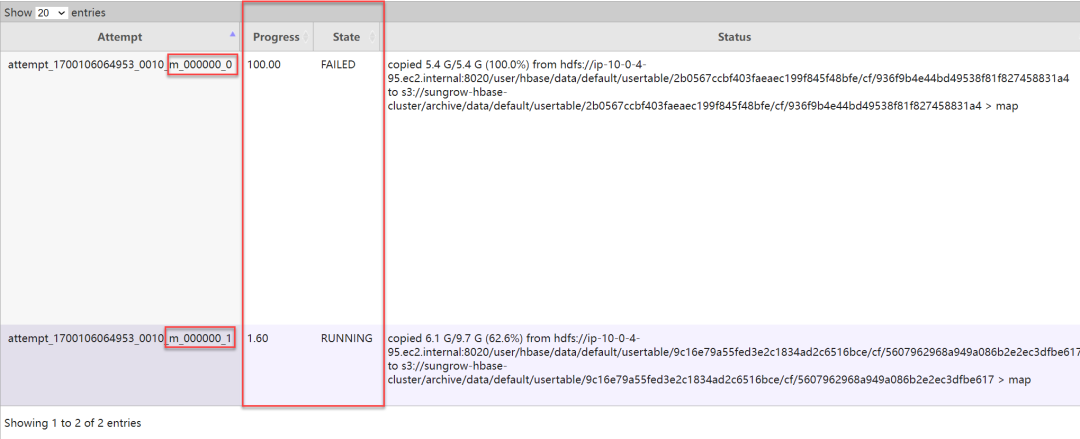 |
本篇作者
耿立超(Laurence)
文章转载自大数据技能圈,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






