public class Test {@Testpublic void test(){List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Java", "C#", "Python", "Golang");list.stream().forEach(x -> {System.out.println(x);});}}
输出内容:
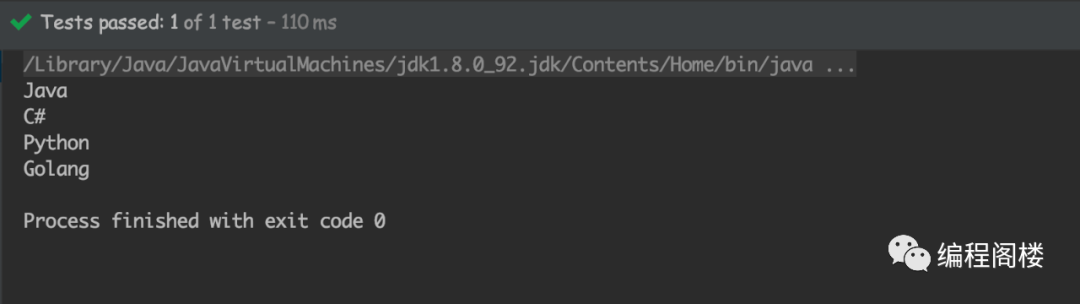
相比之前的Iterator迭代器或者foreach循环,这种函数式的lambda语法简单且优雅很多,爽的飞起。
接下里问题来了,我们应该如何在这个Stream迭代中使用索引呢?
实际上Stream中是无法直接获取当前变量的索引值的。如果确实有需要,可以改变下思路,使用变相方案进行获取。
方法一:使用索引迭代,通过索引反向获取迭代变量。
看下列代码:
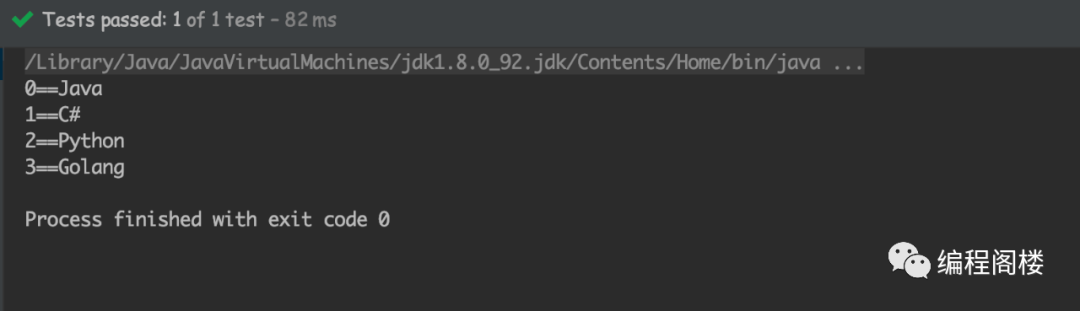
public class Test {@Testpublic void test2(){List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Java", "C#", "Python", "Golang");IntStream.range(0, list.size()).forEach(x -> {System.out.println(x + "==" + list.get(x));});}}
输出结果:
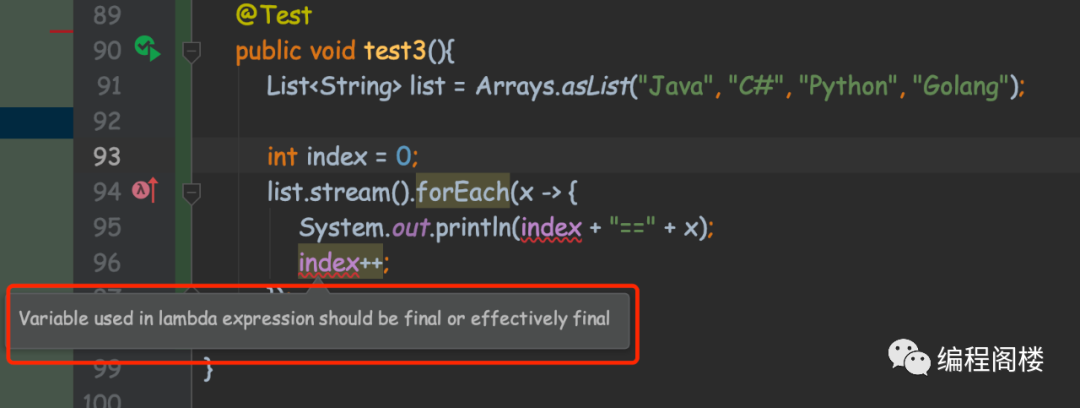
public class Test {@Testpublic void test3(){List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Java", "C#", "Python", "Golang");int index = 0;list.stream().forEach(x -> {System.out.println(index + "==" + x);index++;});}}
public class Test {@Testpublic void test3(){List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Java", "C#", "Python", "Golang");int[] index = {0};list.stream().forEach(x -> {System.out.println(index[0] + "==" + x);index[0]++;});}}

public class Test {public static <E> void forEach(Iterable<? extends E> elements, BiConsumer<Integer, ? super E> action) {Objects.requireNonNull(elements);Objects.requireNonNull(action);int index = 0;for (E element : elements) {action.accept(index++, element);}}@Testpublic void test4(){List<String> list = Arrays.asList("Java", "C#", "Python", "Golang");forEach(list, (index, value) -> {System.out.println(index + "==" + value);});}}
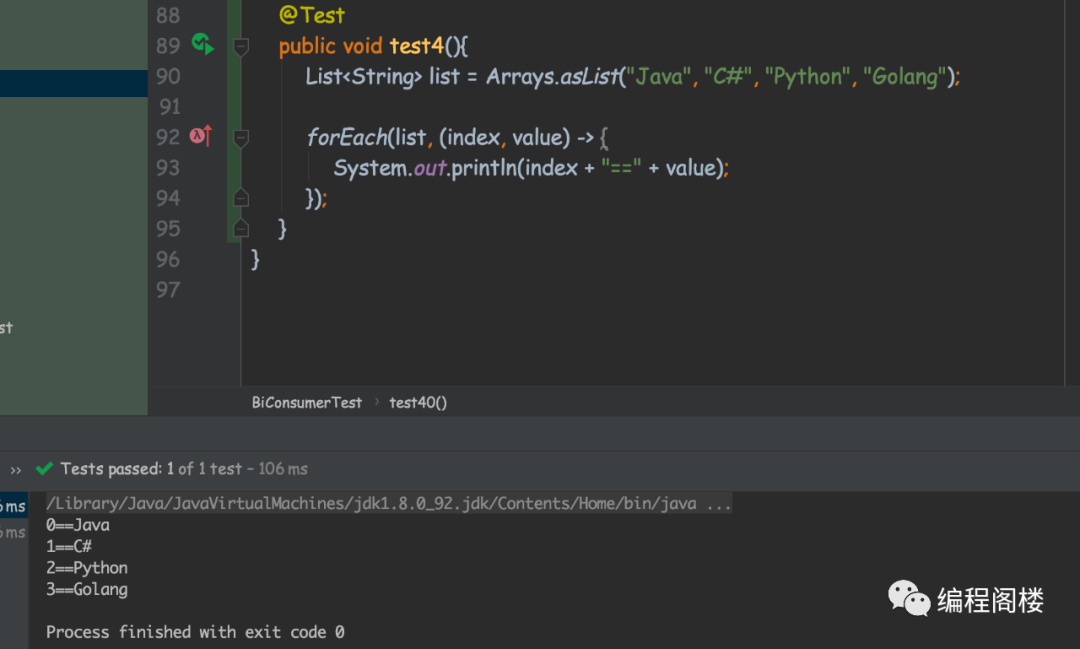
说明:相对来说,小编更喜欢第三种实现,因为更优雅。同时,小编也疑惑,这么简单且常见的需求,为什么Java语言设计者就不提供实现方案呢?
你更喜欢使用哪种实现呢?
文章转载自编程阁楼,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






