
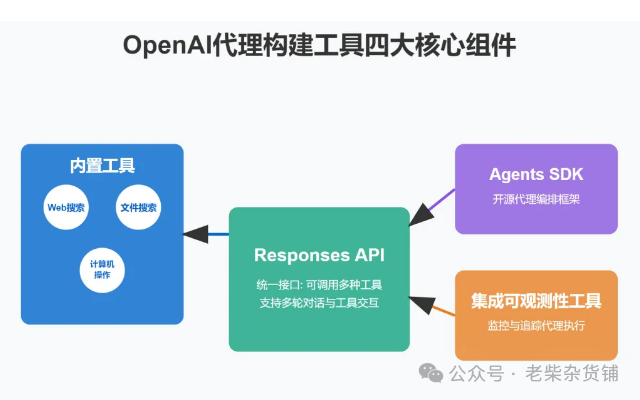
Responses API
统一接口:整合 Chat Completions 的易用性与 Assistants 的工具调用能力
开发效率提升:开发者无需手动编排多步骤流程,一次调用即可实现 "任务目标→工具调用→结果生成" 全流程
典型场景:支持 "先搜索 检索→后推理→最终回答" 的组合任务
内置三大工具
1.Web Search:
实时联网能力:基于 gpt-4o/4o-mini 模型,准确率提升 52%(38%→90%)
应用场景:购物顾问、研究助手、旅行规划等时效性需求场景
2.File Search:
开箱即用 RAG 系统:自动完成文档向量索引、查询优化与结果整合
支持多格式文档:PDF、知识库等,提供元数据过滤与智能排序
3.Computer Use:
界面操作能力:基于 CUA 模型(SOTA 水平),支持网页浏览、表单填写等操作
环境配置:可定义虚拟屏幕尺寸(如 1024x768)与浏览器环境
Agents SDK(Python 开源库)
多代理协作:支持定义角色分工(如购物助手 售后支持)与动态任务交接
核心功能:
智能路由:基于上下文自动转交任务
安全护栏:过滤不合规内容
执行追踪:可视化工作流调试
典型案例:分诊代理根据用户请求自动分配至对应职能代理
二、技术优势
开发简化:从 "指令式编程" 转向 "目标驱动",代码量减少 90% 以上
能力拓展:突破传统 AI 知识边界,实现实时信息获取与物理世界交互
协作升级:通过 SDK 实现 AI 团队化协作,支持复杂业务流程编排
三、应用价值
企业场景:金融分析(Hebbia 案例)、客服自动化、文档处理等
个人场景:智能助手、旅行规划、学习研究等
开发生态:降低 AGI 应用开发门槛,推动 AI 从工具向智能体演进
该工具链通过 "统一接口 + 智能工具 + 协作框架" 的组合,标志着 AI 开发进入 "声明式编程" 新阶段,开发者可专注于业务逻辑而非底层实现,为 2025 年 "Agent 年" 奠定技术基础。
四、应用示例
基于 OpenAI Agents SDK 的 Linux 运维智能代理系统。这个系统可以帮助自动化 Linux 服务器的运维工作,通过 AI 来解析和执行运维任务。
from openai import OpenAIimport subprocessimport jsonimport osimport reimport platformimport psutilimport socketimport time# 初始化OpenAI客户端client = OpenAI(api_key="sk-NDYyLTU2LTE3NDE0OTk1MzM2MjM=", base_url="https://api.scnet.cn/api/llm/v1")class LinuxOpsAgent:def __init__(self):self.client = clientself.model = "DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B"self.system_info = self.get_system_info()def get_system_info(self):"""获取系统信息"""try:info = {"os": platform.system(),"os_version": platform.version(),"hostname": socket.gethostname(),"cpu_count": psutil.cpu_count(),"memory_total": round(psutil.virtual_memory().total (1024**3), 2), # GB"disk_usage": self.get_disk_usage(),"network_interfaces": self.get_network_interfaces()}return infoexcept Exception as e:return {"error": str(e)}def get_disk_usage(self):"""获取磁盘使用情况"""disk_info = []for partition in psutil.disk_partitions():try:usage = psutil.disk_usage(partition.mountpoint)disk_info.append({"device": partition.device,"mountpoint": partition.mountpoint,"total_gb": round(usage.total (1024**3), 2),"used_gb": round(usage.used (1024**3), 2),"percent": usage.percent})except:passreturn disk_infodef get_network_interfaces(self):"""获取网络接口信息"""interfaces = []for iface, addrs in psutil.net_if_addrs().items():for addr in addrs:if addr.family == socket.AF_INET:interfaces.append({"interface": iface,"ip": addr.address,"netmask": addr.netmask})return interfacesdef execute_command(self, command, safe_mode=True):"""执行Shell命令"""# 安全模式下禁止执行危险命令dangerous_commands = ["rm -rf", "mkfs", "dd", ">", "format"]if safe_mode:for cmd in dangerous_commands:if cmd in command:return {"error": f"危险命令被拒绝执行: {command}"}try:result = subprocess.run(command, shell=True, capture_output=True, text=True)return {"stdout": result.stdout,"stderr": result.stderr,"returncode": result.returncode}except Exception as e:return {"error": str(e)}def analyze_log(self, log_path):"""分析日志文件"""try:if not os.path.exists(log_path):return {"error": f"日志文件不存在: {log_path}"}# 读取日志文件with open(log_path, 'r') as f:log_content = f.read()# 使用AI分析日志response = self.client.chat.completions.create(model=self.model,messages=[{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个专业的Linux日志分析专家,请分析以下日志内容,找出异常和潜在问题。"},{"role": "user", "content": f"请分析以下日志内容:\n\n{log_content[:4000]}"} # 限制长度],stream=False)return {"analysis": response.choices[0].message.content,"log_sample": log_content[:200] + "..." if len(log_content) > 200 else log_content}except Exception as e:return {"error": str(e)}def monitor_resources(self, duration=60, interval=5):"""监控系统资源使用情况"""try:start_time = time.time()end_time = start_time + durationmetrics = []while time.time() < end_time:cpu_percent = psutil.cpu_percent(interval=1)memory = psutil.virtual_memory()disk_io = psutil.disk_io_counters()net_io = psutil.net_io_counters()metrics.append({"timestamp": time.time(),"cpu_percent": cpu_percent,"memory_percent": memory.percent,"disk_read_mb": round(disk_io.read_bytes (1024**2), 2),"disk_write_mb": round(disk_io.write_bytes (1024**2), 2),"net_sent_mb": round(net_io.bytes_sent (1024**2), 2),"net_recv_mb": round(net_io.bytes_recv (1024**2), 2)})time.sleep(interval)# 使用AI分析资源使用情况response = self.client.chat.completions.create(model=self.model,messages=[{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个专业的系统性能分析专家,请分析以下系统资源使用数据,找出性能瓶颈和优化建议。"},{"role": "user", "content": f"请分析以下系统资源使用数据:\n\n{json.dumps(metrics, indent=2)}"}],stream=False)return {"metrics": metrics,"analysis": response.choices[0].message.content}except Exception as e:return {"error": str(e)}def process_query(self, query):"""处理用户查询,返回运维建议和可执行命令"""try:system_info_str = json.dumps(self.system_info, indent=2)response = self.client.chat.completions.create(model=self.model,messages=[{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个专业的Linux运维专家,请根据用户的查询和系统信息,提供专业的运维建议和可执行的命令。"},{"role": "user", "content": f"系统信息:\n{system_info_str}\n\n用户查询: {query}"}],stream=False)advice = response.choices[0].message.content# 提取建议中的命令commands = re.findall(r'```bash\n(.*?)\n```', advice, re.DOTALL)return {"query": query,"advice": advice,"suggested_commands": commands}except Exception as e:return {"error": str(e)}# 示例使用if __name__ == "__main__":agent = LinuxOpsAgent()print("Linux运维智能代理系统已启动")print(f"系统信息: {json.dumps(agent.system_info, indent=2)}")while True:query = input("\n请输入您的运维问题 (输入'exit'退出): ")if query.lower() == 'exit':breakif query.startswith("执行:"):# 直接执行命令cmd = query[3:].strip()print(f"正在执行命令: {cmd}")result = agent.execute_command(cmd)print(json.dumps(result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))elif query.startswith("分析日志:"):# 分析日志文件log_path = query[5:].strip()print(f"正在分析日志: {log_path}")result = agent.analyze_log(log_path)print(json.dumps(result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))elif query == "监控资源":# 监控系统资源print("开始监控系统资源 (60秒)...")result = agent.monitor_resources(duration=60, interval=5)print(json.dumps(result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))else:# 处理普通查询print("正在处理您的查询...")result = agent.process_query(query)print("\n运维建议:")print(result["advice"])if result["suggested_commands"]:print("\n建议执行的命令:")for i, cmd in enumerate(result["suggested_commands"], 1):print(f"{i}. {cmd}")
这个 Linux 运维智能代理系统具有以下功能:
1. 系统信息收集 :自动获取操作系统、CPU、内存、磁盘和网络接口等信息
2. 命令执行 :安全地执行 Shell 命令,并防止危险操作
3. 日志分析 :使用 AI 分析日志文件,找出异常和潜在问题
4. 资源监控 :监控系统资源使用情况,并提供性能分析
5. 智能查询处理 :根据用户的问题,提供专业的运维建议和可执行命令
使用方法:
1. 运行脚本后,系统会显示当前系统信息
2. 输入运维问题,系统会提供专业建议和可执行命令
3. 使用特殊命令格式:
- 执行:命令 - 直接执行指定命令
- 分析日志:路径 - 分析指定日志文件
- 监控资源 - 监控系统资源使用情况
注意事项:
1. 需要安装 psutil 库: pip install psutil
2. 在 Windows 上运行时,某些 Linux 特定功能可能不可用
3. 命令执行功能有安全限制,防止危险操作
这个系统可以帮助运维人员更高效地管理 Linux 服务器,通过 AI 辅助分析和决策,减少人工操作的复杂性和错误率。






