揭秘PostgreSQL SELECT查询中的意外“写”行为
在众多数据库中,SELECT 语句被广泛认知为纯粹的“只读”操作,其使命在于从数据库中检索所需数据,而不涉及对底层数据状态的任何改动。然而,当我们深入探究 PostgreSQL 这一强大的开源关系型数据库系统的内部运作时,会发现即使是看似无害的 SELECT 查询,也可能在特定场景下触发对缓冲区的写操作。
本文将介绍三种在 SELECT 查询过程中可能触发写操作的场景。
Hint Bits
原理简介
PostgreSQL 将事务状态记录在 CLOG(Commit LOG) 日志中,在内存中维护一个 SLRU Buffer Pool 用于缓存 CLOG。事务在判断元组可见性时,需要从 SLRU Buffer Pool 甚至磁盘中读取事务的状态。由于判断元组可见性的操作可能非常频繁,因此要求读取事务状态的操作尽量高效,为避免每次都从 CLOG 缓存或磁盘文件中读取,引入 Hint Bits 在元组中直接标识插入/删除该元组的事务的状态。
Hint Bits 并不是在插入/删除事务结束时设置,而是在后续 DML、DQL、Vacuum 等操作扫描到对应 tuple 时,才会设置。设置 Hint Bits 是通过 SetHintBits 函数完成的,具体的函数说明及实现如下:
/*
* SetHintBits()
*
* Set commit/abort hint bits on a tuple, if appropriate at this time.
*
* It is only safe to set a transaction-committed hint bit if we know the
* transaction's commit record is guaranteed to be flushed to disk before the
* buffer, or if the table is temporary or unlogged and will be obliterated by
* a crash anyway. We cannot change the LSN of the page here, because we may
* hold only a share lock on the buffer, so we can only use the LSN to
* interlock this if the buffer's LSN already is newer than the commit LSN;
* otherwise we have to just refrain from setting the hint bit until some
* future re-examination of the tuple.
*
* We can always set hint bits when marking a transaction aborted. (Some
* code in heapam.c relies on that!)
*
* Also, if we are cleaning up HEAP_MOVED_IN or HEAP_MOVED_OFF entries, then
* we can always set the hint bits, since pre-9.0 VACUUM FULL always used
* synchronous commits and didn't move tuples that weren't previously
* hinted. (This is not known by this subroutine, but is applied by its
* callers.) Note: old-style VACUUM FULL is gone, but we have to keep this
* module's support for MOVED_OFF/MOVED_IN flag bits for as long as we
* support in-place update from pre-9.0 databases.
*
* Normal commits may be asynchronous, so for those we need to get the LSN
* of the transaction and then check whether this is flushed.
*
* The caller should pass xid as the XID of the transaction to check, or
* InvalidTransactionId if no check is needed.
*/
static inline void
SetHintBits(HeapTupleHeader tuple, Buffer buffer,
uint16 infomask, TransactionId xid)
{
if (polar_is_split_xact())
return;
if (TransactionIdIsValid(xid))
{
/* NB: xid must be known committed here! */
XLogRecPtr commitLSN = TransactionIdGetCommitLSN(xid);
if (BufferIsPermanent(buffer) && XLogNeedsFlush(commitLSN) &&
BufferGetLSNAtomic(buffer) < commitLSN)
{
/* not flushed and no LSN interlock, so don't set hint */
return;
}
}
tuple->t_infomask |= infomask;
MarkBufferDirtyHint(buffer, true);
}
示例
在 tuple insert 完毕后,并没有直接设置 Hint Bits。

在 SELECT 扫描到该条 tuple 后,HEAP_XMIN_COMMITTED 被成功设置。

设置 Hint Bits 的函数调用栈如下,因此 SELECT 可能会设置 Hint Bits,并且将 buffer 标记为 dirty。
(gdb) bt 5
#0 SetHintBits (xid=<optimized out>, infomask=<optimized out>, buffer=<optimized out>, tuple=<optimized out>) at heapam_visibility.c:129
#1 HeapTupleSatisfiesMVCC (buffer=501, snapshot=0x21a9e58, htup=0x7fff6d1910c0) at heapam_visibility.c:1056
#2 HeapTupleSatisfiesVisibility (tup=tup@entry=0x7fff6d191140, snapshot=snapshot@entry=0x21a9e58, buffer=buffer@entry=501)
at heapam_visibility.c:1771
#3 0x0000000000567a38 in heapgetpage (sscan=sscan@entry=0x228be48, page=page@entry=0) at heapam.c:468
#4 0x000000000056847a in heapgettup_pagemode (scan=scan@entry=0x228be48, dir=ForwardScanDirection, nkeys=0, key=0x0) at heapam.c:901
heap pruning
原理简介
当 heap page 被读取或更新时,会尝试对页面做一些快速的清理和修剪。页面修剪触发的条件(其中条件 1 必须满足,条件 2、3 满足其中之一即可):
pageheader 中的 pd_prune_xid 有效,即当前页面进行过 update/delete 操作,存在死元组;
pageheader 中有设置 PD_PAGE_FULL 标记,即 heap_update 函数在更新 tuple 时,发现当前页面没有足够空间;
页面剩余空间不足(剩余空间要大于 fillfactor 要求的预留空间并且大于页面总空间的 10%)
页面的修剪是通过 heap_page_prune_opt 函数完成的,具体的函数说明及声明如下:
/*
* Optionally prune and repair fragmentation in the specified page.
*
* This is an opportunistic function. It will perform housekeeping
* only if the page heuristically looks like a candidate for pruning and we
* can acquire buffer cleanup lock without blocking.
*
* Note: this is called quite often. It's important that it fall out quickly
* if there's not any use in pruning.
*
* Caller must have pin on the buffer, and must *not* have a lock on it.
*/
void
heap_page_prune_opt(Relation relation, Buffer buffer)
页面修剪不会删除行指针,因为行指针可能仍然被索引引用,也不会更新 fsm 和 vm,整理后的空闲空间用于更新(update)操作,不会用于 insert 操作。
索引扫描时,发现对应 tuple 的行指针为 dead 状态,这意味着元组已经不存在了,这个行指针应该被忽略。
示例
创建一个表并设置 fillfactor 为 75,每条 tuple 的大小为 2028,一个 page 最多可以容纳 4 个 tuple。
create table t(a int, b char(2000)) with (fillfactor = 75);
create index on t(a);
create index on t(b);
insert into t values (1, 'A');
update t set b = 'B';
update t set b = 'C';
update t set b = 'D';
没有执行 SELECT 前,4 条 tuple 的状态都为 normal。

执行 SELECT 后,页面发生了修剪,其中有 3 条 tuple 被回收,并且其行指针被标记为 dead。

页面修剪的函数调用堆栈如下:
(gdb) bt 5
#0 MarkBufferDirty (buffer=buffer@entry=614) at bufmgr.c:1589
#1 0x00000000005749dd in heap_page_prune (relation=0x7f63718d5898, buffer=<optimized out>,
vistest=<optimized out>, old_snap_xmin=<optimized out>, old_snap_ts=<optimized out>,
nnewlpdead=0x7fff6d190ac4, off_loc=0x0) at pruneheap.c:411
#2 0x00000000005752ed in heap_page_prune_opt (relation=0x7f63718d5898, buffer=buffer@entry=614)
at pruneheap.c:209
#3 0x00000000005677d6 in heapgetpage (sscan=sscan@entry=0x2297b00, page=page@entry=0)
at heapam.c:415
#4 0x000000000056847a in heapgettup_pagemode (scan=scan@entry=0x2297b00,
dir=ForwardScanDirection, nkeys=0, key=0x0) at heapam.c:901
kill index tuple
原理简介
通过 index_fetch_heap 函数获取堆表 tuple 时,如果发现该 tuple 已经对所有事务都不可见了(dead),会设置 kill_prior_tuple 标志,后续会在 _bt_killitems 函数中将该索引项标记为 dead,以避免重复访问堆表页面。
index_fetch_heap 函数的源码如下:
bool
index_fetch_heap(IndexScanDesc scan, TupleTableSlot *slot)
{
bool all_dead = false;
bool found;
found = table_index_fetch_tuple(scan->xs_heapfetch, &scan->xs_heaptid,
scan->xs_snapshot, slot,
&scan->xs_heap_continue, &all_dead);
if (found)
pgstat_count_heap_fetch(scan->indexRelation);
/*
* If we scanned a whole HOT chain and found only dead tuples, tell index
* AM to kill its entry for that TID (this will take effect in the next
* amgettuple call, in index_getnext_tid). We do not do this when in
* recovery because it may violate MVCC to do so. See comments in
* RelationGetIndexScan().
*/
if (!scan->xactStartedInRecovery)
scan->kill_prior_tuple = all_dead;
return found;
}
在 btgettuple 函数中会将 dead tuple 添加到 BTScanOpaqueData 的 killedItems 中:
···
/*
* Check to see if we should kill the previously-fetched tuple.
*/
if (scan->kill_prior_tuple)
{
/*
* Yes, remember it for later. (We'll deal with all such
* tuples at once right before leaving the index page.) The
* test for numKilled overrun is not just paranoia: if the
* caller reverses direction in the indexscan then the same
* item might get entered multiple times. It's not worth
* trying to optimize that, so we don't detect it, but instead
* just forget any excess entries.
*/
if (so->killedItems == NULL)
so->killedItems = (int *)
palloc(MaxTIDsPerBTreePage * sizeof(int));
if (so->numKilled < MaxTIDsPerBTreePage)
so->killedItems[so->numKilled++] = so->currPos.itemIndex;
}
···
最终 _bt_killitems 函数会将 killedItems 中的索引项标记为 dead,后续扫描时就会跳过这些索引项。
示例
在 SELECT 执行前,索引所有项的 dead 标记都没有设置。
create table t(a int, b char(2000)) with (fillfactor = 75);
create index on t(a);
create index on t(b);
insert into t values (1, 'A');
update t set b = 'B';
update t set b = 'C';
update t set b = 'D';

执行 SELECT 后,有 3 条索引 item 被标记为 dead。
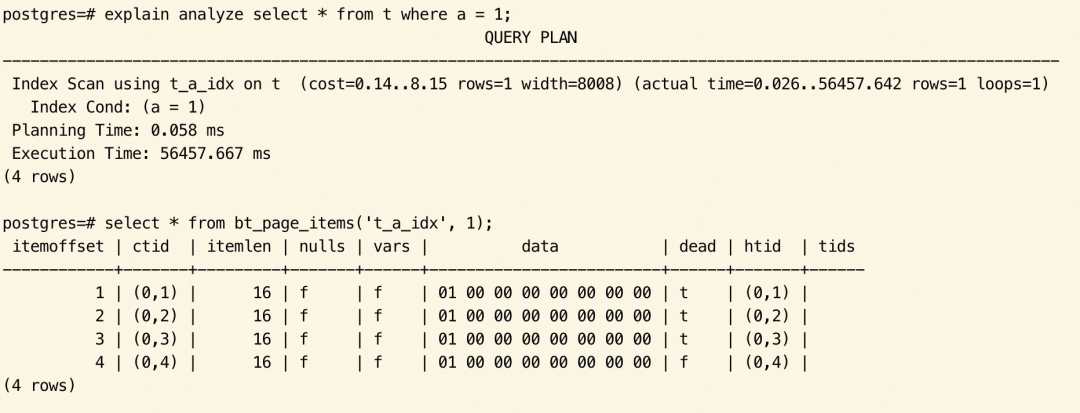
索引 item 被标记为 dead 的函数调用堆栈如下:
(gdb) bt 5
#0 _bt_killitems (scan=0x226a1a8) at nbtutils.c:1742
#1 0x000000000058e235 in _bt_steppage (scan=scan@entry=0x226a1a8, dir=ForwardScanDirection) at nbtsearch.c:1896
#2 0x000000000058f796 in _bt_next (scan=scan@entry=0x226a1a8, dir=dir@entry=ForwardScanDirection)
at nbtsearch.c:1492
#3 0x000000000058a98e in btgettuple (scan=0x226a1a8, dir=ForwardScanDirection) at nbtree.c:269
#4 0x000000000057db30 in index_getnext_tid (scan=0x226a1a8, direction=<optimized out>) at indexam.c:575
总结
本文介绍了三种在 SELECT 查询过程中可能导致写操作发生的机制:Hint Bits设置、Heap Page Pruning 以及 Kill Index Tuple。






