一、基础介绍
XLOG 通常也叫做 WAL (Write-Ahead Log 预写式日志),是数据库中用于存储事务日志的一种数据格式。它是一种二进制格式,用于记录数据库中的所有操作,包括 DDL、DML 和 DCL 操作。
XLOG 归档是指将数据库中的 XLOG 数据进行备份和存储的过程,通常这是一个持续的过程,以确保归档数据的完整性和可用性。
二、XLOG 归档的价值
XLOG 归档的价值主要体现在以下几点:
数据恢复
通过归档日志,可以创建数据库的备份,并在有需要时使用这些备份进行数据恢复。这是 PITR (Point-In-Time-Recovery) 的基础,它允许数据恢复到其运行历史中的任意一个有记录的时间点。
保证数据一致性
归档日志可以保证数据库在崩溃或重启时,所有已经提交的事务都得到了持久的保存,确保数据的一致性和完整性。
三、资源池化 XLOG 归档的约束
资源池化 XLOG 归档的约束主要体现在以下几个方面:
仅支持主节点开启归档参数,进行归档
当wal_level参数为minimal时,归档功能无法开启使用。
本特性不会检测已归档的XLOG是否还有存在价值,若出现归档路径的盘空间满,则归档会停止直到归档路径盘存在可用空间(>1G,因为资源池化环境下的XLOG文件规格是1G),因此需要用户自行进行归档的XLOG维护清理。
资源池化环境下,归档命令参数(archive_command)为dsscmd cp,暂时仅支持 cp 基本的复制操作,并且文件路径参数不支持使用相对路径。
四、资源池化 XLOG 归档的使用
怎么开启资源池化 XLOG 归档功能?
归档有以下四个基本参数,分别为:archive_mode、archive_command、archive_timeout、archive_dest。
当archive_mode参数为on时(wal_level需要设置为minimal以上级别),同时配置有正确的archive_command参数或者archive_dest参数,即可开启资源池化 XLOG 归档功能。
当archive_mode参数为off时,资源池化 XLOG 归档功能关闭,即就是其余的归档参数不会生效。
# - Archiving -#archive_mode = off # allows archiving to be done# (change requires restart)#archive_command = '' # command to use to archive a logfile segment# placeholders: %p = path of file to archive# %f = file name only# e.g. 'test ! -f mnt/server/archivedir/%f && cp %p mnt/server/archivedir/%f'#archive_timeout = 0 # force a logfile segment switch after this# number of seconds; 0 disables#archive_dest = '' # path to use to archive a logfile segment
1. archive_mode
该参数用于控制数据库是否启用归档模式。
默认为 off。
2. archive_command
该参数用于指定归档日志文件的写入命令。该命令可以是一个脚本,也可以是一个外部程序。在归档模式下,数据库会将日志数据写入到归档日志文件中,然后执行该命令,将归档日志文件复制到指定的位置。
默认为空,需要手动指定归档文件的写入命令。
3. archive_timeout
该参数用于指定归档日志文件的写入超时时间。如果在指定的时间内没有完成归档日志文件的写入,数据库会自动停止归档操作。
默认为 0,需要手动指定归档文件的写入超时时间,若设置为 0 表示禁用这个功能,即不根据时间强制切换日志文件段。
如果在一个不繁忙的系统可能需要很长时间才能写满一个日志,而如果将归档超时设置的过于频繁,会导致产生大量的空白的归档日志文件,从而影响系统的性能。
4. archive_dest
该参数用于指定归档日志文件的存储路径。在归档模式下,数据库会将日志数据写入到归档日志文件中,然后执行 archive_command 命令,将归档日志文件复制到指定的位置。
默认为空,需要手动指定归档文件的存储路径。当archive_dest和archive_command同时配置时,WAL日志优先保存到archive_dest所设置的目录中,archive_command配置的命令不生效。
需要注意的点:
参数archive_command和archive_dest同时配置一个即可,若同时配置,archive_dest会优先生效。
archive_timeout参数并不完全代表归档文件生成的时间间隔。这一点在下面第五节会介绍。
archive_command若配置为多条命令,需要写成shell脚本形式去配置。比如想要先创建一个新目录目录,然后选择创建的目录为归档目录,则test.sh脚本内容如下:
#!/bin/bashif [ ! -d "/mnt/server/archivedir" ]; thenmkdir -p mnt/server/archivedirficp $1 /mnt/server/archivedir/$2
archive_command = 'sh dir/test.sh %p %f'
五、归档触发的时机
首先触发归档的一定是接收到归档通知,即收到归档信号。当切换日志段的时候,会发送归档信号,此时会触发归档操作,去归档切换前的日志。
然后,什么时候会切换日志段?
有两种情况,一种日志段被写满时,会触发切换,然后来提供新的段去写。另一种是干预触发强制切换日志段。
正常情况下写满而切换日志段的部分源码如下:
static void XLogWrite(const XLogwrtRqst &WriteRqst, bool flexible){/** If we just wrote the whole last page of a logfile segment,* fsync the segment immediately. This avoids having to go back* and re-open prior segments when an fsync request comes along* later. Doing it here ensures that one and only one backend will* perform this fsync.** We also do this if this is the last page written for an xlog* switch.** This is also the right place to notify the Archiver that the* segment is ready to copy to archival storage, and to update the* timer for archive_timeout, and to signal for a checkpoint if* too many logfile segments have been used since the last* checkpoint.*///一个段写满了if (finishing_seg) {instr_time startTime;instr_time endTime;uint64 elapsedTime;INSTR_TIME_SET_CURRENT(startTime);issue_xlog_fsync(t_thrd.xlog_cxt.openLogFile, t_thrd.xlog_cxt.openLogSegNo);INSTR_TIME_SET_CURRENT(endTime);INSTR_TIME_SUBTRACT(endTime, startTime);elapsedTime = INSTR_TIME_GET_MICROSEC(endTime);/* Add statistics *///统计信息更新if (g_instance.wal_cxt.xlogFlushStats->statSwitch) {++g_instance.wal_cxt.xlogFlushStats->syncTimes;g_instance.wal_cxt.xlogFlushStats->totalSyncTime += elapsedTime;}/* signal that we need to wakeup walsenders later *///唤醒walsenderWalSndWakeupRequest();//更新日志写入结果,当前页已写完t_thrd.xlog_cxt.LogwrtResult->Flush = t_thrd.xlog_cxt.LogwrtResult->Write; /* end of page *///更新ssd信息并唤醒后台进程UpdateSSDoradoCtlInfoAndSync();AddShareStorageXLopCopyBackendWakeupRequest();//归档如果开启,通知归档进程进行归档if (XLogArchivingActive()) {XLogArchiveNotifySeg(t_thrd.xlog_cxt.openLogSegNo);}t_thrd.shemem_ptr_cxt.XLogCtl->lastSegSwitchTime = (pg_time_t)time(NULL);/** Request a checkpoint if we've consumed too much xlog since* the last one. For speed, we first check using the local* copy of RedoRecPtr, which might be out of date; if it looks* like a checkpoint is needed, forcibly update RedoRecPtr and* recheck.*/if (IsUnderPostmaster && XLogCheckpointNeeded(t_thrd.xlog_cxt.openLogSegNo)) {(void)GetRedoRecPtr();if (XLogCheckpointNeeded(t_thrd.xlog_cxt.openLogSegNo)) {RequestCheckpoint(CHECKPOINT_CAUSE_XLOG);}}}}
这里可以通过调用pg_switch_xlog()函数来触发强制切换日志段。参数archive_timeout就是在业务量较小的情况下,定时触发强制切换日志段。这里如果业务量较大,但配置了较长的时间,还是会优先触发写满日志段,然后切换日志段。
archive_timeout 源码如下:
static void CheckArchiveTimeout(void){pg_time_t now;pg_time_t last_time;if (u_sess->attr.attr_common.XLogArchiveTimeout <= 0 || RecoveryInProgress())return;now = (pg_time_t)time(NULL);/* First we do a quick check using possibly-stale local state. */if ((int)(now - t_thrd.checkpoint_cxt.last_xlog_switch_time) < u_sess->attr.attr_common.XLogArchiveTimeout)return;/** Update local state ... note that t_thrd.checkpoint_cxt.last_xlog_switch_time is the last time* a switch was performed *or requested*.*/last_time = GetLastSegSwitchTime();t_thrd.checkpoint_cxt.last_xlog_switch_time = Max(t_thrd.checkpoint_cxt.last_xlog_switch_time, last_time);//如果已经超时,则切换日志段/* Now we can do the real check */if ((int)(now - t_thrd.checkpoint_cxt.last_xlog_switch_time) >= u_sess->attr.attr_common.XLogArchiveTimeout) {XLogRecPtr switchpoint;/* OK, it's time to switch *///切换日志段switchpoint = RequestXLogSwitch();/** If the returned pointer points exactly to a segment boundary,* assume nothing happened.*/if ((switchpoint % XLogSegSize) != 0)ereport(DEBUG1,(errmsg("transaction log switch forced (archive_timeout=%d)",u_sess->attr.attr_common.XLogArchiveTimeout)));/** Update state in any case, so we don't retry constantly when the* system is idle.*/t_thrd.checkpoint_cxt.last_xlog_switch_time = now;}}
六、归档的进程
归档交互流程图如下
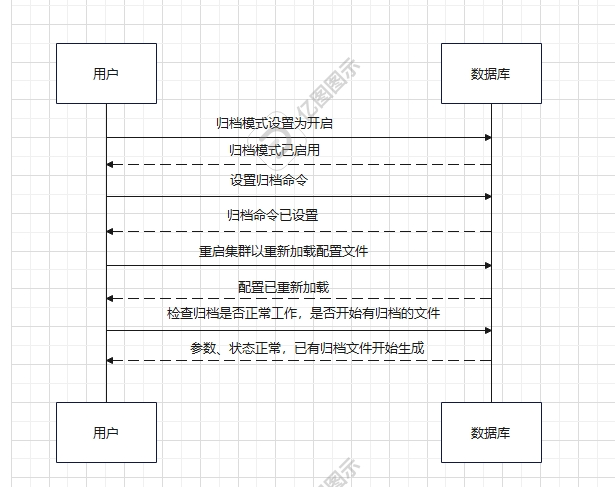

部分源码如下:
归档进程主函数 PgArchiverMain
主要进行一些全局变量的初始化以及初始化信号处理,之后进入主循环函数 pgarch_MainLoop(),最后退出线程。
PgArchiverMain(knl_thread_arg* arg){ereport(LOG, (errmsg("PgArchiver started")));//执行归档主循环函数pgarch_MainLoop();//线程退出gs_thread_exit(0);}
pgarch_MainLoop(void){//判断归档目录是否设置,若没有设置则退出归档线程,归档停止if (XLogArchiveDestSet()) {//验证归档目录是否为空或是否成功创建,若目录创建失败或无法正常访问则退出归档线程,归档停止VerifyDestDirIsEmptyOrCreate(u_sess->attr.attr_storage.XLogArchiveDest);}do{//执行归档拷贝循环函数pgarch_ArchiverCopyLoop();}while(PostmasterIsAlive() && !time_to_stop&& (XLogArchivingActive() || getArchiveReplicationSlot() != NULL));//1.主进程存活;2.没有被设置为停止;3.还有归档事件(归档仍为活跃状态)或者存在有归档复制槽。这三种条件必须同时满足,才会继续执行归档复制循环函数。}
pgarch_ArchiverCopyLoop(void){//获取下一个需要归档的事务日志文件名,将其存储再xlog数组中,返回值为bool值,表示是否成功获取文件名while (pgarch_readyXlog(xlog, MAX_XFN_CHARS + 1)) {//不断尝试归档当前的事务日志文件,直到归档成功或达到最大重试次数for(;;) {//1.检查是否接收到SIGTERM信号或主进程是否已经死亡,如果是,则函数立即返回,停止归档操作//2.检查是否接收到SIGHUP信号,如果是,则ProcessConfigFile(PGC_SIGHUP);//3.检查archive_command和archive_dest是否已设置。若均未设置,则报错并停止归档操作//4.以上条件都满足则pgarch_archiveXlog(xlog),若归档成功则标记当前事务日志已归档并退出无限循环//若归档失败,则计数器的值+1,并检查是否达到最大重试次数,如果达到则报错并停止归档操作//若没有达到最大重试次数,则等待一秒,继续尝试归档if (t_thrd.arch.got_SIGTERM || !PostmasterIsAlive())return;if (t_thrd.arch.got_SIGHUP) {ProcessConfigFile(PGC_SIGHUP);if (!XLogArchivingActive()) {return;}t_thrd.arch.got_SIGHUP = false;}if (!XLogArchiveCommandSet() && !XLogArchiveDestSet()) {ereport(WARNING, (errmsg("archive_mode enabled, yet archive_command or archive_dest is not set")));return;}if (pgarch_archiveXlog(xlog)) {/* successful */pgarch_archiveDone(xlog);break; /* out of inner retry loop */} else {if (++failures >= NUM_ARCHIVE_RETRIES) {ereport(WARNING,(errmsg("xlog file \"%s\" could not be archived: too many failures", xlog)));return; /* give up archiving for now */}pg_usleep(1000000L); /* wait a bit before retrying */}}}}
pgarch_readyXlog(char* xlog, int xlog_length){//打开归档状态目录,并将返回的目录指针赋值给rldirrldir = AllocateDir(XLogArchiveStatusDir);//如果打开失败,则报错并返回if (rldir == NULL)ereport(ERROR,(errcode_for_file_access(),errmsg("could not open archive status directory \"%s\": %m", XLogArchiveStatusDir)));//进入while循环,不断读取一个目录项,将其存再rlde中,如果失败则退出循环while ((rlde = ReadDir(rldir, XLogArchiveStatusDir)) != NULL) {int basenamelen = (int)strlen(rlde->d_name) - 6;//检查当前目录项的文件名是否符合格式要求,包括文件名长度、字符集和后缀名//如果文件名符合要求,会进一步检查是否找到了更早的事务日志文件//如果没有找到更早的文件,会将当前的文件名复制到newxlog数组中,并将found标记为true//如果找到了更早的文件,会将当前的文件名与newxlog数组中存储的文件名进行比较,//如果当前文件名更早,则将其复制到newxlog数组中,并将found标记为trueif (basenamelen >= MIN_XFN_CHARS && basenamelen <= MAX_XFN_CHARS &&strspn(rlde->d_name, VALID_XFN_CHARS) >= (size_t)basenamelen &&strcmp(rlde->d_name + basenamelen, ".ready") == 0) {errno_t rc = EOK;if (!found) {rc = strcpy_s(newxlog, MAX_XFN_CHARS + 6 + 1, rlde->d_name);securec_check(rc, "\0", "\0");found = true;} else {if (strcmp(rlde->d_name, newxlog) < 0) {rc = strcpy_s(newxlog, MAX_XFN_CHARS + 6 + 1, rlde->d_name);securec_check(rc, "\0", "\0");}}}}FreeDir(rldir);//如果found标记为true,则将newxlog数组中的文件名复制到xlog数组中,并返回trueif (found) {errno_t rc = EOK;/* truncate off the .ready */newxlog[strlen(newxlog) - 6] = '\0';rc = strcpy_s(xlog, (size_t)xlog_length, newxlog);securec_check(rc, "\0", "\0");}return found;}
pgarch_archiveXlog(char* xlog){//判断归档目录是否存在,如果不存在则创建if (XLogArchiveDestSet()) {return PgarchArchiveXlogToDest(xlog);}//判断筛选一下xlogarchcmd,并执行,若rc不为0则执行失败,返回false,否则返回truerc = gs_popen_security(xlogarchcmd);}
//主要是将归档目录下的.ready文件重命名为.done文件,至此完成归档流程static void pgarch_archiveDone(const char* xlog){char rlogready[MAXPGPATH];char rlogdone[MAXPGPATH];StatusFilePath(rlogready, MAXPGPATH, xlog, ".ready");StatusFilePath(rlogdone, MAXPGPATH, xlog, ".done");(void)durable_rename(rlogready, rlogdone, WARNING);}






