openGemini中对于时间的筛选分散于代码的各个位置和层级。因为数据在存储时就根据时间进行了分片,将不同时间段的数据存储在不同的shards中。除此之外,在tssp文件中,不同时间线的数据分割成不同的block存放,每个block中的时间又分别有序。而当插入数据时出现时间乱序时,顺序和乱序的数据也会分开存放。为了应对这些在不同层级根据时间切分数据的策略,以及对性能的考量,导致了openGemini对于时间的处理比较复杂。
一、编译和准备
当一条查询SQL传到ts-sql节点,该语句会经过解析成AST,再经过编译和准备。
在编译阶段的preprocess方法中,这里从condition中将查询限制的时间范围提取出来,并将时间过滤条件和condition中的其他条件分开,单独储存在timeRange字段中。因为时间的特殊性,所以会将时间和其他condition分开来处理。
// preprocess retrieves and records the global attributes of the current statement.func (c *compiledStatement) preprocess(stmt *influxql.SelectStatement) error {c.Ascending = stmt.TimeAscending()c.Limit = stmt.Limitc.HasTarget = stmt.Target != nilvaluer := influxql.NowValuer{Now: c.Options.Now, Location: stmt.Location}// 解析编译condition并分离时间条件cond, t, err := influxql.ConditionExpr(stmt.Condition, &valuer)if err != nil {return err}// Verify that the condition is actually ok to use.if err := c.validateCondition(cond); err != nil {return err}// 条件和时间分开存放c.Condition = condc.TimeRange = t...}
二、Shard层面的时间筛选
在准备阶段,我们会根据Shard自身的时间范围和查询携带的时间条件,筛选出目标数据所属shards。
对于每一个拿到的shards,逻辑计划会生成一个对应的LogicalIndexScan和其下层算子。
func (c *compiledStatement) Prepare(shardMapper ShardMapper, sopt SelectOptions) (PreparedStatement, error) {// we need to limit the possible time range that can be used when mapping shards but not when actually executing// the select statement. Determine the shard time range here.timeRange := c.TimeRange...// Create an iterator creator based on the shards in the cluster.shards, err := shardMapper.MapShards(c.stmt.Sources, timeRange, sopt, c.stmt.Condition)if err != nil {return nil, err}...return NewPreparedStatement(stmt, &opt, shards, columns, sopt.MaxPointN, c.Options.Now), nil}
目标shards的查找逻辑在mapMstShards方法中,通过csm.MetaClient.ShardGroupsByTimeRange方法,可以拿到包含查询时间的ShardGroups。
func (csm *ClusterShardMapper) mapMstShards(s *influxql.Measurement, csming *ClusterShardMapping, tmin, tmax time.Time, condition influxql.Expr, opt *query.SelectOptions) error {source, shardKeyInfo, measurements, engineTypes, err := csm.getTargetShardMsg(s)if err != nil {return err}// Retrieve the list of shards for this database. This list of// shards is always the same regardless of which measurement we are// using.if _, ok := csming.ShardMap[source]; !ok {groups, err := csm.MetaClient.ShardGroupsByTimeRange(s.Database, s.RetentionPolicy, tmin, tmax)if err != nil {return err}...}return nil}
MetaClient可以看做是连接Meta集群的客户端,用来给Meta节点发送命令和接收元数据,其中的cacheData字段保存着元数据快照,在SQL节点启动时,会从Meta集群获取一份元数据快照保存,并定期拉取更新。这里从元数据中根据查询的Database名和RP名获取到对应的RetentionPolicy元数据,通过遍历切片组找到包含所查询时间的切片组并返回。OpenGemini根据保留策略的Shard Duration划分Shards,同一个切片组的切片拥有相同起始时间。当一个Shard Group到期后,系统会创建新的Shard Group,并为每个节点分配新的分片 (Shard)。
// ShardGroupsByTimeRange returns a list of all shard groups on a database and policy that may contain data// for the specified time range. Shard groups are sorted by start time.func (c *Client) ShardGroupsByTimeRange(database, policy string, min, max time.Time) (a []meta2.ShardGroupInfo, err error) {c.mu.RLock()defer c.mu.RUnlock()// Find retention policy.rpi, err := c.cacheData.RetentionPolicy(database, policy)if err != nil {return nil, err} else if rpi == nil {return nil, meta2.ErrRetentionPolicyNotFound(policy)}groups := make([]meta2.ShardGroupInfo, 0, len(rpi.ShardGroups))for _, g := range rpi.ShardGroups {if g.Deleted() || !g.Overlaps(min, max) {continue}groups = append(groups, g)}return groups, nil}
// Client is used to execute commands on and read data from// a meta service cluster.type Client struct {...cacheData *meta2.Data...// send RPC message interface.SendRPCMessage}
// Data represents the top level collection of all metadata.type Data struct {Term uint64 // associated raft termIndex uint64 // associated raft indexClusterID uint64ClusterPtNum uint32 // default number is the total cpu number of 16 nodes.PtNumPerNode uint32NumOfShards int32 // default number of shard for measurement created by `CREATE MEASUREMENT ... SHARDS AUTO`MetaNodes []NodeInfo // careful: metaNode.gossipAddr is not use.DataNodes []DataNode // data nodesSqlNodes []DataNode // sql nodesPtView map[string]DBPtInfos // PtView's key is dbname, value is PtInfo's slice.ReplicaGroups map[string][]ReplicaGroup // key is dbname, value is the replication group of the databaseDatabases map[string]*DatabaseInfoStreams map[string]*StreamInfoUsers []UserInfo...
拿到ShardGroups后,对每一个group进行遍历,通过TargetShards方法找到其中存活且可读的Shards,如果创建表时指定了ShardKey,这里也会根据ShardKey和查询的Tags条件做一个筛选。
func (csm *ClusterShardMapper) mapMstShards(s *influxql.Measurement, csming *ClusterShardMapping, tmin, tmax time.Time, condition influxql.Expr, opt *query.SelectOptions) error {source, shardKeyInfo, measurements, engineTypes, err := csm.getTargetShardMsg(s)if err != nil {return err}// Retrieve the list of shards for this database. This list of// shards is always the same regardless of which measurement we are// using.if _, ok := csming.ShardMap[source]; !ok {groups, err := csm.MetaClient.ShardGroupsByTimeRange(s.Database, s.RetentionPolicy, tmin, tmax)if err != nil {return err}if len(groups) == 0 {csming.ShardMap[source] = nilreturn nil}shardInfosByPtID := make(map[uint32][]executor.ShardInfo)//firstSetTimeRange := truefor i, g := range groups {// ShardGroupsByTimeRange would get all shards with different engine type in the TimeRange,// we only need to process shards with engine type in engineTypes or equals to engineType.if !engineTypes[g.EngineType] {continue}if shardKeyInfo == nil {shardKeyInfo = measurements[0].GetShardKey(groups[i].ID)}aliveShardIdxes := csm.MetaClient.GetAliveShards(s.Database, &groups[i], true)var shs []meta2.ShardInfoif opt.HintType == hybridqp.FullSeriesQuery || opt.HintType == hybridqp.SpecificSeriesQuery {shs, csming.seriesKey = groups[i].TargetShardsHintQuery(measurements[0], shardKeyInfo, condition, opt, aliveShardIdxes)} else {shs = groups[i].TargetShards(measurements[0], shardKeyInfo, condition, aliveShardIdxes)}csm.updateShardInfosByPtID(s, g, shs, &shardInfosByPtID)}csming.ShardMap[source] = shardInfosByPtID}return nil}
三、TSSP文件
经过了shards的筛选,我们接下来会做tssp文件中的进一步筛选。
在IndexScanTransform中,会完成对索引的扫描,获取到对应的serieskeys和sids,这之后会生成ChunkReader,创建GroupCursor,TagSetCursor,SeriesCursor等用于读取数据。需要注意的是,当我们打印逻辑计划,可以看到LogIcalIndexScan和下层的LogicalReader等逻辑算子,而在生成物理计划执行Pipeline时,LogIcalIndexScan下层的算子并没有立即生成对应的物理算子。而是等待IndexScanTransform索引扫描完成,确定了数据所在的文件范围后,再进行延迟展开,将ChunkReader以及下层的Cursors创建并在IndexScanTransform下的sub-pipeline中执行。
以下述SQL为例:
> select * from mstname: mst+---------------------+-----------+-------+-------+----------+--------+--------+| time | address | age | alive | country | height | name |+---------------------+-----------+-------+-------+----------+--------+--------+| 1629129600000000000 | shenzhen | 12.3 | true | china | 70 | azhu || 1629129601000000000 | shanghai | 20.5 | false | american | 80 | alan || 1629129602000000000 | beijin | 3.4 | true | germany | 90 | alang || 1629129603000000000 | guangzhou | 30 | false | japan | 121 | ahui || 1629129604000000000 | chengdu | 35 | true | canada | 138 | aqiu || 1629129605000000000 | wuhan | 48.8 | <nil> | china | 149 | agang || 1629129606000000000 | <nil> | 52.7 | true | american | 153 | agan || 1629129607000000000 | anhui | 28.3 | false | germany | <nil> | alin || 1629129608000000000 | xian | <nil> | true | japan | 179 | ali || 1629129609000000000 | hangzhou | 60.8 | false | canada | 180 | <nil> || 1629129610000000000 | nanjin | 102 | true | <nil> | 191 | ahuang || 1629129611000000000 | zhengzhou | 123 | false | china | 203 | ayin || 1629129612000000000 | liuzhou | 15.4 | true | china | 68 | azhu |+---------------------+-----------+-------+-------+----------+--------+--------+7 columns, 13 rows in set> select * from mst where time >= 1629129606000000000 and time <= 1629129611000000000name: mst+---------------------+-----------+-------+-------+----------+--------+--------+| time | address | age | alive | country | height | name |+---------------------+-----------+-------+-------+----------+--------+--------+| 1629129606000000000 | <nil> | 52.7 | true | american | 153 | agan || 1629129607000000000 | anhui | 28.3 | false | germany | <nil> | alin || 1629129608000000000 | xian | <nil> | true | japan | 179 | ali || 1629129609000000000 | hangzhou | 60.8 | false | canada | 180 | <nil> || 1629129610000000000 | nanjin | 102 | true | <nil> | 191 | ahuang || 1629129611000000000 | zhengzhou | 123 | false | china | 203 | ayin |+---------------------+-----------+-------+-------+----------+--------+--------+7 columns, 6 rows in set
在shard的CreateCursor方法中,通过Scan方法扫描获取到seireskeys后,会调用createGroupCursor方法创建GroupCursor,接着在createGroupSubCursor方法中的newTagSetCursor创建TagSetCursor,在itrsInit方法中创建SeriesCursor,最后创建TsmMergeCursor以及其下面的LocationCursor。
type LocationCursor struct {rowNum intpos intlcs []*LocationfilterRecPool *record.CircularRecordPool}
locationCursor的lcs字段保存着需要被读取的tssp文件以及Chunk Meta,其数据结构Location如下:
type Location struct {ctx *ReadContextr TSSPFilemeta *ChunkMetasegPos intfragPos int // Indicates the sequence number of a fragment range.fragRgs []*fragment.FragmentRange}
初始化TsmMergeCursor时,会通过AddLoc方法将需要读取的Location加入到lcs字段中。在OpenGemini中,顺序数据和乱序数据由插入数据时,是否按时间顺序插入来区分。为了保证读写效率,顺序数据和乱序数据会分开存放。
func (c *tsmMergeCursor) AddLoc() error {var err error...// 顺序数据err = AddLocationsWithInit(c.locations, c.ctx.readers.Orders, c.ctx, c.sid)if err != nil {return err}// 乱序数据err = AddLocationsWithInit(c.outOfOrderLocations, c.ctx.readers.OutOfOrders, c.ctx, c.sid)if err != nil {return err}}...return nil}
func AddLocationsWithInit(l *immutable.LocationCursor, files immutable.TableReaders, ctx *idKeyCursorContext, sid uint64) error {var chunkMetaContext *immutable.ChunkMetaContext...if err := AddLocations(l, files, ctx, sid, chunkMetaContext); err != nil {return err}return nil}
接着会进入到AddLocations方法中,在loc.Cotations方法会进行条件筛选
func AddLocations(l *immutable.LocationCursor, files immutable.TableReaders, ctx *idKeyCursorContext, sid uint64, metaCtx *immutable.ChunkMetaContext) error {for _, r := range files {if ctx.IsAborted() {return nil}loc := immutable.NewLocation(r, ctx.decs)contains, err := loc.Contains(sid, ctx.tr, metaCtx)if err != nil {return err}if contains {l.AddLocation(loc)}}return nil}
func (l *Location) Contains(sid uint64, tr util.TimeRange, ctx *ChunkMetaContext) (bool, error) {// use bloom filter and file time range to filter generallycontains, err := l.r.ContainsValue(sid, tr)if err != nil {return false, err}if !contains {return false, nil}// read file meta to judge whether file has data, chunk meta will also initerr = l.readChunkMeta(sid, tr, ctx)if err != nil {return false, err}if l.meta == nil {return false, nil}if l.ctx.Ascending {return l.segPos < int(l.fragRgs[len(l.fragRgs)-1].End), nil}return l.segPos >= int(l.fragRgs[0].Start), nil}
这里首先会通过bloom过滤器过滤sid,以及trainler中的min/maxTime做一个文件级的时间过滤。trainler的min/max time表示文件储存的所有数据的最大和最小时间。
四、Chunk Meta Index
在通过了这个过滤后,我们会读取这个sid对应的chunk meta Index,chunk meta index是一个稀疏索引,多个Chunk Meta对应其中一个index,在这一步进行Chunks级别的稀疏索引时间筛选,并找到index。
func (r *tsspFileReader) MetaIndex(id uint64, tr util.TimeRange) (int, *MetaIndex, error) {if err := r.lazyInit(); err != nil {errInfo := errno.NewError(errno.LoadFilesFailed)log.Error("MetaIndex", zap.Error(errInfo))return -1, nil, err}if id < r.trailer.minId || id > r.trailer.maxId {return 0, nil, nil}idx := searchMetaIndexItem(r.metaIndexItems, id)if idx < 0 {return -1, nil, nil}metaIndex := &r.metaIndexItems[idx]// Chunk级的时间过滤if !tr.Overlaps(metaIndex.minTime, metaIndex.maxTime) {return 0, nil, nil}return idx, metaIndex, nil}
五、Chunk Meta&Meta Block
通过上述index,我们可以将sid对应的目标缩小到几个chunk meta。接着通过二分查找的方式最终找到sid对应的meta block(一个chunk meta实际对应一个meta block)。chuck meta的timeranges记录着该block中包含的segment的时间范围,据此我们进行了block级的时间筛选。
func (l *Location) readChunkMeta(id uint64, tr util.TimeRange, ctx *ChunkMetaContext) error {idx, m, err := l.r.MetaIndex(id, tr)if err != nil {return err}if m == nil {return nil}ctx.meta = l.metameta, err := l.r.ChunkMeta(id, m.offset, m.size, m.count, idx, ctx, fileops.IO_PRIORITY_ULTRA_HIGH)if err != nil {return err}if meta == nil {return nil}// block级的时间过滤if !tr.Overlaps(meta.MinMaxTime()) {return nil}l.meta = meta// init a new FragmentRange as [0, meta.segCount) if not SetFragmentRanges.if len(l.fragRgs) == 0 {if cap(l.fragRgs) <= 0 {l.fragRgs = []*fragment.FragmentRange{{Start: 0, End: meta.segCount}}} else {l.fragRgs = l.fragRgs[:1]l.fragRgs[0].Start, l.fragRgs[0].End = 0, meta.segCount}l.fragPos = 0}if !l.ctx.Ascending {l.fragPos = len(l.fragRgs) - 1l.segPos = int(l.fragRgs[l.fragPos].End - 1)}return nil}
经过上述过滤,我们可以具体拿到包含在查询时间范围内的所有Chunk,并添加到Location中,最后层层包装到GroupCursor中。
六、ChunkReader
完成Cursor和LogicalIndexScan以下延迟生成的store层逻辑计划后,我们创建新的物理计划和sub-pipeline,将GroupCursor填入ChunkReader中。
接着在sub-pipeline中执行ChunkReader,真正地从tssp文件中读取数据,具体实现在ChunkReader的readChunk方法中。
func (r *ChunkReader) readChunk() (executor.Chunk, error) {if r.isPreAgg || r.multiCallsWithFirst {return r.readChunkByPreAgg()}for {if r.cursorPos >= len(r.cursor) {return nil, nil}// 读取数据为recordrec, _, err := r.nextRecord()if err != nil {return nil, err}if rec == nil {r.cursorPos++continue}name := r.cursor[r.cursorPos].Name()ck := r.ResultChunkPool.GetChunk()ck.SetName(influx.GetOriginMstName(name))ck.(*executor.ChunkImpl).Record = rectracing.SpanElapsed(r.transSpan, func() {// record转换成chunk用来在算子之间传递数据err = r.transToChunk(rec, ck)})if err != nil {return nil, err}executor.IntervalIndexGen(ck, r.schema.Options().(*query.ProcessorOptions))return ck, nil}}
在nextRecord方法,用cursor.Next()方法获取record,Next()在Cursor中层层传递,从GroupCursor.Next()到TagCursor.Next(),再到SeriesCursor.Next(),tsmMergeCursor.Next(),到LocationCursor的ReadData(),最后到Location的readData。数据在向上传递时会在不同cursor进行包装、聚合、字段处理、分组、聚合等操作,这里暂不赘述。重点关注数据从文件的获取。在这个方法中,对时间进行了segment级和行级的筛选。
func (l *Location) readData(filterOpts *FilterOptions, dst, filterRec *record.Record, filterBitmap *bitmap.FilterBitmap,unnestOperator UnnestOperator) (*record.Record, int, error) {var rec *record.Recordvar err errorvar oriRowCount intif !l.ctx.tr.Overlaps(l.meta.MinMaxTime()) {l.nextSegment(true)return nil, 0, nil}for rec == nil && l.hasNext() {if l.ctx.IsAborted() {return nil, oriRowCount, nil}// 判断当前segment是否包含时间范围if (!l.ctx.tr.Overlaps(l.getCurSegMinMax())) ||(!l.overlapsForRowFilter(filterOpts.rowFilters)) {l.nextSegment(false)continue}tracing.StartPP(l.ctx.readSpan)// 读取当前segment的数据rec, err = l.r.ReadAt(l.meta, l.segPos, dst, l.ctx, fileops.IO_PRIORITY_ULTRA_HIGH)if err != nil {return nil, 0, err}l.nextSegment(false)...tracing.SpanElapsed(l.ctx.filterSpan, func() {if rec != nil {oriRowCount += rec.RowNums()if l.ctx.Ascending {// 对每个数据行进行时间筛选rec = FilterByTime(rec, l.ctx.tr)} else {rec = FilterByTimeDescend(rec, l.ctx.tr)}}// filter by fieldif rec != nil {rec = FilterByField(rec, filterRec, filterOpts.options, filterOpts.cond, filterOpts.rowFilters, filterOpts.pointTags, filterBitmap, &filterOpts.colAux)}})}return rec, oriRowCount, nil}
总结
从SQL时间的过滤过程,我们可以一窥OpenGemini数据从文件中被筛选获取的过程。正如tssp layout文件所示:
https://github.com/openGemini/openGemini/wiki/V1.3-tssp-layout
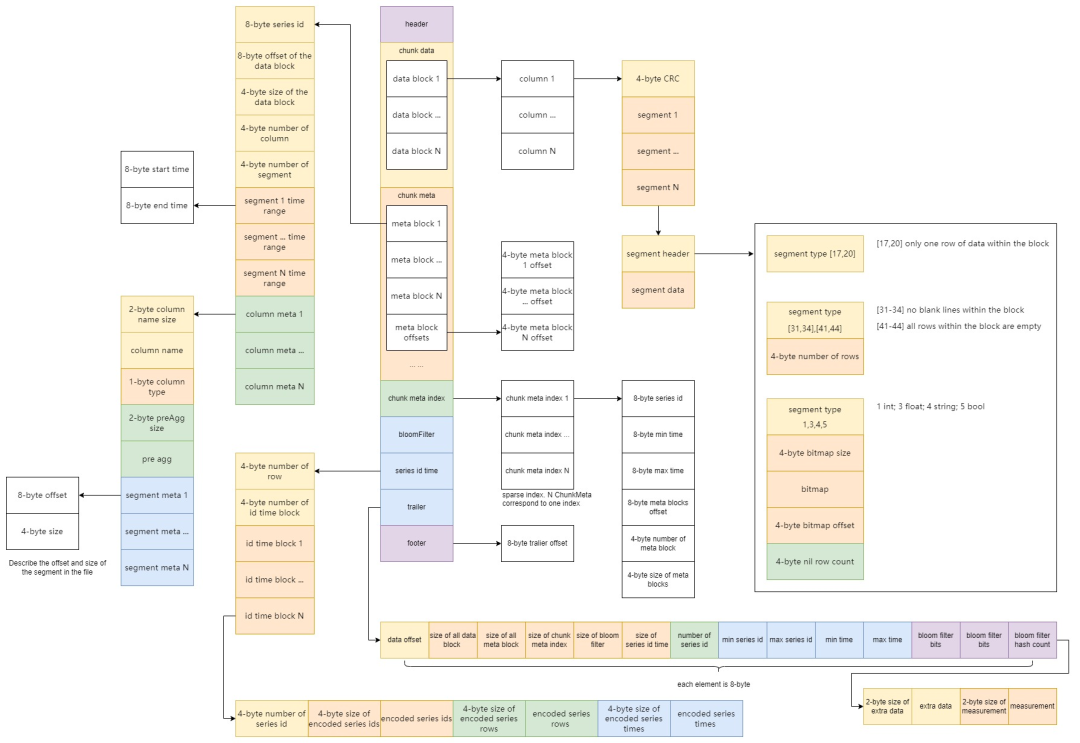
从SQL层拿到查询SQL后,先根据时间范围从Meta获取到shards分片。进入STORE层后,对Shard进行索引扫描获取到sids。
接着通过sid查询各个tssp文件,首先通过文件的trailer找到文件的min/max time做过滤,再借助chunk meta index稀疏索引的min/max time过滤并找到chunk meta和meta block,通过meta block的segment times在查询数据前做最后筛选。接着通过meta block拿到data block的offset和size,以此真正获取数据,并通过数据的time完成时间过滤。
欢迎访问WELCOME TO VISIT
openGemini官网
https://www.openGemini.org
Star for me 🌟
https://github.com/openGemini
更多精彩内容,可以关注openGemini微信公众号查看,还有交流群等你加入哦~






