ELK环境部署
【历史库存文档】
之前做的ELK的环境,只用了logstash作为收集日志的agent,而logstash消耗系统资源很大,在生产环境下将logstash作为agent和服务跑在一起并不理想,今天有空闲时间,在自己本地对原来的结构做了调整,收集日志的agent采用轻量的filebeat,并且中间使用redis进行数据写入的缓冲,整体架构如下图
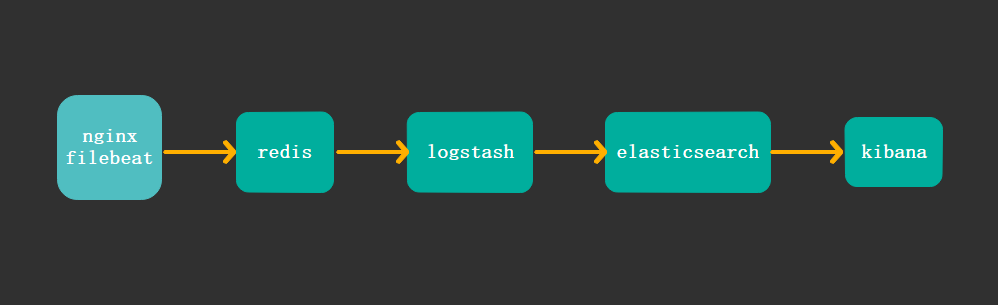
主机规划:
192.168.2.141 :部署应用 nginx, filebeat
192.168.2.142 :部署redis
192.168.2.143 :部署logstash
192.168.2.144 :部署elasticsearch
192.168.2.145 :部署kibana
部署nginx与filebeat
安装nginx
[root@nginx-filebeat ~]# yum install nginx -y
安装filebeat
[root@nginx-filebeat sowft]# yum install filebeat-5.6.10-x86_64.rpm -y
查看filebeat安装后的相关路径
[root@nginx-filebeat sowft]# rpm -ql filebeat
配置filebeat,将日志输出到redis
在
/etc/filebeat/filebeat.full.yml
文件中有对redis配置的内容,将里面的对应内容复制添加到/etc/filebeat/filebeat.yml
中,如下配置
#------------------------------- Redis output ----------------------------------
output.redis:
# Boolean flag to enable or disable the output module.
enabled: true
# The list of Redis servers to connect to. If load balancing is enabled, the
# events are distributed to the servers in the list. If one server becomes
# unreachable, the events are distributed to the reachable servers only.
hosts: ["192.168.2.142:6379"]
# The Redis port to use if hosts does not contain a port number. The default
# is 6379.
port: 6379
# The name of the Redis list or channel the events are published to. The
# default is filebeat.
key: filebeat
# The password to authenticate with. The default is no authentication.
#password:
# The Redis database number where the events are published. The default is 0.
db: 0
# The Redis data type to use for publishing events. If the data type is list,
# the Redis RPUSH command is used. If the data type is channel, the Redis
# PUBLISH command is used. The default value is list.
datatype: list
部署redis
[root@redis-server ~]# yum install reids -y
修改监听端口,其他设置可以暂不修改
bind 0.0.0.0
安装logstash
安装jdk
yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel.x86_64 -y
安装logstash
[root@logstash logstash]# yum localinstall logstash-5.6.10.rpm -y
将logstash指令加入环境变量
[root@logstash ~]# vim /etc/profile.d/logstash.sh
export PATH=/usr/share/logstash/bin:$PATH
[root@logstash ~]# source /etc/profile.d/logstash.sh
修改vim /etc/logstash/jvm.options文件
-Xms1g
-Xmx1g
#两个值保持一样,如果不一样logstash无法传输文档到ESserver
测试logstash正确性
[root@logstash ~]# cd /etc/logstash/conf.d
[root@logstash conf.d]# vim test.conf
input {
stdin{}
}
output {
stdout{}
}
执行测试指令
[root@logstash conf.d]# logstash -f ./test.conf -t
Configuration OK
logstash上的配置文件暂时可以不配置,等部署完elasticsearch后在配置logstash的过滤规则,这里只做正确性测试即可
部署elasticsearch
安装jdk
[root@elastic ~]# yum install java-1.8.0-openjdk-devel.x86_64 -y
安装elasticsearch
[root@elastic opt]# yum install elasticsearch-5.6.10.rpm -y
修改配置
[root@elastic ~]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: my-application
node.name: node-1
path.data: /elk/data
path.logs: /elk/logs
network.host: 192.168.2.144
http.port: 9200
创建日志和数据目录
[root@elastic ~]# mkdir -p /elk/{data,logs}
将目录属主改为elasticsearch用户
[root@elastic ~]# chown -R elasticsearch.elasticsearch /elk/
启动服务
[root@elastic ~]# systemctl start elasticsearch
在nginx应创建测试数据访问
创建测试页面
[root@nginx-filebeat html]# for i in {1..150};do echo test$i > test$i.html;done
模拟不同地址访问生成日志
[root@nginx-filebeat ~]# while true; do ip=$[$RANDOM%223+1]; curl --header "X-Forwarded-For: $ip.33.22.100" http://192.168.2.141/test$ip.html; sleep 2;done
以上的配置可以自动测试访问nginx,并生成不同的ip地址段
配置logstash过滤规则
input {
# file {
#
# start_position => "end"
# path => ["/var/log/nginx/access.log"]
#
# }
# 以上file段配置是针对logstash作为agent端收集日志的场景使用,从本地文件输入
redis {
host => "192.168.2.142"
port => "6379"
key => "filebeat" #这里的key要与filebeat.yml中定义的key相同
data_type => "list"
# threads => "5"
db => "0"
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{HTTPD_COMBINEDLOG} \"%{DATA:realclient}\"" }
remove_field => "message"
}
# \"%{DATA:realclient}\" 可以记录nginx的真实客户端地址
date {
match => [ "timestamp","dd/MMM/YYYY:H:m:s Z" ]
remove_field => "timestamp"
}
}
output {
# elasticsearch { #输出到elasticsearch服务器,先输出到本地终端查看,没有问题后输出到elasticsearch
# hosts => "192.168.2.144:9200"
# index => "logstash-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
# document_type => "nginx_logs"
# }
stdout { #输出到屏幕测试
codec => rubydebug
}
}
以上的logstash的日志输出格式如下:
{
"request" => "/test1.html",
"agent" => "\"curl/7.29.0\"",
"offset" => 11699,
"auth" => "-",
"ident" => "-",
"input_type" => "log",
"verb" => "GET",
"source" => "/var/log/nginx/access.log",
"type" => "log",
"referrer" => "\"-\"",
"@timestamp" => 2018-09-27T08:35:35.000Z,
"realclient" => "1.33.22.100",
"response" => "200",
"bytes" => "6",
"clientip" => "192.168.2.141",
"beat" => {
"name" => "nginx-filebeat",
"hostname" => "nginx-filebeat",
"version" => "5.6.10"
},
"@version" => "1",
"httpversion" => "1.1"
}
把配置文件中的配置output输出对象改为输出到elasticsearch
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "192.168.2.144:9200"
index => "logstash-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
document_type => "nginx_logs"
}
# stdout { #输出到屏幕测试
# codec => rubydebug
# }
}
注意:/etc/logstash/conf.d/ 目录下的所有文件都会被加载,不仅仅是以.conf结尾的文件,所以正常情况下该目录只存在一个确定使用的配置文件,其他文件都不要放在这
启动logstash服务
systemctl start logstash
查看elasticsearch服务生成的数据文件,实时访问服务,看看数据文件大小是否变化
[root@logstash ~]# curl -XGET 192.168.2.144:9200/_cat/indices
yellow open logstash-2018.09.27 vOhS-Hq7RG-oAYTUJng91Q 5 1 93 0 560.7kb 560.7kb
[root@logstash ~]# curl -XGET 192.168.2.144:9200/_cat/indices
yellow open logstash-2018.09.27 vOhS-Hq7RG-oAYTUJng91Q 5 1 106 0 651.2kb 651.2kb
#最开头以yellow开头说明配置项有点小问题。
#这个地方以红黄蓝颜色标记数据传输状态。
#黄色是缺失索引文件副本,ESserver是以集群的方式工作的,但这里是单节点
部署配置kibana
[root@kibana opt]# yum localinstall kibana-5.6.1-x86_64.rpm -y
配置
server.port: 5601
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
server.name: "kibana"
elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.2.144:9200"
启动
[root@kibana ~]# systemctl start kibana
登录Kibana只需在浏览器数据kibana服务器地址+5601端口即可,经过访问测试,以上配置登录kibana调取日志访问成功
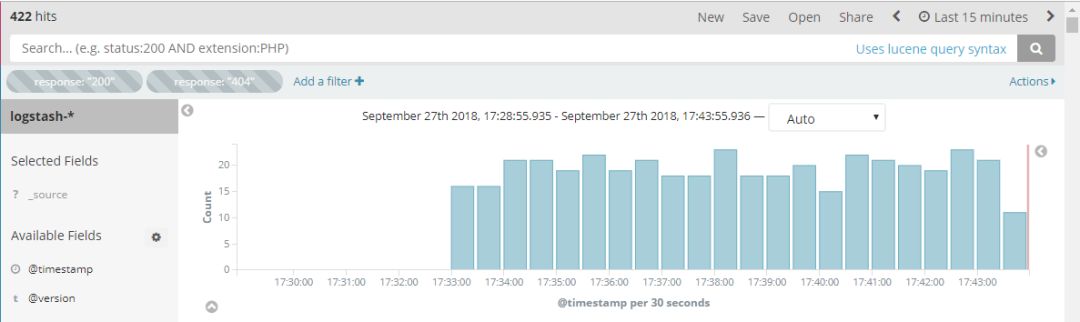
配置用户的ip归属地
ip地址的归属地查询需要使用互联网上的地图的解析库,地图的解析库会定期地更新,下载到服务器本地,解压,在logstash的配置文件中指定解压后的
.mmdb
后缀的文件路径
地图解析库下载地址:https://dev.maxmind.com/geoip/geoip2/geolite2/
logstash的配置文件添加 geoip段,最终配置段如下:
redis {
host => "192.168.2.142"
port => "6379"
key => "filebeat"
data_type => "list"
# threads => "5"
db => "0"
}
}
filter {
grok {
match => {
"message" => "%{HTTPD_COMBINEDLOG} \"%{DATA:realclient}\""
}
remove_field => "message"
}
date {
match => [ "timestamp","dd/MMM/YYYY:H:m:s Z" ]
remove_field => "timestamp"
}
geoip { #ip地址归属配置段
source => "realclient"
target => "geoip"
database => "/home/city/GeoLite2-City_20180925/GeoLite2-City.mmdb"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => "192.168.2.144:9200"
index => "logstash-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
document_type => "nginx_logs"
}
# 注意:
# 1、输出的日志文件名必须以“logstash-”开头,方可将geoip.location的type自动设定为"geo_point";
# 2、target => "geoip"
# stdout { #输出到屏幕调试
# codec => rubydebug
# }
}
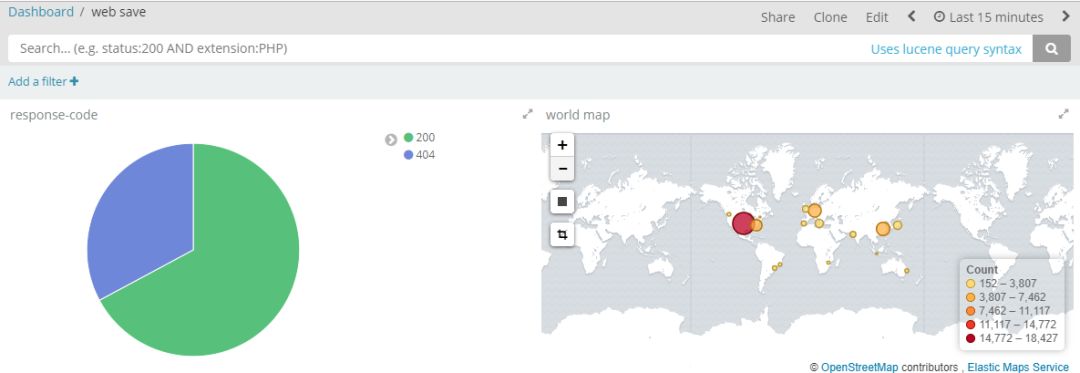
至此,基于filebeat+redis+logstash+elasticsearch+kibana的日志收集系统部署完成






