机器学习之路
预测未来股价(二)
首先我们要对得到的股票行情信息进行数据清洗,将数据中的空值写成-99999,并定义预测的天数。这样将数据喂给机器时,机器会比对其他正常的数据,判别出此为异常值。代码如下:
future_value='close'df.fillna(value=-99999,inplace=True) #填充数据中空值为-99999,检测时剔除异常值far_forecast=int(math.ceil(0.01*len(df))) #预测的天数变成整数print(far_forecast)
打印结果,可以看到预测天数正好为7,也就是一周:

接下来对收盘价做偏移,作为未来七天的预测值的标签:
df['label']=df[future_value].shift(-far_forecast) #将7天的收盘价格放到预测的label上df.dropna(inplace=True) #删除掉shift偏移为空的值#print(df)print(df.head(10))print(df.tail())
可以看到收盘价已做偏移,并且最后含有Null值的数据也被删掉了:
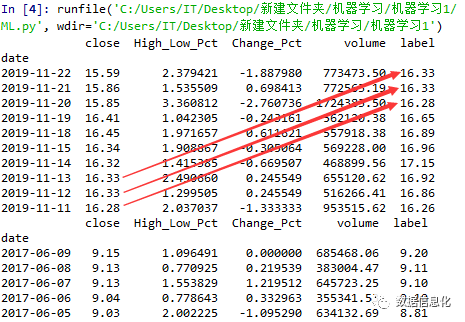
接下来我们要定义变量以及贴上对应的标签。从上面的数据可以看到每行的数据相差较大,从-1.887980到773473.50,所以我们要做数据标准化处理:
x = np.array(df.drop(['label'],1)) #只保留close,High_Low_Pct,Change_Pct,volume等变量x = preprocessing.scale(x) # 将数据集标准化处理,使预处理量纲保持一致x_Recent_Real_Data = x[-far_forecast:] #只用尾部的部分来做预测y = np.array(df['label'])
进行交叉验证,用75%的数据进行训练:
x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.25) #进行交叉验证,设置测试数据预留25%,不断洗牌,避免结果有偏见
下面将采用两种算法,来看下机器预测的准确度:
算法一(线性回归算法:LinearRegression):
具体算法数学模型请看:
https://blog.csdn.net/lilong_csdn/article/details/81937496
代码如下:
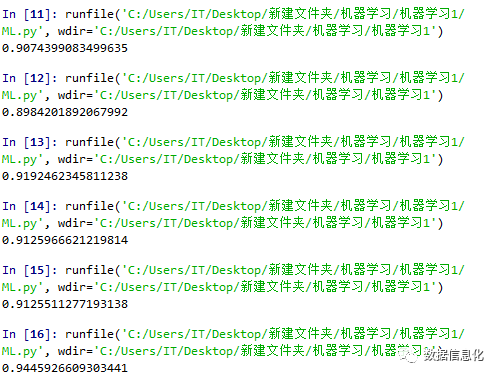
black_box = LinearRegression() #采用线性回归算法black_box.fit(x_train,y_train) #适配过程转化,将训练数据喂给机器forecast_set=black_box.predict(x_Recent_Real_Data) #用尾部数据做测试#print(forecast_set)#print(df.tail(7))accuracy = black_box.score(x_test,y_test) #对比模拟数据,显示正确率print(accuracy)
可以看到预测的正确率高达94%:
算法二(支持向量机算法:Support Vector Machine):
具体算法数学模型请看:
https://blog.csdn.net/u011630575/article/details/78916747
代码如下:
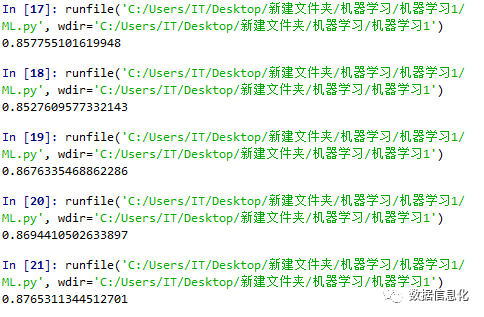
black_box = svm.SVR()#采用支持向量机算法black_box.fit(x_train,y_train) #适配过程 转化forecast_set=black_box.predict(x_Recent_Real_Data)#print(forecast_set)#print(df.tail(7))accuracy = black_box.score(x_test,y_test) #对比模拟数据,显示正确率print(accuracy)
这里注意在调用svm算法的时候,可能以为版本的原因出现warning,要去除显示添加代码:
import warningswarnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=FutureWarning, module="sklearn", lineno=193) #忽略警告
可以看到预测的正确率高达87%:
虽然这两种算法的准确率都达到了80%以上,但是实际情况按照预测的股价来买的话肯定是赔钱的,这是因为机器预测只是一个大致的方向,而实际收盘价会在此方向上下浮动。
代码全量展示:
import pandas as pdimport tushare as tsimport mathimport numpy as npfrom sklearn import preprocessing, svmfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegressionimport warningswarnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=FutureWarning, module="sklearn", lineno=193) #忽略警告df=ts.get_hist_data('000001')df=df[['open','high','close','low','volume']]df['High_Low_Pct']=(df['high']-df['low'])/df['low']*100 #增幅比:(最高价-最低价)/最低价df['Change_Pct']=(df['close']-df['open'])/df['open']*100 #涨幅比:(收盘价-开盘价)/开盘价df=df[['close','High_Low_Pct','Change_Pct','volume']]pd.set_option('display.max_rows',1000)pd.set_option('display.max_columns',1000)#print(df.head(20))future_value='close'df.fillna(value=-99999,inplace=True) #填充数据中空值为-99999,检测时剔除异常值far_forecast=int(math.ceil(0.01*len(df))) #预测的天数变成整数#print(far_forecast)df['label']=df[future_value].shift(-far_forecast) #将7天的收盘价格放到预测的label上df.dropna(inplace=True) #删除掉shift偏移为空的值#print(df)#print(df.head(10))#print(df.tail())x = np.array(df.drop(['label'],1)) #只保留close,High_Low_Pct,Change_Pct,volume等变量x = preprocessing.scale(x) # 将数据集标准化处理,使预处理量纲保持一致x_Recent_Real_Data = x[-far_forecast:] #只用尾部的部分来做预测y = np.array(df['label'])x_train,x_test,y_train,y_test = train_test_split(x,y,test_size=0.25) #进行交叉验证,设置测试数据预留25%,不断洗牌,避免结果有偏见#black_box = LinearRegression() #采用线性回归算法black_box = svm.SVR()#采用支持向量机算法black_box.fit(x_train,y_train) #适配过程 转化forecast_set=black_box.predict(x_Recent_Real_Data)#print(forecast_set)#print(df.tail(7))accuracy = black_box.score(x_test,y_test) #对比模拟数据,显示正确率print(accuracy)
下一章我们将继续深度研究支持向量机算法(Support Vector Machine),并且窥探黑盒(black_box)中到底发生了什么,通过可视化形象来展现。
下一章:【Python的机器学习】支持向量机算法(三)






