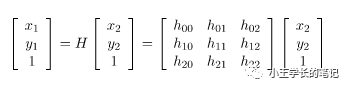一、介绍
1.1 图像对齐是什么?
1.2 图像对齐算法的应用场景有哪些?
1.3 图像对齐算法有哪些?
1.4 Homopgraphy是什么?

1.5 ORB是什么?
二、Demo展示
from __future__ import print_function
import cv2
import numpy as np
MAX_FEATURES = 500
GOOD_MATCH_PERCENT = 0.15
def drawMatches(img1, kp1, img2, kp2, matches):
"""
My own implementation of cv2.drawMatches as OpenCV 2.4.9
does not have this function available but it's supported in
OpenCV 3.0.0
This function takes in two images with their associated
keypoints, as well as a list of DMatch data structure (matches)
that contains which keypoints matched in which images.
An image will be produced where a montage is shown with
the first image followed by the second image beside it.
Keypoints are delineated with circles, while lines are connected
between matching keypoints.
img1,img2 - Grayscale images
kp1,kp2 - Detected list of keypoints through any of the OpenCV keypoint
detection algorithms
matches - A list of matches of corresponding keypoints through any
OpenCV keypoint matching algorithm
"""
# Create a new output image that concatenates the two images together
# (a.k.a) a montage
rows1 = img1.shape[0]
cols1 = img1.shape[1]
rows2 = img2.shape[0]
cols2 = img2.shape[1]
out = np.zeros((max([rows1,rows2]),cols1+cols2,3), dtype='uint8')
# Place the first image to the left
out[:rows1,:cols1,:] = np.dstack([img1, img1, img1])
# Place the next image to the right of it
out[:rows2,cols1:cols1+cols2,:] = np.dstack([img2, img2, img2])
# For each pair of points we have between both images
# draw circles, then connect a line between them
for mat in matches:
# Get the matching keypoints for each of the images
img1_idx = mat.queryIdx
img2_idx = mat.trainIdx
# x - columns
# y - rows
(x1,y1) = kp1[img1_idx].pt
(x2,y2) = kp2[img2_idx].pt
# Draw a small circle at both co-ordinates
# radius 4
# colour blue
# thickness = 1
cv2.circle(out, (int(x1),int(y1)), 4, (255, 0, 0), 1)
cv2.circle(out, (int(x2)+cols1,int(y2)), 4, (255, 0, 0), 1)
# Draw a line in between the two points
# thickness = 1
# colour blue
cv2.line(out, (int(x1),int(y1)), (int(x2)+cols1,int(y2)), (255, 0, 0), 1)
# Show the image
# cv2.imshow('Matched Features', out)
# cv2.waitKey(0)
# cv2.destroyAllWindows()
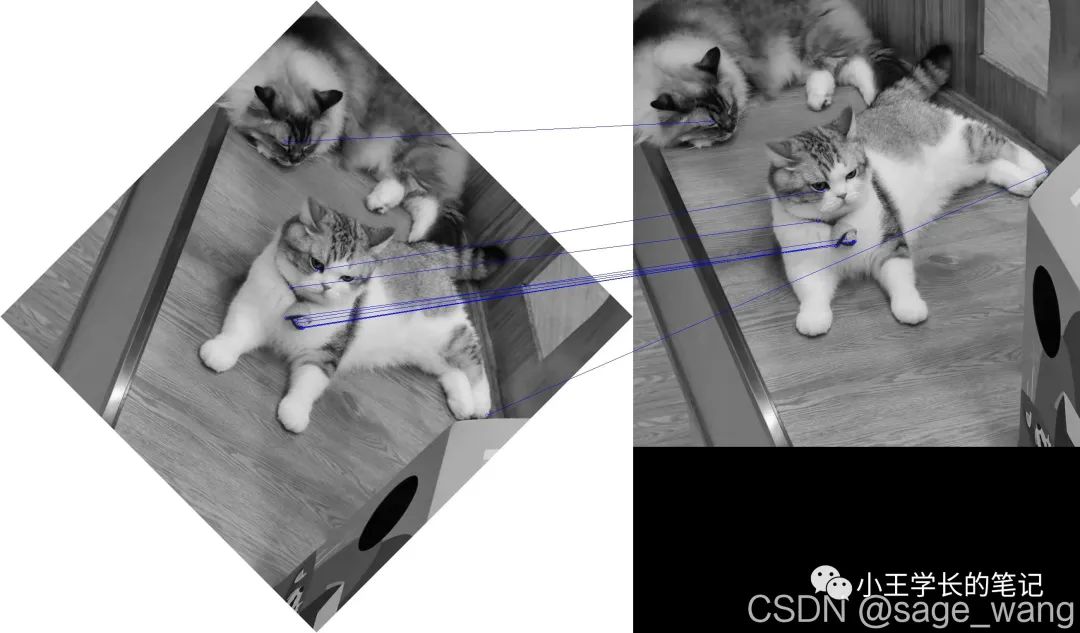
cv2.imwrite("matches.jpg", out)
def alignImages(im1, im2):
# Convert images to grayscale
im1Gray = cv2.cvtColor(im1, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
im2Gray = cv2.cvtColor(im2, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# Detect ORB features and compute descriptors.
# orb = cv2.ORB_create(MAX_FEATURES)
orb = cv2.ORB(MAX_FEATURES)
keypoints1, descriptors1 = orb.detectAndCompute(im1Gray, None)
keypoints2, descriptors2 = orb.detectAndCompute(im2Gray, None)
# Match features.
# matcher = cv2.DescriptorMatcher_create(cv2.DESCRIPTOR_MATCHER_BRUTEFORCE_HAMMING)
# matcher = cv2.DescriptorMatcher_create('BruteForce-Hamming')
bf = cv2.BFMatcher(cv2.NORM_HAMMING, crossCheck=True)
# matches = matcher.match(descriptors1, descriptors2, None)
matches = bf.match(descriptors1,descriptors2)
# Sort matches by score
matches.sort(key=lambda x: x.distance, reverse=False)
# Remove not so good matches
numGoodMatches = int(len(matches) * GOOD_MATCH_PERCENT)
matches = matches[:numGoodMatches]
# Draw top matches
# imMatches = cv2.drawMatches(im1, keypoints1, im2, keypoints2, matches, None)
# imMatches = cv2.DRAW_MATCHES_FLAGS_DEFAULT(im1, keypoints1, im2, keypoints2, matches, None)
drawMatches(im1Gray, keypoints1, im2Gray, keypoints2, matches[:10])
# cv2.imwrite("matches.jpg", imMatches)
# Extract location of good matches
points1 = np.zeros((len(matches), 2), dtype=np.float32)
points2 = np.zeros((len(matches), 2), dtype=np.float32)
for i, match in enumerate(matches):
points1[i, :] = keypoints1[match.queryIdx].pt
points2[i, :] = keypoints2[match.trainIdx].pt
# Find homography
h, mask = cv2.findHomography(points1, points2, cv2.RANSAC)
# Use homography
height, width, channels = im2.shape
im1Reg = cv2.warpPerspective(im1, h, (width, height))
return im1Reg, h
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Read reference image
# refFilename = "form.jpg"
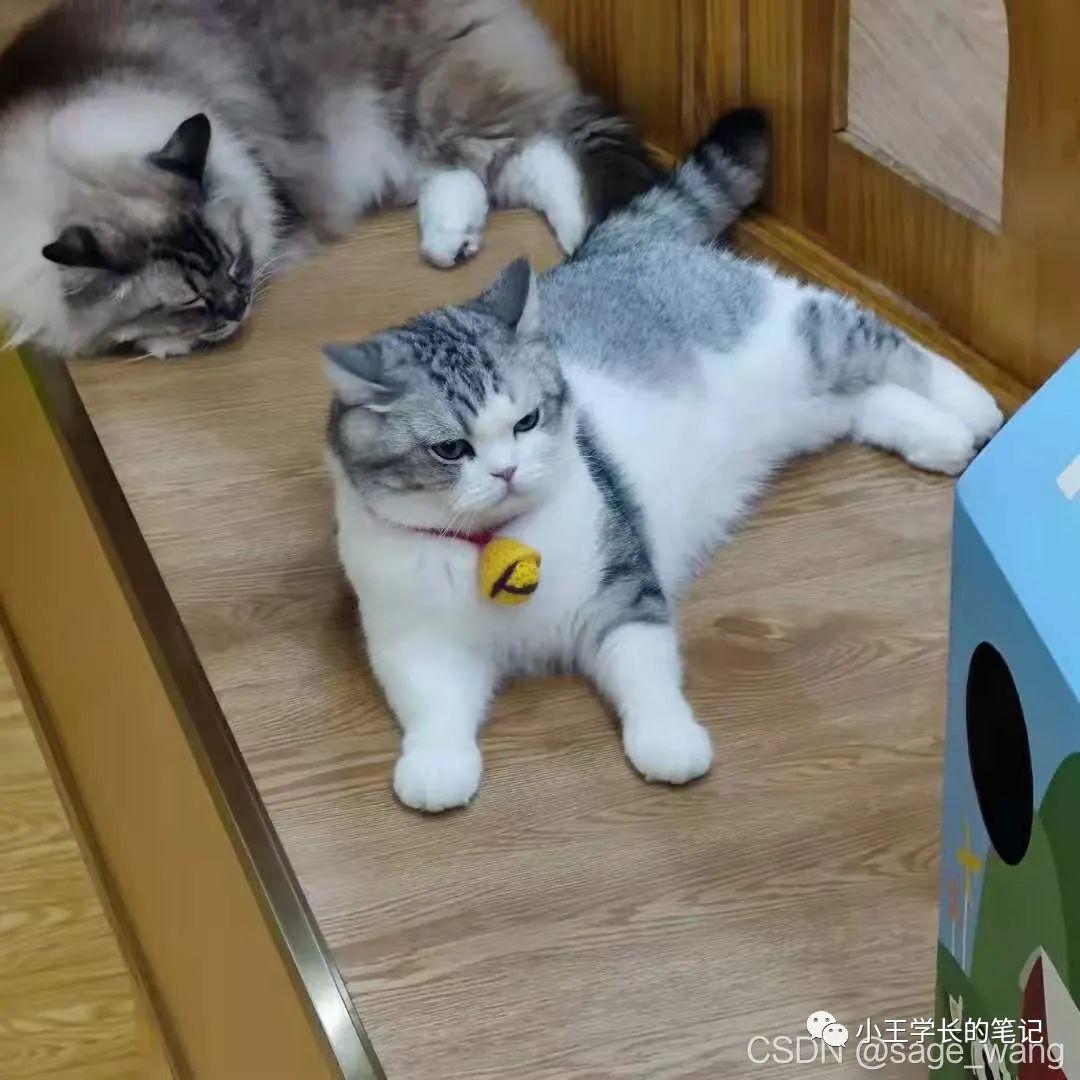
refFilename = "bighead_cat.jpg"
print("Reading reference image : ", refFilename)
imReference = cv2.imread(refFilename, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
# Read image to be aligned
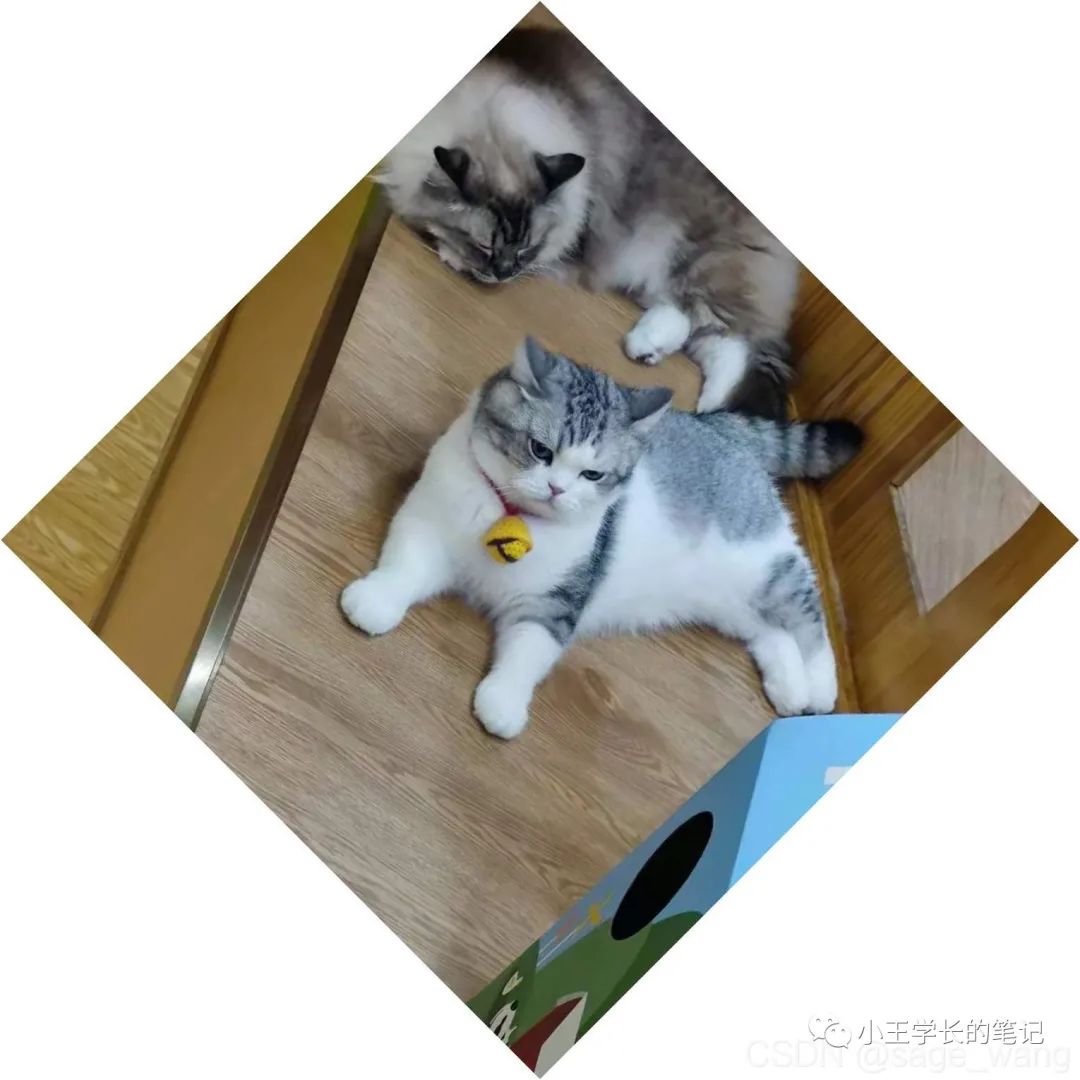
imFilename = "bighead_cat_45.jpg"
print("Reading image to align : ", imFilename);
im = cv2.imread(imFilename, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
print("Aligning images ...")
# Registered image will be resotred in imReg.
# The estimated homography will be stored in h.
imReg, h = alignImages(im, imReference)
# Write aligned image to disk.
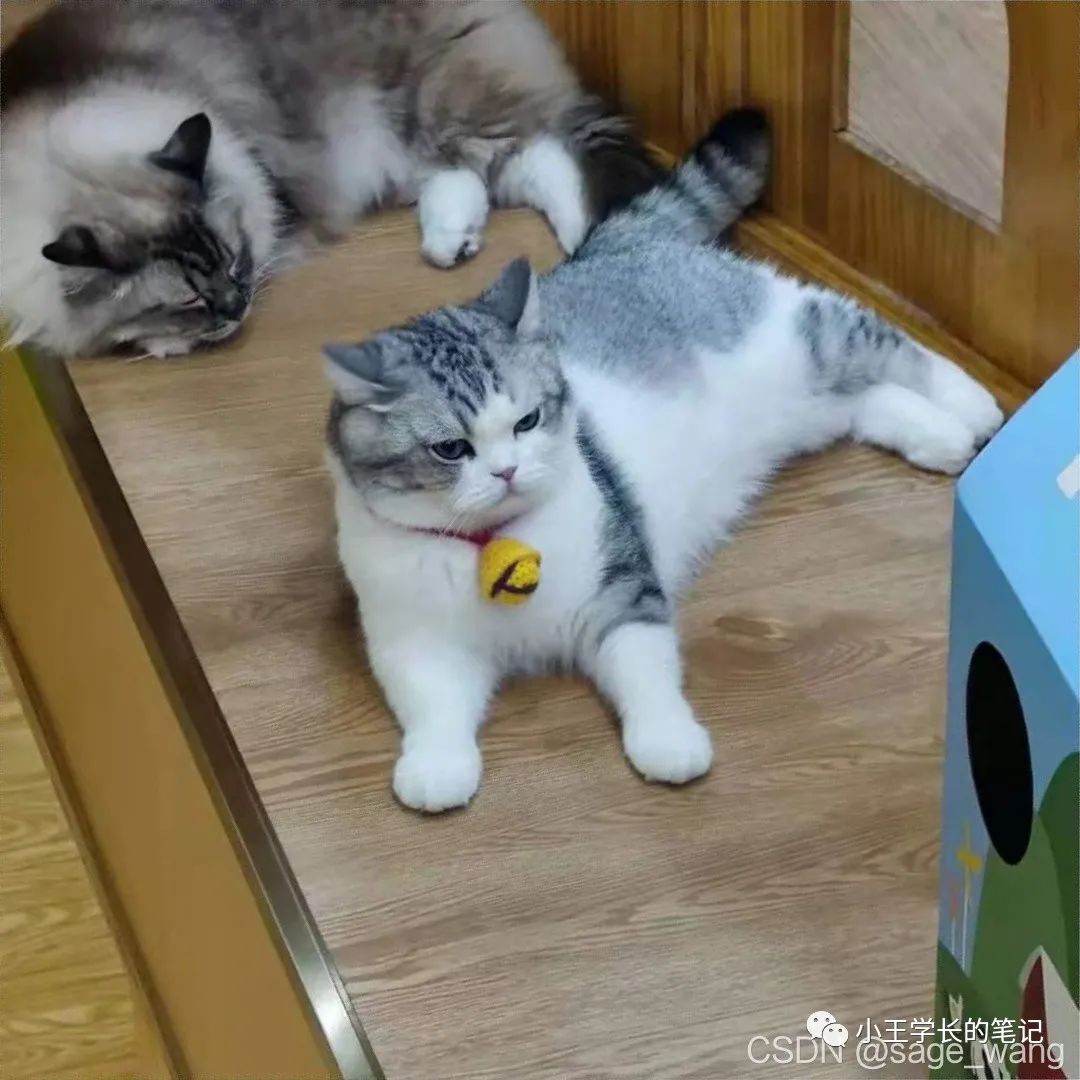
outFilename = "aligned.jpg"
print("Saving aligned image : ", outFilename);
cv2.imwrite(outFilename, imReg)
# Print estimated homography
print("Estimated homography : \n", h)
参考资料
文章转载自小王学长的笔记,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。