PAL(Program-Aided Language models) 思想成为大模型 Agent 领域的重要范式。核心思路是 LLM 只负责语言任务,复杂的逻辑/计算交由程序执行。
通过合理设计 prompt,模型生成代码/SQL/逻辑描述,外部程序再执行,得到结果后反馈给 LLM,LLM 再生成最终答案。
本文将通过一个 LangChain + MySQL + Postgres Checkpoint 实例,完整演示 PAL 的设计流程,帮助大家理解和复现。
项目结构
.├── llm_env.py # 初始化 LLM└── main.py # PAL 交互主流程
llm_env.py:初始化 LLM
from langchain.chat_models import init_chat_modelllm = init_chat_model("gpt-4o-mini", model_provider="openai")
简单封装一个 LLM 对象,这里用 gpt-4o-mini
,通过 llm_env.llm
调用。
main.py:PAL 主流程
导入库 & 初始化
import osimport syssys.path.append(os.getcwd())from langchain_community.utilities import SQLDatabasefrom langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplatefrom langchain_community.tools.sql_database.tool import QuerySQLDatabaseToolfrom langgraph.graph import START, StateGraphfrom langgraph.checkpoint.postgres import PostgresSaverimport timefrom typing import TypedDict, Annotatedfrom llm_set import llm_envllm = llm_env.llm
亮点:
用
StateGraph
组织整个流程用
PostgresSaver
持久化 checkpoint,方便中断恢复
初始化 MySQL 数据库
db = SQLDatabase.from_uri("mysql+pymysql://root:123456@localhost:3306/javademo",engine_args={"pool_size": 5, "max_overflow": 10},)
数据库连接,示例用 javademo
库,用户可根据实际修改。
State 定义
class State(TypedDict):"""State for the demo."""question: strquery: strresult: stranswer: strapproved: bool
定义流程中的共享变量,典型 PAL 模式的中间态。
Prompt 设计
system_message = """Given an input question, create a syntactically correct {dialect} query torun to help find the answer. Unless the user specifies in his question aspecific number of examples they wish to obtain, always limit your query toat most {top_k} results. You can order the results by a relevant column toreturn the most interesting examples in the database.Never query for all the columns from a specific table, only ask for a thefew relevant columns given the question.Pay attention to use only the column names that you can see in the schemadescription. Be careful to not query for columns that do not exist. Also,pay attention to which column is in which table.Only use the following tables:{table_info}"""user_prompt = "Question:{input}"query_prompt_template = ChatPromptTemplate([("system", system_message), ("human", user_prompt)],)
亮点:
系统提示明确要求 安全、规范 的 SQL
限定
top_k
结果避免
SELECT *
LLM 生成 SQL
class QueryOutput(TypedDict):"""Generated the SQL query."""query: Annotated[str, "Syntactically valid SQL query."]def write_query(state: State):"""Generate SQL query to fetch information."""prompt = query_prompt_template.invoke({"dialect": db.dialect,"top_k": 5,"table_info": db.get_table_info(),"input": state["question"],})structured_llm = llm.with_structured_output(QueryOutput)result = structured_llm.invoke(prompt)return {"query": result["query"]}
PAL 核心步骤 1
LLM 不直接回答问题,而是生成 SQL 查询。
用户确认
def wait_for_user_approve(state: State):"""Pause here and wait for user approval before executing query."""try:user_approval = input("Do you want to go to execute query? (yes/no): ")except Exception:user_approval = "no"if user_approval.lower() == "yes":return {"query": state["query"],"approved": True,}else:return {"query": state["query"],"approved": False,}
用户确认 SQL 是否执行,保证安全性 —— 很关键。
执行 SQL
def excute_query(state: State):"""Execute the SQL query and return the result."""if state["approved"]:execute_query_tool = QuerySQLDatabaseTool(db=db)return {"result": execute_query_tool.invoke(state["query"])}else:return {"result": "excute denied."}
PAL 核心步骤 2
SQL 执行交给程序完成,LLM 不直接操作数据库。
回答用户
def generate_answer(state: State):"""Answer question using retrieved information as context."""if state["approved"]:prompt = ("Given the following user question, corresponding SQL query, ""and SQL result, answer the user question.\n\n"f'Question: {state["question"]}\n'f'SQL Query: {state["query"]}\n'f'SQL Result: {state["result"]}')response = llm.invoke(prompt)return {"answer": response.content}else:prompt = f'{"同意" if state["approved"] else "拒绝"} 用户拒绝当前执行'response = llm.invoke(prompt)return {"answer": response.content}
PAL 核心步骤 3
LLM 根据 SQL 结果生成最终自然语言答案。
流程图
graph_builder = StateGraph(State).add_sequence([write_query, wait_for_user_approve, excute_query, generate_answer])graph_builder.add_edge(START, "write_query")
用 LangGraph 编排整个 PAL 流程。
持久化 checkpoint + 启动循环
DB_URI = "postgresql://postgres:123456@localhost:5432/langchaindemo?sslmode=disable"with PostgresSaver.from_conn_string(DB_URI) as checkpointer:checkpointer.setup()input_thread_id = input("输入thread_id:")time_str = time.strftime("%Y%m%d", time.localtime())config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": f"{time_str}-{input_thread_id}-agent-demo"}}graph = graph_builder.compile(checkpointer=checkpointer)print("输入问题,输入 exit 退出。")while True:query = input("你: ")if query.strip().lower() == "exit":breakresponse = graph.invoke({"question": query},config,)print(response)
Checkpoint 存入 Postgres
用户可断点续跑
CLI 交互友好
总结:PAL 模式的好处
1.LLM 不做逻辑执行,只负责「写程序」
2.复杂逻辑交给程序完成,结果回传给 LLM
3.SQL 查询避免安全风险
4.有明确「用户确认」步骤
5.checkpoint 持久化,支持中断恢复
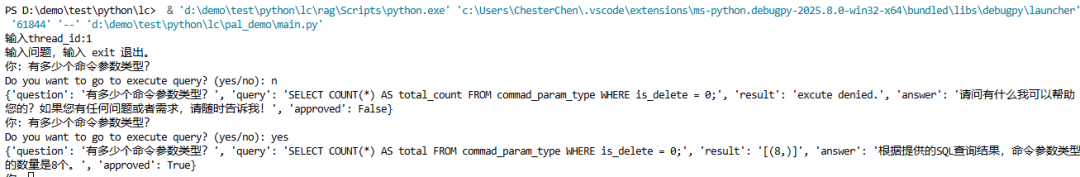
运行效果示例
关注获取技术分享

文章转载自chester技术分享,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






