前面的章节我们了解到了redisson的分布式可重入锁是怎么加锁的,并且会给锁添加一个过期时间30s,那么如果30s内我们的业务没有执行完成会怎么办呢?释放掉锁?这显然是不合理的
在redisson的官方文档我们看到redisson在加锁之后会有一个lock watchdog,他的作用是判断如果业务端获取锁之后,业务没有执行完成的时候会自动进行锁续约,保证锁不会被自动过期释放掉
那么lock watchdog的原理是怎样实现的呢? 我们来进一步分析一下
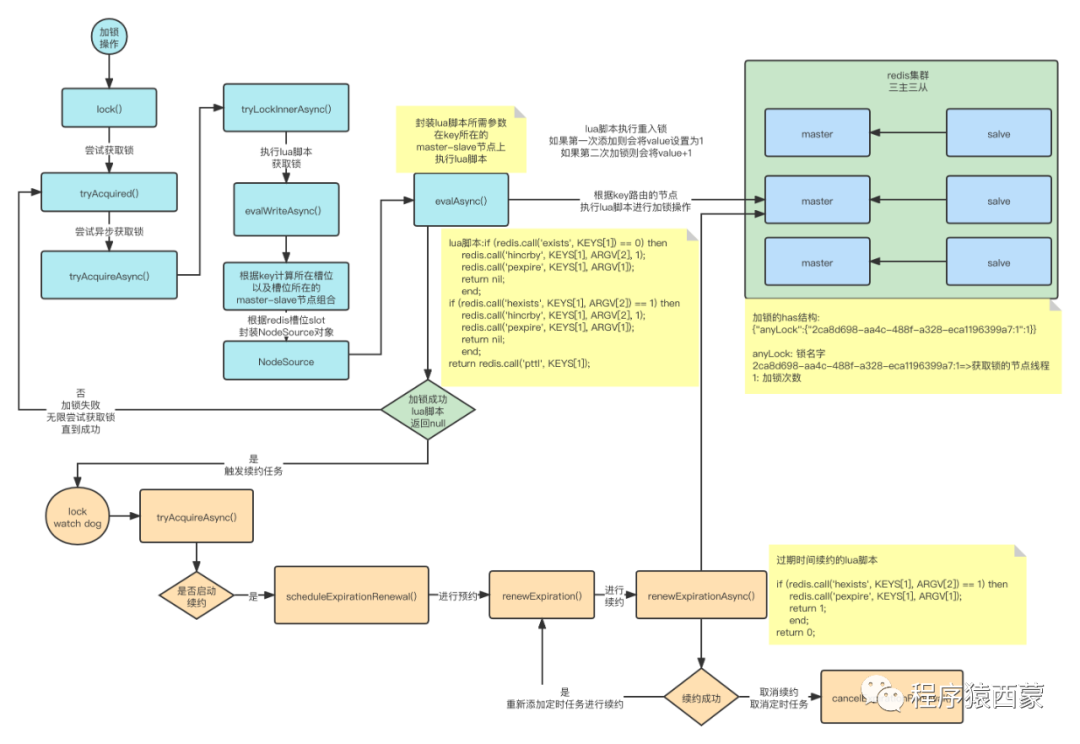
在上节的分析中我们知道调用加锁的时候会调用RedissonLock的tryAcquireAsync()方法来获取锁,其实lock watchdog的启动也是在这个方法内部
private <T> RFuture<Long> tryAcquireAsync(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit, long threadId) {RFuture<Long> ttlRemainingFuture;if (leaseTime != -1) {ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);} else {ttlRemainingFuture = tryLockInnerAsync(waitTime, internalLockLeaseTime,TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS, threadId, RedisCommands.EVAL_LONG);}ttlRemainingFuture.onComplete((ttlRemaining, e) -> {if (e != null) {return;}// lock acquiredif (ttlRemaining == null) {if (leaseTime != -1) {internalLockLeaseTime = unit.toMillis(leaseTime);} else {scheduleExpirationRenewal(threadId);}}});return ttlRemainingFuture;}
1. 先调用tryLockInnerAsync尝试加锁然后会返回一个RFuture对象
2. 然后给这个对象添加了一个监听事件
3. 在监听时间内部会判断是否抛出异常了,抛出异常则返回不会启动lock watchdog来进行锁续约
4. 判断ttlRemaining是否为null,如果为null表明获取锁成功,接着会判断续约时间是否为-1(代表永久续约),lock()方法的leaseTime=-1,因此这里会调用scheduleExpirationRenewal()来定时的进行过期续约
我们来分析一下scheduleExpirationRenewal是怎么进行定时续约的
protected void scheduleExpirationRenewal(long threadId) {ExpirationEntry entry = new ExpirationEntry();ExpirationEntry oldEntry = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.putIfAbsent(getEntryName(), entry);if (oldEntry != null) {oldEntry.addThreadId(threadId);} else {entry.addThreadId(threadId);try {renewExpiration();} finally {if (Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) {cancelExpirationRenewal(threadId);}}}}
1. 创建一个ExpirationEntry对象,里面会保存线程id
2. 判断这个entryName(uuid:threadId)是否已经创建过ExpirationEntry对象,如果创建过则把当前线程的id放进去,说明已经在续约中了
3. 如果未创建过则把线程id放入心创建的ExpirationEntry对象中并且执行renewExpiration()进行续约操作
4. 最后如果线程被中断则取消redis的过期时间续约
我们再来分析下renewExpiration()方法是怎么为分布式锁续约的
private void renewExpiration() {ExpirationEntry ee = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());if (ee == null) {return;}Timeout task = commandExecutor.getConnectionManager().newTimeout(new TimerTask() {@Overridepublic void run(Timeout timeout) throws Exception {ExpirationEntry ent = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());if (ent == null) {return;}Long threadId = ent.getFirstThreadId();if (threadId == null) {return;}RFuture<Boolean> future = renewExpirationAsync(threadId);future.onComplete((res, e) -> {if (e != null) {log.error("Can't update lock " + getRawName() + " expiration", e);EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(getEntryName());return;}if (res) {// reschedule itselfrenewExpiration();} else {cancelExpirationRenewal(null);}});}}, internalLockLeaseTime / 3, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);ee.setTimeout(task);}protected RFuture<Boolean> renewExpirationAsync(long threadId) {return evalWriteAsync(getRawName(), LongCodec.INSTANCE, RedisCommands.EVAL_BOOLEAN,"if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) then " +"redis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]); " +"return 1; " +"end; " +"return 0;",Collections.singletonList(getRawName()),internalLockLeaseTime, getLockName(threadId));}protected void cancelExpirationRenewal(Long threadId) {ExpirationEntry task = EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.get(getEntryName());if (task == null) {return;}if (threadId != null) {task.removeThreadId(threadId);}if (threadId == null || task.hasNoThreads()) {Timeout timeout = task.getTimeout();if (timeout != null) {timeout.cancel();}EXPIRATION_RENEWAL_MAP.remove(getEntryName());}}
1. 根据线程编号来获取ExpirationEntry对象里面保存的线程id
2. 创建一个定时任务每隔10s执行一次来定时调度
3. 定时任务会判断ExpirationEntry是否被移除,不需要再进行续约
4. 判断第一个线程是否已经被取消,取消则不需要进行续约
5. 如果需要续约则调用renewExpirationAsync()方法来进行过期时间续约
6. 注册一个监听器,如果续约成功,则会在调用renewExpiration()方法进行再次续约(这样来实现重复的调度任务),如果执行失败则会调用cancelExpirationRenewal()方法来取消继续续约(这里可能是锁释放了)
7. renewExpirationAsync()方法中是通过执行lua脚本,判断是否要进行续约还是不进行续约,不续约则删除线程id,并且取消定时任务
if (redis.call('hexists', KEYS[1], ARGV[2]) == 1) thenredis.call('pexpire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1]);return 1;end;return 0;
keys[1] = anyLock
argv[2] =2ca8d698-aa4c-488f-a328-eca1196399a7:1 (uuid:threadId) argv[1] = 30s
1. 上面lua脚本的意思是判断 获取锁的key是否存在,如果存在则重新进行过期时间的设定,并且返回成功 1
2. 如果锁的key不存在,则直接返回失败
总结
1. lock watchdog原理其实就是,当线程加锁成功之后,就会启动给一个定时任务每10s执行一次
2. 判断这个线程是否还持有锁,如果持有锁则进行续约(重置过期时间为30s)
3. 如果这个线程释放掉了锁,则不进行再次续约
4. 如果续约失败(锁释放了),则取消续约的任务
一张图看下整体流程