课程导言:数据流动的本质
"程序如同生命体,I/O系统是它的血管网络——数据如同血液在其中流动,滋养着每一个计算细胞。掌握数据流动的艺术,就是掌握程序的生命线!"
现实世界类比
传统I/O:单车道公路 - 一次只能通过一辆车(阻塞式)
NIO:多车道高速公路 - 多辆车可并行(非阻塞式+选择器)
内存映射:空中走廊 - 直达目的地(零拷贝)
一、Java I/O基础:字节与字符的世界(40分钟)
1.1 I/O流分类体系
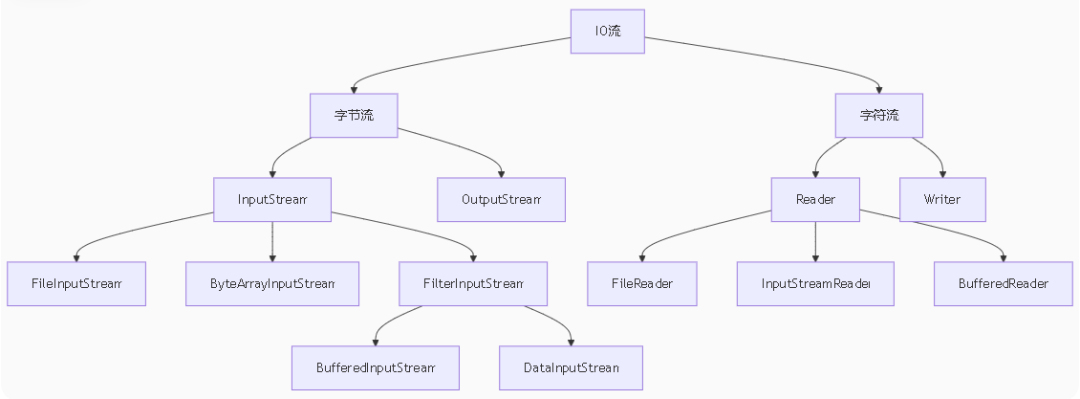
1.2 装饰器模式在I/O中的运用
// 基础流FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("data.bin");// 装饰器:增加缓冲功能BufferedInputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(fis);// 装饰器:增加对象序列化功能ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(bis);// 最终使用MyObject obj = (MyObject) ois.readObject();
1.3 文件操作最佳实践
// 自动资源管理(try-with-resources)try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("text.txt"))) {String line;while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {System.out.println(line);}}// 二进制文件复制try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream("source.jpg");OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("copy.jpg")) {byte[] buffer = new byte[8192]; // 8KB缓冲int bytesRead;while ((bytesRead = in.read(buffer)) != -1) {out.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);}}
二、NIO核心:缓冲区与通道(50分钟)
2.1 Buffer工作机制
// 缓冲区状态流转ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024); // 创建缓冲区// 写模式buffer.put("Hello".getBytes()); // position移动// 切换到读模式buffer.flip(); // limit=position, position=0// 读取数据while (buffer.hasRemaining()) {System.out.print((char) buffer.get());}// 重置缓冲区buffer.clear(); // position=0, limit=capacity
2.2 通道(Channel)类型对比
2.3 文件操作实战
// 使用FileChannel复制文件(高效)try (FileChannel in = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("source.zip"),out = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("copy.zip"),StandardOpenOption.CREATE)) {in.transferTo(0, in.size(), out);}// 内存映射文件(随机访问)try (RandomAccessFile file = new RandomAccessFile("data.bin", "rw")) {FileChannel channel = file.getChannel();MappedByteBuffer buffer = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, 1024);buffer.putInt(0, 123); // 直接修改文件内容}
三、非阻塞I/O与选择器(40分钟)
3.1 选择器(Selector)工作原理
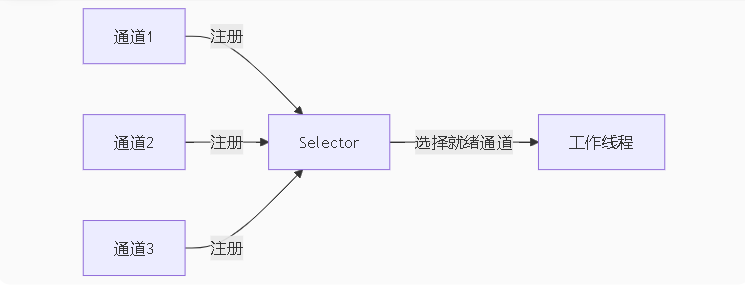
3.2 非阻塞服务器原型
Selector selector = Selector.open();ServerSocketChannel server = ServerSocketChannel.open();server.bind(new InetSocketAddress(8080));server.configureBlocking(false);server.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);while (true) {selector.select(); // 阻塞直到有事件Set<SelectionKey> keys = selector.selectedKeys();Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = keys.iterator();while (iter.hasNext()) {SelectionKey key = iter.next();iter.remove();if (key.isAcceptable()) {// 处理新连接SocketChannel client = server.accept();client.configureBlocking(false);client.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);} else if (key.isReadable()) {// 处理读事件SocketChannel client = (SocketChannel) key.channel();ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);client.read(buffer);buffer.flip();processRequest(buffer); // 处理请求key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);} else if (key.isWritable()) {// 处理写事件// ...}}}
四、NIO.2:文件操作现代化(30分钟)
4.1 Path与Files工具类
// 路径操作Path path = Paths.get("data", "sub", "file.txt");Path absPath = path.toAbsolutePath();Path parent = path.getParent();// 文件操作Files.createDirectories(path.getParent());Files.copy(source, target, StandardCopyOption.REPLACE_EXISTING);Files.lines(path).forEach(System.out::println); // 流式读取// 遍历目录Files.walk(Paths.get(".")).filter(Files::isRegularFile).forEach(System.out::println);
4.2 文件系统监控
WatchService watchService = FileSystems.getDefault().newWatchService();Path dir = Paths.get("/data");dir.register(watchService,StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_CREATE,StandardWatchEventKinds.ENTRY_MODIFY);while (true) {WatchKey key = watchService.take();for (WatchEvent<?> event : key.pollEvents()) {Path filename = (Path) event.context();System.out.println("文件变化: " + filename);}key.reset();}
五、实战:高性能文件服务器(20分钟)
5.1 架构设计
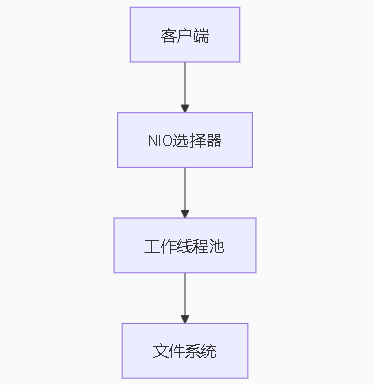
5.2 核心代码片段
// 文件传输方法private void transferFile(SocketChannel client, Path filePath) throws IOException {try (FileChannel fileChannel = FileChannel.open(filePath, StandardOpenOption.READ)) {long position = 0;long remaining = fileChannel.size();while (remaining > 0) {long transferred = fileChannel.transferTo(position, remaining, client);position += transferred;remaining -= transferred;}}}
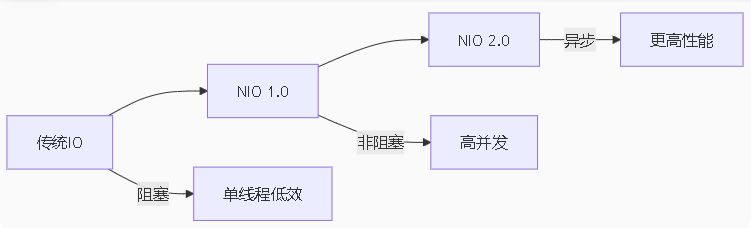
课程总结:I/O进化三阶段
传统I/O:
阻塞模型
流式处理
简单易用
NIO 1.0:
非阻塞模型
缓冲区与通道
选择器机制
NIO 2.0:
异步I/O
文件系统API
完整路径操作
课后挑战
文件加密工具:
void encryptFile(Path source, Path target, SecretKey key) {// 使用AES加密文件// 要求:支持大文件(>1GB)}
简易HTTP服务器:
class SimpleHttpServer {public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {// 实现功能:// 1. 处理GET请求// 2. 返回静态文件// 3. 支持并发访问}}
目录同步工具:
class DirectorySynchronizer {void sync(Path source, Path target) {// 实现:// 1. 监控源目录变化// 2. 实时同步到目标目录// 3. 支持增量同步}}
下节课预告:《Java网络编程:连接世界的桥梁》
你将学到:
TCP/UDP协议差异
Socket编程核心API
HTTP客户端实现
WebSocket双向通信
RPC框架原理
网络调试工具使用
"掌握I/O就是掌握数据的命脉。记住:在编程世界里,数据不会自己流动——是优秀的程序员赋予它生命和方向!"

文章转载自让天下没有难学的编程,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






