关于对数据库第一范式的理解,大部分人都存在误区(比如认为元组的分量不可以是集合、数组、map 等类型的“多值”,而应该是整数、字符串等类型的“单值”),以下内容参考了部分经典书籍和 page (主要基于 C.J.Date 的观点);
注:分量(Component)就是元组中的某个属性对应的值,全部分量的集合就是该元组的值;
关于 1NF 的定义
- 1NF(First Normal Form) 最初是由 E.F.Codd 提出的,但 E.F.Codd 曾多次修改其定义,并且他对 1NF 的定义也是模糊的:
1972 年《Further Normalization of the Data Base Relational Model》:
A relation is in first normal form if ... none of its domains has elements which are themselves sets. An unnormalized relation is one which is not in first normal form.
即属性的值不可以是集合;
1990 年《The Relational Model for Database Management Version 2》:
The values in the domains on which each relation is defined are required to be atomic with respect to the DBMS.
Atomic data [is data that cannot] be decomposed into smaller pieces by the DBMS (excluding certain special functions).即属性的值是原子的,而原子数据是不可以被 DBMS 再进行分解的;
- 到目前为止,对 1NF 的定义并没有达成统一:
2000 年 Ramez Elmasri 和 Shamkant B. Navathe 的《Fundamentals of Database Systems》:
First normal form (1NF) ... states that the domain of an attribute must include only atomic (simple, indivisible) values and that the value of any attribute in a tuple must be a single value from the domain of that attribute ... Hence, 1NF disallows having a set of values, a tuple of values, or a combination of both as an attribute value for a single tuple.
2002 年 Hector Garcia-Molina、Jeffrey D. Ullman 和 Jennifer Widom 的《Database Systems: The Complete Book》:
First normal form is simply the condition that every component of every tuple is an atomic value.
2002 年 Abraham Silberschatz、Henry F. Korth 和 S. Sudarshan 的《Database System Concepts》:
A domain is atomic if elements of the domain are considered to be indivisible units ... We say that a relation schema R is in first normal form (1NF) if the domains of all attributes of R are atomic.
2003 年 Raghu Ramakrishnan 和 Johannes Gehrke 的《Database Management Systems》:
A relation is in first normal form if every field contains only atomic values, that is, no lists or sets.
根据上述定义,可以看出一种对 1NF 普遍的认知是“属性值是原子值”:即属性不可以是数组、集合、列表、元组、关系 等非原子类型。而 C.J Date 认为 E.F.Codd 对原子的描述不够准确,比如:
- 字符串类型的值可以通过 substring 进行分解为子串;
- 日期和时间类型的值可以分解为 年、月、日、时、分、秒;
- 浮点数类型的值可以分解为小数部分和整数部分;
所以严格来说,几乎很少有类型不能再被分解。而如果将字符串、日期时间和浮点数视作原子类型,那么集合类型为什么不是。他在 《Date on Database Writings 2000-2006》 的 “What First Normal Form Really Means” 章节中提出了自己对 1NF 的定义:
- 关系的属性是左右无序的;
- 关系的元组是上下无序的;
- 关系中不允许重复的元组;
- 属性值只能是其值域中的单个值;
- 所有属性都是普通属性:即不可以有隐藏的属性,比如隐藏的 rowid 属性、隐藏的时间戳属性,而这些属性并不是由用户显式定义在关系中(上述限制条件 1-4 不足以排除这些隐藏属性,所以才有这第 5 条规定);
后文会着重展开一下对第 4 点的理解。
关系的属性可以是任意类型
在我的另一篇文章中有详细描述:【数据库理论】关系模型 - 概念与理解;
属性值只能是其值域中的单个值
假设属性
ATTR的值域为 [ v1, v2, …, vn ],则元组中ATTR对应的分量只能为其中的一个,而不可以是这些值构成的集合、列表或数组等。所以以下示例中R1满足该条件而R2不满足: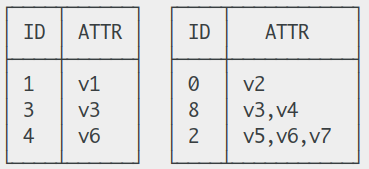
但这并不表示分量不可以是集合、列表或数组等类型,因为关系的属性可以是任意类型的,所以如果属性
ATTR本身就是这些类型,分量当然也可以。假设属性ATTR_SET的类型为集合,集合的元素可以是 [ v1, v2, …, vn ],那么从某种抽象层面上来看,该集合类型的每个值也是单个值。所以以下示例中R3满足该条件而R4不满足:
小结
- “属性值只能是其值域中的单个值”这一特点也是大部分人认为的 1NF;
- 1NF 本身就是关系定义的一部分,是关系模型强制要求遵循的,违反了 1NF 就不可以称之为关系,所以在关系模型中“关系”本来就是规范化的,或者说它总是遵循 1NF 。而其他具有更高要求的范式则不然,遵循这些规则是为了让数据库更易于管理;






