跑得最快的的OpenAI模型来了,还开源!
近日,OpenAI时隔多年重回开源赛道,并发布了最新的开源模型GPT-oss,效果直接登顶开源模型王座。
从各大benchmark效果来看,GPT-oss不仅力压deepseek R1,就连刚刚发布的Qwen 3、Kimi K2系列新模型,也被挑落马下。
但实话实话,最近几个月的开源SOTA不断被刷新,用户体验上,可以说有进步,却也难说惊艳。GPT-oss也不例外,非要说最大的亮点的,大概有三处:
亮点一:适合端侧部署,跑得快。
GPT-oss有两个版本,120B和20B,推理时分别仅使用 36 亿和 51 亿活跃参数。其中,gpt-oss-120b能在单个80GB GPU上部署,gpt-oss-20b只要有个16GB内存的边缘设备,手机都能跑。而推理速度上,这可能是史上最快的OpenAI模型。
亮点二:成本低。
据OpenAI官方说法,GPT-oss-120B的效果,基本与闭源的o4-mini持平。但训练算力消耗上,GPT-oss-120B只花费了210万H100小时,20B版本则只花了21万H100小时。对应成本上,120B的成本约为1000万美金,20B约为100万美金。
亮点三:可能是GPT-5的前菜。
技术细节上,OpenAI对此还是遮遮掩掩。外界推测,采用的依然是MoE架构,注意力机制上,则借鉴 GPT-3 设计理念,采用的还是交替的密集注意力和局部带状稀疏注意力模式,但整体的注意力头更多,对每个输入,分配的专家数量为4个。此外,GPT-2之后就没再使用过的偏差单元这一次又杀回来了。
(不妨猜一把,这些技术路线,有多少会在几天发布的GPT-5上看到)
那么它效果究竟如何,怎么用它搭建一个RAG,本文将一一解读。
01
模型测评:gpt-oss-120b vs o4-mini
我们上来先测难度低一点的,第100个质数是多少
gpt-oss-120b(思考0.9秒,消耗 231 tokens)
可以看到效果还不错,,而且还有情绪价值

gpt-o4-mini(消耗 25 tokens)
可以看到效果真是简单直接

再让我们来测评一下推理任务
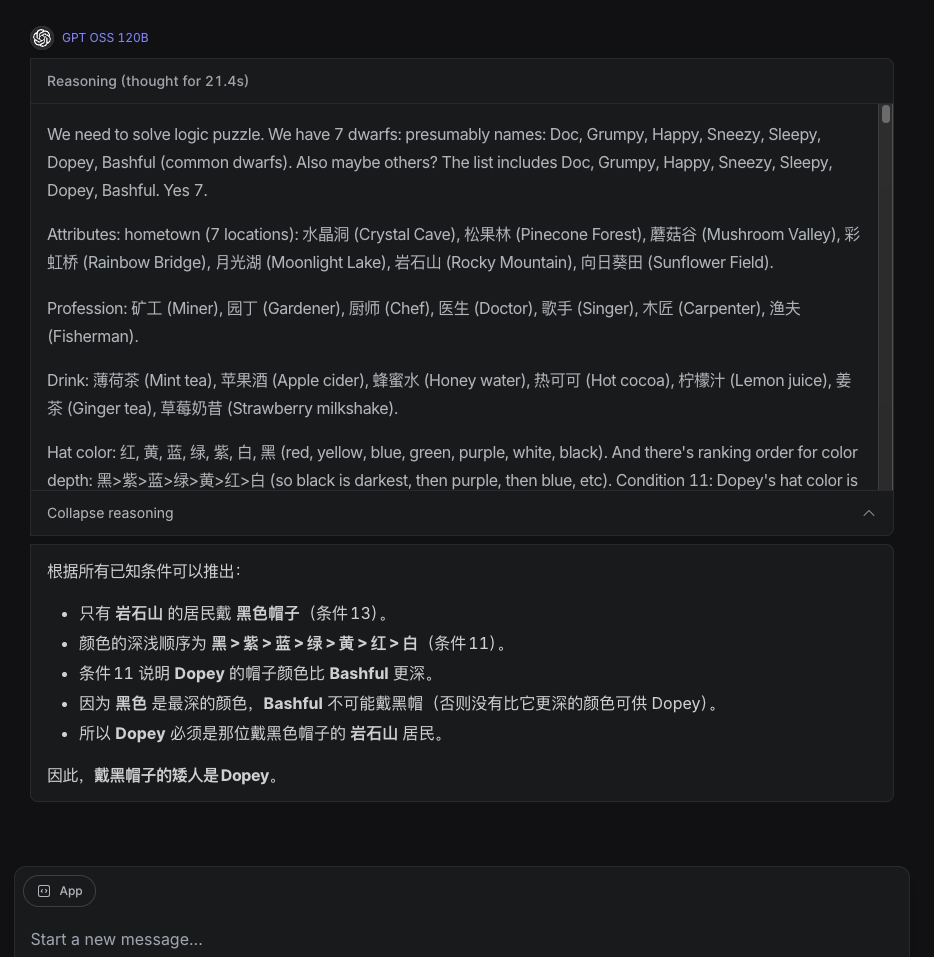
七个小矮人的秘密七个小矮人在遇到白雪公主前,他们来自不同家乡:水晶洞、松果林、蘑菇谷、彩虹桥、月光湖、岩石山、向日葵田;从事不同职业:矿工、园丁、厨师、医生、歌手、木匠、渔夫;喝不同饮料:薄荷茶、苹果酒、蜂蜜水、热可可、柠檬汁、姜茶、草莓奶昔;戴不同颜色帽子:红、黄、蓝、绿、紫、白、黑;使用不同交通工具:独轮车、滑板、雪橇、三轮车、马车、小船、自行车。有一天,他们的交通工具从左到右排成一行,请根据以下条件推理:1、Doc戴红色帽子2、Grumpy的交通工具是雪橇3、Happy来自向日葵田,职业是歌手d.矿工喝热可可5、三轮车紧邻小船左侧6、月光湖居民戴紫色帽子7、医生的交通工具在正中间8、Sneezy 住在彩虹桥,戴黄色帽子9、Sleepy的交通工具在滑板右侧第三位j.喝苹果酒者的交通工具与渔夫相邻11、Dopey 的帽子颜色比 Bashful深(黑>紫>蓝>绿>黄>红>白)12、园丁使用独轮车13、岩石山居民戴黑色帽子,交通工具在马车左边第二位14、喝柠檬汁者的交通工具与医生相隔一辆15、蘑菇谷居民喝姜茶16、厨师的交通工具紧邻戴蓝色帽子者17、使用小船的人来自松果林18、Happy 不戴白帽子请问谁戴黑帽子?
gpt-oss-120b (思考21.4秒,消耗 6144 tokens)
思考时间较久,而且没答对
gpt-o4-mini
从结果可以看到其推理时间较长,回答简洁,但错误

综合上面的测评,我们可以看到gpt-oss-120b在进行类似数学方面表现突出,而gpt-o4-mini也不逊色。
而在推理任务中,gpt-oss-120b消耗较多tokens,还回答错误;gpt-o4-mini表现同样一般,消耗非常小的tokens时,但不正确回答。
能力的确不相上下,从Tokens消耗量来看,gpt-o4-mini消耗的tokens是明显小于gpt-oss-120b的。
02
RAG教程
虽然没有完全比得上闭源模型,但gpt-oss胜在开源,我们用它搭个RAG,锻炼一下动手能力,还是不错的。
(1)准备工作
安装必要环境
! pip install --upgrade "pymilvus[model]" openai requests tqdm
数据集准备
我们可以使用Milvus文档2.4. x中的FAQ页面作为RAG中的私有知识,这是构建一个基础RAG的良好数据源。
下载zip文件并将文档解压缩到文件夹milvus_docs
! wget https://github.com/milvus-io/milvus-docs/releases/download/v2.4.6-preview/milvus_docs_2.4.x_en.zip! unzip -q milvus_docs_2.4.x_en.zip -d milvus_docs
我们从文件夹milvus_docs/en/faq中加载所有markdown文件,对于每个文档,我们只需用“#”来分隔文件中的内容,就可以大致分隔markdown文件各个主要部分的内容。
from glob import globtext_lines = []for file_path in glob("milvus_docs/en/faq/*.md", recursive=True):with open(file_path, "r") as file:file_text = file.read()text_lines += file_text.split("# ")
准备LLM 和Embedding模型
OpenRouter是一家提供统一API接口聚合多个主流AI模型(如OpenAI、Claude等)的服务平台,让开发者通过单一接入点调用不同大语言模型。在OpenRouter上免费创建OpenAI gpt-oss-120b的API KEY就可以尝鲜使用啦。
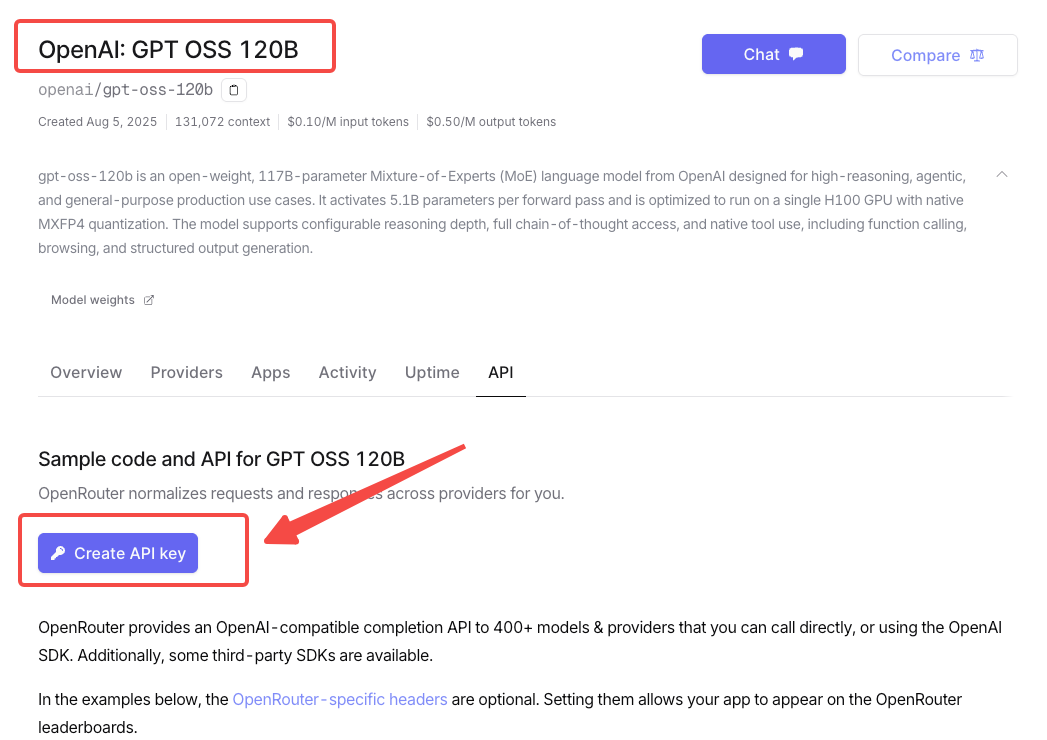
from openai import OpenAIopenai_client = OpenAI(api_key="<OPENROUTER_API_KEY>",base_url="https://openrouter.ai/api/v1",)
选择一个embedding模型,使用milvus_model
来做文本向量化。我们以DefaultEmbeddingFunction
模型为例,它是一个预训练的轻量级embedding模型。
from pymilvus import model as milvus_modelembedding_model = milvus_model.DefaultEmbeddingFunction()
生成测试向量,并输出向量维度以及测试向量的前几个元素。
test_embedding = embedding_model.encode_queries(["This is a test"])[0]embedding_dim = len(test_embedding)print(embedding_dim)print(test_embedding[:10])
768[-0.04836066 0.07163023 -0.01130064 -0.03789345 -0.03320649 -0.01318448-0.03041712 -0.02269499 -0.02317863 -0.00426028]
(2)将数据加载到Milvus
创建集合
from pymilvus import MilvusClientmilvus_client = MilvusClient(uri="http://localhost:19530",token="root:Miluvs")collection_name = "my_rag_collection"
对于
MilvusClient
需要说明:
将
uri
设置为本地文件,例如./milvus. db
,是最方便的方法,因为它会自动使用Milvus Lite将所有数据存储在此文件中。如果你有大规模数据,你可以在docker或kubernetes上设置一个更高性能的Milvus服务器。在此设置中,请使用服务器uri,例如
http://localhost:19530
,作为你的uri
。如果要使用Milvus的全托管云服务Zilliz Cloud,请调整
uri
和token
,分别对应Zilliz Cloud中的Public Endpoint和Api密钥。
检查集合是否已经存在,如果存在则将其删除。
if milvus_client.has_collection(collection_name):milvus_client.drop_collection(collection_name)
使用指定的参数创建一个新集合。
如果我们不指定任何字段信息,Milvus将自动为主键创建一个默认的id
字段,并创建一个向量字段来存储向量数据。保留的JSON字段用于存储未在schema里定义的标量数据。
milvus_client.create_collection(collection_name=collection_name,dimension=embedding_dim,metric_type="IP", # Inner product distanceconsistency_level="Strong", # Strong consistency level)
插入数据
逐条取出文本数据,创建嵌入,然后将数据插入Milvus。
这里有一个新的字段“text”,它是集合schema中的非定义字段,会自动添加到保留的JSON动态字段中。
from tqdm import tqdmdata = []doc_embeddings = embedding_model.encode_documents(text_lines)for i, line in enumerate(tqdm(text_lines, desc="Creating embeddings")):data.append({"id": i, "vector": doc_embeddings[i], "text": line})milvus_client.insert(collection_name=collection_name, data=data)
Creating embeddings: 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 72/72 [00:00<00:00, 1222631.13it/s]{'insert_count': 72, 'ids': [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, 26, 27, 28, 29, 30, 31, 32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47, 48, 49, 50, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 57, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63, 64, 65, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71], 'cost': 0}
(3)构建RAG
检索查询数据
让我们指定一个关于Milvus的常见问题。
question = "How is data stored in milvus?"在集合中搜索问题并检索语义top-3匹配项。
search_res = milvus_client.search(collection_name=collection_name,data=embedding_model.encode_queries([question]), # Convert the question to an embedding vectorlimit=3, # Return top 3 resultssearch_params={"metric_type": "IP", "params": {}}, # Inner product distanceoutput_fields=["text"], # Return the text field)
我们来看一下query的搜索结果
import jsonretrieved_lines_with_distances = [(res["entity"]["text"], res["distance"]) for res in search_res[0]]print(json.dumps(retrieved_lines_with_distances, indent=4))
[[" Where does Milvus store data?\n\nMilvus deals with two types of data, inserted data and metadata. \n\nInserted data, including vector data, scalar data, and collection-specific schema, are stored in persistent storage as incremental log. Milvus supports multiple object storage backends, including [MinIO](https://min.io/), [AWS S3](https://aws.amazon.com/s3/?nc1=h_ls), [Google Cloud Storage](https://cloud.google.com/storage?hl=en#object-storage-for-companies-of-all-sizes) (GCS), [Azure Blob Storage](https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/products/storage/blobs), [Alibaba Cloud OSS](https://www.alibabacloud.com/product/object-storage-service), and [Tencent Cloud Object Storage](https://www.tencentcloud.com/products/cos) (COS).\n\nMetadata are generated within Milvus. Each Milvus module has its own metadata thatarestored in etcd.\n\n###",0.6572664976119995],["How does Milvus flush data?\n\nMilvus returns success when inserted data are loaded to the message queue. However, the data are not yet flushed to the disk. Then Milvus' data node writes the data in the message queue to persistent storage as incremental logs. If `flush()` is called, the data node is forced to write all data in the message queue to persistent storage immediately.\n\n###",0.6312144994735718],["How does Milvus handle vector data types and precision?\n\nMilvus supports Binary, Float32, Float16, and BFloat16 vector types.\n\n- Binary vectors: Store binary data as sequences of 0s and 1s, used in image processing and information retrieval.\n- Float32 vectors: Default storage with a precision of about 7 decimal digits. Even Float64 values are stored with Float32 precision, leading to potential precision loss upon retrieval.\n- Float16 and BFloat16 vectors: Offer reduced precision and memory usage. Float16 is suitable for applications with limited bandwidth and storage, while BFloat16 balances range and efficiency, commonly used in deep learning to reduce computational requirements without significantly impacting accuracy.\n\n###",0.6115782856941223]]
使用LLM获取RAG响应
将检索到的文档转换为字符串格式。
context = "\n".join([line_with_distance[0] for line_with_distance in retrieved_lines_with_distances])为LLM定义系统和用户提示。这个提示是由从Milvus检索到的文档组装而成的。
SYSTEM_PROMPT = """Human: You are an AI assistant. You are able to find answers to the questions from the contextual passage snippets provided."""USER_PROMPT = f"""Use the following pieces of information enclosed in <context> tags to provide an answer to the question enclosed in <question> tags.<context>{context}</context><question>{question}</question>"""使用OpenAI提供的openai/gpt-oss-120b模型根据提示生成响应。
response = openai_client.chat.completions.create(model="openai/gpt-oss-120b",messages=[{"role": "system", "content": SYSTEM_PROMPT},{"role": "user", "content": USER_PROMPT},],)print(response.choices[0].message.content)
Milvus stores its data in two distinct layers:| Type of data | Where it is stored | How it is stored ||-------------|-------------------|-----------------|| **Inserted data** (vector data, scalar fields, collection‑specific schema) | In the **persistent object storage** configured for the cluster. The data are written as **incremental logs** (append‑only logs) that are persisted by the DataNode. | The DataNode reads from the message‑queue and writes the incoming data into the storage backend (MinIO, AWS S3, GCS, Azure Blob, Alibaba OSS, Tencent COS, etc.). When a `flush()` call is issued, the DataNode forces all queued data to be written to the persistent storage immediately. || **Metadata** (information about collections, partitions, indexes, etc.) | In **etcd**. Each Milvus module (catalog, index, etc.) keeps its own metadata. | The metadata is generated and managed by Milvus and persisted in the distributed key‑value store **etcd**. |**Summary:**- **Inserted data** = incremental logs stored in the chosen object‑storage backend.- **Metadata** = stored in the distributed configuration store **etcd**.Together, these two storage mechanisms (object storage for the actual data and etcd for metadata) make up Milvus’s data‑storage architecture.
至此,通过Milvus和OpenAI GPT-oss构建了一个RAG pipeline的完整流程正式完成。
尾声
实话实说,GPT-oss 效果的确不错,也当得起开源模型SOTA的地位。但给人更多的感觉依旧是中规中矩,少了一点惊艳的感觉。
但GPT-oss-20B都能在手机端跑了,还要什么自行车?(获取方法,下载LM Studio,直接搜索你想要的模型即可)。
当然,如果你的对话语言是中文、日本、法语这些非英文语言的话,GPT-oss系列可能会出现拼写错误、表达混乱之类的问题,效果比预想中的差很多。
据推测,GPT-oss系列应该都是基于英文文本进行训练的,所以对多语言的支持并不擅长。可以考虑下载Multilingual-Thinking数据集,用此对模型做一下微调。
不过,目前来看,GPT-oss看起来更像是传闻中GPT-5的前菜。就在今天,OpenAI在X上发文,将于周四上午10点(北京时间周五凌晨1点)进行直播。并且,将“LIVESTREAM”(意为网络直播)的字母“S”改成了数字“5”。
那大家不妨猜猜,GPT-oss的技术路线,究竟会有几分像GPT-5?
作者介绍
王舒虹
Zilliz Social Media Advocate