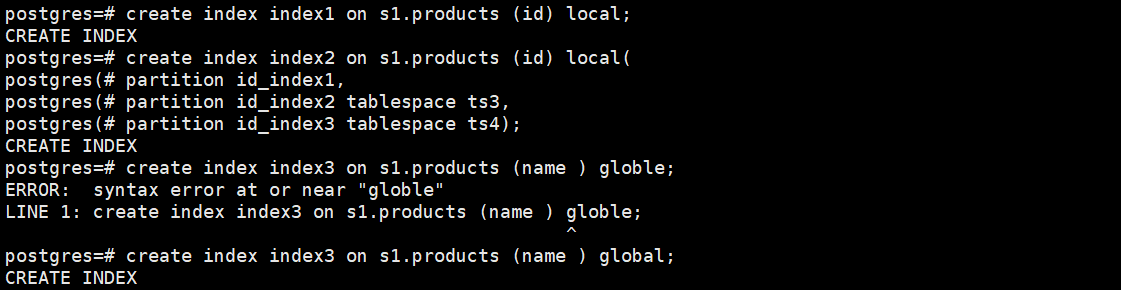
1.创建范围分区表products, 为表创建分区表索引1,不指定索引分区的名称,创建分区表索引2,并指定索引分区的名称,创建GLOBAL分区索引3
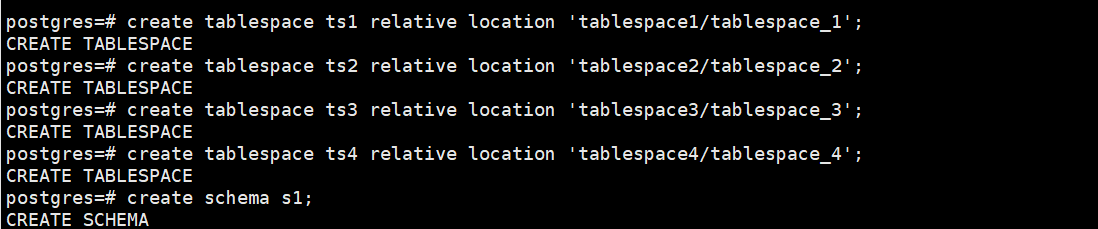
postgres=# create tablespace ts1 relative location 'tablespace1/tablespace_1';
postgres=# create tablespace ts2 relative location 'tablespace2/tablespace_2';
postgres=# create tablespace ts3 relative location 'tablespace3/tablespace_3';
postgres=# create tablespace ts4 relative location 'tablespace4/tablespace_4';
postgres=# create schema s1;
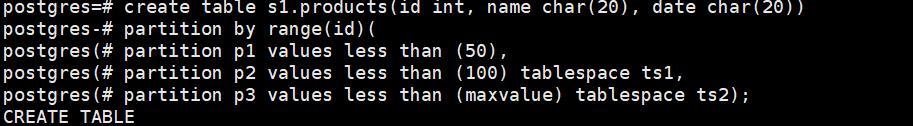
postgres=# create table s1.products(id int, name char(20), date char(20))
postgres-# partition by range(id)(
postgres(# partition p1 values less than (50),
postgres(# partition p2 values less than (100) tablespace ts1,
postgres(# partition p3 values less than (maxvalue) tablespace ts2);
postgres=# create index index1 on s1.products (id) local;
postgres=# create index index2 on s1.products (id) local(
postgres(# partition id_index1,
postgres(# partition id_index2 tablespace ts3,
postgres(# partition id_index3 tablespace ts4);
postgres=# create index index3 on s1.products (name ) global;
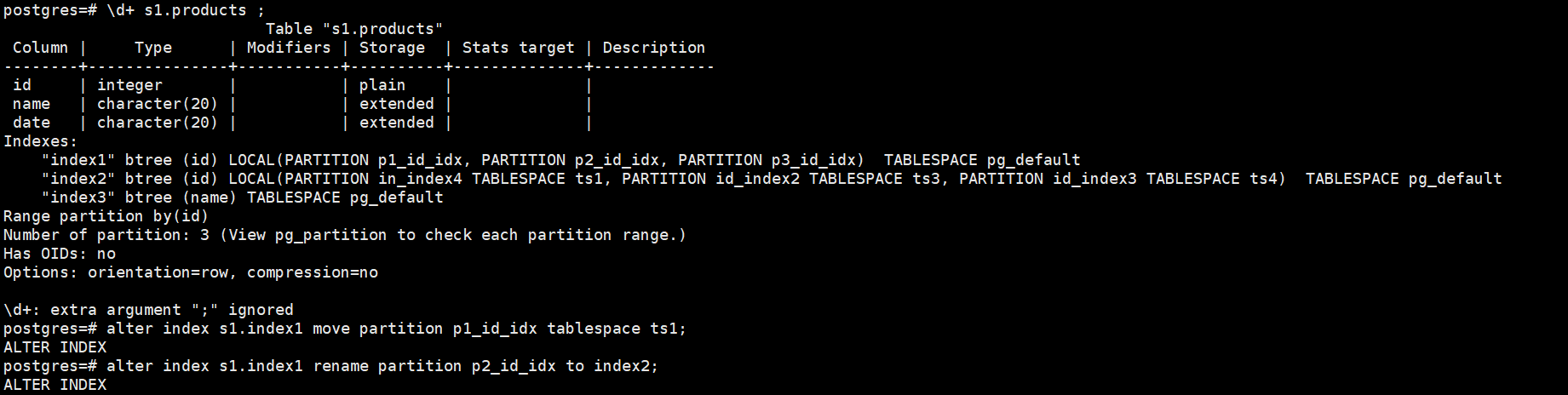
2.在分区表索引1上,修改分区表索引的表空间,重命名分区表索引
postgres=# \d+ s1.products ;
postgres=# alter index s1.index1 move partition p1_id_idx tablespace ts1;
postgres=# alter index s1.index1 rename partition p2_id_idx to index2;
3.在分区表索引2上,重建单个索引分区和分区上的所有索引
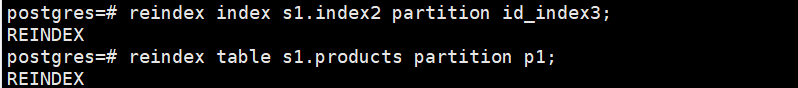
postgres=# reindex index s1.index2 partition id_index3;
postgres=# reindex table s1.products partition p1;
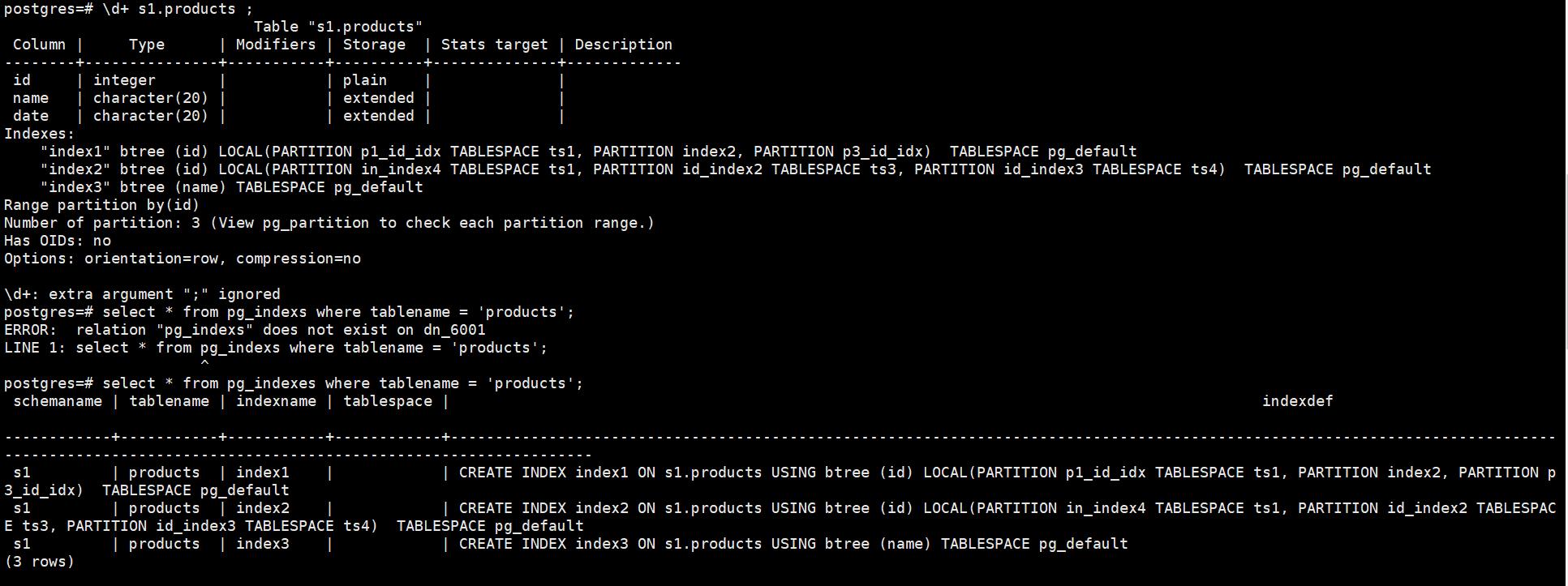
4.使用\d+、系统视图pg_indexes和pg_partition查看索引信息
postgres=# \d+ s1.products ;
postgres=# select * from pg_indexes where tablename = 'products';
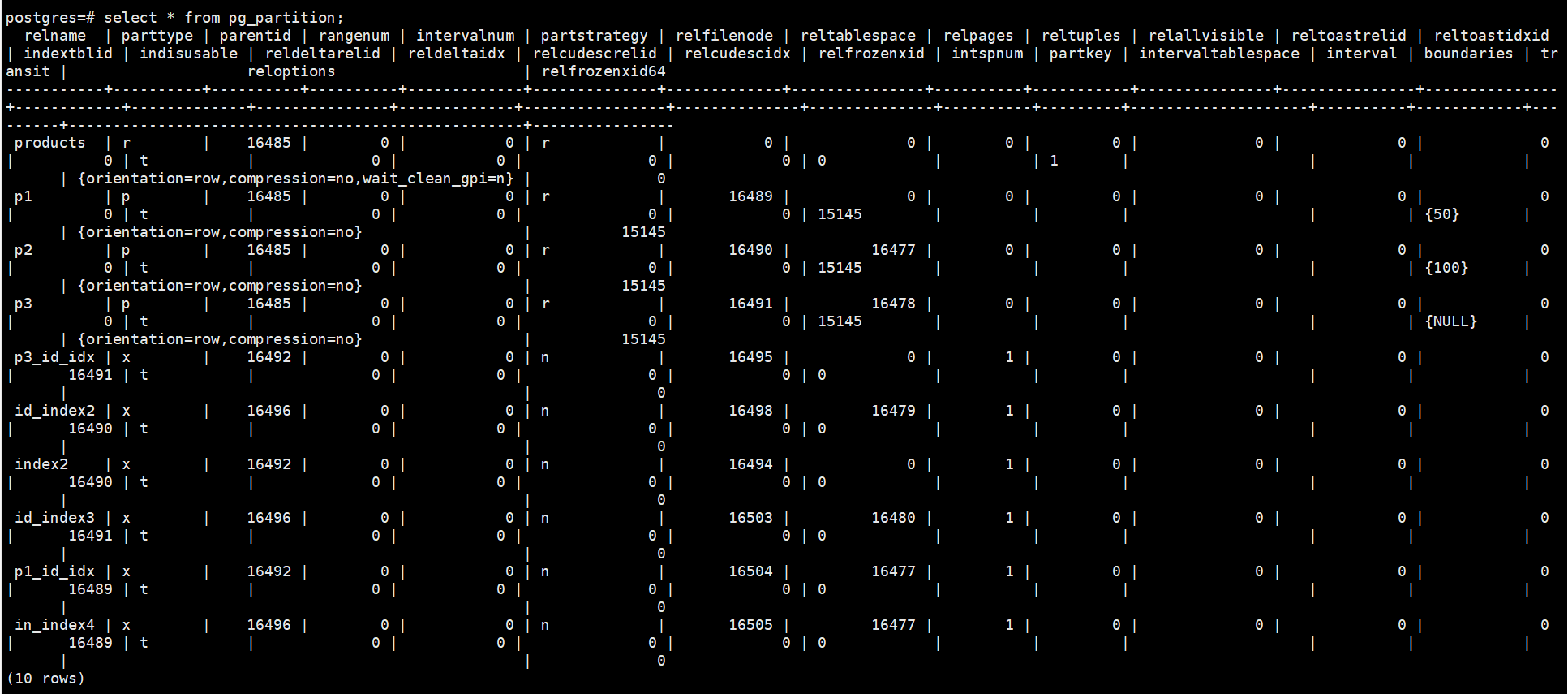
postgres=# select * from pg_partition;
5.删除索引、表和表空间
postgres=# drop index s1.index1;
postgres=# drop index s1.index2;
postgres=# drop index s1.index3;
postgres=# drop table s1.products ;
postgres=# drop tablespace ts1;
postgres=# drop tablespace ts2;
postgres=# drop tablespace ts3;
postgres=# drop tablespace ts4;
postgres=# drop schema s1;


「喜欢这篇文章,您的关注和赞赏是给作者最好的鼓励」
关注作者
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文章的来源(墨天轮),文章链接,文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






