事件机制
事件采用的是观察者模式。
同步事件:在一个线程里,按顺序执行业务,做完一件事再去做下一件事。
异步事件:在一个线程里,做一个事的同时,可以另起一个新的线程执行另一件事,这样两件事可以同时执行。
spring事件发送监听涉及三个部分
ApplicationEvent:表示事件本身,自定义事件需要继承该类,可以用来传递数据。
ApplicationEventPublisherAware:事件发送器,通过实现这个接口,来触发事件。
ApplicationListener:事件监听器接口,事件的业务逻辑封装在监听器里面。
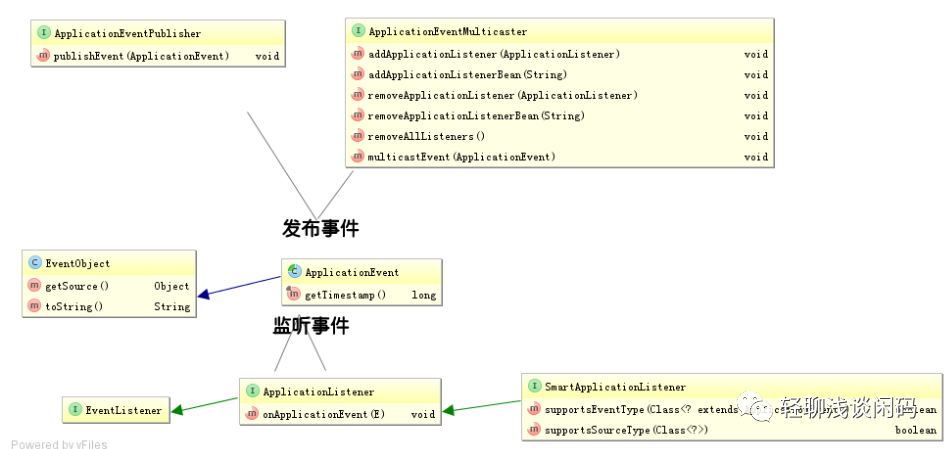
事件原理
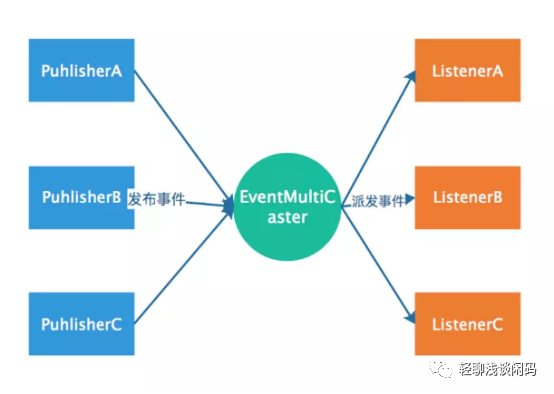
发布者调用applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(msg)将事件发送给EventMultiCaster,EventMultiCaster中注册着所有的Listener,然后就会根据事件类型决定转发给那个Listener。
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, ResolvableType eventType) {
// 这个是用来根据event的类型找到合适的listener的
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType :resolveDefaultEventType(event));
for (final ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)){
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// executor不是空的时候会在executor中激活listener
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
});
} else {
// 否则就直接在当前调用线程中激活listener
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
默认SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster在创建SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster时,executor是null,所以默认情况下所有的listener 的onApplicationEvent是直接在当前线程(事件发布者所在线程)中调用,所以如果onApplicationEvent有阻塞操作也会导致事件发布者被阻塞,后续的其他listener也会被阻塞无法调用。
自定义multicaster
<!-- 使用线程池运行listener -->
<bean id="executorService" class="java.util.concurrent.Executors" factory-method="newCachedThreadPool" />
<bean id="applicationEventMulticaster" class="org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster">
<property name="taskExecutor" ref="executorService" />
</bean>
<bean id="applicationEventAsyncMulticaster" class="org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster">
<property name="taskExecutor">
<bean class="org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor">
<property name="corePoolSize" value="5"/>
<property name="keepAliveSeconds" value="3000"/>
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="50"/>
<property name="queueCapacity" value="200"/>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
备注:如果加
事件传播
当我们监听一个事件处理完成时,还需要发布另一个事件,一般我们想到的是调用ApplicationEventPublisher#publishEvent发布事件方法,但Spring提供了另一种更加灵活的新的事件继续传播机制,监听方法返回一个事件,也就是方法的返回值就是一个事件对象。
也可以使用注解
@Async
@EventListener
从Spring 4.2开始,框架提供了一个新的@TransactionalEventListener注解,它是@EventListener的扩展,允许将事件的侦听器绑定到事务的一个阶段。绑定可以进行以下事务阶段:
AFTER_COMMIT(默认的):在事务成功后触发
AFTER_ROLLBACK:事务回滚时触发
AFTER_COMPLETION:事务完成后触发,不论是否成功
BEFORE_COMMIT:事务提交之前触发
@TransactionalEventListener(phase = BEFORE_COMMIT)
public void txEvent(Order order) {
System.out.println("事物监听");
}
事件类一定要继承ApplicationEvent吗?
当然不是,我们还可以自定义泛型类实现事件调度
1.写个通用泛型类事件
public class GenericEvent<T> {
private T data;
private boolean success;
public GenericEvent(T data,boolean success){
this.data = data;
this.success = success;
}
public T getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(T data) {
this.data = data;
}
public boolean isSuccess() {
return success;
}
public void setSuccess(boolean success) {
this.success = success;
}
}
2.写个具体类型的事件
public class OrderGenericEvent extends GenericEvent<Order> {
public OrderGenericEvent(Order data, boolean success) {
super(data, success);
}
}
3.在service的方法中发布事件
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new OrderGenericEvent(order,true));
4.事件处理
@Componentpublic class OrderGenericEventListener {
@EventListener(condition = "#event.success")
public void orderListener(GenericEvent<Order> event){
System.out.println(this.getClass().getName()+"--处理泛型条件事件。。。");
}
}
测试结果表明,成功处理了事件。
success为true时,我们把发布事件的代码改为如下内容再测试,则不会收到事件通知。
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new OrderGenericEvent(order,false));
配置事件监听器的一些方法
SpringApplication.addListeners 添加监听器
把监听器纳入到spring容器中管理
使用context.listener.classes配置项配置
使用@EventListener注解,在方法上面加入@EventListener注解,且该类需要纳入到spring容器中管理
spring和springboot已经定义好的事件
spring的事件
springboot的事件