我们在Wrapper中了解过DefaultServlet,WebDevServlet这几个Tomcat内置的静态资源处理类,其实后端的静态资源查找都是由StandardRoot(WebResource)来完成的。
其作为一个在StandContext中的一个组件存在,当应用路由需要查询资源的时候,都会找到这个StandardRoot的getResources方法进行查询,而该方法其实是通过StandardRoot中维护的一个allResources的属性获取的,该资源是一个当前应用的资源大合集,包括JAVA EE规范定义的,也包括用户可以在context.xml文件中定义的;
在StandardRoot中维护着n种资源:

上述的5种资源最终都是以顺序加入到allResources:
Ordering
In addition to the sets of resources described above, the standard implementation also maintains ClassResources which represent the classes contained in the JAR files mapped to /WEB-INF/classes
. This allows other components to search for classes with a single call rather than one call to search /WEB-INF/classes
followed by another to search the JARs in /WEB-INF/lib
. The ClassResources are populated from the JARs mapped to /WEB-INF/lib
when the web application starts.
Therefore, the complete search order is:
PreResources
MainResources
ClassResources
JarResources
PostResources
mainResources指的是当前应用目录的/,通过定义当前根目录的DirResourceSet进行资源查找和路由:
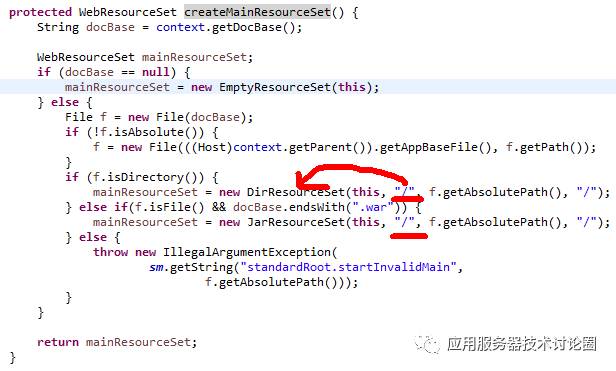
ClassResources指的是web-inf/classes;
jarResources指的是web-inf/lib;
上述的二者没什么可说的;
主要是PreResources和PostResources,这两个属性都需要在<Context>元素中进行定义:
<Resources> <PreResources base="D:\Projects\external\classes" className="org.apache.catalina.webresources.DirResourceSet" webAppMount="/WEB-INF/classes"/> <PostResources base="D:\Projects\lib\library1.jar" className="org.apache.catalina.webresources.FileResourceSet" webAppMount="/WEB-INF/lib/library1.jar"/> </Resources>
PreResources是先于mainResources进行查找资源,是最先开始进行查找的;
PostResources是最后进行查找;
这两个配置有如下的属性,以PreResources为例:
base | Identifies where the resources to be used are located. This attribute is required by the |
该属性就是查找资源的路径,一般为一个和tomcat服务器端部署的磁盘地址;
className | Java class name of the implementation to use. This class must implement the |
在Tomcat的webresource包中,有很多资源Set的实现:
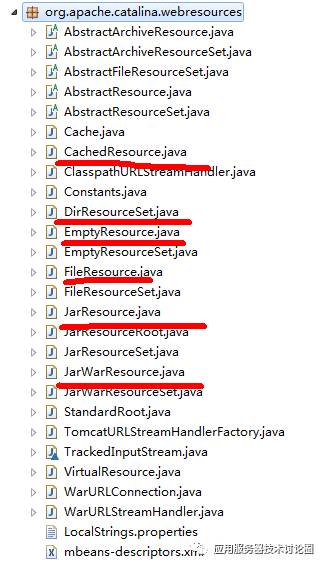
代表不同的资源,不同资源再查找也不同:
JarResources,是通过JarFile进行查找,查找的路径是直接进入Jar中就开始了;
而JarWarResources,虽然也是通过JarFile进行查找,但war需要有自己的规范,例如web-inf/classes的目录结构去搜索资源(Tomcat文档中没有开放出来)
DirResources,是文件目录的形式;
FileResources,是将文件单体资源进行添加的形式,如果你要一个一个添加资源,那你选这个FileResources;
internalPath | Identifies the path within the base where the resources are to be found. This is typically only used with JAR files when the resources are not located at the root of the JAR as is the case with resource JARs. This attribute is required by the |
如果className属性你定义了JarResources,那么你想增加的资源在这个jar包的xxx位置,而除了这个xxx位置的其余地方,其它jar中的资源我不想要,那么这个属性就需要定义;
readOnly | If |
告知该资源是只读的,这有啥用呢?
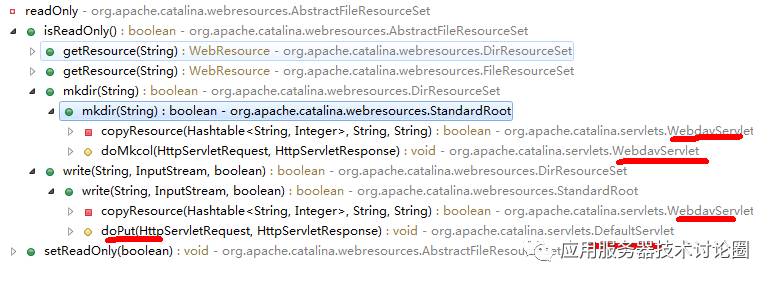
我们看到调用到该属性都是WebdevServlet,其实现的是服务器上的资源规范,可以对资源进行各种管理,前面我们讲到了其中有如剪切,拷贝,创建等都需要非只读权限,而我们如果在这里设置这个readOnly的话,那么会反馈到WebdevServlet中的这些操作中;
其次,DefaultServlet中的doPut请求,也是对资源进行修改的,设置readOnly也可以对其进行控制;
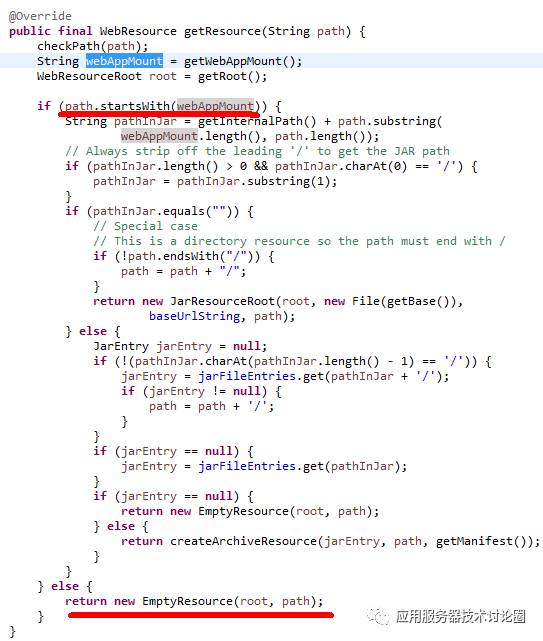
webAppMount | Identifies the path within the web application that these resources will be made available. For the |
如果配置了该属性,该路径指示的是在web应用目录中,哪一些资源是有效的;
从代码的角度来看,就是如果定义了webAppMount的话,查找的资源以webAppMount的路径为开头的才行,否则根本不予查找:
总结:
本文主要讲述了Tomcat中的资源查找对象StandardRoot中的几种资源,这些资源有的是Tomcat内置的,如MainResources,有的可以配置的,如PreResources,PostResources,本文后面着力描述一下这两个可配置项的实现;






