12.mapperContextRootRedirectEnabled
mapperContextRootRedirectEnabled | If enabled, requests for a web application context root will be redirected (adding a trailing slash) if necessary by the Mapper rather than the default Servlet. This is more efficient but has the side effect of confirming that the context path exists. If not specified, the default value of |
通常来讲,我们访问一个hahaha应用中,
http://localhost:8080/hahaha 这种方式和 http://localhost:8080/hahaha/ 二者只是多了一个/,有什么不一样吗?
对于第二种多了一个/,那就相当于context path是/,也就会请求hahaha应用的根;
而第一种如果该属性设置为false的话,那么就context path就是null,直接返回一个404了,我们可以看一下Mapper映射类中internalMapWrapper方法中,怎么关联的这个类的:
幸运的是,默认这个属性就是true,也就是说,即使你不定义这个属性,当你访问 http://localhost:8080/hahaha Tomcat也会给你这个链接补上一个/;
13.mapperDirectoryRedirectEnabled
mapperDirectoryRedirectEnabled | If enabled, requests for a web application directory will be redirected (adding a trailing slash) if necessary by the Mapper rather than the default Servlet. This is more efficient but has the side effect of confirming that the directory is exists. If not specified, the default value of |
这个属性和上一个基本类似,只不过mapperContextRootRedirectEnabled 针对的是contextroot,这个属性针对于的是应用当中出现的所有的目录:
如 http://localhost:8080/hahaha/sss ,那么就相当于在该路径上补充一个 http://localhost:8080/hahaha/sss/
14.override
override | Set to |
在全局conf/defaultxml和Host级别有默认的Context配置,对于Context元素来说如果没有指定这些属性,默认会将父类的配置进行继承下来;
而如果这个overide属性设置为true的话,直接忽略掉继承的设置,
从代码上来看,StandardContext读取配置是通过Digest进行解析:
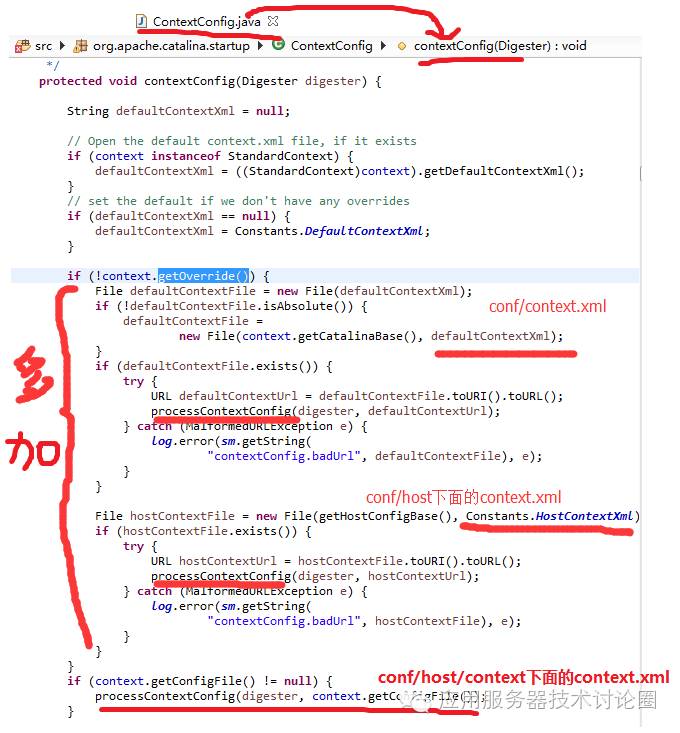
context.xml出现的位置较多,一共是三级,如果overide的话,相当于对defaultContextxml和hostContextxml加上对StandardContext的属性继承;
15.preemptiveAuthentication
preemptiveAuthentication | When set to |
Tomcat安全认证模块,是基于Tomcat默认的security constraint(logContext)进行验证的,该逻辑是在Tomcat默认的流程中的;
但如果你不想使用这些认证模块,屏蔽掉这块,而要自定义进行认证,那么你需要设置这个属性,可以将默认的忽略掉:
这个属性是怎么实现呢?
首先,需要在配置读取的时候不让其设置loginContext
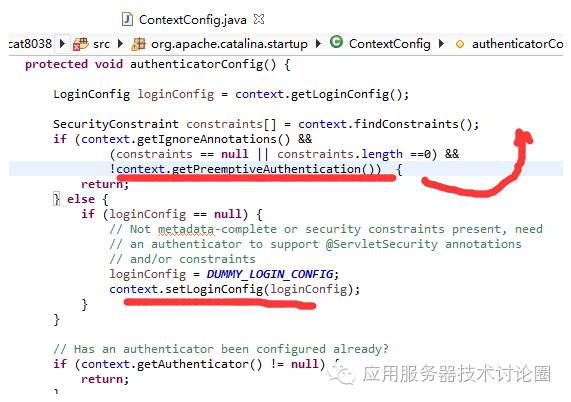
其次,在invoke调用的时候,如果该属性为true,可以看到AuthenticatorBase就不会进行invoke了
这样,就相当于把原来的logContext给去掉了,而你可以配置一个自定义的valve,如下面:
进行自己设置安全验证;
16.privileged
privileged | Set to |
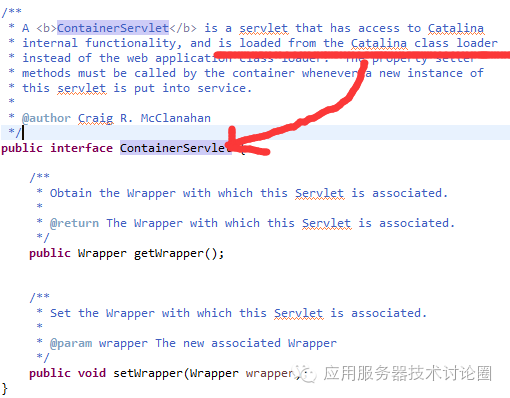
这个属性也挺有意思,privileged是特权,也就是让当前Context越权,越权的目的是让应用可以用container Servlet;
什么是ContainerServlet呢?我们从类的继承关系可以看到:
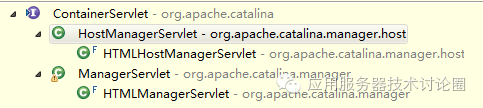
就是管理控制台中ManagerServlet和HostManagerServlet,这两个Servlet基本上可以对Tomcat进行基本的管理,而应用如果越权以后,就可以方便的复用这个功能,很容易的在自己的应用对tomcat管控起来;
要想完成这个工作,需要做两件事:
第一件,需要修改当前的context的classloader,让其classLoader升一级,这样才能load到tomcat中的lib的代码,我们先看看Tomcat的类加载器结构:
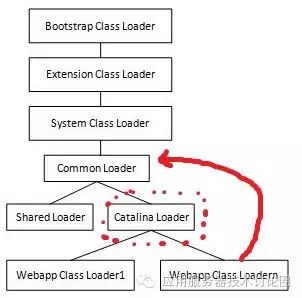
catalina Loader这一层级一般在catalina.properies默认是不配置的,也就是说webappClassLoader这一级别class的父类就是CommonLoader;
Tomcat的代码都是Common Loader这一层级加载的,我们需要将Context的层级按照上图进行提到这个层级中:
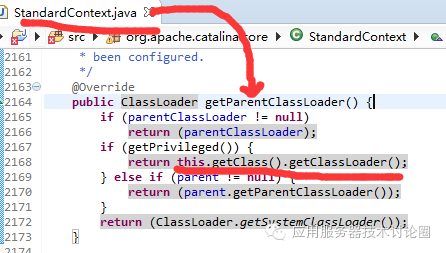
从代码的角度来看,当Context配置特权,直接返回的就是Tomcat的代码这一级别的ClassLoader,也就是说,应用的类加载器和Tomcat的代码的类加载器是一样的;
第二件,为什么要费这么大的劲去提高ClassLoader的层级呢?因为对于Tomcat管理控制台的两个ManagerServlet和HostManagerServlet,这两个Servlet都是属于ContainerServlet,也就是该Servlet级别较高,一般人不能调用,从ClassLoader的角度来看,其是由webappClassLoader的上一级进行加载的(如果没配置catalina loader那就是commonClassloader):
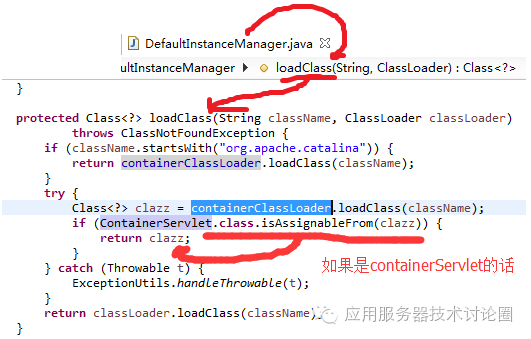
在loadServlet的时候,可以看到如果不是ContainerServlet的话,才会使用传入的该Context的Webappclassloader进行加载;
17.reloadable
reloadable | Set to |
这个属性非常关键,是热部署的触发开关,其重点监测/WEB-INF/classes/ ,/WEB-INF/lib 这两个目录,如果一旦发现有风吹草动,
Tomcat的应用就会进行reload;
该流程在Tomcat热部署中展开进行详细讲述,敬请期待;
18.resourceOnlyServlets
resourceOnlyServlets | Comma separated list of Servlet names (as used in |
这个属性不好理解,说大白话吧,实际就是你一个url去访问Tomcat,Tomcat得处理流程是首先去找Wrapper,也就是看看Mapper中有哪个Servlet能处理你这个url,如果找不到的话,那就说明当前的url访问的是资源Resource了,这个时候就需要DefaultServlet出场处理了;
但是,例如:
http://localhost:8080/hahaha/xixi 这个请求,/xixi在web.xml中也进行了配置,而实际对应部署应用中也确实有xixi这样的一个目录,那么需求就来了,当设置这个属性的时候,我想识别为对应目录资源,而不是servlet;
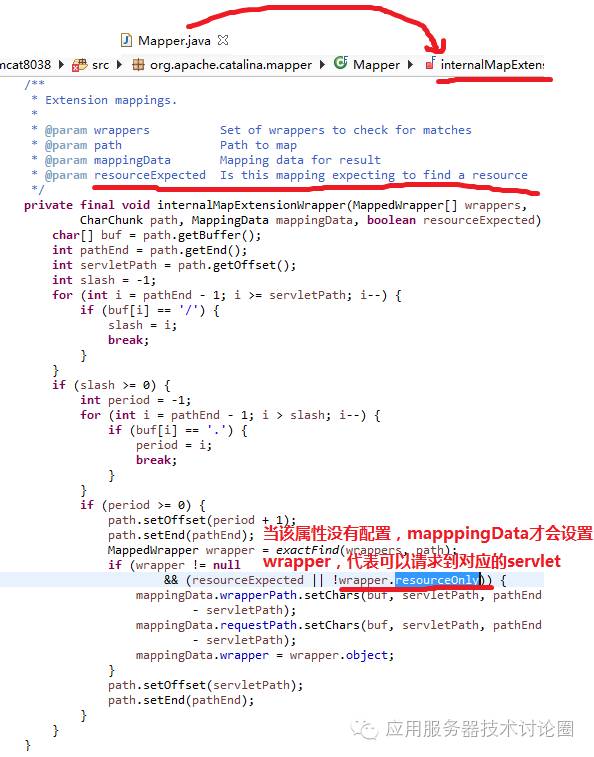
我们来看看代码,主要这个属性起作用的位置就在Mapper中,当进行扩展匹配的时候,如果设置了这个属性,那么mappingData中的wrapper就不设置了,那么自然该url请求就会被映射为资源,被DefaultServlet所处理了:
19.sendRedirectBody
sendRedirectBody | If |
RFC2616也就是http1.1协议中,对于跳转的response,建议包含一个response body,从代码上来看:
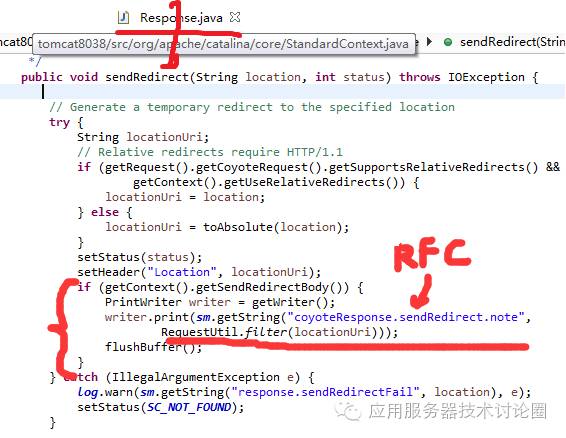
在Response的sendRedirect方法中,如果设置该属性,调用输出流,向缓冲区写入;
这个属性主要就是实现规范而已,当需要Tomcat满足http1.1规范的时候,可以将该属性打开;
20.sessionCookie相关
sessionCookieDomain | The domain to be used for all session cookies created for this context. If set, this overrides any domain set by the web application. If not set, the value specified by the web application, if any, will be used. |
sessionCookieName | The name to be used for all session cookies created for this context. If set, this overrides any name set by the web application. If not set, the value specified by the web application, if any, will be used, or the name |
sessionCookiePath | The path to be used for all session cookies created for this context. If set, this overrides any path set by the web application. If not set, the value specified by the web application will be used, or the context path used if the web application does not explicitly set one. To configure all web application to use an empty path (this can be useful for portlet specification implementations) set this attribute to Note: Once one web application using |
sessionCookiePathUsesTrailingSlash | Some browsers, such as Internet Explorer, Safari and Edge, will send a session cookie for a context with a path of |
这几个属性都是与sessionCookie相关的;
sessionCookieDomain是服务器的session的cookie存放的domain可以进行自定义,
sessionCookieName默认的session存放的cookie名就是JSESSIONID
,而这个属性可以对其进行修改,
sessionCookiePath是你可以定义cookie存放路径,
sessionCookiePathUsesTrailingSlash是基于RFC6265规范,防止不同应用之间互访问,做法就是在其cookiepath最后加一个反斜杠,
以sessionCookieName为例,如果当前Tomcat支持cookie方式记录session的话,那么在创建cookie的时候,首先会从当前的Context去读取这几个属性,如果没有设置,再按照默认的SessionConfig的配置进行创建cookie:
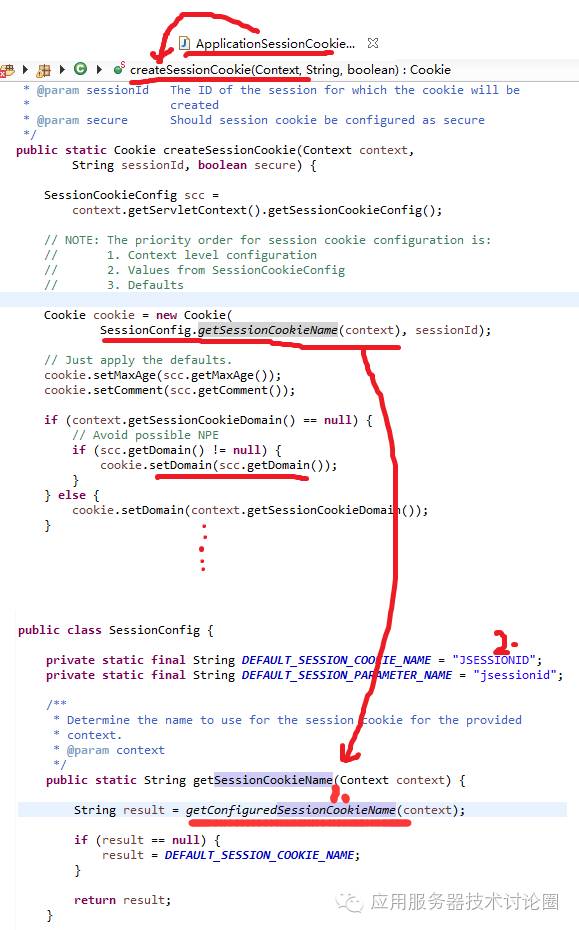
上述代码中,如果Context中定义了cookieName的值,优先使用这个,如果没有定义,那就使用SessionConfig中的JSESSIONID了;






