访问日志作为Tomcat日志类型中的一个相当重要的环节,也需要仔细的进行分解。它所记录的内容是对Tomcat的访问情况,默认的文件位置在Tomcat_Home/logs下面:
在该txt中记录的是Tomcat的文件访问情况:
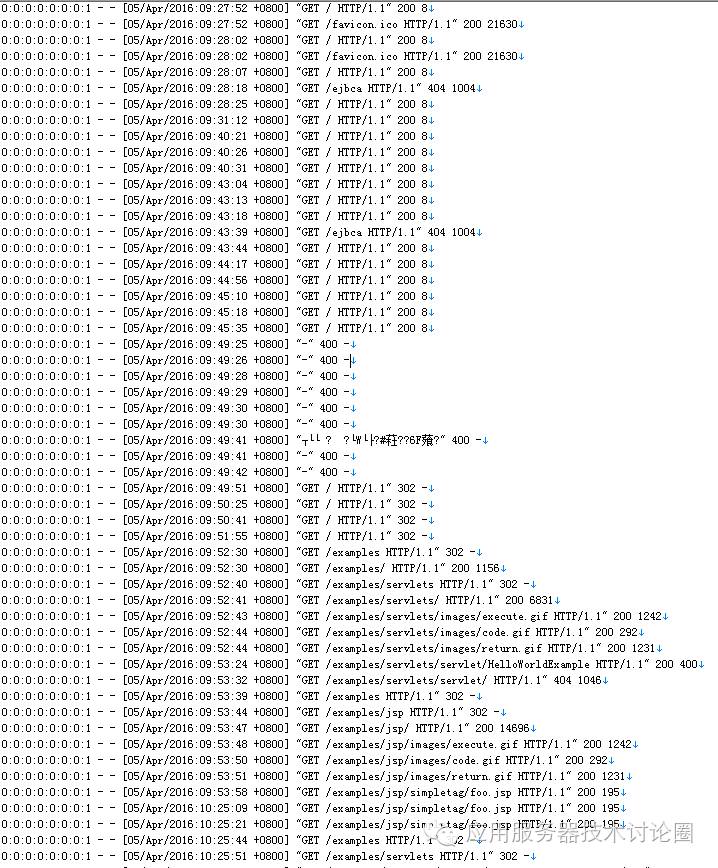
我们从这个文件中,能看到是哪一个remoteIP访问的,什么时间访问的,http访问的方法,访问的内容,返回值等等;
这个文件的内容是可以进行定制的,我们翻译一下AccessLog的属性配置:
Attributes
The Access Log Valve supports the following configuration attributes:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
className | Java class name of the implementation to use. This MUST be set to org.apache.catalina.valves.AccessLogValve to use the default access log valve. 可以定制访问日志的类,默认是AccessLogValve ,这个AccessLogValve 是按照自己的一套pattern的,在Tomcat中; 还有一个可选的Extended Access Log Valve 这个也是一个pattern,它主要针对于的是W3c规范的pattern,也就是https://www.w3.org/TR/WD-logfile.html 这个链接的规范; 如果你足够牛B或者需要对默认的AccessLogValve进行修改,你自己也可以继承这个AccessLogValve 进行自定义的实现; |
directory | Absolute or relative pathname of a directory in which log files created by this valve will be placed. If a relative path is specified, it is interpreted as relative to $CATALINA_BASE. If no directory attribute is specified, the default value is "logs" (relative to $CATALINA_BASE). 访问日志的目录位置,默认就在logs下; |
prefix | The prefix added to the start of each log file's name. If not specified, the default value is "access_log". logfile文件名的前缀,默认就是access_log; |
suffix | The suffix added to the end of each log file's name. If not specified, the default value is "" (a zero-length string), meaning that no suffix will be added. logfile文件名的后缀,默认是“”; |
fileDateFormat | Allows a customized timestamp in the access log file name. The file is rotated whenever the formatted timestamp changes. The default value is logfile文件名中会有基于年月日的部分,作为文件名中的中间部分; |
rotatable | Flag to determine if log rotation should occur. If set to
|
renameOnRotate | By default for a rotatable log the active access log file name will contain the current timestamp in 如果设置了日志轮转,那么无论是原有文件和新文件中都有时间戳,而这个renameOnRotate 的意思是目前正在写入的访问日志中,名称中不包含这个时间戳,只有在轮转文件关闭,时间戳才被加上; 这个实际上是为了和一些日志框架做兼容,大多数日志框架为了区分正在写入的log,该文件通常都不会加时间戳; |
pattern | A formatting layout identifying the various information fields from the request and response to be logged, or the word 对访问日志进行格式化,对于格式的写法,见Tomcat中有非常明确的定义:
|
encoding | Character set used to write the log file. An empty string means to use the system default character set. Default value: use the system default character set. 日志输出的字符集 |
locale | The locale used to format timestamps in the access log lines. Any timestamps configured using an explicit SimpleDateFormat pattern ( 如果在访问日志中使用了预定义的 %{xxx}t,相当于使用timestamp,对于Locale时区的定义,就是通过这个属性; |
requestAttributesEnabled | Set to 如果该属性不设置,在访问日志中通过pattern记录的ip,port,协议等信息,都是从request中获得的; 而该属性的意思在于,可以通过RemoteIpValve对一些request的信息做一些手脚,是一个开关; |
conditionIf | Turns on conditional logging. If set, requests will be logged only if 对于reqeust的属性进行条件过滤,当request.getAttribute为null的时候,访问日志什么都不会记录; 或者你也可以指定,当reqeust的哪一个属性存在时,访问日志进行记录; 这个属性整体上来说,是一个条件记录的功能; |
conditionUnless | Turns on conditional logging. If set, requests will be logged only if conditionIf的反过来; |
condition | The same as 和conditionUnless一样; |
buffered | Flag to determine if logging will be buffered. If set to 访问日志是否采用缓冲区的方式,实际上就是用Buffered缓冲输出流进行输出; |
maxLogMessageBufferSize | Log message buffers are usually recycled and re-used. To prevent excessive memory usage, if a buffer grows beyond this size it will be discarded. The default is 如果设置了buffered 这个属性,那么需要找一个byte[]数组进行倒,这个属性就是设置这个数组大小的; |
resolveHosts | This attribute is no longer supported. Use the connector attribute If you have 该属性已不被支持了; |
前面我们已经讲过tomcat中的日志体系,除了这个访问日志,其它所有都是基于JDK Log的基础之上,Tomcat封装了juli日志,扩展了JDK Log;
juli这个日志体系,用在Tomcat的内部log上,JAVAEE规范(ServletContext.log),还有拦截System.out/err这种标准输出,但对于访问日志而言,其并没有需要扩展JDK Log这种handler,Formatter这种体系,要求的就是效率,越复杂的设计,越会带来效率的降低,所以,访问日志是单独的做的日志处理,它采用的是AccessLogValve来实现这个功能;
对于AccessLogValve来说,其是作为请求调用链条中的一个环节,在Tomcat后端处理每一个请求的流转都会经过这个配置的AccessLogValve,在server.xml中有如下定义:

对于该Host来说,配置的AccessLogValve是放在Tomcat_home/logs目录下的,前缀是localhost_access_log,后缀采用txt的格式来进行存储,存储的pattern是%h %l %u %t "%r" %s %b,这些其实就是本文最上面的两张图;
从代码角度去分析, CoyoteAdapter 中的service方法,是Tomcat前后端的调用分界线,在这个方法中,Tomcat会从Connector中读取的数据转化为Request,Response,并传递到Tomcat后端层次结构中去,每一次经过这个方法,都算作一次请求调用;
因此,在该方法的最后进行记录访问日志:
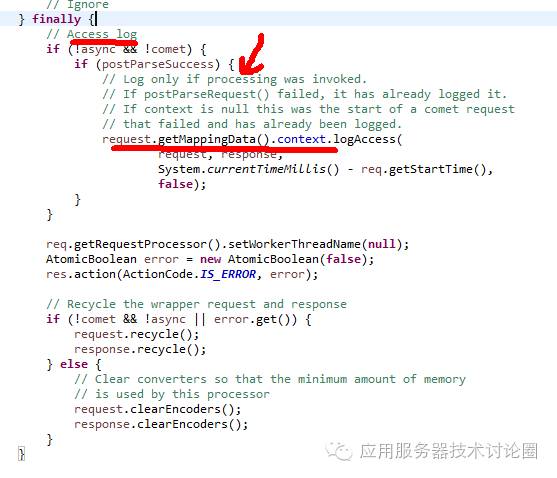
传入的参数为request,response,
第三个参数是,从req调入后端的时间 - tomcat后端请求处理完的时间,这个时间差是整个处理请求一共用多少时间;
最后一个参数是useDefault,如果为true的话,就会使用默认的StandardEngine的AccessLogValve访问日志进行记录,如果为false的话,否则就会使用server.xml配置文件中的AccessLogValve;
我们继续看看logAccess方法:
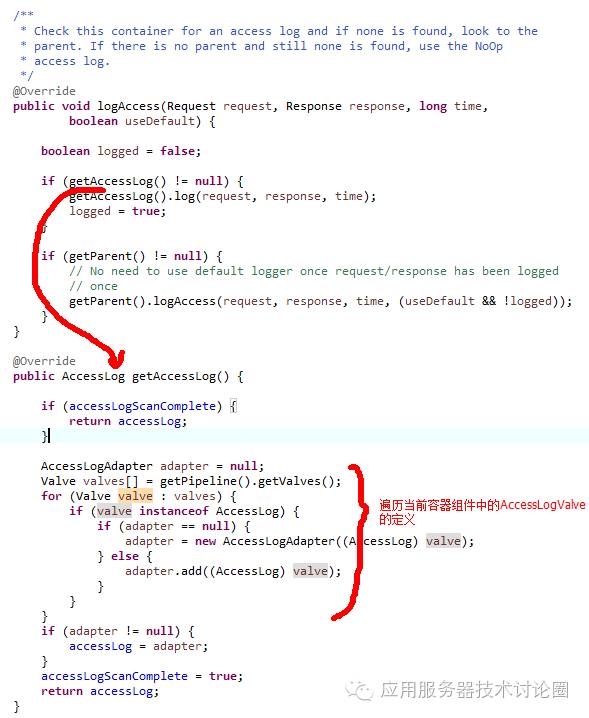
当前容器组件中会定义一系列的Valves,如上面Host配置的AccessLogValve,那么这里将其遍历出来,并包装为AccessLogAdapter,这个AccessLogAdapter实际可以包装n个AccessLogValve,其使用的场景就是在server.xml中定义了多个AccessLogValve,而每一次请求调用,都需要对应配置的AccessLogValve进行记录n份;
对于AccessLog接口,在Tomcat系统中一共有4个实现类:
a.AbstractAccessLogValve:是AccessLogValve实现类的抽象类,
这个抽象类中实现了Pattern解析的基本功能,可以看到下面的各种Element,都是对整个Pattern字符串进行解析的;
它的实现类就是AccessLogValve,AccessLogValve中的各种属性对应前面这张表,
这里以rotate为例,看看AccessLog是怎么实现的:
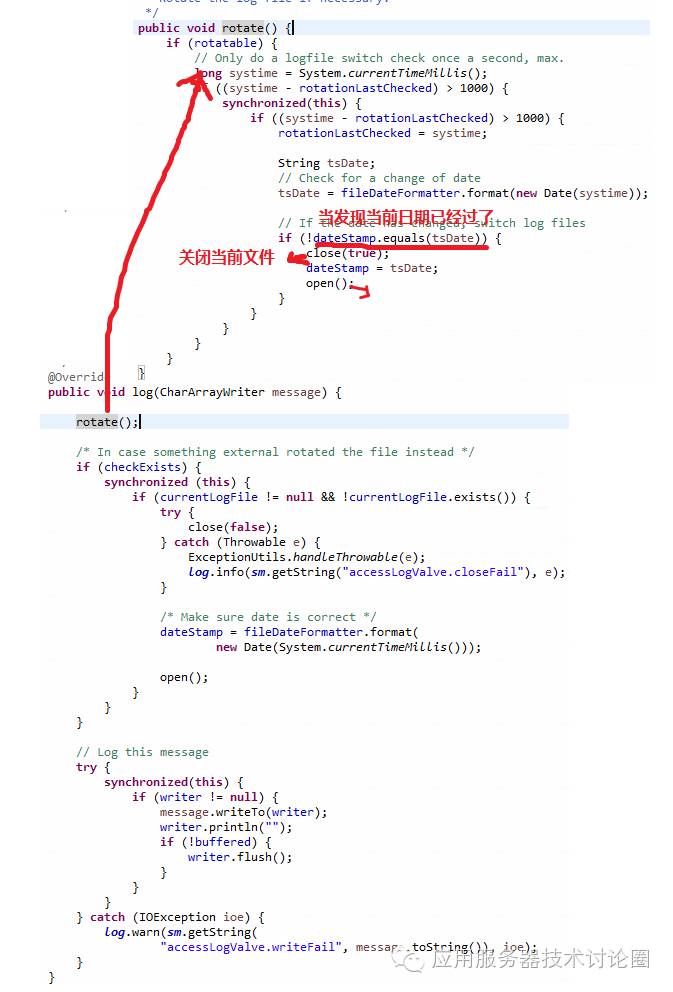
rotate的规则是,基于当天的一份文件,如果是第二天再换一份文件;
这种方式是文件可能会很大,因此才有了下面的JDBCAccessLogValve这种往数据库中插的方式;
b. AccessLogAdapter:包装n份AccessLogvalve,如前面的解释,这个适配器不能出现在server.xml的配置文件中作为一个AccessLogValve的类型,只是在Tomcat中内部使用,对n份AccessLogvalve进行包装;
c.JDBCAccessLogValve:这个AccessLog是对应一张数据库的表,
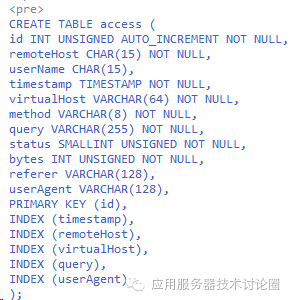
将AccessLog的内容都记录在数据库上,这样会大大提高访问日志的文件操作的效率;
该JDBCAccessLogValve,可以配置在server.xml中,
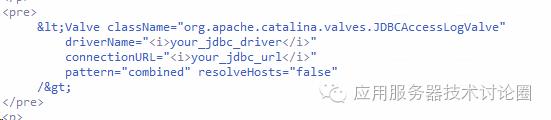
当对于AccessLogValve写文件的速度不满的时候,可以尝试的往数据库中进行插入;
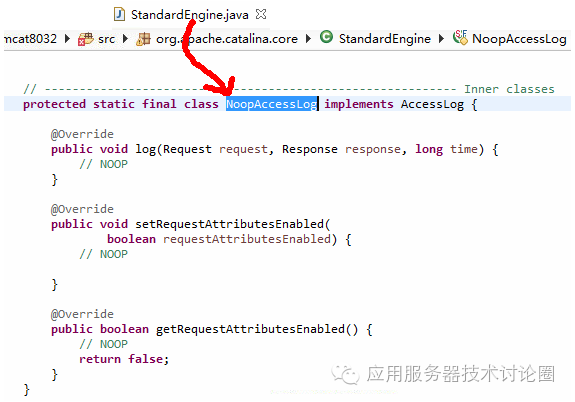
d.StandardEngine的内置的AccessLogValve,这个就对应前面的useDefault属性,当设置为true的时候,默认就会通过这个NoopAccessLog来进行记录,不过从实现的角度来看,什么都没有做,因此,还需要你在server.xml中进行定义;
总结:
AccessLogValve并没有使用Tomcat的juli系统进行记录日志,主要是因为用不到handler,formateer等复杂功能,尽可能的减少复杂架构带来的效率的降低,其采用一套单独pattern并且很精炼的几个类完成日志的记载;







