蹲厕所的熊 转载请注明原创出处,谢谢!
在上一篇 说说Java中资源文件的读取 中我们知道了如何加载类路径下的资源文件,对于其他的资源访问通常使用 java.net.URL 和文件IO来完成,在web项目里,我们也可以通过ServletContext来获取到资源,那么Spring为什么要搞出来一个Resource呢?
资源抽象接口Resource
Spring为了统一资源的访问,定义了Resource接口。为了针对不同的底层资源,Spring提供了不同资源的实现类来负责不同的资源访问逻辑。
Spring的Resource设计是一种典型的策略模式,通过使用Resource接口,客户端程序可以在不同的资源访问策略之间自由切换。

这其中有一些比较常见的资源实现类:
ByteArrayResource:二进制数组表示的资源,二进制数组资源可以在内存中通过程序构造。
ClassPathResource:类路径下的资源,资源以相对于类路径的方式表示。
FileSystemResource:文件系统资源,资源以文件系统路径的方式表示,如
/Users/benjamin/Desktop/a.txt
。InputStreamResource:对应一个InputStream的资源。
ServletContextResource:为访问Web容器上下文中的资源而设计的类,负责以相对于Web应用根目录的路径加载资源,它支持以流和URL的方式访问,在WAR解包的情况下,也可以通过File的方式访问,该类还可以直接从JAR包中访问资源。
UrlResource:封装了java.net.URL,它使用户能够访问任何可以通过URL表示的资源,如文件系统的资源、HTTP资源、FTP资源等。
// 1、文件系统资源
Resource res1 = new FileSystemResource("/Users/benjamin/Desktop/a.txt");
// 2、类路径下的资源
Resource res2 = new ClassPathResource("conf/a.txt");
// 3、web应用资源
Resource res3 = new ServletContextResource("/WEB-INF/classes/conf/a.txt");
资源加载
为了访问不同类型的资源,必须使用相应的Resource实现类,这是比较麻烦的。是否可以在不显示使用Resource实现类的情况下,仅通过资源地址的特殊标识就可以加载相应的资源呢?
Spring提供了一个强大的加载资源的机制,不但能通过 "classpath:"、"file:" 等资源地址前缀识别不同的资源类型,还支持Ant风格贷通配符的资源地址。
资源加载器
Spring定义了一套以 ResourceLoader 为顶层的资源加载接口和实现类。
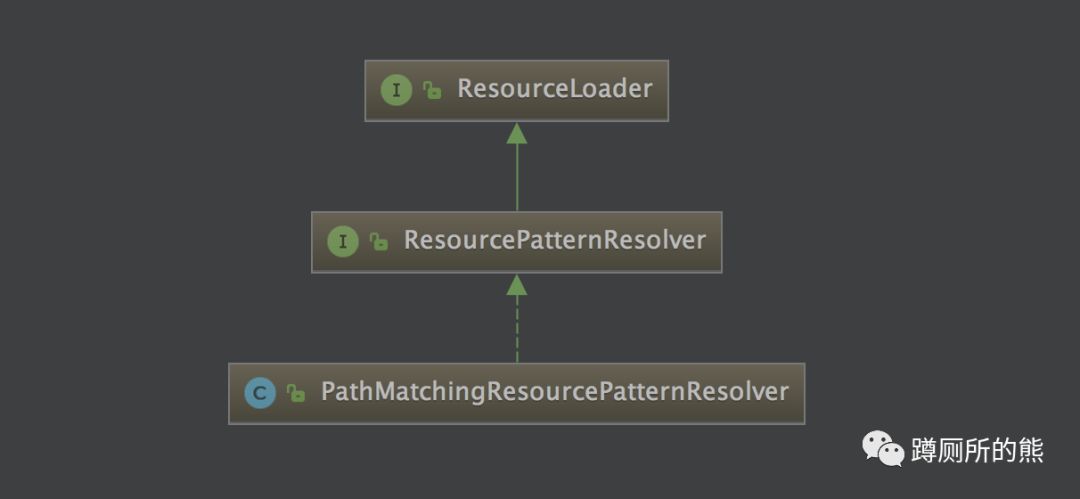
ResourceLoader 接口仅有一个 getResource() 方法,可以根据一个资源地址加载文件资源,不过,资源地址仅支持带资源类型前缀的表达式,不支持Ant风格的资源路径表达式。 ResourcePatternResolver 扩展自 ResourceLoader 接口,定义了一个新的接口方法:getResources() ,该方法支持贷资源类型前缀及Ant风格的资源路径表达式。
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver是Spring提供的标准实现类,看个例子:
public class ResourceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
// 获取单个文件
Resource resource = resolver.getResource("classpath:spring.xml");
System.out.println(resource.getDescription());
// 获取多个文件
Resource[] resources = resolver.getResources("classpath*:spring*.xml");
for (Resource r : resources) {
System.out.println(r.getDescription());
}
}
}
getResource()
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
return getResourceLoader().getResource(location);
}
默认情况下,getResourceLoader()会拿到 DefaultResourceLoader
,这个赋值操作是在类初始化的时候完成的。
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver() {
this.resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
}
DefaultResourceLoader
会使用ClassLoader来加载资源,如果不指定ClassLoader,会使用默认的ClassLoader,更多ClassLoader的知识可以参考:理解TCCL:线程上下文加载器 、 JVM类加载的那些事
public DefaultResourceLoader() {
this.classLoader = ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader();
}
public static ClassLoader getDefaultClassLoader() {
// 1、首先使用TCCL
ClassLoader cl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (cl == null) {
// 2、TCCL比存在,取得当前类的ClassLoader
cl = ClassUtils.class.getClassLoader();
if (cl == null) {
// 3、最后取得系统ClassLoader,默认AppClassLoader
cl = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
}
}
return cl;
}
最后定位到getResource方法,它会根据传入的路径解析protocol,解析逻辑如下:
如果用户自定义了protocol的解析器,直接用它来进行解析资源,默认没有自定义解析器。
如果资源以
/
开头,使用 ClassPathContextResource 来解析资源,最终使用的就是JDK的ClassLoader.getResource()。如果资源以
classpath:
开头,解析出classpath:
后面的内容,使用ClassPathResource
解析资源。URL类型的资源都可以使用 UrlResource 来解析资源,如
file:http:ftp:
。没有前缀的资源使用 ClassPathContextResource 来解析资源,如:
com/xx/a.xml
。
public Resource getResource(String location) {
// 先走自定义protocol的resolver,默认protocolResolvers为空
for (ProtocolResolver protocolResolver : this.protocolResolvers) {
Resource resource = protocolResolver.resolve(location, this);
if (resource != null) {
return resource;
}
}
if (location.startsWith("/")) {
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
// 以 classpath: 开头
else if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()), getClassLoader());
}
else {
try {
// 解析URL类型的资源,ftp: http: file:
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
}
catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
// 没有前缀的资源
return getResourceByPath(location);
}
}
}
protected Resource getResourceByPath(String path) {
return new ClassPathContextResource(path, getClassLoader());
}
可能有的同学对第二点的 /
开头使用ClassLoader.getResource()解析有点疑问,因为之前我说过ClassLoader解析的资源不能以 /
开头啊。其实ClassPathResource对路径做了一层处理,把 /
去掉了:
public ClassPathResource(String path, Class<?> clazz) {
this.path = StringUtils.cleanPath(path);
this.clazz = clazz;
}
自定义ProtocolResolver解析资源
资源解析器 ProtocolResolver
提供了一个resolve方法供我们自己解析特定protocol的资源:
public interface ProtocolResolver {
Resource resolve(String location, ResourceLoader resourceLoader);
}
我们可以定义 resource:
开头的protocol代表自己工程下的资源文件目录:
public class ResourceProtocolResolver implements ProtocolResolver {
private static final String RESOURCE_PREFIX = "resource";
@Override
public Resource resolve(String location, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
if (location.startsWith(RESOURCE_PREFIX)) {
return resourceLoader.getResource(location.replace(RESOURCE_PREFIX, "classpath"));
}
return null;
}
}
最后,我们把自定义的解析器add到资源加载器中:
public class ResourceTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DefaultResourceLoader resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
// 增加自定义资源解析器
resourceLoader.addProtocolResolver(new MyProtocolResolver());
PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver resolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(resourceLoader);
resolver.getResource("my:spring.xml");
}
}
getResources()
public Resource[] getResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
if (locationPattern.startsWith("classpath*:")) {
// classpath*:后的路径存在*或者?
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring("classpath*:".length()))) {
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// 返回classpath下所有匹配路径的资源
return findAllClassPathResources(locationPattern.substring(CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
}
else {
// 得到路径的前缀。war:是专门针对tomcat解析用的
int prefixEnd = (locationPattern.startsWith("war:") ? locationPattern.indexOf("*/") + 1 : locationPattern.indexOf(":") + 1);
// 路径存在*或者?
if (getPathMatcher().isPattern(locationPattern.substring(prefixEnd))) {
return findPathMatchingResources(locationPattern);
}
else {
// 单个资源使用 getResource 方法加载
return new Resource[] {getResourceLoader().getResource(locationPattern)};
}
}
}
该方法把资源的查找分为3种类型:
解析后的路径中存在Ant风格的资源路径表达式走
findPathMatchingResources
方法查找所有资源。以
classpath*:
开头并且不存在Ant风格的资源路径表达式的走findAllClassPathResources
方法查找所有资源。其他路径走getResource的查找单个资源逻辑。
我们重点来看一下 findPathMatchingResources
方法,看看它是怎么通过Ant风格的资源路径表达式匹配到资源的:
protected Resource[] findPathMatchingResources(String locationPattern) throws IOException {
// 返回第一个不包含Ant通配符的目录,比如/WEB-INF/*.xml 返回 /WEB-INF/
String rootDirPath = determineRootDir(locationPattern);
// 路径除去rootDirPath的另外一部分
String subPattern = locationPattern.substring(rootDirPath.length());
// 获取匹配到目录的所有资源
Resource[] rootDirResources = getResources(rootDirPath);
Set<Resource> result = new LinkedHashSet<Resource>(16);
// 拿到所有资源挨个去匹配,把匹配到的资源放入result中
for (Resource rootDirResource : rootDirResources) {
rootDirResource = resolveRootDirResource(rootDirResource);
URL rootDirURL = rootDirResource.getURL();
if (equinoxResolveMethod != null) {
if (rootDirURL.getProtocol().startsWith("bundle")) {
rootDirURL = (URL) ReflectionUtils.invokeMethod(equinoxResolveMethod, null, rootDirURL);
rootDirResource = new UrlResource(rootDirURL);
}
}
if (rootDirURL.getProtocol().startsWith(ResourceUtils.URL_PROTOCOL_VFS)) {
result.addAll(VfsResourceMatchingDelegate.findMatchingResources(rootDirURL, subPattern, getPathMatcher()));
}
// jar资源
else if (ResourceUtils.isJarURL(rootDirURL) || isJarResource(rootDirResource)) {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingJarResources(rootDirResource, rootDirURL, subPattern));
}
// 其他资源
else {
result.addAll(doFindPathMatchingFileResources(rootDirResource, subPattern));
}
}
return result.toArray(new Resource[result.size()]);
}
因流程较长,我们直接来看重点的方法 doRetrieveMatchingFiles
中有一段拿到AntPathMatcher来进行匹配的逻辑。
if (getPathMatcher().match(fullPattern, currPath)) {
result.add(content);
}
至此,资源加载器中重要的部分都已经讲完了。
小结
通过源码我们可以知道对于Spring支持以下几种前缀的资源地址表达式:
| 地址前缀 | 示例 | 对应资源类型 |
|---|---|---|
| classpath: | classpath:com/xx/a.xml | 从类路径中加载资源,classpath:和classpath:/是等价的,都是相对于类的根路径。资源文件可以在标准的文件系统中,也可以在jar或zip的类包中。 |
| file: | file:/conf/com/xx/a.xml | 使用UrlResource从文件系统目录中装载资源,可采用绝对或相对路径 |
| http:// | http://www.xx.com/a.xml | 使用UrlResource从web服务器中装载资源 |
| ftp:// | ftp://www.xx.com/a.xml | 使用UrlResource从FTP服务器中装载资源 |
| 没有前缀 | com/xx/a.xml | 从类路径中加载资源 |
其中 classpath:
和 classpath*:
的区别为: classpath:
只会在第一个包下查找,而 classpath*:
会扫描所有这些JAR包及类路径下出现的包。
Ant风格资源地址支持3种匹配符:
?
:匹配文件名中的一个字符。*
:匹配文件名中的任意个字符。**
:匹配多层路径。
如果读完觉得有收获的话,欢迎点赞、关注、加公众号【蹲厕所的熊】,查阅更多精彩历史!!!






