接着上次的话题继续往下,这次的主要任务是完成对Ioc和Aop的实现,AOP在前一篇已经有过一定的认识,那么接下来简单的介绍下Ioc。
1.2 Ioc(Inversion of Control:控制反转)
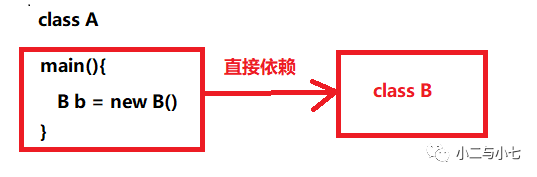
Ioc其实一种技术思想,而不是实现,在传统的开发模式中如果需要在类A中使用类B,通常我们会在类A中new 一个B的对象,这样类A对类B就会有一种强依赖关系,导致代码间的耦合度过高。
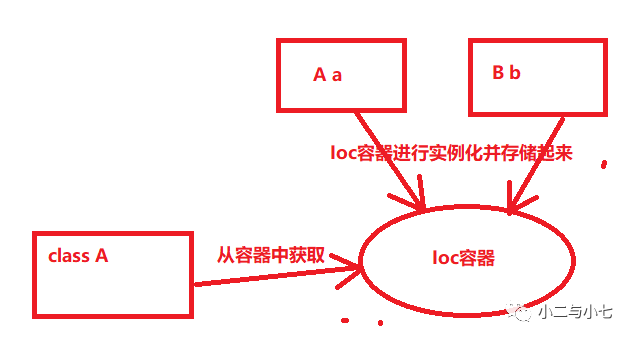
那么Ioc的思想是,不直接在类A中new B,而是通过Ioc容器去实例化对象,当我们需要的时候直接从容器中获取,将对象的创建和管理交给Ioc容器去控制,这样做虽然会使我们失去对对象管理的权力,但它的好处是降低了程序间的耦合。
为什么叫做控制反转?
控制:指的是对象创建(实例化、管理)的权利
反转:将控制权交给了外部环境(spring框架、IoC容器)
画图说明:
Ioc之前
Ioc思想
DI(依赖注入)和Ioc(控制反转)
这是两个比较容易混淆的概念,但其本质是站在不同的角度描述同一件事,对象依赖关系的维护,DI站在容器的角度,将实例化的对象注入给需要它的地方,Ioc站在对象的角度,表示对象的创建管理交给容器完成。
1.3 Ioc和AOP的实现
1.3.1 相关注解
如下先定义Autowired,Service,Component,Bean,Transactional这五个注解
@Autowired(用来实现自动注入)
package huashibimo.transfer.annocation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 自动注入
* @author 笔墨画诗
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.FIELD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Autowired {
public String name() default "";
}
@Service(用来实例化Service层对象:加载到Ioc容器中)
package huashibimo.transfer.annocation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 业务层注解
* @author 笔墨画诗
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Service {
String value() default "";
}
@Component(生成该类的实例化对象并加载到Ioc容器中)
package huashibimo.transfer.annocation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 组件注解
* @author 笔墨画诗
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Component {
String value() default "";
}
@Bean
package huashibimo.transfer.annocation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 可以通过方法注入
* @author 笔墨画诗
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Bean {
String value() default "";
}
@Transactional(AOP用的,用来实现事务的控制)
package huashibimo.transfer.annocation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 事务控制的注解
* @author 笔墨画诗
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Transactional {
String value() default "";
}
@Configuration(配置注解表明当前类是一个配置类)
package huashibimo.transfer.annocation;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
/**
* 配置
* @author 笔墨画诗
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Configuration{
String value() default "";
}
1.3.2 扫描注解维护IOC容器
1.3.2.1 配置扫描的包名(application.properties)
scanPackName = "com.xichuangyue"
1.3.2.2 定义bean工厂(BeanFactory.java)
扫描指定包路径下的class文件,初始化Ioc容器,并提供一个获取bean对象的方法
先声明两个集合一个用来存放生成的类的实例(ioc容器),另一个用来获取类的全限定类名。
private static Set<String> classNames = new HashSet<>(); // 存放类的全限定类名
private static HashMap<String,Object> iocCore = new HashMap<>(); // ioc容器
(1) doScanPackage 扫描指定包下的class,获取需要被ioc管理的类的全限定类名
/**
* 扫描所有的包获取所有类的全限定类名
* @param scanPackage
*/
public static void doScanPackage(String scanPackage){
// 获取磁盘路径
String scanPackagePath = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()
.getResource("").getPath() +
scanPackage.replaceAll("\\.","/");
File file = new File(scanPackagePath);
File[] files = file.listFiles();
for (File scanFile : files) {
// 排除注解所在的包
if (scanFile.getName() == "annotation") continue;
if (scanFile.isDirectory()){
doScanPackage(scanPackage + "." + scanFile.getName());
}else if (scanFile.getName().endsWith(".class")){
// 取得全限定类名
String name = scanFile.getName().replaceAll(".class","");
String className = scanPackage + "." + name;
classNames.add(className);
}
}
}
(2) initIocCore 初始化Ioc容器
/**
* 初始化ioc容器
*/
public static void initIocCore(){
if (classNames.size() == 0) return;
try {
for (String name : classNames) {
// 反射
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName(name);
// 使用了Service和Service注解的类会交给ioc管理
if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Component.class)){
putIocCore(aClass,Component.class);
}else if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Service.class)){
String className = aClass.getAnnotation(Service.class).name();
// 实例化
Object obj = aClass.newInstance();
// 未传入初始化时的name
if ("".equals(className)){
// 将类名首字母小写作为key,类的实例作为value存放在ioc容器中
String simpleName = aClass.getSimpleName();
String lowerFirstName = toLowerFirst(simpleName);
iocCore.put(lowerFirstName,obj);
}else {
iocCore.put(className,obj);
}
// 被注解的类是接口
// 获取该接口的所有实现
Class<?>[] interfaces = aClass.getInterfaces();
for (int j = 0; j < interfaces.length; j++) {
Class<?> anInterface = interfaces[j];
iocCore.put(anInterface.getName(),aClass.newInstance());
}
// 配置类
}else if (aClass.isAnnotationPresent(Configuration.class)){
Method[] methods = aClass.getMethods();
Object obj = aClass.newInstance();
for (Method method : methods) {
// 被@Bean注解的方法的方法名作为key,返回值作为value,存到ioc容器中
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Bean.class)){
try {
Object invoke = method.invoke(obj);
iocCore.put(method.getName(),invoke);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
(3) getBean 从ioc容器中获取实例
/**
* 获取实例
* @param key
* @return
*/
public static Object getBean(String key){
return iocCore.get(key);
}
(4) doAutoweired 自动注入被@Autoweired注解的类的属性
/**
* 实现依赖自动注入
*/
public static void doAutowired(){
if(iocCore.size() == 0) return;
for (Map.Entry<String, Object> objectEntry : iocCore.entrySet()) {
// 获取实例中的所有字段
Field[] declaredFields = objectEntry.getValue().getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (int i = 0; i < declaredFields.length; i++) {
Field field = declaredFields[i];
// 查看该字段是否被AutoWired注解
if (!field.isAnnotationPresent(Autowired.class)){
continue;
}
Autowired annotation = field.getAnnotation(Autowired.class);
String value = annotation.value();
// 未指定从ioc容器中获取实例的id,则使用被注入对象的类名首字母小写
if (value.equals("")){
value = toLowerFirst(field.getType().getName());
}
// 从ioc容器中获取实例
Object obj = iocCore.get(value);
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
// 注入对象
field.set(objectEntry.getValue(),obj);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
(5) 在静态代码块中执行
static {
InputStream rs = BeanFactory.class.getClassLoader()
.getResourceAsStream("application.properties");
Properties properties = new Properties();
try {
properties.load(rs);
// 扫描包
doScanPackage(properties.getProperty("scanPackage"));
// 初始化ioc容器
initIocCore();
// 自动注入
doAutowired();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
到此简单的ioc的初始化就完成了。
1.3.3 AOP
1.3.3.1 代理工厂(ProxyFactory.java)
定义一个代理工厂用来获取代理对象,提供两种动态代理的实现方式
package com.xichuangyue.aop.factory;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* 获取代理对象的工厂
* @author 画诗笔墨
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2021/7/17 22:50
*/
public class ProxyFactory {
public Object getJDKProxyInstance(Object target){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(Object.class.getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try{
// 前置处理
result = method.invoke(target, args);
// 后置处理
}catch (Exception exp){// 异常处理
throw e;}finally {
// 终了处理
}
return result;
}
});
}
public Object getCglibProxyInstance(Object obj) {
return Enhancer.create(obj.getClass(), new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try{
// 前置
result = method.invoke(obj,objects);
// 后置
}catch (Exception e) {
// 异常
throw e;
}finally {
// 终了处理
}
return result;
}
});
}
}
1.3.3.2 事务处理
下面以事务处理为例来实现AOP。首先得明白事务是谁的事务?为什么要进行事务处理?
事务是谁的事务: 回想一下jdbc对数据库的操作流程,先通过配置获取一个连接对象,然后通过这个连接对象执行db操作,很明显的,事务是连接对象的事务。
为什么要进行事务处理: 有一个很经典的案例----转账,A有100块,B有100块,A转给B 10块,正常情况下B现在有110,A剩余90,如果没有事务假设A转出后B还没收到的时候程序发生了异常,这时的结果就是A剩余90,B还是100,10块钱消失了,事务的开启就是为了保证数据的原子性,如下。
accountDao.updateAccountByCardNo(a);
int c = 1/0;
accountDao.updateAccountByCardNo(b);
现在还有一个问题,我们获取连接对象的时候,一般都是从连接池中获取的,那么想上面这个转账的处理,就会可能从数据库中获取两次连接对象,所以为了事务能够正常处理我们必须保证这两次操作用的是同一个连接对象。
将当前线程和连接对象绑定,如果线程中没有连接对象从连接池获取,如果已经有了,就直接从线程中获取。
package com.xichuangyue.utils;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
* @author 画诗笔墨
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2021/7/17 23:19
*/
public class ConnectionUtils {
private static ThreadLocal<Connection> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Connection>();
/**
* 从当前线程中获取链接对象
* @return
* @throws SQLException
*/
public static Connection getCurrentConnection() {
Connection connection = threadLocal.get();
try{
// 当前线程不存在连接对象时,为线程绑定对象
if (connection == null){
threadLocal.set(DruidUtils.getConnection());
}
}catch (SQLException exp){
exp.printStackTrace();
}
return connection;
}
}
事务的管理
package com.xichuangyue.aop.transaction;
import com.xichuangyue.annotation.Autowired;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.SQLException;
/**
*事务管理
* @author 画诗笔墨
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2021/7/17 22:41
*/
public class TransactionManager {
@Autowired
private Connection connection;
public TransactionManager() throws SQLException {
}
// 开启事务
public void beginTransaction() throws SQLException {
connection.setAutoCommit(false);}
// 提交事务public void commit() throws SQLException {
connection.commit();
}
// 回滚事务public void rollback() throws SQLException {
connection.rollback();
}
// 关闭连接
public void close() throws SQLException {
connection.close();
}
}
然后将事务处理添加到代理工厂中
package com.xichuangyue.aop.factory;
import com.xichuangyue.annotation.Autowired;
import com.xichuangyue.annotation.Transactional;
import com.xichuangyue.aop.transaction.TransactionManager;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
/**
* 获取代理对象的工厂
* @author 画诗笔墨
* @version 1.0.0
* @date 2021/7/17 22:50
*/
public class ProxyFactory {
@Autowired
private TransactionManager transactionManager;
public Object getJDKProxyInstance(Object target){
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(Object.class.getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(),
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try{
// 前置处理
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Transactional.class)){
transactionManager.beginTransaction();
}
result = method.invoke(target, args);
// 后置处理
transactionManager.commit();
}catch (Exception exp){
// 异常处理
transactionManager.rollback();
throw exp;
}finally {
// 终了处理
}
return result;
}
});
}
public Object getCglibProxyInstance(Object obj) {
return Enhancer.create(obj.getClass(), new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object result = null;
try{
// 开启事务(关闭事务的自动提交)
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(Transactional.class)){
transactionManager.beginTransaction();
result = method.invoke(obj,objects);
}
// 提交事务
transactionManager.commit();
}catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// 回滚事务
transactionManager.rollback();
throw e;
}finally {
// 终了处理
}
return result;
}
});
}
}
嗯嗯~~~基本上就这样~~






