关于Redis
Redis是一个基于内存的高性能key-value型数据库,读写性能优异。
如果我们将需要查询的数据存储在Redis缓存中,用来代替关系型数据库的查询访问,性能可以得到大幅提高。
Redis能够支持多种数据类型,包括字符串、散列、列表(链表)、集合、有序集合、基数和地理位置等。
SpringBoot整合Redis
要在SpringBoot中整合Redis,需要先加入关于Redis的依赖。SpringBoot也会为其提供starter,允许我们通过application.properties对其进行配置,能够便捷的对Redis进行配置和使用。
<!--添加Redis依赖--><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId><!--不依赖Redis的异步客户端--><exclusions><exclusion><groupId>io.lettuce</groupId><artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId></exclusion></exclusions></dependency><!--添加Redis客户端驱动Jedis--><dependency><groupId>redis.clients</groupId><artifactId>jedis</artifactId></dependency>
在引入了SpringBoot对Redis的Starter后,在默认情况下,spring-boot-starter-data-redis(2.x)会依赖Lettuce的Redis客户端驱动,在项目中,我们会使用Jedis对Redis进行操作,所以在引入依赖后使用<exclusions>元素对Lettuce依赖进行排除,与此同时引入Jedis依赖。
关于spring-data-redis
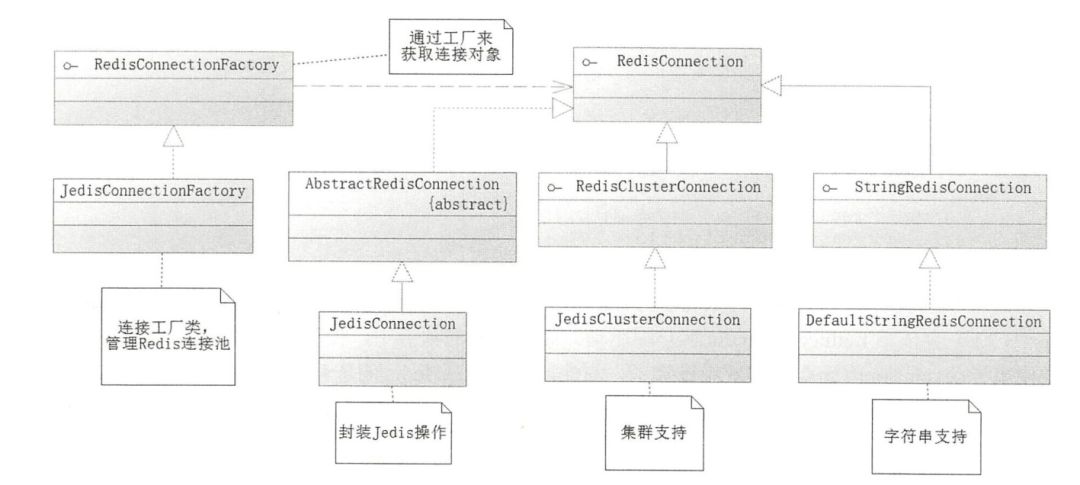
Spring提供了一个RedisConnectionFactory接口,通过RedisConnectionFactory可以生成一个RedisConnection接口对象,RedisConnection接口对象是对Redis底层操作接口的封装。
RedisConnectionFactory
public interface RedisConnectionFactory extends PersistenceExceptionTranslator {//获取连接RedisConnection getConnection();//获取集群连接RedisClusterConnection getClusterConnection();//是否将结果转换为预期的数据类型boolean getConvertPipelineAndTxResults();//与Redis Sentinel交互提供合适的连接RedisSentinelConnection getSentinelConnection();}
要获取RedisConnection接口,需要通过RedisConnectionFactory接口生成,并配置连接池相关属性。
package com.springboot.demo.redis;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisStandaloneConfiguration;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisClientConfiguration;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory;import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;@Configurationpublic class RedisConfig {private RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory=null;/*** 初始化连接* @return connectionFactory*/public RedisConnectionFactory initRedisConnectionFactory(){//不为空返回当前RedisConnectionFactoryif(this.connectionFactory!=null){return connectionFactory;}//初始化Jedis连接池配置JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig=new JedisPoolConfig();//最大空闲数jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(10);//最大连接数jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(30);//最大等待数(毫秒)jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(1000);//初始化Redis单机版配置RedisStandaloneConfiguration rsConfig=new RedisStandaloneConfiguration();//设置主机名或iprsConfig.setHostName("127.0.0.1");//设置端口rsConfig.setPort(6379);//设置密码//rsConfig.setPassword("");//获得Jedis连接池构造器JedisClientConfiguration.JedisPoolingClientConfigurationBuilder jpcb= (JedisClientConfiguration.JedisPoolingClientConfigurationBuilder) JedisClientConfiguration.builder();//设置Jedis连接池配置jpcb.poolConfig(jedisPoolConfig);//通过Jedis连接池构造器创建客户端配置JedisClientConfiguration jedisClientConf=jpcb.build();//通过单机模式+客户端配置初始化Jedis连接工厂JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory=new JedisConnectionFactory(rsConfig,jedisClientConf);connectionFactory=jedisConnectionFactory;return connectionFactory;}}
为了简化Redis操作,Spring提供了RedisTemplate。
RedisTemplate
RedisTemplate会自动从RedisConnectionFactory获取Redis连接,执行对应的Redis操作后关闭Redis连接。这些在RedisTemplate中进行了封装。
/*** 初始化RedisTemplate* @return RedisTemplate*/public RedisTemplate<Object,Object> initRedisTemplate(){RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate=new RedisTemplate<>();return redisTemplate;}
Redis是基于字符串存储的NoSQL,Java是基于对象的语言,操作的Java对象无法直接存储在Redis中。Java提供了序列化机制,只要实现了java.io.Serializable序列化接口,可以对类对象进行序列化操作。通过将类对象序列化既可以得到二进制字符串(Redis可以进行存储),通过对字符串进行反序列化就可以得到Java对象。
在Spring中提供了Redis序列化接口RedisSerializer,可以通过该接口的serialize将对象序列化为二进制字符串,也可以通过deserialize将二进制字符串反序列化为对象。
public interface RedisSerializer<T> {//序列化对象转换为二进制字符串@Nullablebyte[] serialize(@Nullable T var1) throws SerializationException;//二进制字符串反序列化化为对象@NullableT deserialize(@Nullable byte[] var1) throws SerializationException;//默认序列化转化器static RedisSerializer<Object> java() {return java((ClassLoader)null);}//Jdk与Redis序列化转换器static RedisSerializer<Object> java(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {return new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(classLoader);}//Json与Redis序列化转换器,API过时static RedisSerializer<Object> json() {return new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer();}//字符串与Redis序列化转换器static RedisSerializer<String> string() {return StringRedisSerializer.UTF_8;}}
RedisTemplate序列化器属性
| 属性 | 作用 | 备注 |
defaultSerializer | 默认序列化器 | 未设置则使用JdkSerializationRedisSerializer |
keySerializer | 键序列化器 | 未设置使用默认序列化器 |
valueSerializer | 值序列化器 | 未设置使用默认序列化器 |
hashKeySerializer | 散列结构field序列化器 | 未设置使用默认序列化器 |
hashValueSerializer | 散列结构value序列化器 | 未设置使用默认序列化器 |
stringSerializer | 字符串序列化器 | RedisTemplate自动赋值为StringRedisSerializer |
/*** 初始化RedisTemplate* @return RedisTemplate*/public RedisTemplate<Object,Object> initRedisTemplate(){RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate=new RedisTemplate<>();//获取RedisTemplate序列化器RedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer=redisTemplate.getStringSerializer();//设置key序列化器redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);//设置HashKey序列化器redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);//设置HashValue序列化器redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(stringRedisSerializer);//设置RedisTemplate连接工厂redisTemplate.setConnectionFactory(initRedisConnectionFactory());return redisTemplate;}
在使用RedisTemplate操作缓存数据时,每次都从连接工厂获取连接,执行对应Redis命令进行操作后关闭连接,存在资源浪费的问题。我们更希望在同一个连接执行所有Redis命令进行操作。为了解决这个问题,Spring为我们提供了RedisCallBack和SessionCallBack两个接口。
/*** 使用RedisCallBack* 需要处理底层转换规则,不考虑改写底层规则,不建议使用* @param redisTemplate*/public void useRedisCallback(RedisTemplate redisTemplate){redisTemplate.execute(new RedisCallback() {@Nullable@Overridepublic Object doInRedis(RedisConnection redisConnection) throws DataAccessException {redisConnection.set("key1".getBytes(),"value1".getBytes());redisConnection.hSet("hash".getBytes(),"field".getBytes(),"hvalue".getBytes());return null;}});}/*** 使用SessionCallBack* 高级接口,优先使用* @param redisTemplate*/public void useSessionCallback(RedisTemplate redisTemplate){redisTemplate.execute(new SessionCallback() {@Nullable@Overridepublic Object execute(RedisOperations redisOperations) throws DataAccessException {redisOperations.opsForValue().set("key1","value1");redisOperations.opsForHash().put("hash","field","hvalue");return null;}});}
Spring对Redis数据类型操作封装
Redis支持7种类型数据结构:字符串、散列、列表(链表)、集合、有序集合、基数、地理位置。Spring针对每一种数据结构的操作都提供了对应的操作接口。
| 操作接口 | 作用 | 备注 |
GeoOperations | 地理位置操作接口 | 不常使用 |
HashOperations | 散列操作接口 | |
HyperLogLogOperations | 基数操作接口 | 不常使用 |
ListOperations | 列表(链表)操作接口 | |
SetOperations | 集合操作接口 | |
ValueOperations | 字符串操作接口 | |
ZSetOperations | 有序集合操作接口 |
获取Redis数据类型操作接口
| 操作方法 | 作用 |
redisTemplate.opsForGeo(); | 获取地理位置操作接口 |
| redisTemplate.opsForHash(); | 获取散列操作接口 |
| redisTemplate.opsForHyperLogLog(); | 获取基数操作接口 |
| redisTemplate.opsForList() | 获取列表操作接口 |
| redisTemplate.opsForSet() | 获取集合操作接口 |
| redisTemplate.opsForValue() | 获取字符串操作接口 |
| redisTemplate.opsForZSet() | 获取有序集合操作接口 |
这样我们就可以通过redisTemplate提供的各种操作接口来对不同数据类型执行操作,需要我们熟悉Redis各种命令。有时候我们需要对一个键值对做连续操作,Spring也提供了支持,提供了如下接口:
| 接口 | 说明 |
BoundGeoOperations | 绑定一个地理位置数据类型键操作 |
BoundHashOperations | 绑定一个散列数据类型的键操作 |
BoundListOperations | 绑定一个列表(链表)数据类型的键操作 |
BoundSetOperations | 绑定一个集合数据类型的键操作 |
BoundValueOperations | 绑定一个字符串集合数据类型的键操作 |
BoundZSetOperations | 绑定一个有序集合数据类型的键操作 |
在SpringBoot中配置和使用Redis
在SpringBoot中使用Redis更为简便。在application.properties中添加如下配置信息。
#配置Redis相关内容#配置连接池属性spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=5spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=10spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=10spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=2000#配置Redis服务器属性spring.redis.port=6379spring.redis.host=localhostspring.redis.timeout=1000
功能测试
package com.springboot.demo.redis;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.SortParameters;import org.springframework.data.redis.core.*;import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;import java.awt.font.NumericShaper;import java.util.*;public class RedisOperate {@Autowiredprivate RedisTemplate redisTemplate;@Autowiredprivate StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate;/*** 定义自定义后初始化方法*/@PostConstructpublic void init(){setRedisTemplateSerializer();}/*** 设置RedisTemplate序列化器* @return RedisTemplate*/public RedisTemplate<Object,Object> setRedisTemplateSerializer(){//获取RedisTemplate序列化器RedisSerializer stringRedisSerializer=redisTemplate.getStringSerializer();//设置key序列化器redisTemplate.setKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);//设置HashKey序列化器redisTemplate.setHashKeySerializer(stringRedisSerializer);//设置HashValue序列化器redisTemplate.setHashValueSerializer(stringRedisSerializer);return redisTemplate;}/*** 操作字符串类型* @param key* @param value*/public void operateString(String key,String value){redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("redisKey","redisValue");}/*** 对字符串类型数值执行运算* @param key* @param value*/public void operateStringByValue(String key,String value){//设置初始化数值stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().set("intOperate","2");stringRedisTemplate.opsForValue().increment("intOperate",1);//获取Jedis连接Jedis jedis=(Jedis)stringRedisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection().getNativeConnection();jedis.decr("intOperate");}/*** 操作散列* @param hashKey:散列键* @param hashValue:散列值*/public void operateHash(String hashKey,Map<String,String> hashValue){//添加测试数据hashValue.put("field1","value1");hashValue.put("field2","value2");//将Map中的所有值填入散列数据类型stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(hashKey,hashValue);//散列数据新增一个字段stringRedisTemplate.opsForHash().put(hashKey,"field3","value3");//绑定散列操作的Key,对同一个散列数据类型进行操作BoundHashOperations hashOperations=stringRedisTemplate.boundHashOps(hashKey);//删除field1和field2hashOperations.delete("field1","field2");hashOperations.put("field4","value4");}/*** 操作链表(列表)*/public void operateList(){//从左至右插入链表stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushAll("leftToRightList","leftValue1","leftValue2","leftValue3");//从右至左插入链表stringRedisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll("rightToLeftList","rightValue1","rightValue2","rightValue3");//绑定从右至左链表操作BoundListOperations listOperations=stringRedisTemplate.boundListOps("rightToLeftList");//右边弹出一个成员Object rightPopResult=listOperations.rightPop();//获取定位元素Object indexValue=listOperations.index(1);//从左边插入新元素值listOperations.leftPush("rightValueNew");//获取链表元素数量long listSize=listOperations.size();//获取链表所有元素List listElement=listOperations.range(0,listSize-1);}/*** 操作集合信息*/public void operateSet(){//添加两个set集合stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("set1","value1","value2","value3","value4","value5","value6");stringRedisTemplate.opsForSet().add("set2","value2","value4","value6","value8","value10");//绑定key为set1的集合BoundSetOperations setOperations=stringRedisTemplate.boundSetOps("set1");//添加元素setOperations.add("value7","value8");//移除元素setOperations.remove("value1","value2");//获取set1所有元素Set set1=setOperations.members();//获取元素数量Long size=setOperations.size();//求set1与set2交集Set inter=setOperations.intersect("set2");//求交集并存入新集合setOperations.intersectAndStore("set2","interSet");//求差集Set diff=setOperations.diff("set2");//求差集并存入新集合setOperations.diffAndStore("set2","diffSet");//求并集Set union=setOperations.union("set2");//求并集并存入新集合setOperations.unionAndStore("set2","unionSet");}/*** 操作有序集合*/public void operateZSet(){//初始化有序集合并添加内容Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> typedTuples=new HashSet<>();for(int i=0;i<=5;i++){double scoreValue=i*10;ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String> typedTuple=new DefaultTypedTuple<>("value"+i,scoreValue);typedTuples.add(typedTuple);}//添加有序集合stringRedisTemplate.opsForZSet().add("zSet1",typedTuples);//获取zSet1操作器BoundZSetOperations<String,String> zSetOperations=stringRedisTemplate.boundZSetOps("zSet1");//添加元素zSetOperations.add("6",60);//获取indexStart和indexEnd区间内的元素Set<String> setIndexRange=zSetOperations.range(1,4);//获取分数在10-40区间的元素Set<String> setRangeByScore=zSetOperations.rangeByScore(10,40);//删除元素zSetOperations.remove("value0");//求分数double scoreValue=zSetOperations.score("value6");//获取下标区间元素内容(同时返回value和score)Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> rangeSets=zSetOperations.rangeWithScores(0,5);//获取下标区间元素内容(同时返回value和score),按分数排序Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<String>> rangeScoreSets=zSetOperations.rangeByScoreWithScores(0,5);//获取下标区间元素内容(同时返回value和score),下标从大到小排序Set<String> reverSet=zSetOperations.reverseRange(1,4);}}






