1 官方文档
DM7 系统管理员
第16章 管理分区表和分区索引
16.3 创建水平分区表
2 范围分区range partition:
2.1 创建范围分区表
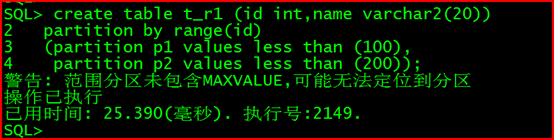
create table t_r1 (id int,name varchar2(20))
partition by range(id)
(partition p1 values less than (100),
partition p2 values less than (200));
2.2 插入150行数据
begin
for i in 1…150 loop
insert into t_r1 values(i,‘a’||i);
end loop;
commit;
end;
/

2.3 查询分区情况
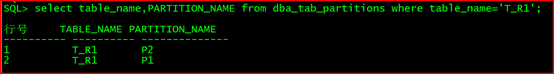
select table_name,PARTITION_NAME from dba_tab_partitions where table_name=‘T_R1’;
行号 TABLE_NAME PARTITION_NAME
1 T_R1 P2
2 T_R1 P1
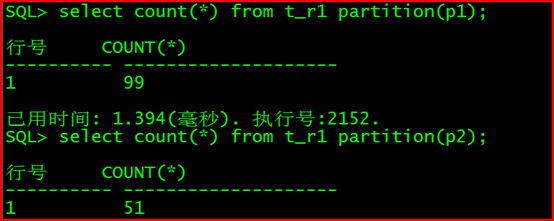
查询分区的数据:
select count() from t_r1 partition(p1);
SQL> select count() from t_r1 partition(p1);
行号 COUNT(*)
1 99
SQL> select count(*) from t_r1 partition(p2);
行号 COUNT(*)
1 51
2.4 增加分区
插入数据:
insert into t_r1 values(500,‘test’);

此时提示报错:没有找到合适的分区
查询分区的最大值:
select table_name,high_value,partition_name from dba_tab_partitions where table_name=‘T_R1’;
行号 TABLE_NAME HIGH_VALUE PARTITION_NAME
1 T_R1 200 P2
2 T_R1 100 P1
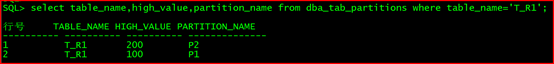
alter table t_r1 add partition p3 values less than (maxvalue);
2.5 分区键问题
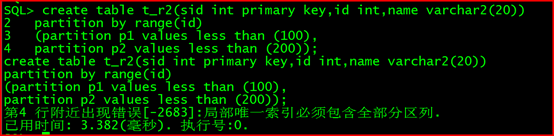
普通表(IOT索引组织表)中有主键,分区键必须为主键
create table t_r2(sid int primary key,id int,name varchar2(20))
partition by range(id)
(partition p1 values less than (100),
partition p2 values less than (200));
此时报错:第4 行附近出现错误[-2683]:局部唯一索引必须包含全部分区列
2.6 指定表空间
SQL> create tablespace tbs01 datafile ‘/dm7/data/DAMENG/tbs01.dbf’ size 100;
SQL> create tablespace tbs02 datafile ‘/dm7/data/DAMENG/tbs02.dbf’ size 100;
SQL> create tablespace tbs03 datafile ‘/dm7/data/DAMENG/tbs03.dbf’ size 100;
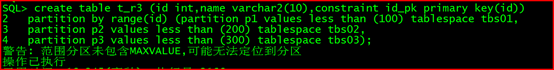
create table t_r3 (id int,name varchar2(10),constraint id_pk primary key(id))
partition by range(id) (partition p1 values less than (100) tablespace tbs01,
partition p2 values less than (200) tablespace tbs02,
partition p3 values less than (300) tablespace tbs03);
2.7 堆表分区
create table t_r4 (id int,name varchar2(10))
partition by range(id)
(partition p1 values less than (100) tablespace tbs01,
partition p2 values less than (200) tablespace tbs02) storage(nobranch);
第4 行附近出现错误[-2757]:水平分区堆表各子表必须位于同一个表空间
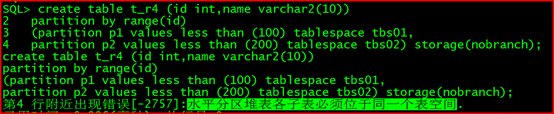
如上提示报错
修正:
create table t_r5(id int,name varchar2(10))
partition by range(id)
(partition p1 values less than (100),
partition p2 values less than (200)) storage(on tbs01,nobranch);
2.8 合并分区
select table_name,high_value,partition_name from dba_tab_partitions where table_name=‘T_R1’;
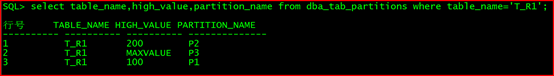
alter table t_r1 merge partitions p2,p1 into partition p2_3;
select table_name,high_value,partition_name from dba_tab_partitions where table_name=‘T_R1’;
行号 TABLE_NAME HIGH_VALUE PARTITION_NAME
1 T_R1 MAXVALUE P3
2 T_R1 200 P2_3
2.9 拆分分区
alter table t_r1 split partition p2_3 at(100) into (partition p02,partition p03);

2.10 删除分区
alter table t_r1 drop partition p3;

2.11 交换分区
SQL> desc t_r1;
行号 NAME TYPE$ NULLABLE
1 ID INTEGER Y
2 NAME VARCHAR(20) Y
SQL> create table test (id int,name varchar2(20));

SQL> alter table t_r1 exchange partition p02 with table test;

验证:
SQL> select * from test limit 10;
行号 ID NAME
1 100 a100
2 1 a1
3 2 a2
4 3 a3
5 4 a4
6 5 a5
7 6 a6
8 7 a7
9 8 a8
10 9 a9

2.12 将非分区表转换为分区表
2.12.1 创建测试表
模拟业务表:
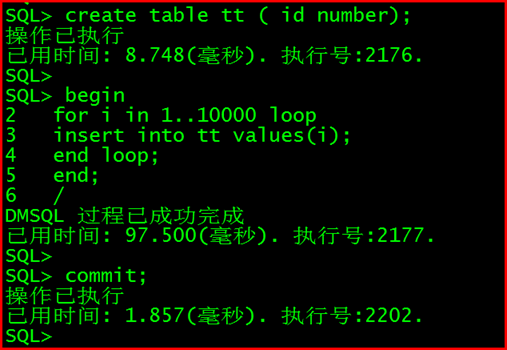
create table tt ( id number);
begin
for i in 1…10000 loop
insert into tt values(i);
end loop;
end;
/
commit;
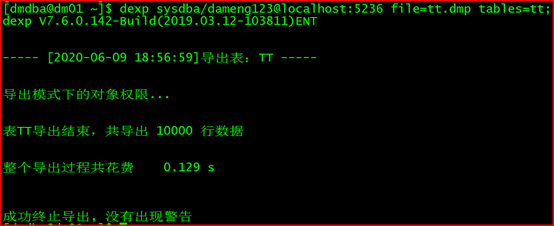
2.12.2 导出tt表的数据:
[dmdba@dm01 ~]$ dexp sysdba/dameng123@localhost:5236 file=tt.dmp tables=tt;
2.12.3 删除表tt;
SQL> drop table tt;
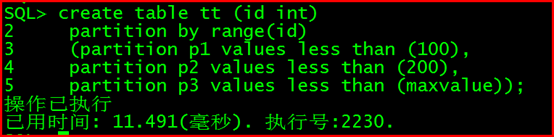
2.12.4 创建分区表:
create table tt (id int)
partition by range(id)
(partition p1 values less than (100),
partition p2 values less than (200),
partition p3 values less than (maxvalue));
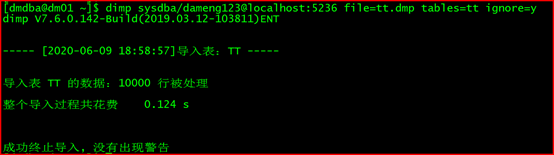
2.12.5 导入:
[dmdba@dm01 ~]$ dimp sysdba/dameng123@localhost:5236 file=tt.dmp tables=tt ignore=y
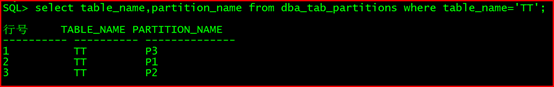
2.12.6 验证结果:
select table_name,partition_name from dba_tab_partitions where table_name=‘TT’;
行号 TABLE_NAME PARTITION_NAME
1 TT P3
2 TT P1
3 TT P2
select count(*) from tt partition(p2);
在导入导出时可以加并行,remap_schema,索引可以不用创建,收集统计信息之后,重新创建。
3 列表list分区
适合字符串类型的。
create table t_l1 (city_id int,city_name varchar(40))
partition by list (city_name)
(partition p1 values(‘华中’),
partition p2 values(‘华东’),
partition p3 values(‘西南’));
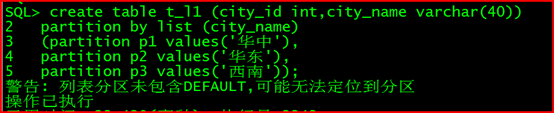
注:支持增加,删除。
添加分区:
alter table t_l1 add partition pn values(default);

4 哈希分区
存数据非常快,取数据慢,数据平均分配到各子分区.
创建:
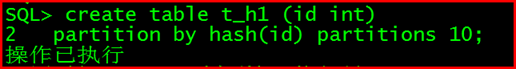
create table t_h1 (id int)
partition by hash(id) partitions 10;
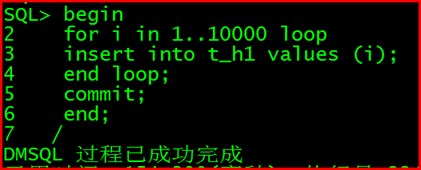
插入数据:
begin
for i in 1…10000 loop
insert into t_h1 values (i);
end loop;
commit;
end;
/
查询数据: select * from t_h1 where id=1;
5 多级分区表(复合分区)
【官方文档】dm8系统管理员手册—>P142
创建多级分区表
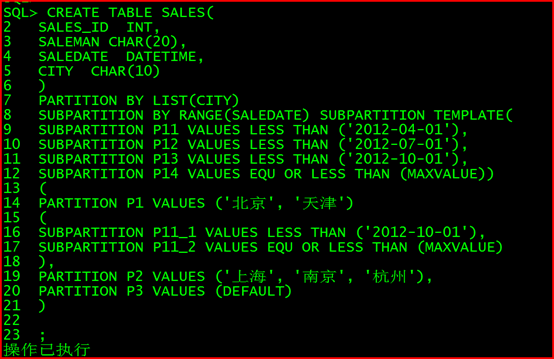
创建一个产品销售记录表 sales,记录产品的销量情况。由于产品需要按地点
和销售时间进行统计,则可以对该表进行 LIST-RANGE 分区.在创建多级分区表时, 指定了子分区模板, 同时子分区 P1 自定义了子分区描述 P11_1和 P11_2。 P1有两个子分区 P11_1和 P11_2。 而子分区 P2和 P3有四个子分区 P11、 P12、P13 和 P14。
CREATE TABLE SALES(
SALES_ID INT,
SALEMAN CHAR(20),
SALEDATE DATETIME,
CITY CHAR(10)
)
PARTITION BY LIST(CITY)
SUBPARTITION BY RANGE(SALEDATE) SUBPARTITION TEMPLATE(
SUBPARTITION P11 VALUES LESS THAN (‘2012-04-01’),
SUBPARTITION P12 VALUES LESS THAN (‘2012-07-01’),
SUBPARTITION P13 VALUES LESS THAN (‘2012-10-01’),
SUBPARTITION P14 VALUES EQU OR LESS THAN (MAXVALUE))
(
PARTITION P1 VALUES (‘北京’, ‘天津’)
(
SUBPARTITION P11_1 VALUES LESS THAN (‘2012-10-01’),
SUBPARTITION P11_2 VALUES EQU OR LESS THAN (MAXVALUE)
),
PARTITION P2 VALUES (‘上海’, ‘南京’, ‘杭州’),
PARTITION P3 VALUES (DEFAULT)
)
6 间隔分区表
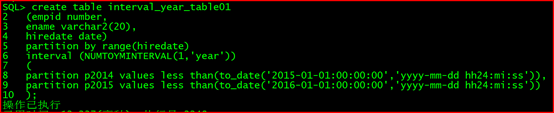
create table interval_year_table01
(empid number,
ename varchar2(20),
hiredate date)
partition by range(hiredate)
interval (NUMTOYMINTERVAL(1,‘year’))
(
partition p2014 values less than(to_date(‘2015-01-01:00:00:00’,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss’)),
partition p2015 values less than(to_date(‘2016-01-01:00:00:00’,‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss’))
);
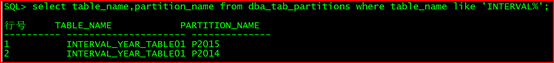
select table_name,partition_name from dba_tab_partitions where table_name like ‘INTERVAL%’;
行号 TABLE_NAME PARTITION_NAME
1 INTERVAL_YEAR_TABLE01 P2015
2 INTERVAL_YEAR_TABLE01 P2014