作为一名DBA,保障数据的安全是最基本的,也是最重要的职责。一旦灾难发生,不管是人为灾难或是自然灾难,备份恢复往往是最后的救命稻草。
通常数据库的备份类型可分为冷备份和热备份。
冷备份主要使用系统命令完成,是基于物理文件的复制,比如命令cp,特点是快速、事务一致,但是前提是需要停服务,适用的场景相对较少。
热备份可以理解为是在线备份,不会中断业务,数据库依然能对外提供服务。我们绝大多数的场景涉及的都是热备份,接下来要细说的备份工具也都是基于热备份的前提。
目前市面上主流的备份工具有:mysqldump,mydumper,mysqlpump和xtrabackup。下图中我们能看到,从各个层面来看,没有一个工具是最优的,选择备份工具时一定要结合自身的场景来选择,绝对不要盲目跟风。
 下面将详细介绍以上4种备份工具。
下面将详细介绍以上4种备份工具。
一、mysqldump
mysqldump 是MySQL的一个命令行工具,用于逻辑备份。可以将数据库和表的结构,以及表中的数据分别导出成:create database, create table, insert into的sql语句。当然也可以导出 存储过程,触发器,函数,调度事件。
mysqldump —help
mysqldump的选项很多,可以给用户提供很多定制化的功能,使用起来十分的灵活,我们可以通过帮助文档来更好的了解这些参数。
mysqldump --help
mysqldump的帮助文档分为两个部分。前一部分是对各种选项的说明,后一部分是mysqldump的各种选项的默认值。
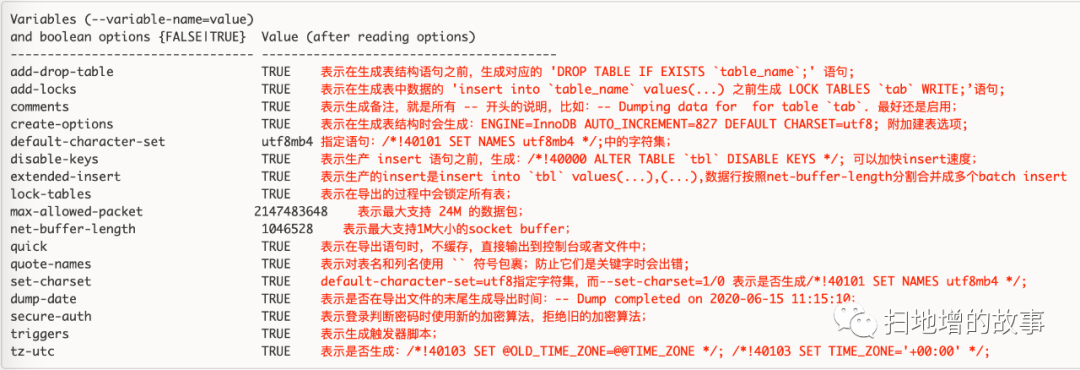
mysqldump默认选项
mysqldump选项的默认值部分是TRUE,部分是FALSE,部分没有默认值。我们主要关心的是默认值为TRUE的选项,看看mysqldump默认给我们打开了哪些选项以及它们的具体含义。
mysqldump登录服务器的相关选项
* Default options are read from the following files in the given order: /etc/my.cnf etc/mysql/my.cnf usr/local/mysql/etc/my.cnf ~/.my.cnf The following groups are read: mysqldump client The following options may be given as the first argument: --no-defaults Don't read default options from any option file, except for login file. --defaults-file=# Only read default options from the given file #. --defaults-extra-file=# Read this file after the global files are read. --defaults-group-suffix=# Also read groups with concat(group, suffix) --login-path=# Read this path from the login file. */ |
mysqldump 作为一个客户端工具,它会去上诉目录中寻找 my.cnf 文件,然后读取该文件中 [mysqldump] 和 [client] 下面的选项;
那些 defaults 相关的选项都是为了另外指定配置文件和登录文件,极少使用;
-u, --user=name User for login if not current user.-p, --password[=name] Password to use when connecting to server. If password is not given it's solicited on the tty.-h, --host=name Connect to host.-P, --port=# Port number to use for connection.--protocol=name The protocol to use for connection (tcp, socket, pipe, memory).--max-allowed-packet=# The maximum packet length to send to or receive from server. —》一般配置在my.cnf--net-buffer-length=# The buffer size for TCP/IP and socket communication. —》为了优化网络连接的socket buffer
使用示例:
mysqldump -h192.168.1.29 -uxxx -p -P3306
mysql选择备份内容的相关选项
我们可以选择备份所有数据库,某几个数据库,某一个数据库,某一个数据库中的某几个表,某一个数据库中的一个表,也可以选择是否备份 存储过程和函数,触发器,调度事件.
1.选择导出的数据库 和 表:
-A, --all-databases Dump all the databases. This will be same as --databases with all databases selected.-B, --databases Dump several databases. Note the difference in usage; in this case no tables are given. All name arguments areregarded as database names. 'USE db_name;' will be included in the output.database [tables] 导出数据库 database 中的表结构 和 表中数据;
2.选择是否导出 建库,建表语句,是否导出 表中的数据:
-n, --no-create-db Suppress the CREATE DATABASE ... IF NOT EXISTS statement that normally is output for each dumped database if --all-databases or --databases is given. (不导出建库语句: CREATE DATABASE,也就是不导库结构)-t, --no-create-info Don't write table creation info. (不导出建表语句)-d, --no-data No row information. (不导出数据,有时我们仅仅需要导出表结构,也就是建表语句就行了)
3.选择是否导出 存储过程和函数,触发器,调度事件:
-R, --routines Dump stored routines (functions and procedures). (导出存储过程和函数)--triggers Dump triggers for each dumped table. (Defaults to on; use --skip-triggers to disable.) (导出触发器)--skip-triggers 不导出触发器-E, --events Dump events. 导出调度事件(根据备份的目的进行选择,如果是搭建slave,那么就不要导出events.)
4.指定不导出 某个库的某个表:
--ignore-table=name Do not dump the specified table. To specify more than one table to ignore, use the directive multiple times,once for each table. Each table must be specified with both database and table names,e.g., --ignore-table=database.table. (在导出数据库时,排除某个或者某几个表不导出)
5.按照 where 条件导出:
-w, --where='where_condition' Dump only selected records. Quotes are mandatory.
6.使用示例:
Dumping structure and contents of MySQL databases and tables.Usage: mysqldump [OPTIONS] database [tables]OR mysqldump [OPTIONS] --databases [OPTIONS] DB1 [DB2 DB3...]OR mysqldump [OPTIONS] --all-databases [OPTIONS]1. 导出单表的结构和数据:mysqldump -uxxx -p db1 tb1 > tb1.sql; 导出数据库 db1 中的 表 tb1 的表结构 和 表中数据;2. 导出多表的结构和数据:mysqldump -uxxx -p db1 tb1 tb2 > tb1_tb2.sql; 导出数据库 db1 中的 表 tb1、tb2 的表结构 和 表中数据;3. 导出单表的结构:mysqldump -uxxx -p --no-data db1 tb1 > tb1.sql; 导出数据库 db1 中的 表 tb1 的表结构; 其实也可以使用: show create table tb14. 我们无法使用 mysqldump 到达 只导出某个或某几个表的数据,而不导出建表语句的目的。但是我们可以使用 select * from table into outfile 'file.sql', 比如:select * from Users into outfile '/tmp/Users.sql'; 注意需要对目录的写权限。5. 导出单个库中库结构、表结构、表数据:mysqldump -uxxx -p --databases db1 > db1.sql6. 导出多个库中库结构、表结构、表数据:mysqldump -uxxx -p --databases db1 db2 > db1_db2.sql7. 导出单个库中库结构、表结构、不要表数据:mysqldump -uxxx -p --no-data --databases db1 > db1.sql8. 导出单个库中数据,不要库结构和表结构:mysqldump -uxxx -p --no-create-db --no-create-info --databases db1 > db1.sql9. 导出多个库中库结构、表结构、不要表数据:mysqldump -uxxx -p --no-data --databases db1 db2 > db1_db2.sql10.导出数据库中所有 库 的库结构,表结构,数据:mysqldump -uxxx -p --all-databases > all.sql11.导出数据库中所有 库 的库结构,表结构,不要数据:mysqldump -uxxx -p --all-databases --no-data > all.sql12.导出单个库中库结构、表结构、表数据,排除某个表:mysqldump -uxxx -p --databases db1 --ignore-table=db1.test > db1.sql
mysqldump事务和数据一致性的相关选项
在使用mysqldump逻辑备份时,事务和数据一致性的选项时至关重要的。
1) --single-transaction
在备份时,不加任何参数,默认是启用--lock-all-tables选项,在备份过程中会全程锁表。
所以在备份时要开启single-transaction选项,保证在一个事务中所有相同的查询获得同样的数据,只在dump开始时短暂获取global read lock。
注意:只能是 innodb 引擎;导出的过程中,不能有任何人执行 alter table, drop table, rename table, truncate table等DDL语句。实际上DDL会被事务所阻塞,因为事务持有表的metadata lock 的共享锁,而DDL会申请metadata lock的互斥锁,所以阻塞了。
mysqldump默认会打开了--lock-tables,它会在导出过程中锁定所有表。--single-transaction 会自动关闭 --lock-tables 选项,所以单独使用--single-transaction是不会使用锁的。与 --master-data 合用才会生成锁。
2)--lock-tables
该选项默认打开的,它的作用是在导出过程中锁定所有表。--single-transaction 和 --lock-all-tables 都会将该选项关闭。
3)--lock-all-tables
表示在备份期间,锁定所有数据库中的所有表,以保证数据的一致性,这是一个全局读锁,并且自动关闭--sinle-transaction和--lock-tables选项,生产环境,慎用此选项。
4)--flush-logs
为了获得导出数据和刷新日志的一致性(同时发生),必须将 --flush-logs 选项和 --lock-all-tables 或者 --master-data 一起使用:
mysqldump --flush-logs --lock-all-tables; mysqldump --flush-logs --master-data=2 ;
5)--flush-privileges
如果导出包含了mysql数据,就应该启用该选项。该选项会在导出的 mysql 数据库的后面加上 flush privileges 语句,因为在向mysql数据库insert语句之后,必须使用 flush privileges,不然权限不生效。
6) --master-data[=#]
/* This causes the binary log position and filename to be appended to the output. If equal to 1, will print it as a CHANGE MASTER command; if equal to 2, that command will be prefixed with a comment symbol. This option will turn --lock-all-tables on, unless--single-transaction is specified too (in which case a global read lock is only taken a short time at the beginning of the dump; don’t forget to read about --single-transaction below). In all cases, any action on logs will happen at the exact moment of the dump.Option automatically turns --lock-tables off. */ |
在备份时,如果要生成整个备份文件的检查点,可以使用master-data选项,在做主从复制时这个参数极为重要。有两种选项:master-data=1和master-data=2,它们的差异就是,master-data=1表示执行,master-data=2表示不执行。
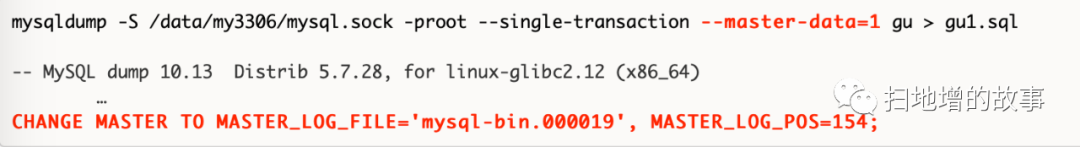

执行mysqldump -uroot -pxxxxxx --single-transaction --master-data=2 -A > db3306.sql 时general log日志输出信息:
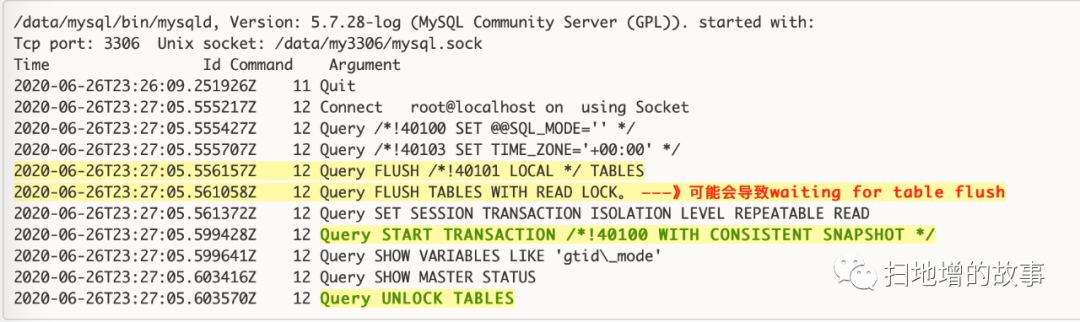
注意:使用 --master-data 会打开 --lock-all-tables 选项,从general log的输出日志看,mysql会将脏数据刷到磁盘,并且加一个全局读锁。从日志输出信息来看,执行了两次flush tables,其目的是:为了避免较长的事务操作造成FLUSH TABLES WITH READ LOCKS操作迟迟得不到锁,但同时又阻塞了其他客户端操作。第一次的flush也是为了尽量减少第二次flush持有锁的时间。
使用--single-transaction ,会开启一个事务一致性快照,并对所有表执行一次select操作,以保证备份时,任意时间点执行select * from table 得到的数据与START TRANSACTION *!40100 WITH CONSISTENT SNAPSHOT */时的数据一致,随后释放锁。
flush 的二进制日志也是在同一个时间点的,不是每一个数据库flush一次的。并且这个时间点 和 --master-data 记录的 binary log position 和 binary log file是同一个时间点,这些都是利用了 --single-transaction 和 --master-data 合用时短暂的使用一个全局的读锁来达到目的的。
mysqldump复制相关的选项
1)--master-data[=#]
在备份时,如果要生成整个备份文件的检查点,可以使用master-data选项。一般会和 --single-transaction一起使用,用于搭建master-slave环境。
2)--dump-slave[=#]
/* This causes the binary log position and filename of the master to be appended to the dumped data output. Setting the value to 1, will print it as a CHANGE MASTER command in the dumped data output; if equal to 2, that command will be prefixed with a comment symbol. This option will turn --lock-all-tables on, unless --single-transaction is specified too (in which case a global read lock is only taken a short time at the beginning of the dump - don't forget to read about --single-transaction below). In all cases any action on logs will happen at the exact moment of the dump.Option automatically turns --lock-tables off. */ |
--dump-slave 和 --master-data 几乎一样。
区别只是--dump-slave用于slave建立下一级的slave;而 --master-data用于master建立slave;
如果在 master 上使用 --dump-slave 会报错:mysqldump: Couldn't execute 'START SLAVE': The server is not configured as slave;
3) --apply-slave-statements
在 change master 之前导出 stop slave 语句, 在 change master 之后导出 start slave语句。其实是一个自动化的处理。和 --master-data=1 类似。
4)--include-master-host-port
该选择要结合 --dump-slave=1/2 使用。会在导出中加入 host。
5)--delete-master-logs
在备份之后,删除 master上的binary log。该选项会自动打开 --master-data 选项(等于2)。该选项一般不用。日志一般不能随便删除。
6)--set-gtid-purged[=name]
该选项用于启用了GTID特性的环境。
mysqldump 字符集 的相关选项
1)--set-charset
--set-charset=1/0 开启和关闭。也可以使用 --skip-set-charset 关闭。该选项我们上面已经说到了。表示是否生成 /*!40101 SET NAMES utf8 */;
2)-N, --no-set-names
不生成 /*!40101 SET NAMES utf8 */; 语句。
3)--default-character-set=name
指定语句:/*!40101 SET NAMES utf8mb4 */;中的字符集;
mysqldump 控制是否生成 DDL 语句 的相关选项
1)--add-drop-database在导入数据时,如果数据库存在,通常有两种策略,一种是使用drop database if exists选项,另一种是直接忽略该操作。2)--add-drop-tableAdd a DROP TABLE before each create. (Defaults to on; use --skip-add-drop-table to disable.)3) --add-drop-triggerAdd a DROP TRIGGER before each create.4)--no-create-db,-n5)--no-create-info,-t
mysqldump 导出格式的相关选项
1)--compatible=name
导出sql语句的兼容格式。如果我们需要从MySQL导出,然后导入到其它数据库,则可使用该选项。--compatible=oracle/postgresql/mssql
2)-Q, --quote-names
将表名和列名使用 ``包裹。以防他们是关键字时报错。
mysqldump 错误处理的相关选项
1)-f, --force
Continue even if we get an SQL error.
2)--log-error=name
Append warnings and errors to given file.
。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。。
累了,写不动了,其他的留着明天再写吧~






