在NLP任务中数据扩增方法是非常重要的,其中常见的方法包括:
EDA 回译 对抗训练
其中EDA(Easy Data Augmentation)
是最为简单的操作,对文本进行同义词替换、词语交换、随机插入和随机删除操作构成。
在今年EMNLP2021也有一篇类似文本数据扩增的论文AEDA(Easier Data Augmentation)
,思路也非常简单,通过对文本随机插入标点符号来完成数据扩增。
AEDA
AEDA: An Easier Data Augmentation Technique for Text Classification
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2108.13230.pdf
代码开源:https://github.com/akkarimi/aeda_nlp
AEDA的思路:对文本随机插入标点符号,插入标点符号个数是1/3句子长度。插入的标签符号为:
['.', ',', '!', '?', ';', ':']
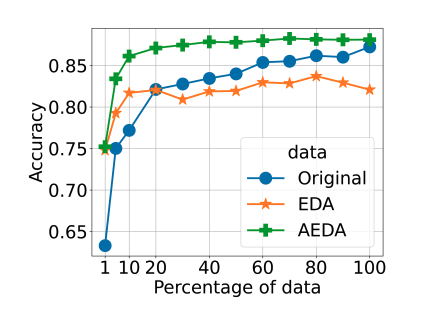
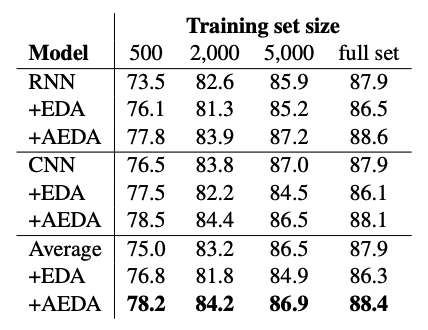
需注意的是,AEDA
只适用于文本分类任务,在其他任务中不适用。与EDA
方法相比,AEDA
会增加模型精度上和收敛速度。
AEDA
的具体实现代码:
import random
random.seed(0)
PUNCTUATIONS = ['.', ',', '!', '?', ';', ':']
DATASETS = ['cr', 'sst2', 'subj', 'pc', 'trec']
NUM_AUGS = [1, 2, 4, 8]
PUNC_RATIO = 0.3
# Insert punction words into a given sentence with the given ratio "punc_ratio"
def insert_punctuation_marks(sentence, punc_ratio=PUNC_RATIO):
words = sentence.split(' ')
new_line = []
q = random.randint(1, int(punc_ratio * len(words) + 1))
qs = random.sample(range(0, len(words)), q)
for j, word in enumerate(words):
if j in qs:
new_line.append(PUNCTUATIONS[random.randint(0, len(PUNCTUATIONS)-1)])
new_line.append(word)
else:
new_line.append(word)
new_line = ' '.join(new_line)
return new_line
AEDA
的想法非常简单,但从实验的角度来看比较有效,建议在文本分类竞赛中加入此类操作


文章转载自Coggle数据科学,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






