oracle 分区表维护导致本地分区索引失效情况
在平常的工作中,我们可能由于业务原因,对分区表进行维护。在官方文档:Database VLDB and Partitioning Guide 一书中,对于分区表,我们可以进行如下维护:

file:///E:/%E5%B7%A5%E4%BD%9C/enmo/oracle/E66230_01/VLDBG/maintenance-partition-tables-indexes.htm#VLDBG1118
file:///E:/%E5%B7%A5%E4%BD%9C/enmo/oracle/E11882_01/server.112/e25523/part_admin002.htm#i1008028
面对如此多的场景,我们挑几个进行说明,merge,split,truncate,drop,add这几种操作。看对上面的索引有何影响。
测试环境准备
环境信息:
单机oracle 11.2.0.4.0
os版本:RHEL 6.8.
关于本地和全局索引的区别,参考:http://blog.itpub.net/31397003/viewspace-2147926/
我们拿range分区来测试:
drop table t_partition_range;
create table t_partition_range (id number,name varchar2(50))
partition by range(id)(
partition t_range_p1 values less than (10),
partition t_range_p2 values less than (20),
partition t_range_p3 values less than (30),
partition t_range_pmax values less than (maxvalue)
);
select table_name,partitioning_type,partition_count
From user_part_tables
where table_name=‘T_PARTITION_RANGE’;
select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name
from user_tab_partitions
where table_name=‘T_PARTITION_RANGE’
order by partition_position;
create index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID on T_PARTITION_RANGE(id) local;
select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
From user_part_indexes
where index_name = ‘IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID’;
select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
where index_name=‘IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID’;
insert into t_partition_range values(4,‘ddd’);
insert into t_partition_range values(13,‘asdewr’);
insert into t_partition_range values(22,‘dasd’);
insert into t_partition_range values(34,‘aasd’);
commit;
select id,name,rowid from t_partition_range;
SQL> create table t_partition_range (id number,name varchar2(50))
2 partition by range(id)(
3 partition t_range_p1 values less than (10),
4 partition t_range_p2 values less than (20),
5 partition t_range_p3 values less than (30),
6 partition t_range_pmax values less than (maxvalue)
7 );
Table created.
SQL> select table_name,partitioning_type,partition_count
2 From user_part_tables
3 where table_name='T_PARTITION_RANGE';
TABLE_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT
------------------------------ --------- ---------------
T_PARTITION_RANGE RANGE 4
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name
2 from user_tab_partitions
3 where table_name='T_PARTITION_RANGE'
4 order by partition_position;
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME
------------------------------ -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS
T_RANGE_P2 20 USERS
T_RANGE_P3 30 USERS
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS
SQL> create index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID on T_PARTITION_RANGE(id) local;
Index created.
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 4 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
SQL> col HIGH_VALUE for a15
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ --------------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P2 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 30 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
SQL> insert into t_partition_range values(4,'ddd');
insert into t_partition_range values(13,'asdewr');
1 row created.
SQL>
1 row created.
SQL> insert into t_partition_range values(22,'dasd');
insert into t_partition_range values(34,'aasd');
1 row created.
SQL>
1 row created.
SQL> commit;
Commit complete.
SQL> select id,name,rowid from t_partition_range;
ID NAME ROWID
---------- -------------------------------------------------- ------------------
4 ddd AAATwMAAEAAABIwAAA
13 asdewr AAATwNAAEAAABYwAAA
22 dasd AAATwOAAEAAAAEwAAA
34 aasd AAATwPAAEAAAAUwAAA
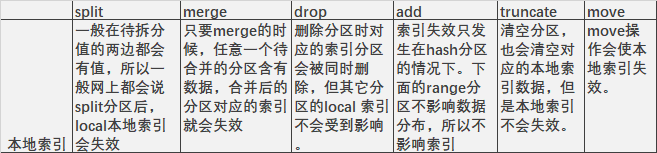
split拆分分区
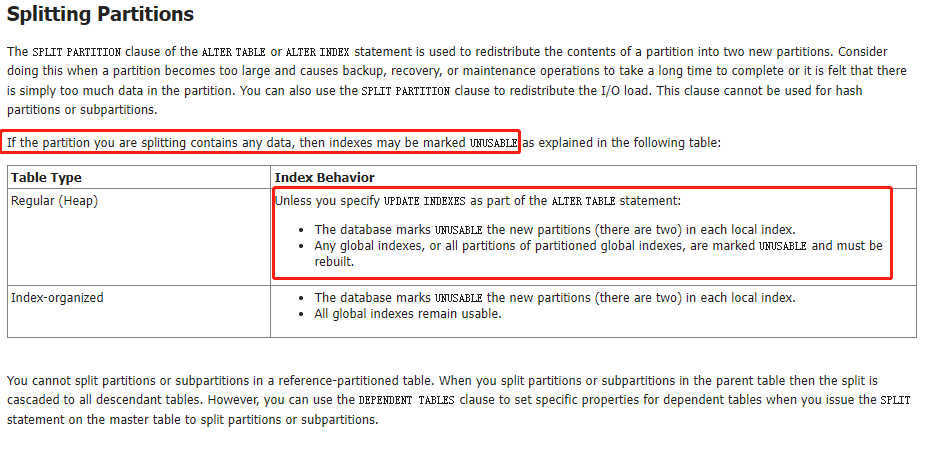
官方文档说的是,只要你要split的分区中包含数据,那么本地还是全局索引都会失效。
但是说的不够详细,测试如下:
本地索引:
第一种情况
SQL> alter table t_partition_range split partition t_range_p3 at (25) into
2 (partition t_range_p3,
3 partition t_range_p4);
Table altered.
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 5 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL>
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P2 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 25 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P4 30 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
SQL> select id,name,rowid from t_partition_range;
ID NAME ROWID
---------- -------------------------------------------------- ------------------
4 ddd AAATwMAAEAAABIwAAA
13 asdewr AAATwNAAEAAABYwAAA
22 dasd AAATwOAAEAAAAEwAAA
34 aasd AAATwPAAEAAAAUwAAA
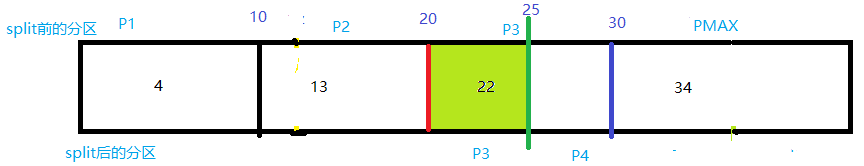
第二种情况
SQL> alter table t_partition_range split partition t_range_p2 at (12) into
2 (partition t_range_p2,
3 partition t_range_p5);
Table altered.
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 6 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL>
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P2 12 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 25 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P4 30 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P5 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
6 rows selected.
SQL> select id,name,rowid from t_partition_range;
ID NAME ROWID
---------- -------------------------------------------------- ------------------
4 ddd AAATwMAAEAAABIwAAA
13 asdewr AAATwNAAEAAABYwAAA
22 dasd AAATwOAAEAAAAEwAAA
34 aasd AAATwPAAEAAAAUwAAA
我们这两种情况是一样的,虽然待split分区里面有数据,但是split之后,索引仍然有效。
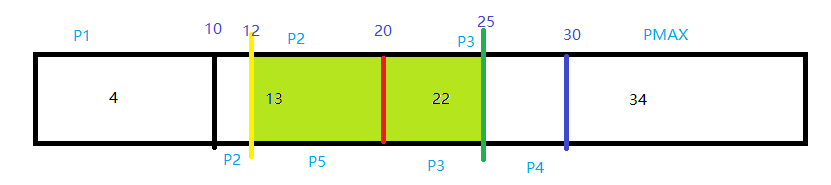
共同点就是,拆分的时候,只有单边有数据,即,待拆分的值,分区里面的数据要么全是大于它,要么全是小于它。
第三种情况:
再插入一条数据,使分区里面的值,分布在待拆分值的两边。
SQL> insert into t_partition_range values(40,'saewfwe');
1 row created.
SQL> commit;
Commit complete.
SQL> select id,name,rowid from t_partition_range;
ID NAME ROWID
---------- -------------------------------------------------- ------------------
4 ddd AAATwMAAEAAABIwAAA
13 asdewr AAATwNAAEAAABYwAAA
22 dasd AAATwOAAEAAAAEwAAA
34 aasd AAATwPAAEAAAAUwAAA
40 saewfwe AAATwPAAEAAAAUwAAB
SQL> alter table t_partition_range split partition T_RANGE_PMAX at (35) into
2 (partition t_range_p6,
3 partition T_RANGE_PMAX);
Table altered.
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 7 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL>
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P2 12 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 25 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P4 30 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P5 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P6 35 USERS UNUSABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS UNUSABLE
7 rows selected.
SQL> select id,name,rowid from t_partition_range;
ID NAME ROWID
---------- -------------------------------------------------- ------------------
4 ddd AAATwMAAEAAABIwAAA
13 asdewr AAATwNAAEAAABYwAAA
22 dasd AAATwOAAEAAAAEwAAA
34 aasd AAATwdAAEAAABoSAAA
40 saewfwe AAATweAAEAAAB4OAAA
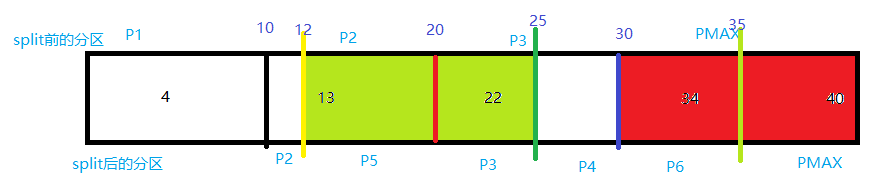
我们把pmax拆分成了p6和pmax两个分区,会看到,p6和pmax上面的local索引已经失效,经查询表,会发现,表里面的数据:id=34和id=40的两条数据,经过拆分,rowid(AAATwPAAEAAAAUwAAA–>AAATwdAAEAAABoSAAA),(AAATwPAAEAAAAUwAAB–>AAATweAAEAAAB4OAAA)发生了变化,因为rowid发生了变化,那么上面的索引肯定会失效(键值与rowid)。
我们继续split max:
SQL> alter table t_partition_range split partition T_RANGE_PMAX at (45) into
2 (partition t_range_p7,
3 partition T_RANGE_PMAX);
Table altered.
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 8 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL>
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P2 12 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 25 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P4 30 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P5 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P6 35 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P7 45 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
8 rows selected.
不会失效。
总结上面四种情况:可知官方文档说的并不是很严谨。对于local索引,不是说我们要拆分的分区中有数据,拆分后对应的索引就会失效。而是要看我们分区中的数据分布,和我们要拆分的取得值,进行比较,如果都是一边倒,即分区里面的数据都比拆分的值大,或者小,那么拆分后,分区对应的索引不会失效。如果分区里面的值比拆分的值大于和小于都有,那么拆分后,分区对应的索引都会失效,因为表数据的rowid发生变化。
在实际情况中,一般在待拆分值的两边都会有值,所以一般网上都会说split分区后,local本地索引会失效,就是这个原因。
merge合并分区
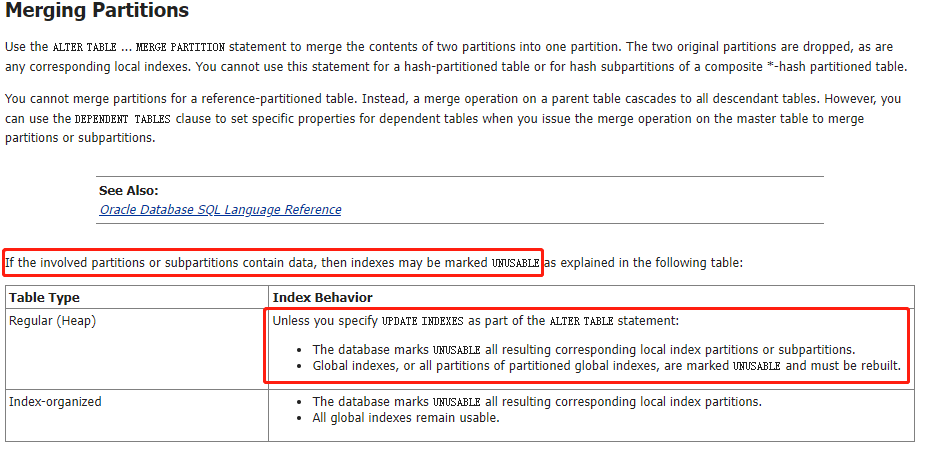
从官方文档的描述来看,和split的情况是一样的。都含有值后,会失效。下面进行测试:
按照上面split的反过程,进行合并。
第一种情况,合并p2,p5
SQL> alter table t_partition_range merge partitions t_range_p2,t_range_p5 into partition t_range_p8;
Table altered.
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 7 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL>
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 25 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P4 30 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P6 35 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P7 45 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P8 20 USERS UNUSABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
7 rows selected.
第二种情况,合并p3,p4
SQL> alter table t_partition_range merge partitions t_range_p3,t_range_p4 into partition t_range_p9;
Table altered.
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 6 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL>
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P6 35 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P7 45 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P8 20 USERS UNUSABLE
T_RANGE_P9 30 USERS UNUSABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
6 rows selected.
SQL> select id,name,rowid from t_partition_range;
ID NAME ROWID
---------- -------------------------------------------------- ------------------
4 ddd AAATwMAAEAAABIwAAA
13 asdewr AAATwnAAEAAACESAAA
22 dasd AAATwpAAEAAAAkSAAA
34 aasd AAATwdAAEAAABoSAAA
40 saewfwe AAATweAAEAAAB4OAAA
第三种情况,合并p6,p7.
SQL> alter table t_partition_range merge partitions t_range_p6,t_range_p7 into partition t_range_p10;
Table altered.
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 5 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL>
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P10 45 USERS UNUSABLE
T_RANGE_P8 20 USERS UNUSABLE
T_RANGE_P9 30 USERS UNUSABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
SQL> select id,name,rowid from t_partition_range;
ID NAME ROWID
---------- -------------------------------------------------- ------------------
4 ddd AAATwMAAEAAABIwAAA
13 asdewr AAATwnAAEAAACESAAA
22 dasd AAATwpAAEAAAAkSAAA
34 aasd AAATwrAAEAAAAESAAA
40 saewfwe AAATwrAAEAAAAESAAB
merge的情况和官方文档描述一致,只要merge的时候,任意一个待合并的分区含有数据,合并后的分区对应的索引就会失效。
rowid 在merge合并后,都会发生变化。
drop分区
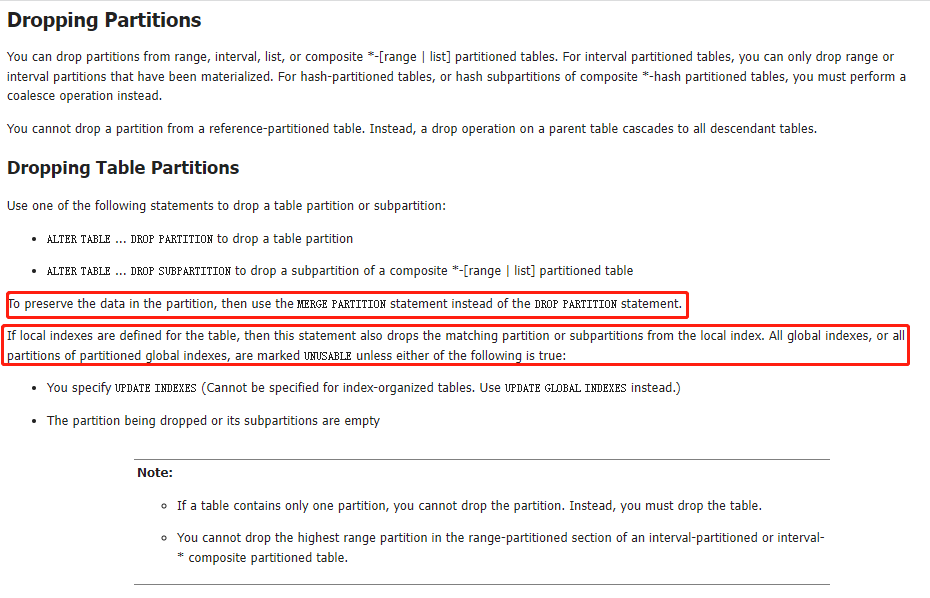
同样,如果你在执行该语句时没有指定update indexes 子句,也会导致glocal 索引的失效,至于local索引,删除分区时对应的索引分区会被同时删除,但其它分区的local 索引不会受到影响。
SQL> alter index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID rebuild partition T_RANGE_P10;
Index altered.
SQL> alter index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID rebuild partition T_RANGE_P8;
Index altered.
SQL> alter index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID rebuild partition T_RANGE_P9;
Index altered.
SQL> select * from T_PARTITION_RANGE partition (T_RANGE_P10);
ID NAME
---------- --------------------------------------------------
34 aasd
40 saewfwe
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 5 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P10 45 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P8 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P9 30 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
SQL> alter table T_PARTITION_RANGE drop partition T_RANGE_P10;
Table altered.
SQL> select * from T_PARTITION_RANGE partition (T_RANGE_P10);
select * from T_PARTITION_RANGE partition (T_RANGE_P10)
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-02149: Specified partition does not exist
---删除T_RANGE_P10分区,数据会被同时删除
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 4 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL>
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P8 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P9 30 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
如果你的本意是希望删除掉指定的分区但保留数据,你应该使用merge partition。
local索引,删除分区时对应的索引分区会被同时删除,但其它分区的local 索引不会受到影响.
add分区
增加表分区适应于所有的分区形式,其语法是alter table tbname add partition …
但是,需要注意对于像list,range 这种存在范围值的分区,所要增加的分区值必须要大于当前分区中的最大值(如果当前存在maxvalue 或default 的分区,add partition 会报错,这种情况只能使用split,hash 分区则无此限制。
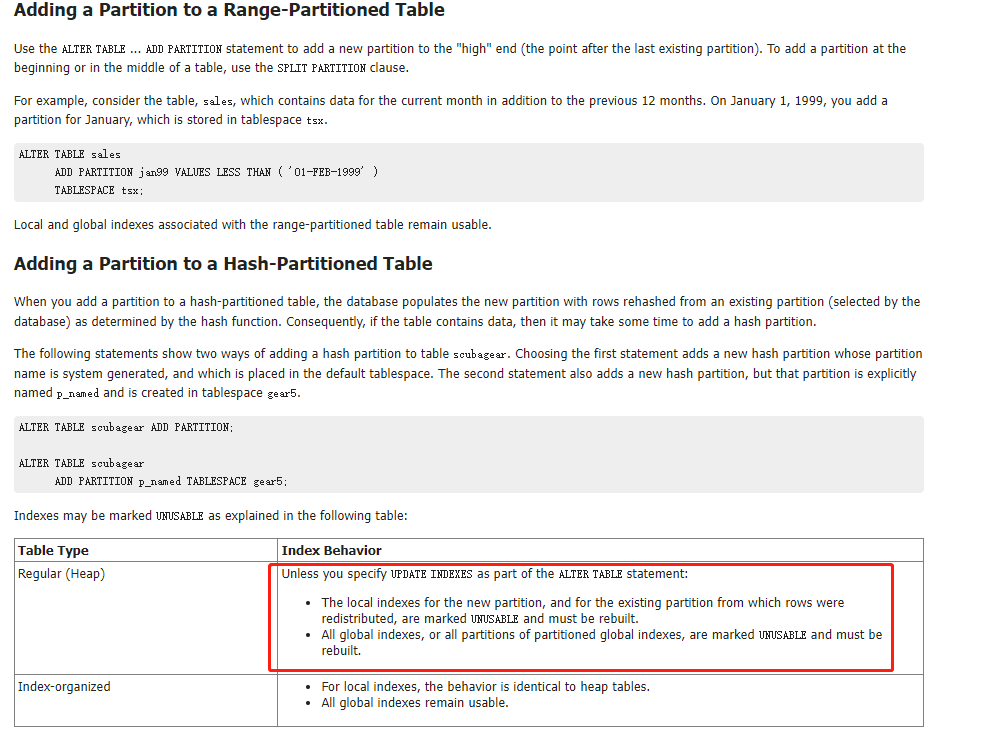
索引失效只发生在hash分区的情况下。下面的range分区不影响数据分布,所以不影响索引。
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P8 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P9 30 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
SQL> alter table t_partition_range add partition t_range_p5 values less than(60);
alter table t_partition_range add partition t_range_p5 values less than(60)
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-14074: partition bound must collate higher than that of the last partition
---需要注意对于像list,range 这种存在范围值的分区,所要增加的分区值必须要大于当前分区中的最大值(如果当前存在maxvalue 或default 的分区,add partition 会报错,这种情况只能使用split.
--下面采用split的方式达到add分区的作用。
SQL> select * from T_PARTITION_RANGE partition (T_RANGE_PMAX);
no rows selected
SQL> alter table t_partition_range split partition T_RANGE_PMAX at (60) into
2 (partition t_range_p2,
3 partition T_RANGE_PMAX);
Table altered.
SQL> select table_name,partitioning_type,partition_count
2 From user_part_tables
3 where table_name='T_PARTITION_RANGE';
TABLE_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT
------------------------------ --------- ---------------
T_PARTITION_RANGE RANGE 5
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name
2 from user_tab_partitions
3 where table_name='T_PARTITION_RANGE'
4 order by partition_position;
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS
T_RANGE_P8 20 USERS
T_RANGE_P9 30 USERS
T_RANGE_P2 60 USERS
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS
或者查看max有无值,没值的话,drop掉,重新add。
SQL> select * from T_PARTITION_RANGE partition (T_RANGE_PMAX);
no rows selected
SQL> alter table T_PARTITION_RANGE drop partition T_RANGE_PMAX;
Table altered.
SQL> alter table T_PARTITION_RANGE add partition T_RANGE_P3 values less than(70);
Table altered.
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 5 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P2 60 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 70 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P8 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P9 30 USERS USABLE
truncate 分区
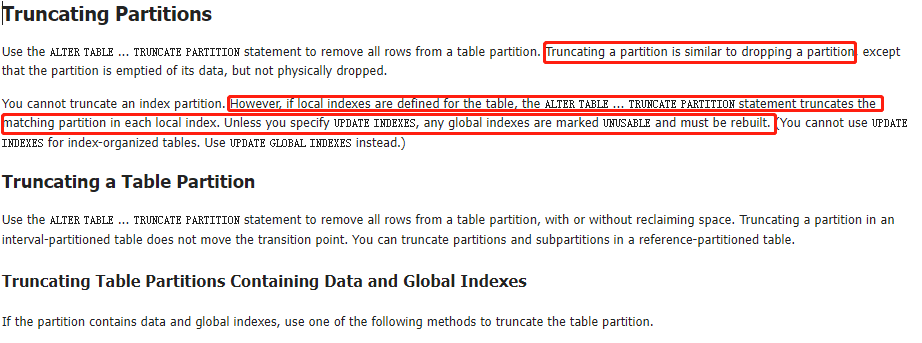
SQL> select * from T_PARTITION_RANGE;
ID NAME
---------- --------------------------------------------------
4 ddd
13 asdewr
22 dasd
SQL> select * from T_PARTITION_RANGE partition (T_RANGE_P8);
ID NAME
---------- --------------------------------------------------
13 asdewr
SQL> alter table T_PARTITION_RANGE truncate partition T_RANGE_P8;
Table truncated.
SQL> select * from T_PARTITION_RANGE partition (T_RANGE_P8);
no rows selected
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 5 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL>
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P2 60 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 70 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P8 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P9 30 USERS USABLE
清空分区,也会清空对应的本地索引数据,但是本地索引不会失效。
move分区
move我们经常用来整理表碎片。测试如下:
SQL> select * from T_PARTITION_RANGE partition (T_RANGE_P1);
ID NAME
---------- --------------------------------------------------
4 ddd
SQL> alter table T_PARTITION_RANGE move partition T_RANGE_P1 tablespace zhuo;
Table altered.
SQL> select index_name, partitioning_type, partition_count,LOCALITY,ALIGNMENT
2 From user_part_indexes
3 where index_name = 'IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
INDEX_NAME PARTITION PARTITION_COUNT LOCALI ALIGNMENT
------------------------------ --------- --------------- ------ ------------
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID RANGE 5 LOCAL PREFIXED
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ ---------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS UNUSABLE
T_RANGE_P2 60 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 70 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P8 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P9 30 USERS USABLE
move操作会使本地索引失效。
rebuild索引时注意事项:
1、使用nologging选项。参考:http://blog.itpub.net/720091/viewspace-1135588/
在create index … nologging 和 alter index … rebuild nologging时,nologging会生效。
在后续DML操作时,会生成redo log。虽然index设置为nologging
2、使用parallel后,要noparallel。修改了索引的并行,这样在我们使用索引时会影响执行计划,会消耗很多的资源。所以,我们需要对这个并行度进行修改,改成noparallel。
验证如下:参考https://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/article/details/7734344
任何参数不加,默认的:
SQL> create index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME on T_PARTITION_RANGE(name);
Index created.
SQL> select INDEX_NAME,DEGREE,LOGGING from dba_indexes where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME';
INDEX_NAME DEGREE LOG
------------------------------ ---------------------------------------- ---
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME 1 YES
DEGREE为1.This is the default,即并行度为1。
LOGGING为YES。默认记录日志。但是由前面可知,这个nologging只在rebuild和create的时候生效,后面的DML并不会生效,依然会产生日志。
修改默认参数:
SQL> drop index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME;
Index dropped.
SQL> create index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME on T_PARTITION_RANGE(name) parallel 6 nologging;
Index created.
SQL> select INDEX_NAME,DEGREE,LOGGING from dba_indexes where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME';
INDEX_NAME DEGREE LOG
------------------------------ ---------------------------------------- ---
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME 6 NO
SQL> alter index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME rebuild noparallel;
Index altered.
SQL> select INDEX_NAME,DEGREE,LOGGING from dba_indexes where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME';
INDEX_NAME DEGREE LOG
------------------------------ ---------------------------------------- ---
IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME 1 YES
所以,在create或者rebuild的时候,只要不加parallel n,那么索引上面的并行度就是默认的1。不加nologging,默认就是logging。这是create和rebuild时候的默认参数。
所以创建或者rebuild的时候最佳语法:
create index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME on T_PARTITION_RANGE(name) parallel 6 nologging;
alter index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME noparallel;
或者
alter index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME rebuild parallel 6 nologging online;
alter index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_NAME noparallel;
或者
分区索引
alter index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID rebuild partition T_RANGE_P3 parallel 6 nologging online;
alter index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID noparallel;
**degree只能在表或者索引级别,分区级别没有。
为了避免在做维护的过程中,所以失效,可以加update语句,自动rebuild。
参考:file:///E:/%E5%B7%A5%E4%BD%9C/enmo/oracle/E66230_01/VLDBG/maintenance-partition-can-be-performed.htm#VLDBG1122
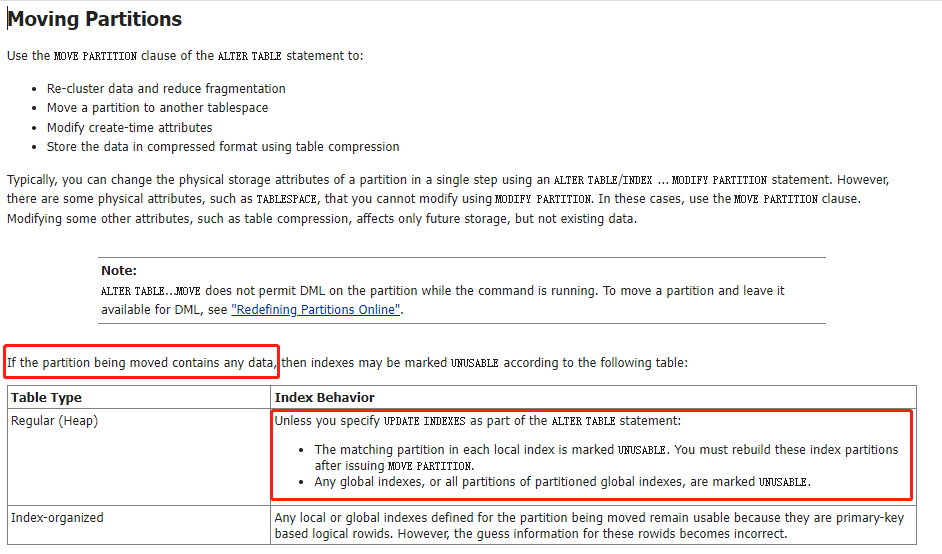
Updating Indexes Automatically
Before discussing the individual maintenance operations for partitioned tables and indexes, it is important to discuss the effects of the UPDATE INDEXES clause that can be specified in the ALTER TABLE statement.
By default, many table maintenance operations on partitioned tables invalidate (mark UNUSABLE) the corresponding indexes or index partitions. You must then rebuild the entire index or, for a global index, each of its partitions. The database lets you override this default behavior if you specify UPDATE INDEXES in your ALTER TABLE statement for the maintenance operation. Specifying this clause tells the database to update the indexes at the time it executes the maintenance operation DDL statement. This provides the following benefits:
The indexes are updated with the base table operation. You are not required to update later and independently rebuild the indexes.
The global indexes are more highly available, because they are not marked UNUSABLE. These indexes remain available even while the partition DDL is executing and can access unaffected partitions in the table.
You need not look up the names of all invalid indexes to rebuild them.
Optional clauses for local indexes let you specify physical and storage characteristics for updated local indexes and their partitions.
You can specify physical attributes, tablespace storage, and logging for each partition of each local index. Alternatively, you can specify only the PARTITION keyword and let the database update the partition attributes as follows:
For operations on a single table partition (such as MOVE PARTITION and SPLIT PARTITION), the corresponding index partition inherits the attributes of the affected index partition. The database does not generate names for new index partitions, so any new index partitions resulting from this operation inherit their names from the corresponding new table partition.
For MERGE PARTITION operations, the resulting local index partition inherits its name from the resulting table partition and inherits its attributes from the local index.
For a composite-partitioned index, you can specify tablespace storage for each subpartition.
See Also:
The update_all_indexes_clause of ALTER TABLE for the syntax for updating indexes
The following operations support the UPDATE INDEXES clause:
ADD PARTITION | SUBPARTITION
COALESCE PARTITION | SUBPARTITION
DROP PARTITION | SUBPARTITION
EXCHANGE PARTITION | SUBPARTITION
MERGE PARTITION | SUBPARTITION
MOVE PARTITION | SUBPARTITION
SPLIT PARTITION | SUBPARTITION
TRUNCATE PARTITION | SUBPARTITION
Rebuilding Local Index Partitions
Rebuild local indexes using either ALTER INDEX or ALTER TABLE as follows:
ALTER INDEX ... REBUILD PARTITION/SUBPARTITION
This statement rebuilds an index partition or subpartition unconditionally.
ALTER TABLE ... MODIFY PARTITION/SUBPARTITION ... REBUILD UNUSABLE LOCAL INDEXES
This statement finds all of the unusable indexes for the given table partition or subpartition and rebuilds them. It only rebuilds an index partition if it has been marked UNUSABLE.
碰上索引分区无效也很常见,比如分区表操作时未指定update indexes 子句就极有可能造成索引分区的无效,一般情况下,你都可以通过:Alter index idxname rebuild partition/subpartition ptname;重新编译。注意global 索引只支持range 分区,local 索引无限制。
而对于local 索引分区,你还可以使用这种命令方式:
alter table tbname modify partition/subpartition ptname rebuild unusable local indexes;
基于如上总结,对于本地分区索引,无效的情况下,可采用如下两种方法之一进行重新编译:
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P2 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 25 USERS UNUSABLE
T_RANGE_P4 30 USERS UNUSABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
SQL> alter table t_partition_range modify partition T_RANGE_P3 rebuild unusable local indexes parallel 6 nologging online;
alter table t_partition_range modify partition T_RANGE_P3 rebuild unusable local indexes parallel 6 nologging online
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-14048: a partition maintenance operation may not be combined with other operations
SQL> alter table t_partition_range modify partition T_RANGE_P3 rebuild unusable local indexes;
Table altered.
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P2 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 25 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P4 30 USERS UNUSABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
SQL> alter index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID rebuild partition T_RANGE_P4 parallel 6 nologging online;
alter index IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID noparallel;
Index altered.
SQL>
Index altered.
SQL> select partition_name,high_value,tablespace_name,status from user_ind_partitions
2 where index_name='IDX_PARTI_RANGE_ID';
PARTITION_NAME HIGH_VALUE TABLESPACE_NAME STATUS
------------------------------ -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- ------------------------------ --------
T_RANGE_P1 10 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P2 20 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P3 25 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_P4 30 USERS USABLE
T_RANGE_PMAX MAXVALUE USERS USABLE
如何对本地分区索引进行维护?
本地索引自带的自动维护特性,使得我们在对表分区做维护时,不需要特别多的维护操作。对于特定的split和merge,完后,要进行rebuild。
总结
对于本地索引,常见维护操作,情况如下:
参考
VLDB and Partitioning Guide






