前言
大家好,前面我们铺垫了一点Parse的知识,今天我们来学一下TiDB的Paser知识点。
quickstart
我们学习使用的材料是官方 github 仓库中Parse文件夹doc下的quickstart.
这个文档是教我们如何快速使用 TiDB 的 Parse。
先决条件
首先我们是需要Golang的版本在1.13之上,运行go version进行检查。
go version
go version go1.17.7 darwin/arm64
创建项目
mkdir colx && cd colx
go mod init colx && touch main.go
导入依赖
go get -v github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser@4a1b2e9
go: downloading github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser v0.0.0-20211124132551-4a1b2e9fe5b5
github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/tidb
golang.org/x/text/internal/utf8internal
golang.org/x/text/encoding/internal/identifier
golang.org/x/text/transform
go.uber.org/zap/buffer
go.uber.org/zap/internal/exit
github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/format
go.uber.org/zap/internal/color
go.uber.org/atomic
go.uber.org/zap/internal/ztest
gopkg.in/natefinch/lumberjack.v2
github.com/remyoudompheng/bigfft
go.uber.org/zap/internal/bufferpool
github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/opcode
golang.org/x/text/encoding
golang.org/x/text/runes
go.uber.org/multierr
github.com/pingcap/errors
golang.org/x/text/encoding/internal
github.com/cznic/mathutil
go.uber.org/zap/zapcore
golang.org/x/text/encoding/charmap
golang.org/x/text/encoding/korean
golang.org/x/text/encoding/japanese
golang.org/x/text/encoding/traditionalchinese
golang.org/x/text/encoding/simplifiedchinese
github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/mysql
golang.org/x/text/encoding/unicode
go.uber.org/zap
go.uber.org/zap/zaptest
github.com/pingcap/log
github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/terror
github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/auth
github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/charset
github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/types
github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/model
github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/ast
github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser
go get: added github.com/cznic/mathutil v0.0.0-20181122101859-297441e03548
go get: added github.com/pingcap/errors v0.11.5-0.20210425183316-da1aaba5fb63
go get: added github.com/pingcap/log v0.0.0-20210625125904-98ed8e2eb1c7
go get: added github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser v0.0.0-20211124132551-4a1b2e9fe5b5
go get: added github.com/remyoudompheng/bigfft v0.0.0-20200410134404-eec4a21b6bb0
go get: added go.uber.org/atomic v1.7.0
go get: added go.uber.org/multierr v1.6.0
go get: added go.uber.org/zap v1.18.1
go get: added golang.org/x/text v0.3.6
go get: added gopkg.in/natefinch/lumberjack.v2 v2.0.0
导入完成之后,查看现在的文件,如果是三个文件则是正常的。
ls -lrt
-rw-r--r-- 1 buddy staff 0 Feb 24 22:47 main.go
-rw-r--r-- 1 buddy staff 624 Feb 24 22:52 go.mod
-rw-r--r-- 1 buddy staff 6101 Feb 24 22:52 go.sum
写一段程序实现解析
接下来我们可以写一段go程序,将SQL text
解析为AST tree
。
1.使用parser.New()
函数来实例化解析器
2.在解析器中调用Parse(sql, charset, collation)
方法。
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser"
"github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/ast"
_ "github.com/pingcap/tidb/parser/test_driver"
)
func parse(sql string) (*ast.StmtNode, error) {
p := parser.New()
stmtNodes, _, err := p.Parse(sql, "", "")
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return &stmtNodes[0], nil
}
func main() {
astNode, err := parse("SELECT a, b FROM t")
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("parse error: %v\n", err.Error())
return
}
fmt.Printf("%v\n", *astNode)
}
直接运行。
go run main.go
&{{{{SELECT a, b FROM t 0}}} 0x140001a8cc0 false 0x1400006a380 <nil> 0x140001a8cf0 <nil> <nil> [] <nil> <nil> <nil> [] false false 0 <nil> <nil> 0 [] <nil>}
下面就是我们解析之后的AST tree
,看起来十分的抽象。
调试代码
返回到我们的go代码中,这里比较重要的是调用了parse
这个函数,并返回了astNode
。我们可以用我们写的代码来调试一下。把断点设置在Parse
函数上。
stmtNodes, _, err := p.Parse(sql, "", "")
我们调试得到的stmtNodes
的值是这样的。

这里stmtNodes
它是一个接口,实现这个接口有很多种方法。
type StmtNode interface {
Node
statement()
}
这里根据下面那个变量反推出实现它的实现方法是SelectStmt
。如果你是delete,这里就是deleteStmt
.
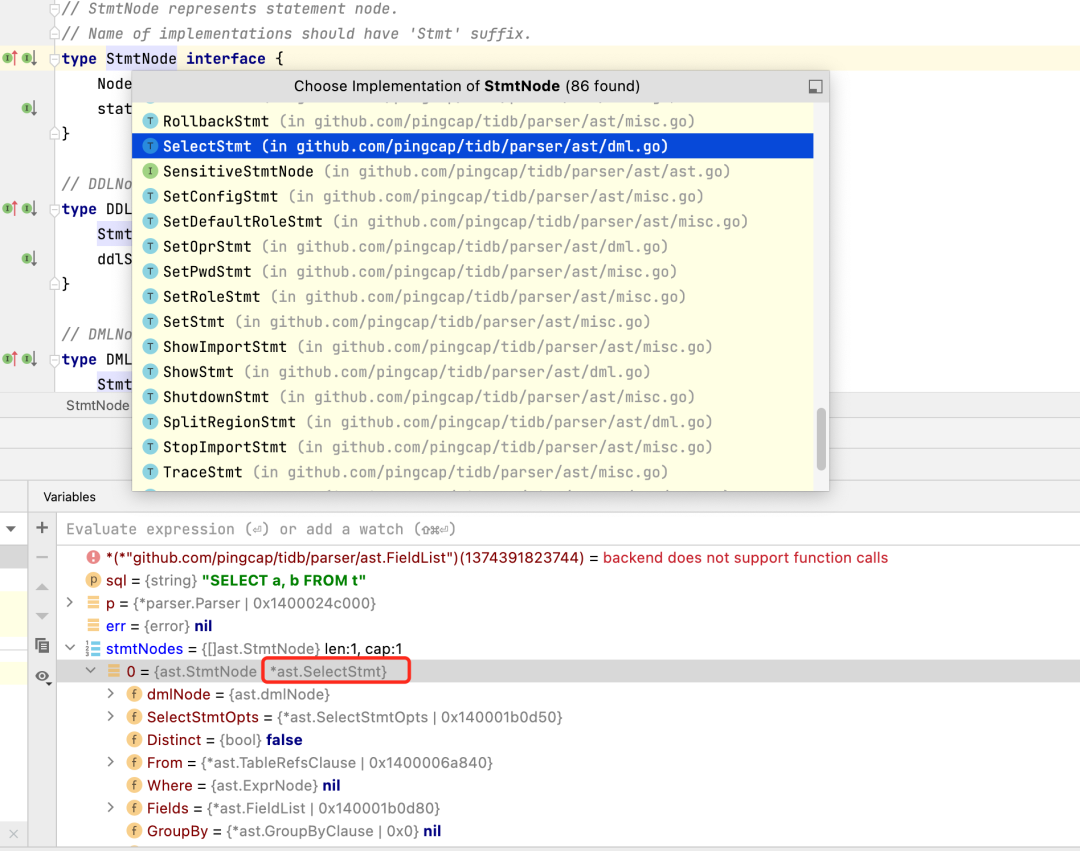
这个SelectStmt
的结构体,就定义了基本的查询语句的结构树。
// SelectStmt represents the select query node.
// See https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/select.html
type SelectStmt struct {
dmlNode
// SelectStmtOpts wraps around select hints and switches.
*SelectStmtOpts
// Distinct represents whether the select has distinct option.
Distinct bool
// From is the from clause of the query.
From *TableRefsClause
// Where is the where clause in select statement.
Where ExprNode
// Fields is the select expression list.
Fields *FieldList
// GroupBy is the group by expression list.
GroupBy *GroupByClause
// Having is the having condition.
Having *HavingClause
// WindowSpecs is the window specification list.
WindowSpecs []WindowSpec
// OrderBy is the ordering expression list.
OrderBy *OrderByClause
// Limit is the limit clause.
Limit *Limit
// LockInfo is the lock type
LockInfo *SelectLockInfo
// TableHints represents the table level Optimizer Hint for join type
TableHints []*TableOptimizerHint
// IsInBraces indicates whether it's a stmt in brace.
IsInBraces bool
// WithBeforeBraces indicates whether stmt's with clause is before the brace.
// It's used to distinguish (with xxx select xxx) and with xxx (select xxx)
WithBeforeBraces bool
// QueryBlockOffset indicates the order of this SelectStmt if counted from left to right in the sql text.
QueryBlockOffset int
// SelectIntoOpt is the select-into option.
SelectIntoOpt *SelectIntoOption
// AfterSetOperator indicates the SelectStmt after which type of set operator
AfterSetOperator *SetOprType
// Kind refer to three kind of statement: SelectStmt, TableStmt and ValuesStmt
Kind SelectStmtKind
// Lists is filled only when Kind == SelectStmtKindValues
Lists []*RowExpr
With *WithClause
}
Fields
:存放相关字段信息。可以看到ast变量中的Fields,确实有a和b这两个字段。
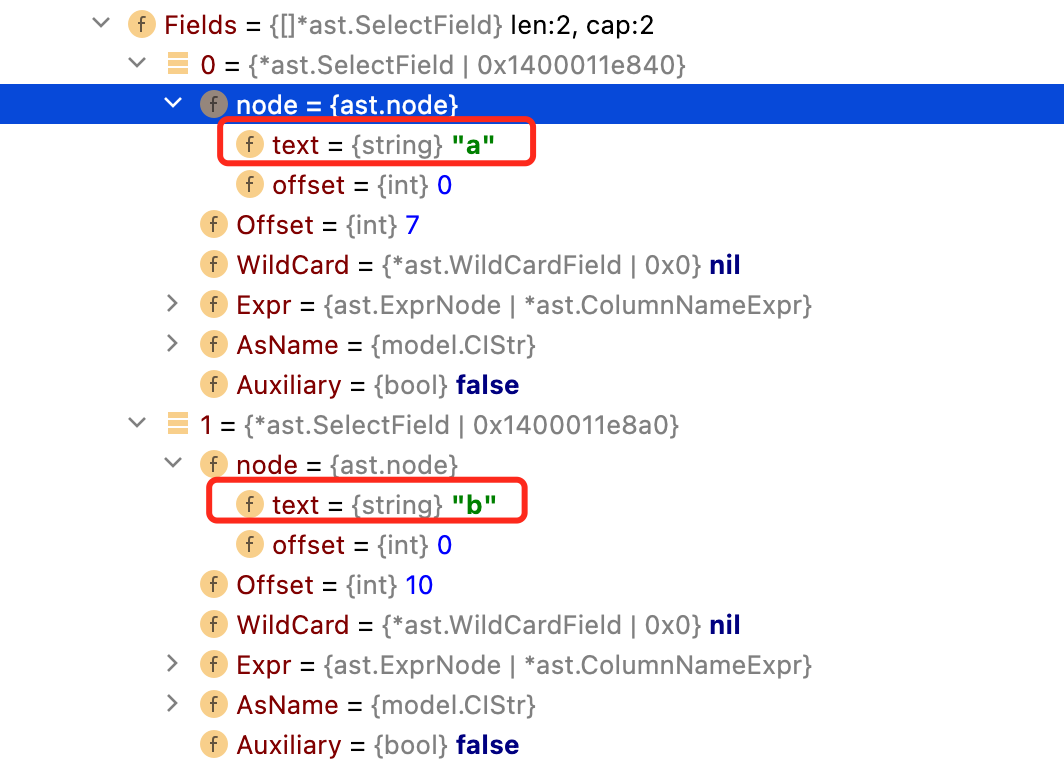
当然还有其他的关键字,这里不做逐一解释,有兴趣的可以翻阅源码中的注释进行查看。
后记
今天就写到这里,每天进步一点点,让我们逐步的抽丝拨茧研究出Parse里面的内容。
Refences
https://github.com/pingcap/tidb/blob/master/parser/docs/quickstart.md






