
(本文阅读预计时间:16分钟)
作为关于Patroni的第四篇文字,总想有些深度,那深度是从哪里而来,首先我们先从patroni运行后,在系统中存储的键值入手。
这里仅仅是从etcd入手,如果是使用了其他方式的DCS的情况下还请查询其他例如zookeeper等方式如何查询键值。另外这里使用的是etcd的V2版本,所以如果您使用的是etcd的V3版本则这里的命令不会适合您。
首先根据patroni的原理,关键的配置数据尤其针对服务器中的数据是要存储在DCS系统中的。
我们先通过etcd的命令来查看我们目前etcd本身的分布式的状态。
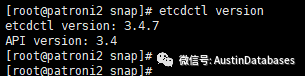
首先我们先确认我们的etcd的版本,这里需要说明的是etcd如果状态不正确,则postgresql patroni的集群状态一定也是不正常的,所以对etcd的一些基本操作也是必须的。
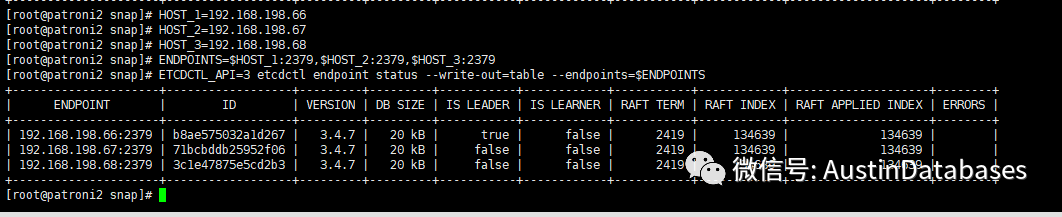
例如查看当前etcd的状态,以及到底谁是leader谁是leader那基本上那个节点上安装的数据库就是主库。
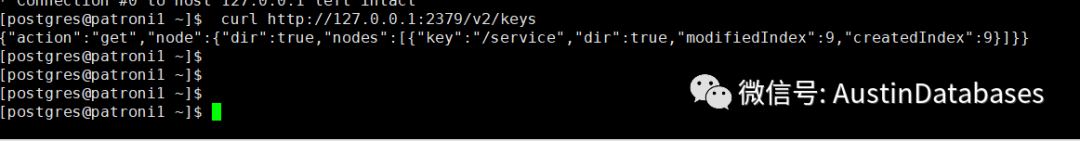
curl http://127.0.0.1:2379/v2/keys
在装有etcd的主机中执行上面的命令,上面的命令是针对V2方式的获取当前etcd中键值信息。
可以从图中看到我们的信息应该在service目录下, 那我们就顺藤摸瓜看看怎么获取相关信息。
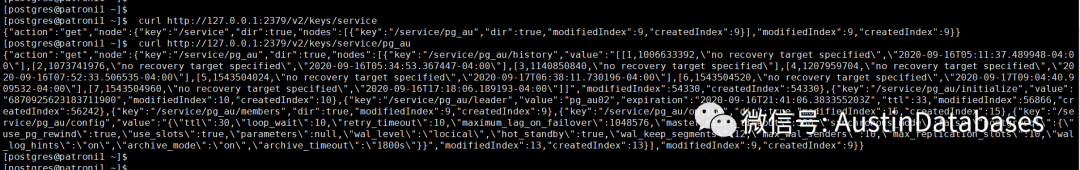
curl http://127.0.0.1:2379/v2/keys/service/pg_au
这里的pg_au其实就是etcd当中的集群名,(请参见此系列的2)
我们将pg_au里面的信息打开
{"action":"get","node":
{"key":"/service/pg_au","dir":true,"nodes":[
{"key":"/service/pg_au/history",
"value":"[[1,1006633392,\"no recovery target specified\",
\"2020-09-16T05:11:37.489948-04:00\"],[2,1073741976,\
"no recovery target specified\",\"2020-09-16T05:34:53.367447-04:00\"],
[3,1140850840,\"no recovery target specified\"],[4,1207959704,\
"no recovery target specified\",\"2020-09-16T07:52:33.506535-04:00\"],[5,1543504024,\
"no recovery target specified\",\"2020-09-17T06:38:11.730196-04:00\"],[6,1543504520,\
"no recovery target specified\",\"2020-09-17T09:04:40.909532-04:00\"],[7,1543504960,\
"no recovery target specified\",\"2020-09-16T17:18:06.189193-04:00\"]]","modifiedIndex":54330,"createdIndex":54330},
{"key":"/service/pg_au/initialize","value":"6870925623183711900","modifiedIndex":10,"createdIndex":10},
{"key":"/service/pg_au/leader","
value":"pg_au02","expiration":"2020-09-16T21:41:06.383355203Z","ttl":33,
"modifiedIndex":56866,"createdIndex":56242},{
"key":"/service/pg_au/members","dir":true,"modifiedIndex":9,"createdIndex":9},
{"key":"/service/pg_au/optime","dir":true,"modifiedIndex":15,"createdIndex":15},
{"key":"/service/pg_au/config",
"value":"{\"ttl\":30,\"loop_wait\":10,\"retry_timeout\":10,
\"maximum_lag_on_failover\":1048576,\"master_start_timeout\":300,
\"synchronous_mode\":false,\"postgresql\":{\"use_pg_rewind\":true,
\"use_slots\":true,\"parameters\":null,\"wal_level\":\"locical\",
\"hot_standby\":true,\"wal_keep_segments\":12,\"max_wal_senders\":10,
\"max_replication_slots\":10,\"wal_log_hints\":\"on\",\"archive_mode\":\"on\",
\"archive_timeout\":\"1800s\"}}","modifiedIndex":13,"createdIndex":13}],
"modifiedIndex":9,"createdIndex":9}}
分析其中获得的information,其中有几个值得注意的地方:
/service/pg_au/members
/service/pg_au/config
/service/pg_au/optime
/service/pg_au/initialize
/service/pg_au/leader
另外在其他位置展现了部分配置的内容
例如:
wal_level
master_start_timeout
use_pg_rewind
host_standby
wal_keep_segments
wal_log_hints
archive_mode
等等这些信息,说明最基本的配置中,这些PG节点在这些信息上是一致的。
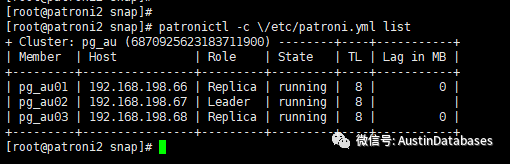
我们继续从上面其他6个键值入手,先从leader入手,可以看到,其中显示的是pg_au02对应的节点是192.168.198.67说明此节点是leader也就是主节点。

通过patronictl进行验证,证明67节点是当前的主节点。
curl http://127.0.0.1:2379/v2/keys/service/pg_au/members
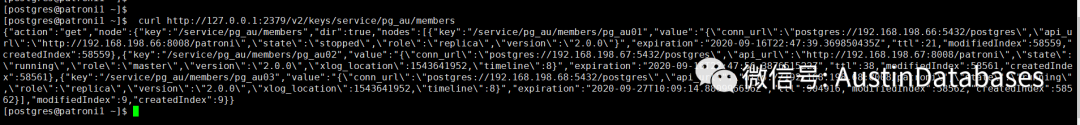
我们继续通过etcd的接口获取members中的内容,可以发现这里的内容(上图),与patroni的工作状态有关,如果patroni在某个节点不在工作,则这里显示\"state\":\"stopped,如果节点是运行的状态,则显示\"state\":\"running\的状态。
所以通过这里面的信息,可以来获取每一个节点中patroni到底是运行了,还是没有运行。
curl http://127.0.0.1:2379/v2/keys/service/pg_au/initialize

initialize里面的值主要是系统初始化时的代表集群的唯一值。
curl http://127.0.0.1:2379/v2/keys/service/pg_au/config

config里面是相关系统的设置值。上面也介绍过。
实际上我们还是要重新来回顾一下:
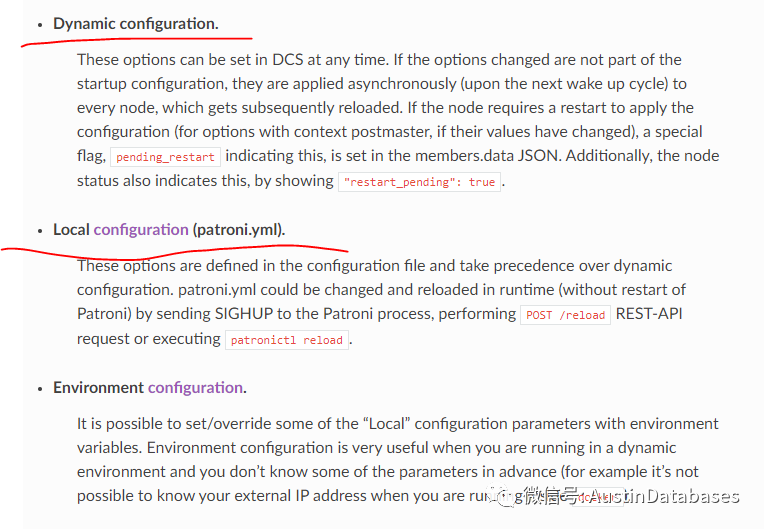
重点在于Dynamic configuration和Local configuration两个点。另外的一个点,和docker下的postgresql有关。上面讲的那些都是关于Dynamic的内容,那么具体在Dynamic中存储的配置信息到底是要做什么的。
下面找了一个官方的patroni.yaml的例子来说说配置文件
scope: batman 集群的名字etcd上显示
namespace: service/ 集群配置信息在etcd的存储位置
name: postgresql0 当前机器的配置的机器名
restapi:
listen: 127.0.0.1:8008
connect_address: 127.0.0.1:8008
etcd:
#Provide host to do the initial discovery of the cluster topology:
host: 127.0.0.1:2379 etcd 的地址
下面是重要的postgresql的配置信息
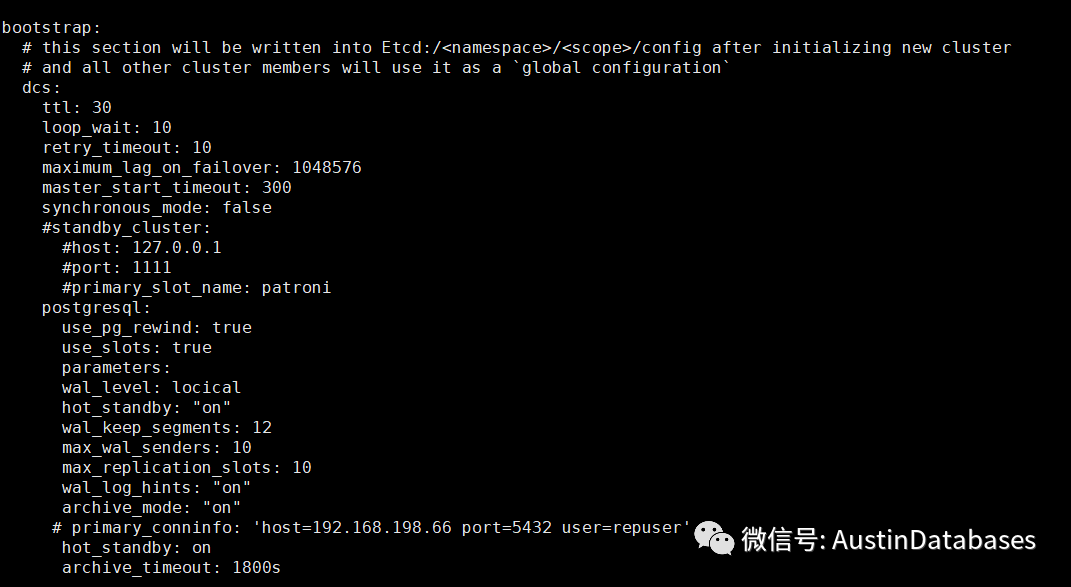
bootstrap:
# this section will be written into Etcd:/<namespace>/<scope>/config after initializing new cluster
# and all other cluster members will use it as a `global configuration`
dcs:
ttl: 30 当数据库系统出现问题,整体集群获得新的Leader 节点的时间
loop_wait: 10 轮训中的等待时间
retry_timeout: 10 当网络出现问题后,保证整体集群不进行跳转的保留时间
maximum_lag_on_failover: 1048576 当前所有从节点到底那些是可以被作为leader的选举的,和主库之间的复制延迟的设定
# master_start_timeout: 300 当前所有从节点到底那些是可以被作为leader的选举的,和主库之间的复制延迟的设定
# synchronous_mode: false
max_timelines_history: 每一次触发来检测系统的信息保留的历史的长度如果选择0,则这些历史信息将不被删除。
master_start_timeout: 这里是系统等待主库重新工作的时间,当主库出现问题后默认需要等待300S在此期间如果主库回归正常,则不再切换。 最大的默认切换时间是loop_wait + master_start_timeout + loop_wait的时间。 synchronous_mode: 大开此模式,则集群中的leader节点和一个从节点将使用同步模式,则这样的情况下将保证在集群切换的过程中,数据不会因为切换而丢失。但需要注意的是,如果使用此模式,备库在不能工作后,将影响整体集群的写操作。
下面是对于从库的设定略过
#standby_cluster:
#host: 127.0.0.1
#port: 1111
#primary_slot_name: patroni
下面是与postgresql集群中所有机器有关的配置
postgresql:
use_pg_rewind: true是否使用pg_rewind
use_slots: true
parameters:
wal_level: hot_standby
hot_standby: "on"
wal_keep_segments: 8
max_wal_senders: 10
max_replication_slots: 10
wal_log_hints: "on"
archive_mode: "on"
archive_timeout: 1800s
archive_command: mkdir -p ../wal_archive && test ! -f ../wal_archive/%f && cp %p ../wal_archive/%f
recovery_conf:
restore_command: cp ../wal_archive/%f %p
数据库初始化的配置
initdb: # Note: It needs to be a list (some options need values, others are switches)
- encoding: UTF8
- data-checksums
对于pg_hba的配置
pg_hba: # Add following lines to pg_hba.conf after running 'initdb'
- host replication replicator 127.0.0.1/32 md5
- host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
下面是针对这台机器的postgresql的配置
postgresql:
listen: 0.0.0.0:5432
connect_address: 0.0.0.0:5432
data_dir: data/postgresql设置当前主机的数据库目录
# bin_dir:
# config_dir:
pgpass: tmp/pgpass0
authentication:
replication:
username: replicator
password: rep-pass
superuser:
username: postgres
password: zalando
rewind: # Has no effect on postgres 10 and lower
username: rewind_user
password: rewind_password
需要配置至少三个相关账号,replication,superuser,rewind三个账号供基础的patroni在操作中使用。也就是我们所有在patroni中运作的数据库都需要有这三个账号,另外还拥有一些通用的系统的账号,可以在pgpass中设定的用户密码文件中使用。
#watchdog:
# mode: automatic # Allowed values: off, automatic, required
# device: dev/watchdog
# safety_margin: 5
watchdog咱们单独拿出来讲一期
tags:
nofailover: false nofailover 说明的到底释放允许这个节点参与leader的可选择
noloadbalance: false 如果设置为true在使用均衡复杂中,rest api将返回给相关应用程序503,则此节点仅仅作为一个standby节点,而不能作为balance的读节点
clonefrom: false 在进行节点添加中如果选择true则添加节点将优先选择此节点作为pg_basebackup的数据复制点
nosync: false 默认false 此节点不能作为事实同步节点





PostgreSQL与Oracle:成本、易用性和功能上的差异









