kubernetes中角色分为Role和ClusterRole,Role是namespace级别的,ClusterRole是集群级别的。回想下mac 上学习k8s系列(17)rbac 源码学习(part I)中的类图:
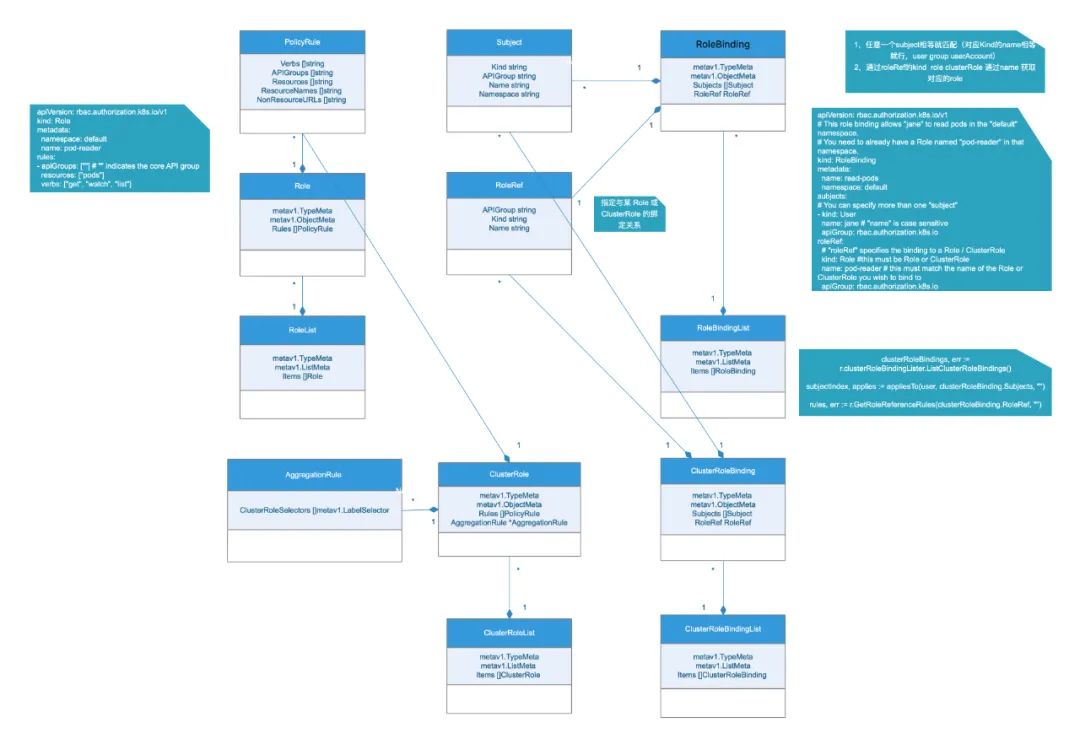
具体的结构体定义中在pkg/apis/rbac/types.go,我们先看下Role和对应的RoleBinding
type Role structmetav1.TypeMetametav1.ObjectMetaRules []PolicyRule
role 包含一系列的的PolicyRule
type PolicyRule structVerbs []stringAPIGroups []stringResources []stringResourceNames []stringNonResourceURLs []string
而RoleBinding定义了role和subject之间的绑定关系:
type RoleBinding structmetav1.TypeMetametav1.ObjectMetaSubjects []SubjectRoleRef RoleRef
当然包含的对象也分两部分
type Subject structKind stringAPIGroup stringName stringNamespace string
type RoleRef structAPIGroup stringKind stringName string
这两个结构体主要看两个属性值,第一个是Subjects,它是绑定的对象,包括User、Group、ServiceAccount;第二个是RoleRef,它是绑定的角色。
文件里也定义了对应的list
type RoleBindingList structmetav1.TypeMetametav1.ListMetaItems []RoleBinding
type RoleList structItems []Role
针对集群的rbac 相关对象定义如下,它没有namespace
type ClusterRole structRules []PolicyRuleAggregationRule *AggregationRule
type AggregationRule structClusterRoleSelectors []metav1.LabelSelector
也有对应的ClusterRoleBinding
type ClusterRoleBinding structSubjects []SubjectRoleRef RoleRef
和对应的list
type ClusterRoleBindingList structItems []ClusterRoleBinding
type ClusterRoleList structItems []ClusterRole
ClusterRole与Role的结构体定义基本是类似的,角色里面都是关联的Rules规则,一个角色有哪些权限,通过Rules去定义。下面是Rule的结构体定义,主要控制访问的资源、访问URL的限制。
那么角色是怎么和使用者或者服务账号绑定的呢?这就要看ClusterRoleBinding和RoleBinding。RoleBinding是把角色在namespace中对资源的权限授权给使用者或服务账号;ClusterRoleBinding允许使用者或服务账号在整个集群中的授权访问。ClusterRoleBinding与RoleBinding的功能是一致的,只是有着更宽的使用范围。
除了rbac,k8s还有很多种权限控制模式,比如abac:
pkg/apis/abac/types.go
type Policy struct {type PolicySpec struct
在kubernetes中,所有的请求都会经由apiserver进行处理。在初始化apiserver时,若指定了鉴权模式包括了RBAC后,将会注册一个RBAC的Handler模块。这样,在apiserver接收请求并处理时,将会调用该Handler,来判断该请求的调用者是否有权限请求该资源。
staging/src/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/endpoints/filters/authorization.go
func WithAuthorization(handler http.Handler, a authorizer.Authorizer, s runtime.NegotiatedSerializer) http.Handlerreturn http.HandlerFunc(func(w http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request) {attributes, err := GetAuthorizerAttributes(ctx)authorized, reason, err := a.Authorize(ctx, attributes)
该Handler做了两件事,一是根据http request提取出鉴权所需的信息,通过函数GetAuthorizerAttributes()实现,二是根据提取出的信息,执行鉴权的核心操作,去判断请求的调用者是否有权限操作相关资源,通过函数Authorize()处理。
vendor/k8s.io/apiserver/pkg/endpoints/filters/authorization.go
func GetAuthorizerAttributes(ctx context.Context) (authorizer.Attributes, error)requestInfo, found := request.RequestInfoFrom(ctx)
主要包括请求的APIGroup、APIVersion、Resource、SubResource、Verbs、Namespace等这些在PolicyRule结构体中定义的信息。
plugin/pkg/auth/authorizer/rbac/rbac.go
func (r *RBACAuthorizer) Authorize(ctx context.Context, requestAttributes authorizer.Attributes) (authorizer.Decision, string, error)r.authorizationRuleResolver.VisitRulesFor(requestAttributes.GetUser(), requestAttributes.GetNamespace(), ruleCheckingVisitor.visit)
pkg/registry/rbac/validation/rule.go
func (r *DefaultRuleResolver) VisitRulesFor(user user.Info, namespace string, visitor func(source fmt.Stringer, rule *rbacv1.PolicyRule, err error) bool)clusterRoleBindings, err := r.clusterRoleBindingLister.ListClusterRoleBindings();subjectIndex, applies := appliesTo(user, clusterRoleBinding.Subjects, "")rules, err := r.GetRoleReferenceRules(clusterRoleBinding.RoleRef, "")for i := range rules {if !visitor(sourceDescriber, &rules[i], nil) {return}}
获取所有的ClusterRoleBindings,并对其进行遍历操作;
根据请求调用者的信息,判断该调用者是否被绑定在该ClusterRoleBinding中;若绑定在该ClusterRoleBinding中,将通过函数GetRoleReferenceRules()获取绑定的Role所控制的访问的资源;将Role所控制的访问的资源,与从API请求中提取出的资源进行比对,若比对成功,即为API请求的调用者有权访问相关资源;若在所有的ClusterRoleBinding中,都没有获得鉴权成功的操作,将会判断提取出的信息中是否包括了namespace的信息,若包括了,将会获取该namespace下的所有RoleBindings。获取了该namesapce下的所有RoleBindings之后,所执行的操作将与ClusterRoleBinding类似,对其进行遍历,获取对应Role控制的访问的资源,与从API请求中提取的资源信息进行比对。若在遍历了所有CluterRoleBindings,及该namespace下的所有RoleBingdings之后,仍没有对资源比对成功,则可判断该API请求的调用者没有权限访问相关资源。








