原文地址:Using SingleStore DB as a JSON Document Database
原文作者:Akmal Chaudhri
了解如何使用SingleStore DB存储、检索和查询JSON数据。
摘要
继续我们关于SingleStore DB的多模型功能的系列文章,我们将在本文中讨论SingleStore DB对JSON数据的支持。
我们将构建一个小型库存系统,以模拟销售各种电子设备的在线商店。此示例来源于DigitalOcean上提供的优秀教程(How To Work with JSON in MySQL)。我们将该教程应用于SingleStore DB,可以看到使用SingleStore DB存储、检索和查询JSON数据会容易很多。我们还将用Laravel和PHP为我们的库存系统构建一个快速的可视化前端。
本文中使用的SQL脚本和PHP代码文件可在GitHub上找到。
介绍
之前,我们讨论过将SingleStore DB用于时间序列数据和地理空间数据,现在我们将继续讨论基于JSON数据的SingleStore DB的多模型功能。
JSON是当下流行的数据格式,对于需要捕获含有不同属性对象信息的应用程序非常有用。JSON对于电子商务等应用程序特别有用,在这些应用程序中,我们可能会存储一系列彼此具有完全不同特征的产品。我们稍后将介绍一些这方面的示例。
首先,我们需要在SingleStore网站上创建一个免费的托管服务帐户。在撰写本文时,SingleStore的托管服务帐户附带$500的积分。这对于本文中描述的案例研究来说绰绰有余。
创建数据库表
在我们的SingleStore托管服务帐户中,让我们使用SQL编辑器创建一个新数据库。命名为e_store,如下:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS e_store
DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8
DEFAULT COLLATE utf8_general_ci;
再创建brands(品牌),categories(类别)和products(产品)三张表,创建语句如下:
USE e_store;
CREATE TABLE brands (
id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(id)
);
CREATE TABLE categories (
id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(id)
);
CREATE TABLE products (
id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
name VARCHAR(250) NOT NULL,
brand_id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
category_id INT UNSIGNED NOT NULL,
attributes JSON NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY(id),
INDEX CATEGORY_ID(category_id ASC),
INDEX BRAND_ID(brand_id ASC)
);
brands和products表之间、以及categories和products表之间存在一对多(1:m)的关系。该设计可以改进,但足以说明本文的焦点,是JSON支持。
我们可以看到,products(产品)表有一个JSON格式的列,列名为attributes。通过将属性attributes列设置为NOT NULL,如果尝试存储无效的JSON数据,SingleStore DB将引发错误。
在表中插入数据
现在,让我们填充这些表。首先,在brands(品牌)表中插入数据:
INSERT INTO brands (name) VALUES
('Samsung'),
('Nokia'),
('Canon');
接下来, 是categories表(插入的类别分别为电视、手机、相机):
INSERT INTO categories (name) VALUES
('Television'),
('Mobile Phone'),
('Camera');
最后是products(产品)表。
接下来,在产品表中插入电视、手机、相机这三种类别的数据。
电视
首先,让我们加载Televisions(电视)这一类别的数据,并在products(产品)表的每个属性列插入对应的值:
-- Televisions
INSERT INTO products (name, brand_id, category_id, attributes) VALUES
('Prime', '1', '1', '{"screen" : "50 inch", "resolution" : "2048 x 1152 pixels", "ports" : {"hdmi" : 1, "usb" : 3}, "speakers" : {"left" : "10 watt", "right" : "10 watt"}}'),
('Octoview', '1', '1', '{"screen" : "40 inch", "resolution" : "1920 x 1080 pixels", "ports" : {"hdmi" : 1, "usb" : 2}, "speakers" : {"left" : "10 watt", "right" : "10 watt"}}'),
('Dreamer', '1', '1', '{"screen" : "30 inch", "resolution" : "1600 x 900 pixels", "ports" : {"hdmi" : 1, "usb" : 1}, "speakers" : {"left" : "10 watt", "right" : "10 watt"}}'),
('Bravia', '1', '1', '{"screen" : "25 inch", "resolution" : "1366 x 768 pixels", "ports" : {"hdmi" : 1, "usb" : 0}, "speakers" : {"left" : "5 watt", "right" : "5 watt"}}'),
('Proton', '1', '1', '{"screen" : "20 inch", "resolution" : "1280 x 720 pixels", "ports" : {"hdmi" : 0, "usb" : 0}, "speakers" : {"left" : "5 watt", "right" : "5 watt"}}');
如果我们检查JSON数据,我们可以看到存在嵌套。例如:
JSON
{
"screen" : "50 inch",
"resolution" : "2048 x 1152 pixels",
"ports" : {
"hdmi" : 1,
"usb" : 3
},
"speakers" : {
"left" : "10 watt",
"right" : "10 watt"
}
}
SingleStore DB可以轻松处理嵌套的JSON数据。
手机
接下来,让我们加载Mobile Phones(手机)这一类别的数据,并在products(产品)表的每个属性列插入对应的值:
-- Mobile Phones
INSERT INTO products (name, brand_id, category_id, attributes) VALUES
('Desire', '2', '2', JSON_BUILD_OBJECT("network",
JSON_ARRAY_PUSH_STRING('["GSM", "CDMA", "HSPA"]', 'EVDO'),
"body",
"5.11 x 2.59 x 0.46 inches",
"weight",
"143 grams",
"sim",
"Micro-SIM",
"display",
"4.5 inches",
"resolution",
"720 x 1280 pixels",
"os",
"Android Jellybean v4.3"
)
),
('Passion', '2', '2', JSON_BUILD_OBJECT("network",
JSON_ARRAY_PUSH_STRING('["GSM", "CDMA"]', 'HSPA'),
"body",
"6.11 x 3.59 x 0.46 inches",
"weight",
"145 grams",
"sim",
"Micro-SIM",
"display",
"4.5 inches",
"resolution",
"720 x 1280 pixels",
"os",
"Android Jellybean v4.3"
)
),
('Emotion', '2', '2', JSON_BUILD_OBJECT("network" ,
JSON_ARRAY_PUSH_STRING('["GSM", "CDMA"]', 'EVDO'),
"body",
"5.50 x 2.50 x 0.50 inches",
"weight",
"125 grams",
"sim",
"Micro-SIM",
"display",
"5.00 inches",
"resolution",
"720 x 1280 pixels",
"os",
"Android KitKat v4.3"
)
),
('Sensation', '2', '2', JSON_BUILD_OBJECT("network",
JSON_ARRAY_PUSH_STRING('["GSM", "HSPA"]', 'EVDO'),
"body",
"4.00 x 2.00 x 0.75 inches",
"weight",
"150 grams",
"sim",
"Micro-SIM",
"display",
"3.5 inches",
"resolution",
"720 x 1280 pixels",
"os",
"Android Lollipop v4.3"
)
),
('Joy', '2', '2', JSON_BUILD_OBJECT("network",
JSON_ARRAY_PUSH_STRING('["CDMA", "HSPA"]', 'EVDO'),
"body",
"7.00 x 3.50 x 0.25 inches",
"weight",
"250 grams",
"sim",
"Micro-SIM",
"display",
"6.5 inches",
"resolution",
"1920 x 1080 pixels",
"os",
"Android Marshmallow v4.3"
)
);
在本例中,我们不是直接使用JSON,而是使用JSON_BUILD_STORAGE函数构建用于存储的JSON结构。我们还会用到JSON_ARRAY_PUSH_STRING函数创建数组。JSON结构的示例如下:
{
"body" : "5.11 x 2.59 x 0.46 inches",
"display" : "4.5 inches",
"network" : [
"GSM",
"CDMA",
"HSPA",
"EVDO"
],
"os" : "Android Jellybean v4.3",
"resolution" : "720 x 1280 pixels",
"sim" : "Micro-SIM",
"weight" : "143 grams"
}
相机
最后,让我们加载Cameras(相机)这一类别的数据,并在products(产品)表的每个属性列插入对应的值:
-- Cameras
INSERT INTO products (name, brand_id, category_id, attributes) VALUES
('Explorer', '3', '3', '{"sensor_type" : "CMOS", "processor" : "Digic DV III", "scanning_system" : "progressive", "mount_type" : "PL", "monitor_type" : "LCD"}'),
('Runner', '3', '3', '{"sensor_type" : "CMOS", "processor" : "Digic DV II", "scanning_system" : "progressive", "mount_type" : "PL", "monitor_type" : "LED"}'),
('Traveler', '3', '3', '{"sensor_type" : "CMOS", "processor" : "Digic DV II", "scanning_system" : "progressive", "mount_type" : "PL", "monitor_type" : "LCD"}'),
('Walker', '3', '3', '{"sensor_type" : "CMOS", "processor" : "Digic DV I", "scanning_system" : "progressive", "mount_type" : "PL", "monitor_type" : "LED"}'),
('Jumper', '3', '3', '{"sensor_type" : "CMOS", "processor" : "Digic DV I", "scanning_system" : "progressive", "mount_type" : "PL", "monitor_type" : "LCD"}');
在本例中,没有嵌套或数组,而是一个平面JSON结构。例如:
{
"sensor_type" : "CMOS",
"processor" : "Digic DV III",
"scanning_system" : "progressive",
"mount_type" : "PL",
"monitor_type" : "LCD"
}
从这些示例中,我们可以看到,可能需要以各种方式存储JSON数据,并且数据的结构可能会因我们希望存储的属性而异。SingleStore DB可以处理这些不同的要求,并附带了多种可以提供帮助的JSON函数。
示例查询
现在,我们的数据已安全地保存在SingleStore DB中,让我们来看看查询该数据的方法。
首先,让我们看看SingleStore DB使用JSON_GET_TYPE为属性列返回的内容:
SELECT JSON_GET_TYPE(attributes)
FROM products;
结果如下:
+---------------------------+
| JSON_GET_TYPE(attributes) |
+---------------------------+
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
| object |
+---------------------------+
15 rows selected
所有行都是JSON对象。
现在,在产品表中,查询具有一个或多个USB端口和一个或多个HDMI端口的任何电视机的类别:
SELECT * FROM products
WHERE category_id = 1
AND attributes::ports::usb > 0
AND attributes::ports::hdmi > 0;
请注意,我们可以使用双冒号(::)指定我们感兴趣的特定属性的路径。输出如下:
+----+----------+----------+-------------+-------------------------+
| id | name | brand_id | category_id | |
+----+----------+----------+-------------+-------------------------+
| 2 | Octoview | 1 | 1 | {"ports":{"hdmi":1,"usb"|
| 1 | Prime | 1 | 1 | {"ports":{"hdmi":1,"usb"|
| 3 | Dreamer | 1 | 1 | {"ports":{"hdmi":1,"usb"|
+----+----------+----------+-------------+-------------------------+
3 rows selected
接下来,让我们尝试一些更新操作。首先,在产品表中为电视机这一类别添加一个新的属性,命名为body_color,语句如下:
UPDATE products
SET attributes::$body_color = 'red'
WHERE category_id = 1;
如果检查属性,可以看到body_color属性已添加:
Plain Text
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| attributes|
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| {"body_color":"red","ports":{"hdmi":1,"usb":2},"resolution":"1920|
| {"body_color":"red","ports":{"hdmi":1,"usb":0},"resolution":"1366|
| {"body_color":"red","ports":{"hdmi":0,"usb":0},"resolution":"1280|
| {"body_color":"red","ports":{"hdmi":1,"usb":3},"resolution":"2048|
| {"body_color":"red","ports":{"hdmi":1,"usb":1},"resolution":"1600|
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
5 rows selected
接下来,在产品表中为手机这一类别添加一个chipset属性:
UPDATE products
SET attributes::$chipset = 'Qualcomm'
WHERE category_id = 2;
如果检查属性,可以看到chipset已添加:
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| {"body":"5.11 x 2.59 x 0.46 inches","chipset":"Qualcomm Snapdrago|
| {"body":"4.00 x 2.00 x 0.75 inches","chipset":"Qualcomm Snapdrago|
| {"body":"6.11 x 3.59 x 0.46 inches","chipset":"Qualcomm Snapdrago|
| {"body":"5.50 x 2.50 x 0.50 inches","chipset":"Qualcomm Snapdrago|
| {"body":"7.00 x 3.50 x 0.25 inches","chipset":"Qualcomm Snapdrago|
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
5 rows selected
我们还可以将chipset的现有值更新为新值,如下:
UPDATE products
SET attributes::$chipset = 'Qualcomm Snapdragon'
WHERE category_id = 2;
如果检查属性,可以看到chipset已经更新:
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| |
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
| {"body":"5.11 x 2.59 x 0.46 inches","chipset":"Qualcomm Snapdrago|
| {"body":"4.00 x 2.00 x 0.75 inches","chipset":"Qualcomm Snapdrago|
| {"body":"6.11 x 3.59 x 0.46 inches","chipset":"Qualcomm Snapdrago|
| {"body":"5.50 x 2.50 x 0.50 inches","chipset":"Qualcomm Snapdrago|
| {"body":"7.00 x 3.50 x 0.25 inches","chipset":"Qualcomm Snapdrago|
+------------------------------------------------------------------+
5 rows selected
我们还可以删除属性。例如,我们从之前创建的数据中知道,在相机这一类别中有一个属性为mount_type。我们可以按如下方式将产品表中的这一属性删除:
UPDATE products
SET attributes = JSON_DELETE_KEY(attributes, 'mount_type')
WHERE category_id = 3;
如果检查属性,可以看到tsmount_type已经删除:
+------------------------+
| attributes::mount_type |
+------------------------+
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
+------------------------+
5 rows selected
我们还可以写更复杂的语句。例如,在这里,我们使用LIKE运算符来检查os属性。在我们的数据库中,我们有两部带有Jellybean操作系统的手机。
DELETE FROM products
WHERE category_id = 2
AND attributes::$os LIKE '%Jellybean%';
运行了以上命令以后,在数据库中会有三种手机类别。
+----+-----------+----------+-------------+------------------------+
| id | name | brand_id | category_id | |
+----+-----------+----------+--------------------------------------+
| 8 | Emotion | 2 | 2 | {"body":"5.50 x 2.50 x |
| 10 | Joy | 2 | 2 | {"body":"7.00 x 3.50 x |
| 9 | Sensation | 2 | 2 | {"body":"4.00 x 2.00 x |
+----+-----------+----------+-------------+------------------------+
3 rows selected
SingleStore DB支持一组可与JSON数据一起使用的扩展函数集。该文档还包含更多详细信息和示例。
收获:使用Laravel和PHP进行可视化
使用托管服务帐户中的SQL编辑器运行上一部分的命令,是测试代码并快速查看结果的好方法。但是,我们可以更进一步,构建一个简单的Web界面,使我们能够查看数据并进行新建,读取,更新和删除(CRUD)操作。在第一个应用程序开发迭代中,主要关注读取、删除和部分更新操作。我们将来会构建一个完整的解决方案。
我们将删除现有数据库并重新创建它以包含原始数据集。
还将使用Laravel和PHP构建我们的Web界面,并使用以下软件:
sudo apt install php7.4-cli
sudo apt install php-xml
sudo apt install php-mysql
我们还需要安装Composer,按照下载页面上的说明进行操作。下载Composer后,我们会将其移动到bin目录下:
sudo mv composer.phar /usr/local/bin/composer
接下来, 我们将创建一个项目,命名为e-store, 如下:
composer create-project laravel/laravel e-store
然后切换项目的目录:
cd e-store
编辑e-store目录下的**.env**文件:
DB_CONNECTION=mysql
DB_HOST=<TO DO>
DB_PORT=3306
DB_DATABASE=e_store
DB_USERNAME="admin"
DB_PASSWORD="<TO DO>"
创建集群时,应将DB_HOST和DB_PASSWORD中的TO DO替换为从SingleStore托管服务获取的值。另请注意对DB_USERNAME和DB_PASSWORD使用双引号(")。
创建文件
我们需要一种生成所有文件最快的方式,如下:
php artisan make:model -a Brand
php artisan make:model -a Category
php artisan make:model -a Product
对于每个品牌,类别和产品,我们有:
For each of Brand, Category and Product, we obtain:
- A migration, in database/migrations
- A model in app/Models
- A controller, in app/Http/Controllers
- A seeder, in database/seeders
迁移(数据库/迁移)
我们将编辑Brand迁移文件,以便:
public function up()
{
Schema::create('brands', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('name');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
我们将编辑Category迁移文件,以便:
public function up()
{
Schema::create('categories', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('name');
$table->timestamps();
});
}
我们将编辑Product迁移文件,以便:
public function up()
{
Schema::create('products', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->id();
$table->string('name');
$table->unsignedInteger('brand_id');
$table->unsignedInteger('category_id');
$table->json('attributes');
$table->timestamps();
// indexes
$table->index('brand_id');
$table->index('category_id');
});
}
Models (app/Models)
我们将编辑Brand模型文件,以便我们与Product建立1:m关系:
class Brand extends Model
{
use HasFactory;
// A brand has many products
public function products(){
return $this->hasMany('Product')
}
}
Category模型文件,以便我们与Product具有1:m关系:
class Category extends Model
{
use HasFactory;
// A category has many products
public function products(){
return $this->hasMany('Product')
}
}
Product模型文件,以便我们可以通过将属性转换为数组以及与品牌和类别的关系来访问JSON数据:
class Category extends Model
{
use HasFactory;
// A category has many products
public function products(){
return $this->hasMany('Product')
}
}
Controllers (app/Http/Controllers)
对于Web应用程序的第一次迭代,让我们重点介绍ProductController。
index()
我们需要检索产品索引页的所有产品数据,并确保我们拥有每个产品的品牌名称和类别名称。这将需要跨各个表进行连接。我们还将使用simplePaginate()函数,通过每页仅显示五条记录来控制输出。
public function index()
{
$products = Product::select('products.*', 'brands.name as brand_name', 'categories.name as category_name')
->join('brands', 'brands.id', '=', 'products.brand_id')
->join('categories', 'categories.id', '=', 'products.category_id')
->orderBy('products.id')
->simplePaginate(5);
return view('admin.index', compact('products'));
}
show()
为了显示单个产品,我们将执行与index()查询类似的查询,但在这里用first()获取单个产品记录。
public function show(Product $product)
{
$one_product = Product::select('products.*', 'brands.name as brand_name', 'categories.name as category_name')
->join('brands', 'brands.id', '=', 'products.brand_id')
->join('categories', 'categories.id', '=', 'products.category_id')
->where('products.id', $product->id)
->first();
return view('admin.show', compact('one_product'));
}
edit()
要编辑现有产品,我们需要找到要编辑的产品,如果用户希望更改这些产品属性,我们还需要在下拉菜单中提供所有品牌和类别。
public function edit($id)
{
$product = Product::findOrFail($id);
$brands = Brand::orderBy('id')->get();
$categories = Category::orderBy('id')->get();
return view('admin.edit', compact('product', 'brands', 'categories'));
}
update()
在第一个应用程序开发迭代中,我们将允许更新产品名称、品牌和类别,但不允许更新JSON属性。
public function update(Request $request, $id)
{
$updateProduct = $request->validate([
'name' => 'required|max:255',
'brand_id' => 'required|numeric',
'category_id' => 'required|numeric',
]);
Product::whereId($id)->update($updateProduct);
return redirect('/products')->with('success', 'Product has been updated');
}
destroy()
我们可以使用delete()方法轻松的移除产品。
public function destroy($id)
{
$product = Product::findOrFail($id);
$product->delete();
return redirect('/products')->with('success', 'Product has been deleted');
}
Routes (routes/web.php)
在routes目录中的web.php文件中,我们将添加以下内容:
Route::resource(
'products',
ProductController::class
);
Route::resource(
'brands',
BrandController::class
);
Route::resource(
'categories',
CategoryController::class
);
Views (resources/views/admin)
可以在GitHub上找到索引页、展示页和编辑页的三个边栏选项卡文件。提供用于使用HTML和PHP格式化数据的代码,以便在这些文件中进行演示和部分编辑。
运行代码
我们将从e-store目录中运行应用程序,如下所示:
php artisan serve
在Web浏览器中,输入以下内容:
http://localhost:8000/products
输出应类似于图 1:
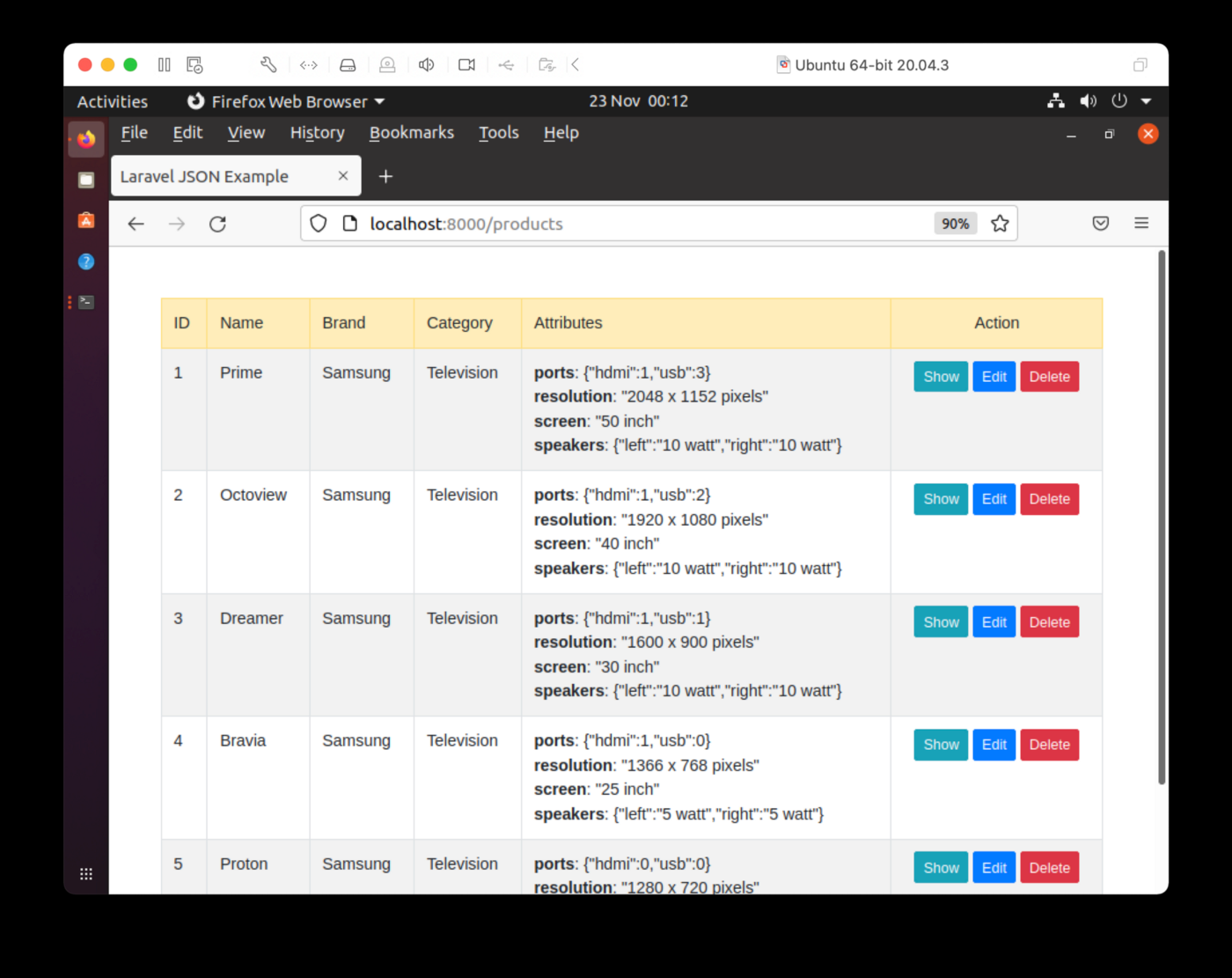
图 1.索引页。
可以看到每个产品的品牌和类别数据都可以准确展示。JSON格式对应的属性展示需要改进,但我们还是可以在第一次迭代中准确看到这些属性的。如果选择“显示”,则可以在单个页面上查看有关产品的详细信息,如图2所示。
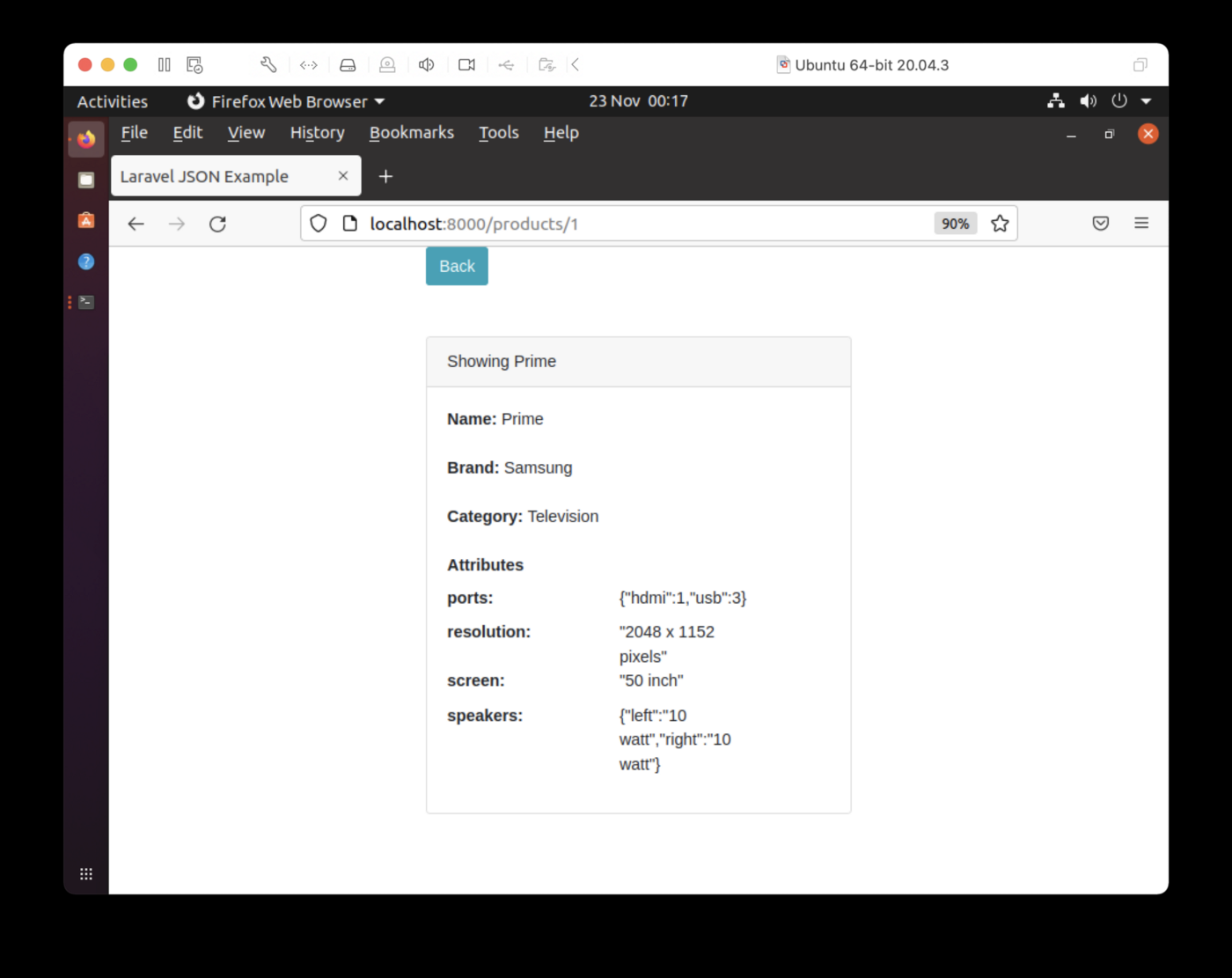
图 2.显示单个产品。
在索引页中,如果选择“编辑”,则可以编辑产品,如图3所示。
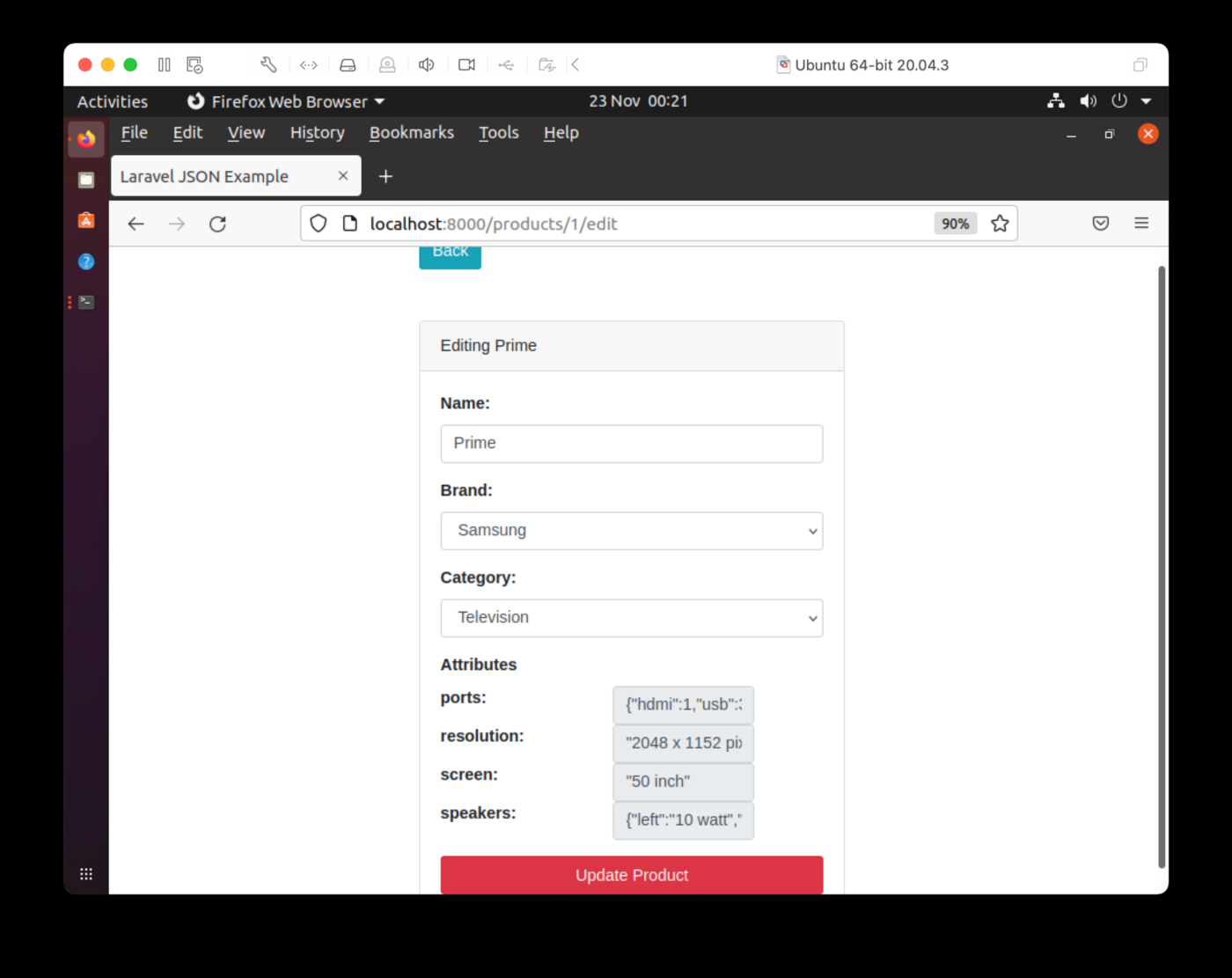
图 3.编辑产品。
我们可以编辑名称并更改品牌和类别。JSON在第一次迭代中不可编辑。
最后,如果我们从索引页中选择“删除”,则可以从数据库中删除产品。在图 4 中,ID 为 1 的产品已被删除。我们可以通过托管服务帐户中的SQL编辑器检查来SingleStore DB并确认这一点。
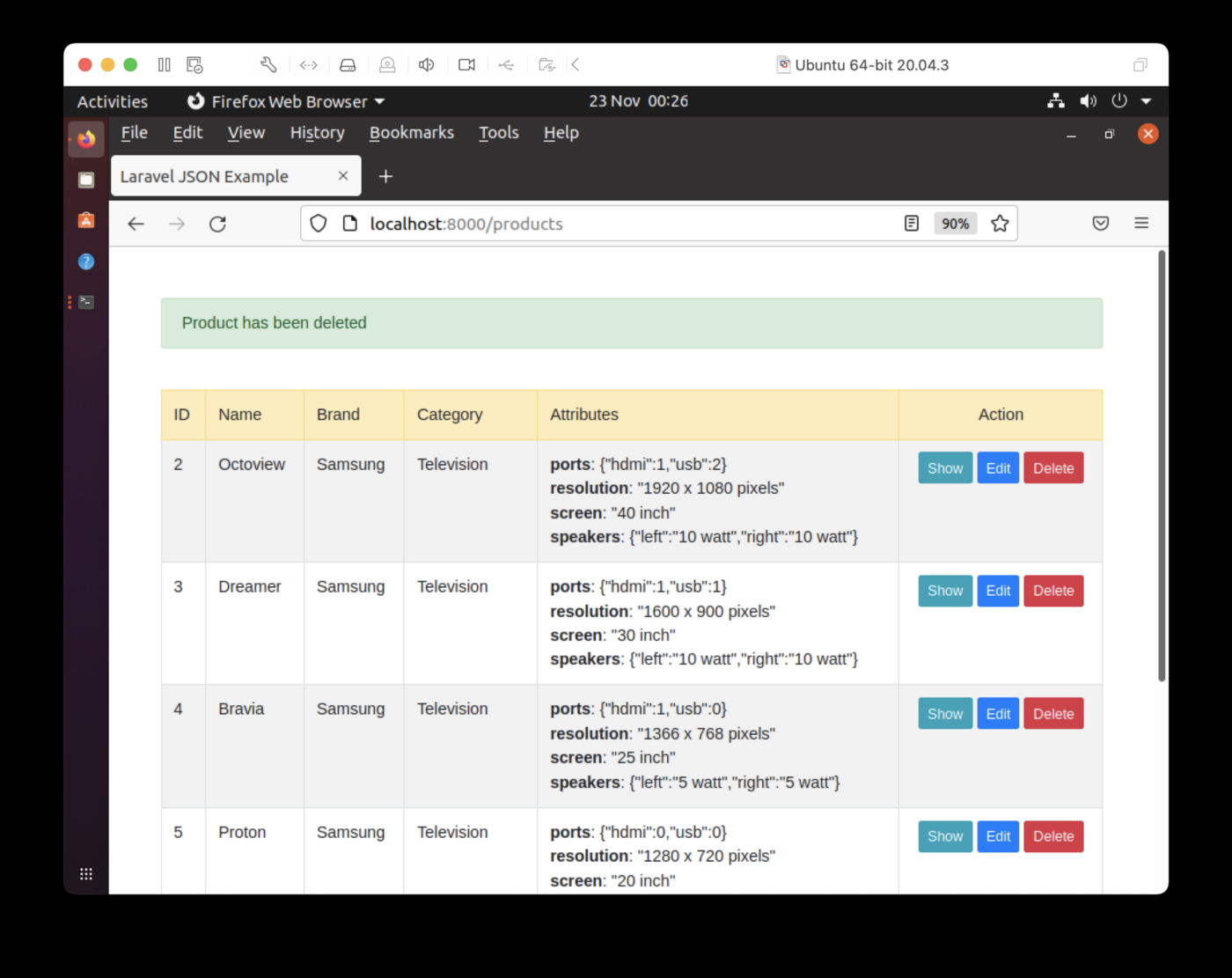
图 4.删除产品。
不同产品JSON的客户端处理
在客户端数据输入和JSON更新方面面临的挑战之一是,对于三种不同产品中的每一种,结构都是可变的。原始DigitalOcean教程中提出的一个解决方案是为每个产品类型创建一个特定的网页。对于少量产品来说,这将是一个很好的解决方案。但是,如果我们存储数十或数百种不同的产品,这不可行。
JSON数据可能是平面的,可能是嵌套的,并且可能含有数组。我们可以通过应用Stackoverflow上提出的解决方案来处理这个问题,使用递归来确定根节点和叶子节点,以正确输出JSON结构。我们可以使用以下示例来演示这一点:
<?php
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/14006609/php-recursion-print-all-elements-of-a-multidimensional-array-with-keys
function pretty_dump($arr, $d=1){
if ($d==1) echo "<pre>"; // HTML Only
if (is_array($arr)){
foreach($arr as $k=>$v){
for ($i=0;$i<$d;$i++){
echo "\t";
}
if (is_array($v)){
echo $k." : ".PHP_EOL;
pretty_dump($v, $d+1);
} else {
echo $k." : ".$v.PHP_EOL;
}
}
}
if ($d==1) echo "</pre>"; // HTML Only
}
$television_json = '{"screen" : "50 inch", "resolution" : "2048 x 1152 pixels", "ports" : {"hdmi" : 1, "usb" : 3}, "speakers" : {"left" : "10 watt", "right" : "10 watt"}}';
$mobile_phone_json = '{"body" : "5.11 x 2.59 x 0.46 inches", "display" : "4.5 inches", "network" : ["GSM", "CDMA", "HSPA", "EVDO"], "os" : "Android Jellybean v4.3", "resolution" : "720 x 1280 pixels", "sim" : "Micro-SIM", "weight" : "143 grams"}';
$camera_json = '{"sensor_type" : "CMOS", "processor" : "Digic DV III", "scanning_system" : "progressive", "mount_type" : "PL", "monitor_type" : "LCD"}';
$television_array = json_decode($television_json, true);
$mobile_phone_array = json_decode($mobile_phone_json, true);
$camera_array = json_decode($camera_json, true);
echo "Television:";
pretty_dump($television_array);
echo "Mobile Phone:";
pretty_dump($mobile_phone_array);
echo "Camera:";
pretty_dump($camera_array);
?>
输出结果如下:
Television:
screen : 50 inch
resolution : 2048 x 1152 pixels
ports :
hdmi : 1
usb : 3
speakers :
left : 10 watt
right : 10 watt
Mobile Phone:
body : 5.11 x 2.59 x 0.46 inches
display : 4.5 inches
network :
0 : GSM
1 : CDMA
2 : HSPA
3 : EVDO
os : Android Jellybean v4.3
resolution : 720 x 1280 pixels
sim : Micro-SIM
weight : 143 grams
Camera:
sensor_type : CMOS
processor : Digic DV III
scanning_system : progressive
mount_type : PL
monitor_type : LCD
这为我们提供了所有正确的keys和values。
总结
在本文中,我们已经看到SingleStore DB可以轻松管理不同复杂性的JSON数据。它支持可用于JSON数据的各种函数,我们在本文中使用了许多这些函数。此外,可以看到,我们可以使用SQL查询来对关系型数据和JSON数据进行联合操作。最后,我们使用Laravel和PHP为我们的数据库系统构建了一个简单的Web界面,这使我们能够探索数据并进行一些改进。
文中相关链接:






