前 言
Oracle的位图索引适用于列的基数很少,可枚举,重复值很多,数据不会被经常更新的列。
它的索引结构是一个键值对应很多行(rowid),对于报表类数据库,重复率高的数据,特定类型的查询例如count、or、and等逻辑操作,只需要进行位运算即可得到我们需要的结果,可以说是相当的效率。
最近项目在进行上云工作,有许多Oracle到PostgreSQL的迁移要做。其中涉及到位图索引,
然而PostgreSQL没有位图索引。怎么改造这种索引,来实现相应的索引场景呢?
今天我们来聊一聊PostgreSQL中的黑科技Brin索引。
索 引 原 理
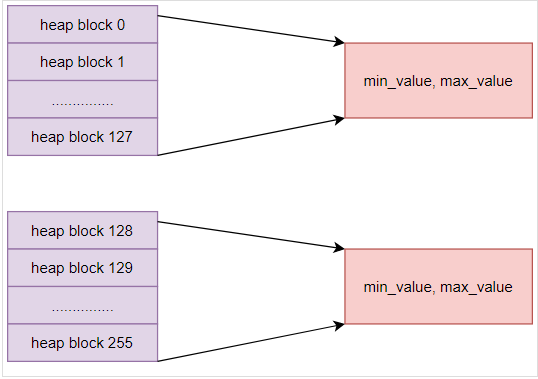
BRIN索引是块级索引,有别于B-TREE等索引,BRIN记录并不是以行号为单位记录索引明细,而是记录每个数据块或者每段连续的数据块的统计信息。因此BRIN索引空间占用特别的小,对数据写入、更新、删除的影响也很小。
BRIN索引的扫描原理很简单,扫描BRIN的元数据,根据元数据和用户输入的条件进行比较,过滤不符合条件的HEAPPAGE,只扫描需要扫描的HEAPPAGE。
如果数据排列的比较随机时,那么索引效果就非常差。达不到索引快速扫描的效果。
索引测试
我们创建两张表,一张顺序插入,一张乱序插入:
--顺序插入tab_brin1:
otter_pg=# create table tab_brin1(id int,name varchar(40),c_time timestamp); CREATE TABLE otter_pg=# insert into tab_brin1 select *,md5(random()::text),clock_timestamp() from generate_series(1,10000000); INSERT 0 10000000 |
--乱序插入tab_brin2:
otter_pg=# create table tab_brin2(id int,name varchar(40),c_time timestamp); CREATE TABLE tter_pg=# insert into tab_brin2 select (random()*(10^6))::integer,md5(random()::text),timestamp '2019-01-10 20:00:00' + random() * (timestamp '2019-01-20 20:00:00' - timestamp '2021-01-10 10:00:00') from generate_series(1,10000000); INSERT 0 10000000 |
--两张表都创建BRIN索引和BTREE索引
otter_pg=# create index idx1_tab_brin1 on tab_brin1 using brin(c_time); CREATE INDEX otter_pg=# create index idx1_tab_brin2 on tab_brin2 using brin(c_time); CREATE INDEX otter_pg=# create index idx2_tab_brin1 on tab_brin1 using btree(c_time); CREATE INDEX otter_pg=# create index idx2_tab_brin2 on tab_brin1 using btree(c_time); CREATE INDEX |
--我们看看索引大小
可以看到表为700M,BTREE索引需要214M,而BRIN索引只有40K。
otter_pg=# select pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size('tab_brin1')); pg_size_pretty ---------------- 730 MB otter_pg=# select pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size('idx1_tab_brin1')); pg_size_pretty ---------------- 40 kB otter_pg=# select pg_size_pretty(pg_relation_size('idx2_tab_brin1')); pg_size_pretty ---------------- 214 MB |
--我们在来看看BRIN索引的使用。
首先看看两表的离散度,如下可以看出tab_brin1表的逻辑顺序和物理顺序一致性更好些。
otter_pg=# select correlation from pg_stats where tablename='tab_brin1'; correlation --------------------- 1 0.0048282277 1 otter_pg=# select correlation from pg_stats where tablename='tab_brin2'; correlation --------------------- 0.0010042704 -0.002086642 0.006167772 |
对比下使用两表BRIN索引时的效率,这里我们需要删除前面创建的BTREE索引。
--tab_brin1的执行计划如下:可以看到耗时0.6ms。
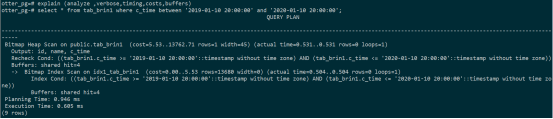
--tab_brin2的执行计划如下:可以看到耗时21ms。
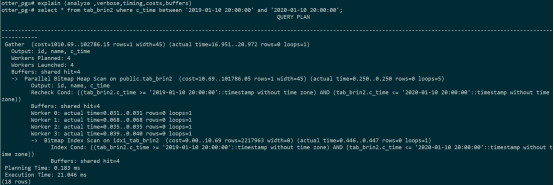
经过分析,物理顺序和逻辑顺序越一致,该列更适合建立BRIN索引。
Pages_per_range参数调优
BRIN索引有一个参数pages_per_range可以用来近一步提升Brin索引的性能。
pages_per_range是粒度,默认为128(表示每128个数据块统计一次边界),它影响BRIN索引的精确度和 BRIN索引的大小。
--精度为1时,耗时46.6ms
otter_pg=# create index idx1_tab_brin1 on tab_brin1 using brin(c_time) with (pages_per_range=1); CREATE INDEX otter_pg=# otter_pg=# explain (analyze ,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select * from tab_brin1 where c_time between '2019-01-10 20:00:00' and '2020-01-10 20:00:00'; QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ----- Bitmap Heap Scan on public.tab_brin1 (cost=424.40..543.34 rows=1 width=45) (actual time=46.544..46.544 rows=0 loops=1) Output: id, name, c_time Recheck Cond: ((tab_brin1.c_time >= '2019-01-10 20:00:00'::timestamp without time zone) AND (tab_brin1.c_time <= '2020-01-10 20:00:00'::timestamp without time zone)) Buffers: shared hit=527 -> Bitmap Index Scan on idx1_tab_brin1 (cost=0.00..424.40 rows=107 width=0) (actual time=46.536..46.536 rows=0 loops=1) Index Cond: ((tab_brin1.c_time >= '2019-01-10 20:00:00'::timestamp without time zone) AND (tab_brin1.c_time <= '2020-01-10 20:00:00'::timestamp without time zo ne)) Buffers: shared hit=527 Planning Time: 0.632 ms Execution Time: 46.639 ms (9 rows) |
--精度为50时,耗时1.18ms
otter_pg=# create index idx1_tab_brin1 on tab_brin1 using brin(c_time) with (pages_per_range=50); CREATE INDEX otter_pg=# explain (analyze ,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select * from tab_brin1 where c_time between '2019-01-10 20:00:00' and '2020-01-10 20:00:00'; QUERY PLAN ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ ----- Bitmap Heap Scan on public.tab_brin1 (cost=10.91..5688.47 rows=1 width=45) (actual time=1.115..1.115 rows=0 loops=1) Output: id, name, c_time Recheck Cond: ((tab_brin1.c_time >= '2019-01-10 20:00:00'::timestamp without time zone) AND (tab_brin1.c_time <= '2020-01-10 20:00:00'::timestamp without time zone)) Buffers: shared hit=11 -> Bitmap Index Scan on idx1_tab_brin1 (cost=0.00..10.91 rows=5348 width=0) (actual time=1.105..1.105 rows=0 loops=1) Index Cond: ((tab_brin1.c_time >= '2019-01-10 20:00:00'::timestamp without time zone) AND (tab_brin1.c_time <= '2020-01-10 20:00:00'::timestamp without time zo ne)) Buffers: shared hit=11 Planning Time: 0.566 ms Execution Time: 1.186 ms (9 rows) |
pages_per_range定义数据块的数量,为BRIN索引的每条记录统计的数据块范围。默认值为128。
如果这个值很大,则索引就会很小,索引扫描就会很迅速,但是后续内存中的Recheck就会很多,因为把大量的不相关数据拉到内存中了。
如果这个值很小,索引的过滤性越好,但索引也会越大。由于每筛选一次字段PostgreSQL 都要扫描全部的BRIN索引,所花费的时间也会变长,因此需要根据表的大小与应用场景去调整其值的大小。
BRIN主要适用于类似时序数据之类的,有着天然的顺序,而且都是添加写的场景。相比于BTREE索引,它的体积小得多,非常适用于大数据量的场景。