提交代码
整个代码的提交流程
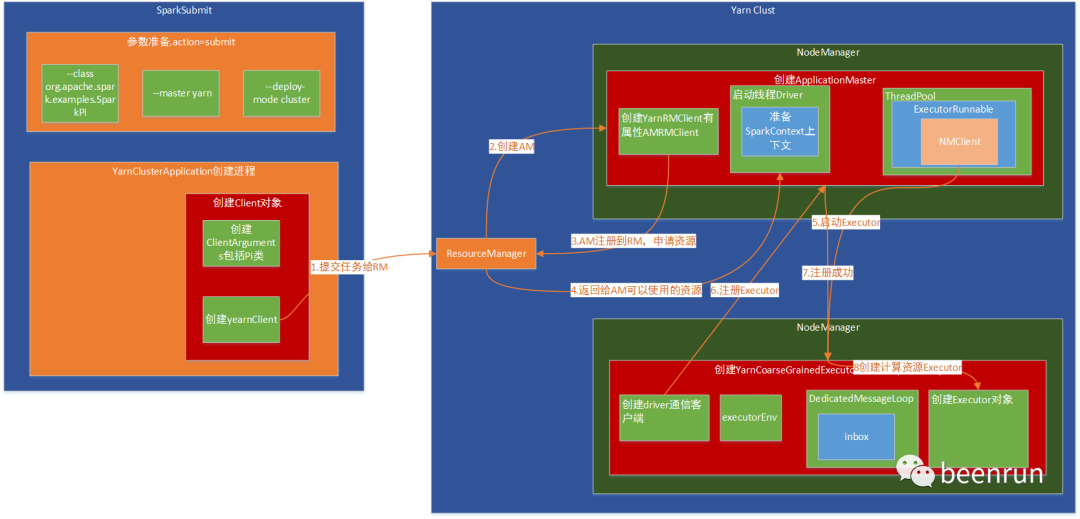
(1)提交任务给RM(ResourceManager)
(2)RM创建AM(ApplicationMaster)
(3)AM注册回RM,并告知RM执行任务需要的资源
(4)RM返回AM需要的资源
(5)启动YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend
(6)注册Executor到AM
(7)Executor注册到AM成果
(8)YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend收到成果消息,进行创建Executor对象
整个执行环境创建完成
./bin/spark-submit --class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \--master yarn \--deploy-mode cluster \--driver-memory 4g \--executor-memory 2g \--executor-cores 1 \--queue thequeue \examples/jars/spark-examples*.jar \10
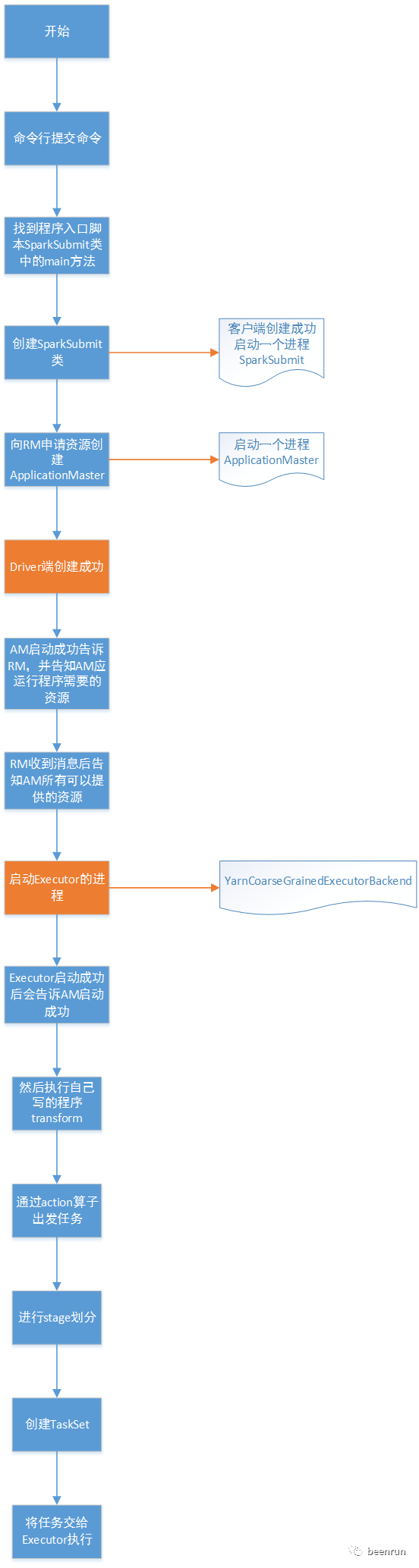
2.入口脚本
exec "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit "$@"
3.入口类为org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit
找到该类的main方法,
在java中遇到入口类,就会有一个main方法,一般一个main方法要创建一个进程。
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {val submit = new SparkSubmit()submit.doSubmit(args)}
4.调用submit.doSubmit(args)
接着会调用模式匹配,需要知道 val appArgs = parseArguments(args) 执行完成后返回结果是什么?
case SparkSubmitAction.SUBMIT => submit(appArgs, uninitLog)
def doSubmit(args: Array[String]): Unit = {// Initialize logging if it hasn't been done yet. Keep track of whether logging needs to// be reset before the application starts. val uninitLog = initializeLogIfNecessary(true, silent = true)val appArgs = parseArguments(args)if (appArgs.verbose) {logInfo(appArgs.toString)}appArgs.action match {case SparkSubmitAction.SUBMIT => submit(appArgs, uninitLog)case SparkSubmitAction.KILL => kill(appArgs)case SparkSubmitAction.REQUEST_STATUS => requestStatus(appArgs)case SparkSubmitAction.PRINT_VERSION => printVersion()}}
4.1对参数进行初始化
这里创建了对象SparkSubmitArguments,该对象的action属性就是上面返回的结果。
从代码中获取提交的时候获取的是SUBMIT
protected def parseArguments(args: Array[String]): SparkSubmitArguments = {new SparkSubmitArguments(args)}// Action should be SUBMIT unless otherwise specifiedaction = Option(action).getOrElse(SUBMIT)
4.2对参数进行初始化--master
获取--class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \
--master yarn \
case MASTER =>master = valuecase CLASS =>mainClass = value
5.进入submit(appArgs, uninitLog) 方法
doRunMain()-->runMain(args, uninitLog)
构建提交的任务的环境,这里的mainClass 就是childMainClass,所以需要通过prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)找到childMainClass是如何进行赋值的。
val (childArgs, childClasspath, sparkConf, childMainClass) = prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)//获取类加载器val loader = getSubmitClassLoader(sparkConf)//通过反射获取类名称mainClass = Utils.classForName(childMainClass)//判断类型信息是否为SparkApplication的子类val app: SparkApplication = if (classOf[SparkApplication].isAssignableFrom(mainClass)) {mainClass.getConstructor().newInstance().asInstanceOf[SparkApplication]} else {new JavaMainApplication(mainClass)}//启动类app.start(childArgs.toArray, sparkConf)
5.1 进入方法prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)进行赋值
查找返回的结果childMainClass,咱们提交方式是isYarnCluster,所以获取
childMainClass=org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.YarnClusterApplicationprivate[deploy] val YARN_CLUSTER_SUBMIT_CLASS ="org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.YarnClusterApplication"
if (isYarnCluster) {childMainClass = YARN_CLUSTER_SUBMIT_CLASSif (args.isPython) {childArgs += ("--primary-py-file", args.primaryResource)childArgs += ("--class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.PythonRunner")} else if (args.isR) {val mainFile = new Path(args.primaryResource).getNamechildArgs += ("--primary-r-file", mainFile)childArgs += ("--class", "org.apache.spark.deploy.RRunner")} else {if (args.primaryResource != SparkLauncher.NO_RESOURCE) {childArgs += ("--jar", args.primaryResource)}childArgs += ("--class", args.mainClass)}if (args.childArgs != null) {args.childArgs.foreach { arg => childArgs += ("--arg", arg) }}}
6.调用start接口
是个接口,一定有实现类,
这里创建Client对象
Client对象中有
private[spark] trait SparkApplication {def start(args: Array[String], conf: SparkConf): Unit}找到实现类,调用run()方法private[spark] class YarnClusterApplication extends SparkApplication {override def start(args: Array[String], conf: SparkConf): Unit = {// SparkSubmit would use yarn cache to distribute files & jars in yarn mode,// so remove them from sparkConf here for yarn mode. conf.remove(JARS)conf.remove(FILES)conf.remove(ARCHIVES)new Client(new ClientArguments(args), conf, null).run()}}
7.在Client类中创建yarnClient
YarnClient是一个抽象类,实现类为YarnClientImpl
private val yarnClient = YarnClient.createYarnClient创建:YarnClient@Publicpublic static YarnClient createYarnClient() {YarnClient client = new YarnClientImpl();return client;}这里会有一个rmClientpublic class YarnClientImpl extends YarnClient {private static final Log LOG = LogFactory.getLog(YarnClientImpl.class);protected ApplicationClientProtocol rmClient;
8.提交应用
提交应用到ResourceManager,资源管理器会根据提交的信息,找一个合适的容器来执行应用。
提交应用
Submit an application to the ResourceManager. If set spark.yarn.submit.waitAppCompletion to true, it will stay alive reporting the application's status until the application has exited for any reason. Otherwise, the client process will exit after submission. If the application finishes with a failed, killed, or undefined status, throw an appropriate SparkException.
def run(): Unit = {//获取appid,每一个应用有一个唯一id后面所有日志都会用到this.appId = submitApplication()if (!launcherBackend.isConnected() && fireAndForget) {val report = getApplicationReport(appId)val state = report.getYarnApplicationStatelogInfo(s"Application report for $appId (state: $state)")logInfo(formatReportDetails(report, getDriverLogsLink(report)))if (state == YarnApplicationState.FAILED || state == YarnApplicationState.KILLED) {throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId finished with status: $state")}} else {val YarnAppReport(appState, finalState, diags) = monitorApplication(appId)if (appState == YarnApplicationState.FAILED || finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED) {diags.foreach { err =>logError(s"Application diagnostics message: $err")}throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId finished with failed status")}if (appState == YarnApplicationState.KILLED || finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.KILLED) {throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId is killed")}if (finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.UNDEFINED) {throw new SparkException(s"The final status of application $appId is undefined")}}}
8.1.提交到ResourceManager
client和ResourceManager建立联系,获取ApplicationId,这里做的事情比较多,后面再详细说
主要的是:准备ApplicationMaster的容器环境和提交环境
建立ResourceManager的链接,然后进行提交
val containerContext = createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse)
def submitApplication(): ApplicationId = {ResourceRequestHelper.validateResources(sparkConf)var appId: ApplicationId = nulltry {launcherBackend.connect()yarnClient.init(hadoopConf)yarnClient.start()logInfo("Requesting a new application from cluster with %d NodeManagers".format(yarnClient.getYarnClusterMetrics.getNumNodeManagers))// Get a new application from our RMval newApp = yarnClient.createApplication()val newAppResponse = newApp.getNewApplicationResponse()appId = newAppResponse.getApplicationId()// The app staging dir based on the STAGING_DIR configuration if configured// otherwise based on the users home directory. scalastyle:off FileSystemGet val appStagingBaseDir = sparkConf.get(STAGING_DIR).map { new Path(_, UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser.getShortUserName) }.getOrElse(FileSystem.get(hadoopConf).getHomeDirectory())stagingDirPath = new Path(appStagingBaseDir, getAppStagingDir(appId))// scalastyle:on FileSystemGetnew CallerContext("CLIENT", sparkConf.get(APP_CALLER_CONTEXT),Option(appId.toString)).setCurrentContext()// Verify whether the cluster has enough resources for our AMverifyClusterResources(newAppResponse)// Set up the appropriate contexts to launch our AM//为AM使用的容器准备,val containerContext = createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse)//准备提交环境val appContext = createApplicationSubmissionContext(newApp, containerContext)// Finally, submit and monitor the applicationlogInfo(s"Submitting application $appId to ResourceManager")yarnClient.submitApplication(appContext)launcherBackend.setAppId(appId.toString)reportLauncherState(SparkAppHandle.State.SUBMITTED)appId} catch {case e: Throwable =>if (stagingDirPath != null) {cleanupStagingDir()}throw e}}
8.2在获取容器中
为创建ApplicationMasterContainer准备。在某个NM中创建ApplicationMaster,
Set up a ContainerLaunchContext to launch our ApplicationMaster container. This sets up the launch environment, java options, and the command for launching the AM.
命令行
// Command for the ApplicationMasterval commands = prefixEnv ++Seq(Environment.JAVA_HOME.$$() + "/bin/java", "-server") ++javaOpts ++ amArgs ++Seq("1>", ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR + "/stdout","2>", ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR + "/stderr")创建类,会创建一个进程。val amClass =if (isClusterMode) {Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster").getName} else {Utils.classForName("org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ExecutorLauncher").getName}
9.ApplicationMaster类
是一个进程,找main,伴生对象
创建了ApplicationMaster类,在这个类中创建了YarnRMClient
private val client = new YarnRMClient()
在后面有一个run方法,开始运行ApplicationMaster
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {SignalUtils.registerLogger(log)val amArgs = new ApplicationMasterArguments(args)val sparkConf = new SparkConf()if (amArgs.propertiesFile != null) {Utils.getPropertiesFromFile(amArgs.propertiesFile).foreach { case (k, v) =>sparkConf.set(k, v)}}// Set system properties for each config entry. This covers two use cases:// - The default configuration stored by the SparkHadoopUtil class - The user application creating a new SparkConf in cluster mode / // Both cases create a new SparkConf object which reads these configs from system properties. sparkConf.getAll.foreach { case (k, v) =>sys.props(k) = v}val yarnConf = new YarnConfiguration(SparkHadoopUtil.newConfiguration(sparkConf))master = new ApplicationMaster(amArgs, sparkConf, yarnConf)val ugi = sparkConf.get(PRINCIPAL) match {// We only need to log in with the keytab in cluster mode. In client mode, the driver// handles the user keytab. case Some(principal) if master.isClusterMode =>val originalCreds = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().getCredentials()SparkHadoopUtil.get.loginUserFromKeytab(principal, sparkConf.get(KEYTAB).orNull)val newUGI = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser()if (master.appAttemptId == null || master.appAttemptId.getAttemptId > 1) {// Re-obtain delegation tokens if this is not a first attempt, as they might be outdated// as of now. Add the fresh tokens on top of the original user's credentials (overwrite). // Set the context class loader so that the token manager has access to jars // distributed by the user. Utils.withContextClassLoader(master.userClassLoader) {val credentialManager = new HadoopDelegationTokenManager(sparkConf, yarnConf, null)credentialManager.obtainDelegationTokens(originalCreds)}}// Transfer the original user's tokens to the new user, since it may contain needed tokens// (such as those user to connect to YARN). newUGI.addCredentials(originalCreds)newUGIcase _ =>SparkHadoopUtil.get.createSparkUser()}ugi.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction[Unit]() {//这里的run方法,开始启动override def run(): Unit = System.exit(master.run())})}
9.1 YarnRMClient类和ApplicationMaster类和RM之间建立通信的客户端
Handles registering and unregistering the application with the YARN ResourceManager.
10.开始运行ApplicationMaster
如果是集群模式就运行runDriver()
//判断是否是集群模式,if (isClusterMode) {runDriver()} else {runExecutorLauncher()}
11.开始运行driver
这里通过一个线程进行创建driver
启动线程startUserApplication()
private def runDriver(): Unit = {addAmIpFilter(None, System.getenv(ApplicationConstants.APPLICATION_WEB_PROXY_BASE_ENV))//获取一个线程,启动应用程序userClassThread = startUserApplication()// This a bit hacky, but we need to wait until the spark.driver.port property has// been set by the Thread executing the user class. logInfo("Waiting for spark context initialization...")val totalWaitTime = sparkConf.get(AM_MAX_WAIT_TIME)try {val sc = ThreadUtils.awaitResult(sparkContextPromise.future,Duration(totalWaitTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))if (sc != null) {val rpcEnv = sc.env.rpcEnvval userConf = sc.getConfval host = userConf.get(DRIVER_HOST_ADDRESS)val port = userConf.get(DRIVER_PORT)registerAM(host, port, userConf, sc.ui.map(_.webUrl), appAttemptId)val driverRef = rpcEnv.setupEndpointRef(RpcAddress(host, port),YarnSchedulerBackend.ENDPOINT_NAME)createAllocator(driverRef, userConf, rpcEnv, appAttemptId, distCacheConf)} else {// Sanity check; should never happen in normal operation, since sc should only be null// if the user app did not create a SparkContext. throw new IllegalStateException("User did not initialize spark context!")}resumeDriver()userClassThread.join()} catch {case e: SparkException if e.getCause().isInstanceOf[TimeoutException] =>logError(s"SparkContext did not initialize after waiting for $totalWaitTime ms. " +"Please check earlier log output for errors. Failing the application.")finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED,ApplicationMaster.EXIT_SC_NOT_INITED,"Timed out waiting for SparkContext.")} finally {resumeDriver()}}
12.开始运行driver
driver进行创建,并且该线程已经运行。
driver是一个线程
driver启动成果,获取SparkContext上下文环境成果,后面可以创建Executor
/*** Start the user class, which contains the spark driver, in a separate Thread. * If the main routine exits cleanly or exits with System.exit(N) for any N * we assume it was successful, for all other cases we assume failure. * * Returns the user thread that was started. */private def startUserApplication(): Thread = {logInfo("Starting the user application in a separate Thread")var userArgs = args.userArgsif (args.primaryPyFile != null && args.primaryPyFile.endsWith(".py")) {// When running pyspark, the app is run using PythonRunner. The second argument is the list// of files to add to PYTHONPATH, which Client.scala already handles, so it's empty. userArgs = Seq(args.primaryPyFile, "") ++ userArgs}if (args.primaryRFile != null &&(args.primaryRFile.endsWith(".R") || args.primaryRFile.endsWith(".r"))) {// TODO(davies): add R dependencies here}val mainMethod = userClassLoader.loadClass(args.userClass).getMethod("main", classOf[Array[String]])val userThread = new Thread {override def run(): Unit = {try {if (!Modifier.isStatic(mainMethod.getModifiers)) {logError(s"Could not find static main method in object ${args.userClass}")finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED, ApplicationMaster.EXIT_EXCEPTION_USER_CLASS)} else {mainMethod.invoke(null, userArgs.toArray)finish(FinalApplicationStatus.SUCCEEDED, ApplicationMaster.EXIT_SUCCESS)logDebug("Done running user class")}} catch {case e: InvocationTargetException =>e.getCause match {case _: InterruptedException =>// Reporter thread can interrupt to stop user classcase SparkUserAppException(exitCode) =>val msg = s"User application exited with status $exitCode"logError(msg)finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED, exitCode, msg)case cause: Throwable =>logError("User class threw exception: " + cause, cause)finish(FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED,ApplicationMaster.EXIT_EXCEPTION_USER_CLASS,"User class threw exception: " + StringUtils.stringifyException(cause))}sparkContextPromise.tryFailure(e.getCause())} finally {// Notify the thread waiting for the SparkContext, in case the application did not// instantiate one. This will do nothing when the user code instantiates a SparkContext // (with the correct master), or when the user code throws an exception (due to the // tryFailure above). sparkContextPromise.trySuccess(null)}}}userThread.setContextClassLoader(userClassLoader)userThread.setName("Driver")userThread.start()userThread}
13.注册AM到RM
接着第11步的注册AM执行,注册成果后,RM知道该应用需要多少资源,后面就根据需要进行资源分配,返回给AM,告诉AM多少资源可以使用,开始创建Executor
registerAM(host, port, userConf, sc.ui.map(_.webUrl), appAttemptId)createAllocator(driverRef, userConf, rpcEnv, appAttemptId, distCacheConf)private def createAllocator(driverRef: RpcEndpointRef,_sparkConf: SparkConf,rpcEnv: RpcEnv,appAttemptId: ApplicationAttemptId,distCacheConf: SparkConf): Unit = {// In client mode, the AM may be restarting after delegation tokens have reached their TTL. So// always contact the driver to get the current set of valid tokens, so that local resources can // be initialized below. if (!isClusterMode) {val tokens = driverRef.askSync[Array[Byte]](RetrieveDelegationTokens)if (tokens != null) {SparkHadoopUtil.get.addDelegationTokens(tokens, _sparkConf)}}val appId = appAttemptId.getApplicationId().toString()val driverUrl = RpcEndpointAddress(driverRef.address.host, driverRef.address.port,CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.ENDPOINT_NAME).toStringval localResources = prepareLocalResources(distCacheConf)// Before we initialize the allocator, let's log the information about how executors will// be run up front, to avoid printing this out for every single executor being launched. // Use placeholders for information that changes such as executor IDs. logInfo {val executorMemory = _sparkConf.get(EXECUTOR_MEMORY).toIntval executorCores = _sparkConf.get(EXECUTOR_CORES)val dummyRunner = new ExecutorRunnable(None, yarnConf, _sparkConf, driverUrl, "<executorId>","<hostname>", executorMemory, executorCores, appId, securityMgr, localResources,ResourceProfile.DEFAULT_RESOURCE_PROFILE_ID)dummyRunner.launchContextDebugInfo()}allocator = client.createAllocator(yarnConf,_sparkConf,appAttemptId,driverUrl,driverRef,securityMgr,localResources)// Initialize the AM endpoint *after* the allocator has been initialized. This ensures// that when the driver sends an initial executor request (e.g. after an AM restart), // the allocator is ready to service requests. rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("YarnAM", new AMEndpoint(rpcEnv, driverRef))//返回集群可以使用的资源列表allocator.allocateResources()val ms = MetricsSystem.createMetricsSystem(MetricsSystemInstances.APPLICATION_MASTER, sparkConf)val prefix = _sparkConf.get(YARN_METRICS_NAMESPACE).getOrElse(appId)ms.registerSource(new ApplicationMasterSource(prefix, allocator))// do not register static sources in this case as per SPARK-25277ms.start(false)metricsSystem = Some(ms)reporterThread = launchReporterThread()}
14.RM告诉AM有多少资源可以使用
allocator.allocateResources()
注意这里使用多线中的同步synchronized
获取可以分配的容器,如果有可以分配的容器, handleAllocatedContainers(allocatedContainers.asScala.toSeq) 开始处理容器
Request resources such that, if YARN gives us all we ask for, we'll have a number of containers equal to maxExecutors.
Deal with any containers YARN has granted to us by possibly launching executors in them.
This must be synchronized because variables read in this method are mutated by other methods.
def allocateResources(): Unit = synchronized {updateResourceRequests()val progressIndicator = 0.1f// Poll the ResourceManager. This doubles as a heartbeat if there are no pending container// requests. val allocateResponse = amClient.allocate(progressIndicator)val allocatedContainers = allocateResponse.getAllocatedContainers()allocatorNodeHealthTracker.setNumClusterNodes(allocateResponse.getNumClusterNodes)if (allocatedContainers.size > 0) {logDebug(("Allocated containers: %d. Current executor count: %d. " +"Launching executor count: %d. Cluster resources: %s.").format(allocatedContainers.size,getNumExecutorsRunning,getNumExecutorsStarting,allocateResponse.getAvailableResources))handleAllocatedContainers(allocatedContainers.asScala.toSeq)}val completedContainers = allocateResponse.getCompletedContainersStatuses()if (completedContainers.size > 0) {logDebug("Completed %d containers".format(completedContainers.size))processCompletedContainers(completedContainers.asScala.toSeq)logDebug("Finished processing %d completed containers. Current running executor count: %d.".format(completedContainers.size, getNumExecutorsRunning))}}
15.获取container后对容器进行处理
运行容器,创建Executors
这里会使用线程池,创建executor
容器按照就近原则使用,
创建ExecutorRunnable
runAllocatedContainers(containersToUse)logInfo("Received %d containers from YARN, launching executors on %d of them.".format(allocatedContainers.size, containersToUse.size))/*** Launches executors in the allocated containers. */private def runAllocatedContainers(containersToUse: ArrayBuffer[Container]): Unit = synchronized {//对容器进行分类,因为容器可能在不同的机器上,也可能在不同的机架上,所以按照就近原则使用for (container <- containersToUse) {val rpId = getResourceProfileIdFromPriority(container.getPriority)executorIdCounter += 1val executorHostname = container.getNodeId.getHostval containerId = container.getIdval executorId = executorIdCounter.toStringval yarnResourceForRpId = rpIdToYarnResource.get(rpId)assert(container.getResource.getMemory >= yarnResourceForRpId.getMemory)logInfo(s"Launching container $containerId on host $executorHostname " +s"for executor with ID $executorId for ResourceProfile Id $rpId")def updateInternalState(): Unit = synchronized {getOrUpdateRunningExecutorForRPId(rpId).add(executorId)getOrUpdateNumExecutorsStartingForRPId(rpId).decrementAndGet()executorIdToContainer(executorId) = containercontainerIdToExecutorIdAndResourceProfileId(container.getId) = (executorId, rpId)val localallocatedHostToContainersMap = getOrUpdateAllocatedHostToContainersMapForRPId(rpId)val containerSet = localallocatedHostToContainersMap.getOrElseUpdate(executorHostname,new HashSet[ContainerId])containerSet += containerIdallocatedContainerToHostMap.put(containerId, executorHostname)}val rp = rpIdToResourceProfile(rpId)val defaultResources = ResourceProfile.getDefaultProfileExecutorResources(sparkConf)val containerMem = rp.executorResources.get(ResourceProfile.MEMORY).map(_.amount).getOrElse(defaultResources.executorMemoryMiB).toIntval containerCores = rp.getExecutorCores.getOrElse(defaultResources.cores)val rpRunningExecs = getOrUpdateRunningExecutorForRPId(rpId).sizeif (rpRunningExecs < getOrUpdateTargetNumExecutorsForRPId(rpId)) {getOrUpdateNumExecutorsStartingForRPId(rpId).incrementAndGet()if (launchContainers) {launcherPool.execute(() => {try {new ExecutorRunnable(Some(container),conf,sparkConf,driverUrl,executorId,executorHostname,containerMem,containerCores,appAttemptId.getApplicationId.toString,securityMgr,localResources,rp.id).run()updateInternalState()} catch {case e: Throwable =>getOrUpdateNumExecutorsStartingForRPId(rpId).decrementAndGet()if (NonFatal(e)) {logError(s"Failed to launch executor $executorId on container $containerId", e)// Assigned container should be released immediately// to avoid unnecessary resource occupation. amClient.releaseAssignedContainer(containerId)} else {throw e}}})} else {// For test onlyupdateInternalState()}} else {logInfo(("Skip launching executorRunnable as running executors count: %d " +"reached target executors count: %d.").format(rpRunningExecs,getOrUpdateTargetNumExecutorsForRPId(rpId)))}}}
16.调用run方法
def run(): Unit = {logDebug("Starting Executor Container")nmClient = NMClient.createNMClient()nmClient.init(conf)nmClient.start()startContainer()}
17.启动container
启动指令val commands = prepareCommand()
def startContainer(): java.util.Map[String, ByteBuffer] = {val ctx = Records.newRecord(classOf[ContainerLaunchContext]).asInstanceOf[ContainerLaunchContext]val env = prepareEnvironment().asJavactx.setLocalResources(localResources.asJava)ctx.setEnvironment(env)val credentials = UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser().getCredentials()val dob = new DataOutputBuffer()credentials.writeTokenStorageToStream(dob)ctx.setTokens(ByteBuffer.wrap(dob.getData()))val commands = prepareCommand()ctx.setCommands(commands.asJava)ctx.setApplicationACLs(YarnSparkHadoopUtil.getApplicationAclsForYarn(securityMgr).asJava)// If external shuffle service is enabled, register with the Yarn shuffle service already// started on the NodeManager and, if authentication is enabled, provide it with our secret // key for fetching shuffle files later if (sparkConf.get(SHUFFLE_SERVICE_ENABLED)) {val secretString = securityMgr.getSecretKey()val secretBytes =if (secretString != null) {// This conversion must match how the YarnShuffleService decodes our secretJavaUtils.stringToBytes(secretString)} else {// Authentication is not enabled, so just provide dummy metadataByteBuffer.allocate(0)}val serviceName = sparkConf.get(SHUFFLE_SERVICE_NAME)logInfo(s"Initializing service data for shuffle service using name '$serviceName'")ctx.setServiceData(Collections.singletonMap(serviceName, secretBytes))}// Send the start request to the ContainerManagertry {nmClient.startContainer(container.get, ctx)} catch {case ex: Exception =>throw new SparkException(s"Exception while starting container ${container.get.getId}" +s" on host $hostname", ex)}}
18.创建进程YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend
创建进程YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend,启动ExecutorBackend完成
val commands = prefixEnv ++Seq(Environment.JAVA_HOME.$$() + "/bin/java", "-server") ++javaOpts ++Seq("org.apache.spark.executor.YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend","--driver-url", masterAddress,"--executor-id", executorId,"--hostname", hostname,"--cores", executorCores.toString,"--app-id", appId,"--resourceProfileId", resourceProfileId.toString) ++userClassPath ++Seq(s"1>${ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR}/stdout",s"2>${ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR}/stderr")
19.YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend找到main方法
使用run方法CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend.run(backendArgs, createFn) 开始运行
private[spark] object YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend extends Logging {def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {val createFn: (RpcEnv, CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend.Arguments, SparkEnv, ResourceProfile) =>CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend = { case (rpcEnv, arguments, env, resourceProfile) =>new YarnCoarseGrainedExecutorBackend(rpcEnv, arguments.driverUrl, arguments.executorId,arguments.bindAddress, arguments.hostname, arguments.cores, arguments.userClassPath.toSeq,env, arguments.resourcesFileOpt, resourceProfile)}val backendArgs = CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend.parseArguments(args,this.getClass.getCanonicalName.stripSuffix("$"))CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend.run(backendArgs, createFn)System.exit(0)}}
20.设置endpoint
setupEndpoint,是一个抽象类RpcEnv中的方法,找到实现类NettyRpcEnv,在spark中通信是通过netty来实现的,进行
env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("Executor", backend)
def run(arguments: Arguments,backendCreateFn: (RpcEnv, Arguments, SparkEnv, ResourceProfile) =>CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend): Unit = {Utils.initDaemon(log)SparkHadoopUtil.get.runAsSparkUser { () =>// Debug codeUtils.checkHost(arguments.hostname)// Bootstrap to fetch the driver's Spark properties.val executorConf = new SparkConfval fetcher = RpcEnv.create("driverPropsFetcher",arguments.bindAddress,arguments.hostname,-1,executorConf,new SecurityManager(executorConf),numUsableCores = 0,clientMode = true)var driver: RpcEndpointRef = nullval nTries = 3for (i <- 0 until nTries if driver == null) {try {driver = fetcher.setupEndpointRefByURI(arguments.driverUrl)} catch {case e: Throwable => if (i == nTries - 1) {throw e}}}val cfg = driver.askSync[SparkAppConfig](RetrieveSparkAppConfig(arguments.resourceProfileId))val props = cfg.sparkProperties ++ Seq[(String, String)](("spark.app.id", arguments.appId))fetcher.shutdown()// Create SparkEnv using properties we fetched from the driver.val driverConf = new SparkConf()for ((key, value) <- props) {// this is required for SSL in standalone modeif (SparkConf.isExecutorStartupConf(key)) {driverConf.setIfMissing(key, value)} else {driverConf.set(key, value)}}cfg.hadoopDelegationCreds.foreach { tokens =>SparkHadoopUtil.get.addDelegationTokens(tokens, driverConf)}driverConf.set(EXECUTOR_ID, arguments.executorId)val env = SparkEnv.createExecutorEnv(driverConf, arguments.executorId, arguments.bindAddress,arguments.hostname, arguments.cores, cfg.ioEncryptionKey, isLocal = false)// Set the application attemptId in the BlockStoreClient if available.val appAttemptId = env.conf.get(APP_ATTEMPT_ID)appAttemptId.foreach(attemptId =>env.blockManager.blockStoreClient.setAppAttemptId(attemptId))val backend = backendCreateFn(env.rpcEnv, arguments, env, cfg.resourceProfile)env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("Executor", backend)arguments.workerUrl.foreach { url =>env.rpcEnv.setupEndpoint("WorkerWatcher",new WorkerWatcher(env.rpcEnv, url, isChildProcessStopping = backend.stopping))}env.rpcEnv.awaitTermination()}}//注册executorprivate val dispatcher: Dispatcher = new Dispatcher(this, numUsableCores)override def setupEndpoint(name: String, endpoint: RpcEndpoint): RpcEndpointRef = {//调用注册方法dispatcher.registerRpcEndpoint(name, endpoint)}
21.创建DedicatedMesageLoop
def registerRpcEndpoint(name: String, endpoint: RpcEndpoint): NettyRpcEndpointRef = {val addr = RpcEndpointAddress(nettyEnv.address, name)val endpointRef = new NettyRpcEndpointRef(nettyEnv.conf, addr, nettyEnv)synchronized {if (stopped) {throw new IllegalStateException("RpcEnv has been stopped")}if (endpoints.containsKey(name)) {throw new IllegalArgumentException(s"There is already an RpcEndpoint called $name")}// This must be done before assigning RpcEndpoint to MessageLoop, as MessageLoop sets Inbox be// active when registering, and endpointRef must be put into endpointRefs before onStart is // called. endpointRefs.put(endpoint, endpointRef)var messageLoop: MessageLoop = nulltry {messageLoop = endpoint match {case e: IsolatedRpcEndpoint =>new DedicatedMessageLoop(name, e, this)case _ =>sharedLoop.register(name, endpoint)sharedLoop}endpoints.put(name, messageLoop)} catch {case NonFatal(e) =>endpointRefs.remove(endpoint)throw e}}endpointRef}
22.inbox发送消息
创建inbox, 在inbox中有给自己发消息,发送消息onStart,这个时候就会CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend收到消息执行onStart方法
通信的生命周期
The life-cycle of an endpoint is:
constructor -> onStart -> receive* -> onStop
/*** A message loop that is dedicated to a single RPC endpoint. */private class DedicatedMessageLoop(name: String,endpoint: IsolatedRpcEndpoint,dispatcher: Dispatcher)extends MessageLoop(dispatcher) {private val inbox = new Inbox(name, endpoint)override protected val threadpool = if (endpoint.threadCount() > 1) {ThreadUtils.newDaemonCachedThreadPool(s"dispatcher-$name", endpoint.threadCount())} else {ThreadUtils.newDaemonSingleThreadExecutor(s"dispatcher-$name")}(1 to endpoint.threadCount()).foreach { _ =>threadpool.submit(receiveLoopRunnable)}// Mark active to handle the OnStart message.setActive(inbox)override def post(endpointName: String, message: InboxMessage): Unit = {require(endpointName == name)inbox.post(message)setActive(inbox)}override def unregister(endpointName: String): Unit = synchronized {require(endpointName == name)inbox.stop()// Mark active to handle the OnStop message.setActive(inbox)setActive(MessageLoop.PoisonPill)threadpool.shutdown()}}在inbox中有给自己发消息protected val messages = new java.util.LinkedList[InboxMessage]()// OnStart should be the first message to processinbox.synchronized {messages.add(OnStart)}
23.CoarseGrainedExecutorBackend收到消息
执行onStart方法,driver端收到消息,注册Executor,
在driver端应该能收到,在上下文SparkContext中收到,
private[spark] trait SchedulerBackend
override def onStart(): Unit = {if (env.conf.get(DECOMMISSION_ENABLED)) {val signal = env.conf.get(EXECUTOR_DECOMMISSION_SIGNAL)logInfo(s"Registering SIG$signal handler to trigger decommissioning.")SignalUtils.register(signal, s"Failed to register SIG$signal handler - disabling" +s" executor decommission feature.") (self.askSync[Boolean](ExecutorDecommissionSigReceived))}logInfo("Connecting to driver: " + driverUrl)try {if (PlatformDependent.directBufferPreferred() &&PlatformDependent.maxDirectMemory() < env.conf.get(MAX_REMOTE_BLOCK_SIZE_FETCH_TO_MEM)) {throw new SparkException(s"Netty direct memory should at least be bigger than " +s"'${MAX_REMOTE_BLOCK_SIZE_FETCH_TO_MEM.key}', but got " +s"${PlatformDependent.maxDirectMemory()} bytes < " +s"${env.conf.get(MAX_REMOTE_BLOCK_SIZE_FETCH_TO_MEM)}")}_resources = parseOrFindResources(resourcesFileOpt)} catch {case NonFatal(e) =>exitExecutor(1, "Unable to create executor due to " + e.getMessage, e)}rpcEnv.asyncSetupEndpointRefByURI(driverUrl).flatMap { ref =>// This is a very fast action so we can use "ThreadUtils.sameThread"driver = Some(ref)//想driver端发消息,注册Executorref.ask[Boolean](RegisterExecutor(executorId, self, hostname, cores, extractLogUrls,extractAttributes, _resources, resourceProfile.id))}(ThreadUtils.sameThread).onComplete {case Success(_) =>self.send(RegisteredExecutor)case Failure(e) =>exitExecutor(1, s"Cannot register with driver: $driverUrl", e, notifyDriver = false)}(ThreadUtils.sameThread)}
24.SchedulerBackend是一个trait
找到对应的实现,CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend在该类中找到receiveAndReply方法
这里会对资源数值进行修改
回复消息,告诉注册成果,发送消息说driver端已经收到消息,注册成果
override def receiveAndReply(context: RpcCallContext): PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {case RegisterExecutor(executorId, executorRef, hostname, cores, logUrls,attributes, resources, resourceProfileId) =>if (executorDataMap.contains(executorId)) {context.sendFailure(new IllegalStateException(s"Duplicate executor ID: $executorId"))} else if (scheduler.excludedNodes.contains(hostname) ||isExecutorExcluded(executorId, hostname)) {// If the cluster manager gives us an executor on an excluded node (because it// already started allocating those resources before we informed it of our exclusion, // or if it ignored our exclusion), then we reject that executor immediately. logInfo(s"Rejecting $executorId as it has been excluded.")context.sendFailure(new IllegalStateException(s"Executor is excluded due to failures: $executorId"))} else {// If the executor's rpc env is not listening for incoming connections, `hostPort`// will be null, and the client connection should be used to contact the executor. val executorAddress = if (executorRef.address != null) {executorRef.address} else {context.senderAddress}logInfo(s"Registered executor $executorRef ($executorAddress) with ID $executorId, " +s" ResourceProfileId $resourceProfileId")addressToExecutorId(executorAddress) = executorIdtotalCoreCount.addAndGet(cores)totalRegisteredExecutors.addAndGet(1)val resourcesInfo = resources.map { case (rName, info) =>// tell the executor it can schedule resources up to numSlotsPerAddress times,// as configured by the user, or set to 1 as that is the default (1 task/resource) val numParts = scheduler.sc.resourceProfileManager.resourceProfileFromId(resourceProfileId).getNumSlotsPerAddress(rName, conf)(info.name, new ExecutorResourceInfo(info.name, info.addresses, numParts))}val data = new ExecutorData(executorRef, executorAddress, hostname,0, cores, logUrlHandler.applyPattern(logUrls, attributes), attributes,resourcesInfo, resourceProfileId, registrationTs = System.currentTimeMillis())// This must be synchronized because variables mutated// in this block are read when requesting executors CoarseGrainedSchedulerBackend.this.synchronized {executorDataMap.put(executorId, data)if (currentExecutorIdCounter < executorId.toInt) {currentExecutorIdCounter = executorId.toInt}}listenerBus.post(SparkListenerExecutorAdded(System.currentTimeMillis(), executorId, data))// Note: some tests expect the reply to come after we put the executor in the mapcontext.reply(true)}
25.收到注册成果消息
这个时候正真创建Executor
override def receive: PartialFunction[Any, Unit] = {case RegisteredExecutor =>logInfo("Successfully registered with driver")try {executor = new Executor(executorId, hostname, env, userClassPath, isLocal = false,resources = _resources)driver.get.send(LaunchedExecutor(executorId))} catch {case NonFatal(e) =>exitExecutor(1, "Unable to create executor due to " + e.getMessage, e)}
总结:
本文从spark提交任务到集群yarn,用cluster模式进行提交,从命令提交,到创建driver,创建ApplicationMaster,再到创建Executor最终成功。从源码中看到了整个流程,在查看源码过程发现有好多使用多线程,进行同步,各个模块直接使用Netty进行通信。
下一个节会讲解,driver和executor之间的通信。






