表分区是一种非常方便的技术,包括 MySQL、Oracle、PostgreSQL 和 YugabyteDB 在内的多个数据库都支持。 在本系列的第一篇文章中,我们讨论了一个自动化大型披萨连锁店运营的应用程序。 我们回顾了 PostgreSQL 如何通过从查询执行计划中消除不必要的分区来通过分区修剪功能提高应用程序的性能。
在本文中,我们将研究 PostgreSQL 的分区维护功能如何进一步影响和简化您的应用程序架构。 我们将再次以比萨连锁应用程序为例,其数据库模式与 PizzaOrders 表一起提供。 提醒您,表格跟踪订单的进度(表格数据在第一篇文章中解释):
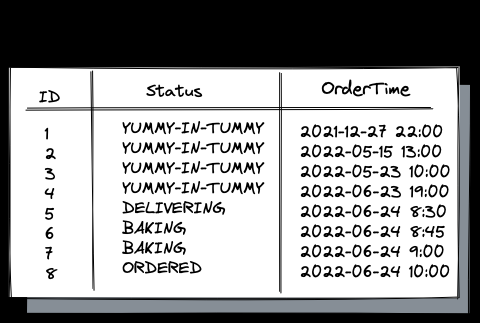
现在,假设您需要将当前月份、上一个月份和所有其他较早月份的订单分开。 因此,您继续按 OrderTime 列对 PizzaOrders 进行分区:
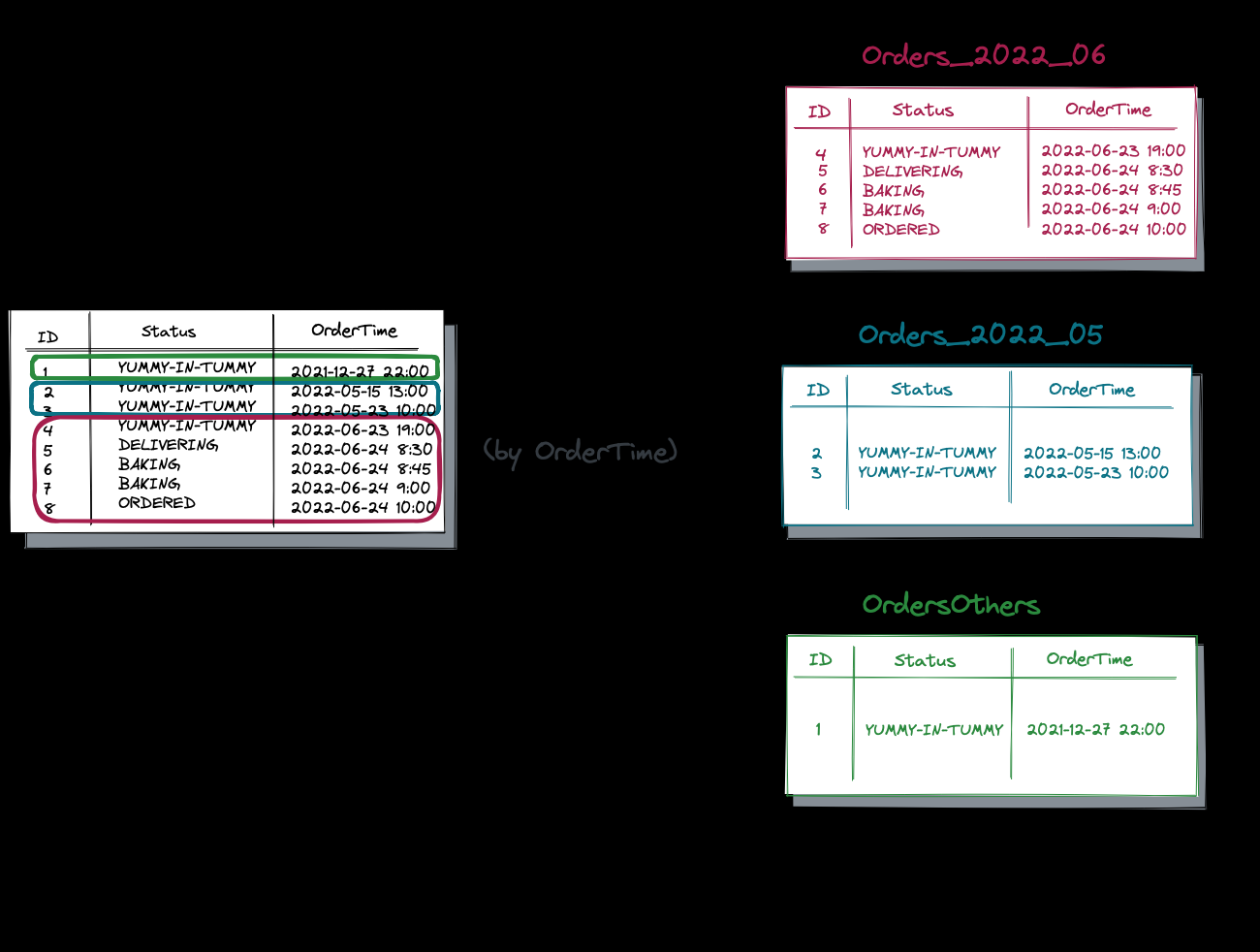
结果,原始表被拆分为三个分区表或分区:
- Orders_2022_06 - 该表保留了当月(2022 年 6 月)的所有订单。假设面向客户的微服务大量使用此分区中的数据。
- Order_2022_05 - 该表存储上个月(2022 年 5 月)的订单。假设促进短期计划的内部微服务定期结合当月数据查询这些数据。
- OrdersOthers - BI 工具用于战略规划的剩余历史数据。
不错,可以按时间对数据进行分区,数据库会保证每个微服务只查询自己需要的数据。但是,等等,当前和过去几个月不是静态的概念。一旦日历页面翻到 7 月 1 日,2020 年 7 月将成为当前月份。但是您如何在数据库级别反映这种变化?让我们谈谈分区维护技术。
分区维护
您的分区结构可能是动态的。很多时候,您可能想要删除保存旧数据的分区并使用新数据添加新分区。我们的披萨连锁店就是这种情况。而且这项维护任务可以在数据库级别轻松完成,无需在应用程序端更改代码。
在 PostgreSQL 中,分区是可以直接查询或更改的常规表。因此,在必要时,您可以使用标准 DDL 命令来创建、附加、分离和删除分区。
创建原始分区
首先,让我们创建上面讨论过的原始分区:
CREATE TYPE status_t AS ENUM('ordered', 'baking', 'delivering', 'yummy-in-my-tummy');
CREATE TABLE PizzaOrders
(
id int,
status status_t,
ordertime timestamp
) PARTITION BY RANGE (ordertime);
CREATE TABLE orders_2022_06 PARTITION OF PizzaOrders
FOR VALUES FROM('2022-06-01') TO ('2022-07-01');
CREATE TABLE orders_2022_05 PARTITION OF PizzaOrders
FOR VALUES FROM('2022-05-01') TO ('2022-06-01');
CREATE TABLE orders_others PARTITION OF PizzaOrders DEFAULT;
PARTITION BY RANGE (order_time) 子句请求使用范围分区方法拆分 PizzaOrders 表。 生成的分区将根据 ordertime 列的值保留订单。 例如,如果 ordertime 在“2022-06-01”(含)和“2022-07-01”(不含)之间,则披萨订单将进入当前月份的分区(即 orders_2022_06)。 orders_others 分区是默认分区,因为它将保留 ordertime 值不适合任何其他分区范围的所有订单。
其次,所有创建的分区都是可以使用 DDL 和 DML 命令处理的常规表。 例如,让我们加载样本数据并直接查询当月的分区表:
INSERT INTO PizzaOrders VALUES
(1, 'yummy-in-my-tummy', '2021-12-27 22:00:00'),
(2, 'yummy-in-my-tummy', '2022-05-15 13:00:00'),
(3, 'yummy-in-my-tummy', '2022-05-23 10:00:00'),
(4, 'yummy-in-my-tummy', '2022-06-23 19:00:00'),
(5, 'delivering', '2022-06-24 8:30:00'),
(6, 'baking', '2022-06-24 8:45:00'),
(7, 'baking', '2022-06-24 9:00:00'),
(8, 'ordered', '2022-06-24 10:00:00');
SELECT * FROM orders_2022_06 WHERE ordertime BETWEEN '2022_06_20' AND '2022_06_30';
id | status | ordertime
----+-------------------+---------------------
4 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2022-06-23 19:00:00
5 | delivering | 2022-06-24 08:30:00
6 | baking | 2022-06-24 08:45:00
7 | baking | 2022-06-24 09:00:00
8 | ordered | 2022-06-24 10:00:00
我们可以直接查询分区表当然很方便。 但是,您不希望面向客户的微服务记住当前的实际月份以及要查询的分区。 相反,微服务将查询顶级 PizzaOrders 表,PostgreSQL 将通过以下方式应用分区修剪优化:
EXPLAIN ANALYZE SELECT * FROM PizzaOrders
WHERE ordertime BETWEEN '2022_06_20' AND '2022_06_30';
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Seq Scan on orders_2022_06 pizzaorders (cost=0.00..37.75 rows=9 width=16) (actual time=0.010..0.012 rows=5 loops=1)
Filter: ((ordertime >= '2022-06-20 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone) AND (ordertime <= '2022-06-30 00:00:00'::timestamp without time zone))
Planning Time: 0.122 ms
Execution Time: 0.040 ms
这是相同的查询,但 PostgreSQL(而不是您的应用程序层)决定哪个分区保存数据。 执行计划显示查询是针对 orders_2022_06 分区运行的,绕过了其他分区。
但是,当您需要更改分区的结构时,这种直接使用分区表的能力非常有用。 现在,假设明天是 2022 年 7 月 1 日。您需要添加一个新分区来保留该新当月(7 月)的订单,并引入一些其他更改。
分离旧分区
让我们首先处理当前保存“上个月”(2022 年 5 月)数据的分区 orders_2022_05。 根据应用程序逻辑,您这样做是因为一旦 7 月成为“当前月份”,6 月将成为“上个月”。
首先,让我们使用 DETACH 命令从分区结构中删除 May 分区:
ALTER TABLE PizzaOrders DETACH PARTITION orders_2022_05;
完成此操作后,尝试从 PizzaOrders 表中读取所有记录,以确认 May 没有任何记录:
SELECT * FROM PizzaOrders;
id | status | ordertime
----+-------------------+---------------------
4 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2022-06-23 19:00:00
5 | delivering | 2022-06-24 08:30:00
6 | baking | 2022-06-24 08:45:00
7 | baking | 2022-06-24 09:00:00
8 | ordered | 2022-06-24 10:00:00
1 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2021-12-27 22:00:00
不要害怕,五月的数据并没有蒸发! 数据仍在同一个分区表中,您可以直接查询:
SELECT * FROM orders_2022_05;
id | status | ordertime
----+-------------------+---------------------
2 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2022-05-15 13:00:00
3 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2022-05-23 10:00:00
接下来,你还记得我们有 orders_others 分区,它保存了 ordertime 列不适合其他分区范围的所有订单吗? 现在继续把五月的记录放在那里。 您可以通过将数据插入顶级 PizzaOrders 表并让 PostgreSQL 跨分区排列记录来做到这一点:
INSERT INTO PizzaOrders (id,status,ordertime)
SELECT detached.id, detached.status, detached.ordertime
FROM orders_2022_05 as detached;
最后,您可以安全地删除 orders_2022_05 分区,因为您在 orders_others 分区中已经有了 May 的订单副本:
DROP TABLE orders_2022_05;
SELECT tableoid::regclass,* from PizzaOrders
ORDER BY id;
tableoid | id | status | ordertime
----------------+----+-------------------+---------------------
orders_others | 1 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2021-12-27 22:00:00
orders_others | 2 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2022-05-15 13:00:00
orders_others | 3 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2022-05-23 10:00:00
orders_2022_06 | 4 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2022-06-23 19:00:00
orders_2022_06 | 5 | delivering | 2022-06-24 08:30:00
orders_2022_06 | 6 | baking | 2022-06-24 08:45:00
orders_2022_06 | 7 | baking | 2022-06-24 09:00:00
orders_2022_06 | 8 | ordered | 2022-06-24 10:00:00
附加新分区
最后,让我们根据应用程序逻辑为即将成为“当前月份”的 7 月创建一个分区。
最直接的方法是将新分区附加到 PizzaOrders 表:
CREATE TABLE orders_2022_07 PARTITION OF PizzaOrders
FOR VALUES FROM('2022-07-01') TO ('2022-08-01');
新分区的名称是 orders_2022_07,它被添加到 partitions 结构中:
\d+ PizzaOrders;
Partitioned table "public.pizzaorders"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Compression | Stats target | Description
-----------+-----------------------------+-----------+----------+---------+---------+-------------+--------------+-------------
id | integer | | | | plain | | |
status | status_t | | | | plain | | |
ordertime | timestamp without time zone | | | | plain | | |
Partition key: RANGE (ordertime)
Partitions: orders_2022_06 FOR VALUES FROM ('2022-06-01 00:00:00') TO ('2022-07-01 00:00:00'),
orders_2022_07 FOR VALUES FROM ('2022-07-01 00:00:00') TO ('2022-08-01 00:00:00'),
orders_others DEFAULT
这是不是很简单? 让我们通过插入 2022 年 7 月的虚拟数据并检查这些记录属于哪个分区来测试更改:
INSERT INTO PizzaOrders VALUES
(9, 'ordered', '2022-07-02 10:00:00'),
(10, 'baking', '2022-07-02 9:50:00'),
(11, 'yummy-in-my-tummy', '2022-07-01 18:10:00');
SELECT tableoid::regclass,* from PizzaOrders
ORDER BY id;
tableoid | id | status | ordertime
----------------+----+-------------------+---------------------
orders_others | 1 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2021-12-27 22:00:00
orders_others | 2 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2022-05-15 13:00:00
orders_others | 3 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2022-05-23 10:00:00
orders_2022_06 | 4 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2022-06-23 19:00:00
orders_2022_06 | 5 | delivering | 2022-06-24 08:30:00
orders_2022_06 | 6 | baking | 2022-06-24 08:45:00
orders_2022_06 | 7 | baking | 2022-06-24 09:00:00
orders_2022_06 | 8 | ordered | 2022-06-24 10:00:00
orders_2022_07 | 9 | ordered | 2022-07-02 10:00:00
orders_2022_07 | 10 | baking | 2022-07-02 09:50:00
orders_2022_07 | 11 | yummy-in-my-tummy | 2022-07-01 18:10:00
完毕! 您可以通过分离 5 月的分区并为 7 月附加一个新的分区来轻松更改分区的结构。 并且在应用程序方面不需要进行任何更改。 我们的微服务继续直接查询 PizzaOrders 表,而不打扰底层分区。
未完待续…
好的,通过本文,我们完成了对分区修剪和维护功能的回顾,这些功能可以提高性能并促进应用程序的设计。 查看此 PostgreSQL 资源以了解更多信息。
在后续文章中,您将学习如何使用地理分区将披萨订单固定到特定地理位置。 毕竟,我们一直在为一家大型比萨连锁店开发应用程序,该连锁店为各国和各大洲的客户提供食物并取悦他们。 敬请关注!
原文标题:What Developers Need to Know About Table Partition Maintenance
原文作者:Denis Magda
原文地址:https://dzone.com/articles/what-developers-need-to-know-about-table-partition-1






