想象一下,有一个工具可以自动检测JPA和Hibernate性能问题。那不是很棒吗?
好吧,Hypersistence Optimizer就是那个工具!它与Spring Boot、Spring Framework、Jakarta EE、Java EE、Quarkus或Play Framework一起工作。
所以,享受把时间花在你喜欢的事情上,而不是在周六晚上解决生产系统中的性能问题!
介绍
在本文中,我们将看到MySQL rewriteBatchedStatements在使用JDBC、JPA或Hibernate时是如何工作的。
在编写高性能Java持久性书籍中的批处理章节时,我首先研究了这个MySQL配置属性,当时我发现这个设置允许通过重写发送到数据库的SQL字符串来批处理普通语句。
然而,MySQL 6 Connector/J文档提到:
对于预备语句,服务器端预备语句当前无法利用此重写选项。
因此,在很长一段时间里,我错误地认为这个特性不适用于批处理JDBC准备的语句。
当我阅读MySQL 8.0.30 Connector/J发行说明时,我意识到文档误导了我们:
连接属性rewriteBatchedStatements的描述已更正,消除了服务器端准备的语句不能利用重写选项的限制。(错误3402210)
因此,很明显,rewriteBatchedStatements使用的是JDBC PreparedStatement,因此,我决定测试这个功能,并在本文中写下我的发现。
将rewriteBatchedStatements与JDBC语句批处理一起使用
大多数Java开发人员在执行INSERT、UPDATE和DELETE语句时使用语句接口的executeUpdate方法。
然而,自Java 1.2以来,语句接口一直提供addBatch,我们可以使用它对多个语句进行批处理,以便在调用executeBatch方法时在单个请求中发送它们,如下例所示:
String INSERT = "insert into post (id, title) values (%1$d, 'Post no. %1$d')";
try(Statement statement = connection.createStatement()) {
for (long id = 1; id <= 10; id++) {
statement.addBatch(
String.format(INSERT, id)
);
}
statement.executeBatch();
}
现在,假设上面的示例将在单个数据库往返中执行INSERT语句,但是如果通过MySQL JDBC驱动程序进行调试,您将发现以下代码块:
if (this.rewriteBatchedStatements.getValue() && nbrCommands > 4) {
return executeBatchUsingMultiQueries(
multiQueriesEnabled,
nbrCommands,
individualStatementTimeout
);
}
updateCounts = new long[nbrCommands];
for (int i = 0; i < nbrCommands; i++) {
updateCounts[i] = -3;
}
int commandIndex = 0;
for (commandIndex = 0; commandIndex < nbrCommands; commandIndex++) {
try {
String sql = (String) batchedArgs.get(commandIndex);
updateCounts[commandIndex] = executeUpdateInternal(sql, true, true);
...
} catch (SQLException ex) {
updateCounts[commandIndex] = EXECUTE_FAILED;
...
}
}
由于rewriteBatchedStatements为false,因此将使用executeUpdateInternal方法调用单独执行每个INSERT语句。
因此,即使我们使用了addBatch和executeBatch,默认情况下,MySQL在使用普通JDBC语句对象时仍然单独执行INSERT语句。
但是,如果启用rewriteBatchedStatements JDBC配置属性:
MysqlDataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost/high_performance_java_persistence?useSSL=false";
dataSource.setURL(url);
dataSource.setUser(username());
dataSource.setPassword(password());
dataSource.setRewriteBatchedStatements(true);
并调试executeBatch方法的执行,您将看到,现在调用了ExecuteBattchusingMultiQueries:
if (this.rewriteBatchedStatements.getValue() && nbrCommands > 4) {
return executeBatchUsingMultiQueries(
multiQueriesEnabled,
nbrCommands,
individualStatementTimeout
);
}
executeBatchUsingMultiQueries方法将把单个INSERT语句连接到StringBuilder中,并运行单个执行调用:
StringBuilder queryBuf = new StringBuilder();
batchStmt = locallyScopedConn.createStatement();
JdbcStatement jdbcBatchedStmt = (JdbcStatement) batchStmt;
...
int argumentSetsInBatchSoFar = 0;
for (commandIndex = 0; commandIndex < nbrCommands; commandIndex++) {
String nextQuery = (String) this.query.getBatchedArgs().get(commandIndex);
...
queryBuf.append(nextQuery);
queryBuf.append(";");
argumentSetsInBatchSoFar++;
}
if (queryBuf.length() > 0) {
try {
batchStmt.execute(queryBuf.toString(), java.sql.Statement.RETURN_GENERATED_KEYS);
} catch (SQLException ex) {
sqlEx = handleExceptionForBatch(
commandIndex - 1, argumentSetsInBatchSoFar, updateCounts, ex
);
}
...
}
因此,对于普通的JDBC语句批处理,MySQL rewriteBatchedStatements配置属性将附加当前批处理的语句,并在单个数据库往返中执行它们。
将rewriteBatchedStatements与JDBC PreparedStatement批处理一起使用
当使用JPA和Hibernate时,所有SQL语句都将使用JDBC PreparedStatement执行,这有很好的理由:
- 准备好的语句可以增加语句缓存的可能性
- 准备好的语句允许您避免SQL注入攻击,因为您绑定了参数值,而不是像我们对前一个字符串所做的那样注入参数值,格式化调用。
但是,由于Hibernate默认情况下不启用JDBC批处理,我们需要提供以下配置属性来激活自动批处理机制:
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.jdbc.batch_size=10
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.order_inserts=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.order_updates=true
因此,当持久化10个Post实体时:
for (long i = 1; i <= 10; i++) {
entityManager.persist(
new Post()
.setId(i)
.setTitle(String.format("Post no. %d", i))
);
}
Hibernate将执行单个JDBC插入,如datasource代理日志条目所示:
Type:Prepared, Batch:True, QuerySize:1, BatchSize:10,
Query:["
insert into post (title, id) values (?, ?)
"],
Params:[
(Post no. 1, 1), (Post no. 2, 2), (Post no. 3, 3),
(Post no. 4, 4), (Post no. 5, 5), (Post no. 6, 6),
(Post no. 7, 7), (Post no. 8, 8), (Post no. 9, 9),
(Post no. 10, 10)
]
如果您使用的是标识实体标识符策略,Hibernate将无法自动批处理insert语句。
因此,使用默认的MySQL JDBC驱动程序设置,一条语句被发送到MySQL数据库服务器。但是,如果检查数据库服务器日志,我们可以看到,在语句到达后,MySQL执行每个语句,就像它们在for循环中运行一样:
Query insert into post (title, id) values ('Post no. 1', 1)
Query insert into post (title, id) values ('Post no. 2', 2)
Query insert into post (title, id) values ('Post no. 3', 3)
Query insert into post (title, id) values ('Post no. 4', 4)
Query insert into post (title, id) values ('Post no. 5', 5)
Query insert into post (title, id) values ('Post no. 6', 6)
Query insert into post (title, id) values ('Post no. 7', 7)
Query insert into post (title, id) values ('Post no. 8', 8)
Query insert into post (title, id) values ('Post no. 9', 9)
Query insert into post (title, id) values ('Post no. 10', 10)
Query commit
因此,在启用rewriteBatchedStatements MySQL JDBC驱动程序设置后:
dataSource.setRewriteBatchedStatements(true);
当我们重新运行上一个插入10个Post实体的测试用例时,我们可以看到以下INSERT语句在数据库端执行:
Query insert into post (title, id)
values ('Post no. 1', 1),('Post no. 2', 2),('Post no. 3', 3),
('Post no. 4', 4),('Post no. 5', 5),('Post no. 6', 6),
('Post no. 7', 7),('Post no. 8', 8),('Post no. 9', 9),
('Post no. 10', 10)
Query commit
该语句发生更改的原因是MySQL JDBC驱动程序现在调用ExecuteBatchWithMultivaluesLause方法,该方法将批处理的INSERT语句重写为单个多值INSERT。
if (!this.batchHasPlainStatements &&
this.rewriteBatchedStatements.getValue()) {
if (getQueryInfo().isRewritableWithMultiValuesClause()) {
return executeBatchWithMultiValuesClause(batchTimeout);
}
...
}
测试时间
对于普通语句,无需测试rewriteBatchedStatements优化,因为您将使用JDBC、JPA、Hibernate或jOOQ执行的大多数SQL语句都是使用JDBC PreparedStatement接口完成的。
因此,当运行一个测试,使用100的批大小插入5000条post记录,持续时间为60秒时,我们得到以下结果:
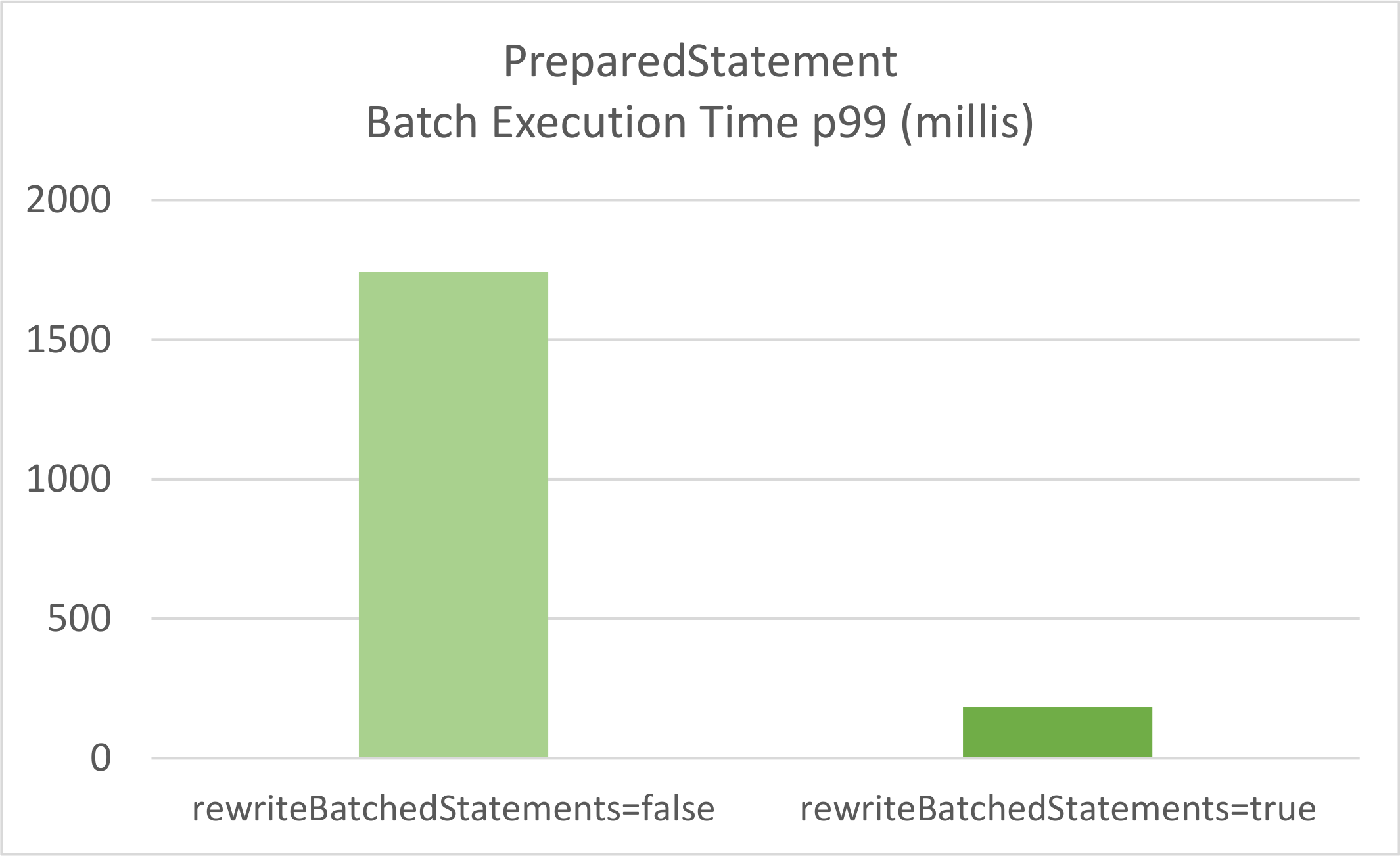
以下是两种情况下的Dropwizard指标:
Test MySQL batch insert with rewriteBatchedStatements=false
type=TIMER, name=batchInsertTimer, count=55, min=909.9544999999999, max=1743.0735,
mean=1072.3787996947426, stddev=128.4560649360703, median=1049.4146,
p75=1106.231, p95=1224.2176, p98=1649.8706, p99=1743.0735, p999=1743.0735,
mean_rate=0.8612772397894758, m1=0.6330960191792878, m5=0.3192705968508436,
m15=0.24209506781664528, rate_unit=events/second, duration_unit=milliseconds
Test MySQL batch insert with rewriteBatchedStatements=true
type=TIMER, name=batchInsertTimer, count=441, min=80.09599999999999, max=565.4343,
mean=112.20623474996226, stddev=29.01211110828766, median=103.52319999999999,
p75=120.9807, p95=161.3664, p98=173.9123, p99=182.2464, p999=565.4343,
mean_rate=7.263224298238385, m1=6.872524588278418, m5=6.547662085190082,
m15=6.453339001683109, rate_unit=events/second, duration_unit=milliseconds
显然,MySQL rewriteBatchedStatements设置提供了一个优势,因为激活此属性时,总批处理执行时间要短得多。
正如MySQL文档中所解释的,您应该注意以下几点:
- 陈述getGeneratedKeys()仅在重写语句仅由INSERT或REPLACE语句组成时工作。在使用JPA和Hibernate时,这并不是一个真正的问题,因为在刷新期间只批处理INSERT。
- 重写INSERT…ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE语句可能无法按预期工作,但这对于JPA和Hibernate来说也不是问题,因为默认INSERT不使用ON DUPLIATE KEY更新子句。
如果你喜欢这篇文章,我打赌你也会喜欢我的书和视频课程。
结论
虽然MySQL JDBC驱动程序提供rewriteBatchedStatements设置已有很长一段时间了,但由于文档中的误导性,不清楚该属性是否适用于PreparedStatement批处理。
因此,如果批处理任务在MySQL上运行,启用rewriteBatchedStatements设置可能会提供更好的性能。
原文标题:MySQL rewriteBatchedStatements configuration property
原文链接:https://vladmihalcea.com/mysql-rewritebatchedstatements









