前言

今天我们来用下HypoPG,HypoPG翻译为低血糖
,但实际上是 hypothetical+ PostgreSQL单词简写合并。hypothetical
是假设的意思。HypoPG支持两种假设:假设索引和假设分区。
HypoPG介绍
HypoPG提供的一个功能是虚拟索引,它实际上并不存在。因此,创建它不需要使用 cpu、磁盘 I/O等任何资源。这与 Oracle中虚拟索引 Virtual Indexes相似。通过创建虚拟索引,我们可以验证所创建的索引是否合理的,是否能够提高查询性能。
另一种由 HypoPG提供的特性是虚拟分区,这是一个真实存在的表,我们可以将不同的分区模拟应用到这个表上,就像声明分区一样。通过仿真测试,我们可以验证哪个分区方案适合业务场景。
HypoPG使用
安装 HypoPG非常简单,可以从Github上(https://github.com/HypoPG/hypopg/)上下载编译。
##选择下载特定的版本,现在最新版是1.1.4
wget https://github.com/HypoPG/hypopg/archive/1.1.4.zip
cd
make
make install
##进入psql,创建hypopg扩展
postgres=# CREATE EXTENSION hypopg;
CREATE EXTENSION
postgres=# \dx
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Schema | Description
--------------------+---------+------------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------
hypopg | 1.1.4 | public | Hypothetical indexes for PostgreSQL
pg_stat_statements | 1.7 | public | track execution statistics of all SQL statements executed
pageinspect | 1.7 | public | inspect the contents of database pages at a low level
下一步,创建一个表测试。
CREATE TABLE test(id integer, name text);
INSERT INTO test SELECT i, 'name ' || i FROM generate_series(1, 100000) i;
VACUUM ANALYZE test1;
postgres=# EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM test WHERE id = 1;
QUERY PLAN
--------------------------------------------------------
Seq Scan on test (cost=0.00..1791.00 rows=1 width=14)
Filter: (id = 1)
(2 rows)
由于我们创建的表没有索引,查询语句将会默认使用全表扫描。下面我们将创建假设索引。
postgres=# SELECT * FROM hypopg_create_index('CREATE INDEX idx_t1 ON test(id)');
indexrelid | indexname
------------+-------------------------
20031848 | <20031848>btree_test_id
postgres=# select * from hypopg_list_indexes();
indexrelid | indexname | nspname | relname | amname
------------+-------------------------+---------+---------+--------
20031848 | <20031848>btree_test_id | public | test | btree
(1 row)
创建完索引生成2列,一个是索引的对象标识符,另一个是假设索引的名称。我们来check一下该索引是否实际存在。
postgres=# \d+ test
Table "public.test"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description
--------+---------+-----------+----------+---------+----------+--------------+-------------
id | integer | | | | plain | |
name | text | | | | extended | |
Access method: heap
postgres=# select * from pg_size_pretty (pg_total_relation_size ('<20031848>btree_test_id'));
ERROR: relation "<20031848>btree_test_id" does not exist
可以看到对象都是不存在的。再次执行 explain查看执行计划发现可以使用 Index Scan了,但是在 explain analyze中实际执行是真实的,真实执行没有使用索引。
postgres=# EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM test WHERE id = 100;
QUERY PLAN
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Index Scan using <20031848>btree_test_id on test (cost=0.04..2.26 rows=1 width=14)
Index Cond: (id = 100)
(2 rows)
postgres=# EXPLAIN analyze SELECT * FROM test WHERE id = 100;
QUERY PLAN
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Seq Scan on test (cost=0.00..1791.00 rows=1 width=14) (actual time=0.061..21.653 rows=1 loops=1)
Filter: (id = 100)
Rows Removed by Filter: 99999
Planning Time: 0.129 ms
Execution Time: 21.748 ms
(5 rows)
您可以通过自带函数查看索引创建的语法,还可以评估索引创建的大小(这很有用),这里的大小评估值为2544 KB。
postgres=# SELECT indexname, hypopg_get_indexdef(indexrelid) FROM hypopg_list_indexes() ;
indexname | hypopg_get_indexdef
-------------------------+----------------------------------------------
<20031848>btree_test_id | CREATE INDEX ON public.test USING btree (id)
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT indexname, pg_size_pretty(hypopg_relation_size(indexrelid)) FROM hypopg_list_indexes();
indexname | pg_size_pretty
-------------------------+----------------
<20031848>btree_test_id | 2544 kB
(1 row)
使用hypopg_drop_index
可以移除索引。
postgres=# SELECT hypopg_drop_index(indexrelid) FROM hypopg_list_indexes();
hypopg_drop_index
-------------------
t
(1 row)
Btree索引测试很简单,那么其它的索引像Brin支持吗?咱们试试。
postgres=# SELECT * FROM hypopg_create_index('CREATE INDEX idx_t1 ON test USING brin (id);');
indexrelid | indexname
------------+------------------------
20032106 | <20032106>brin_test_id
(1 row)
postgres=# explain SELECT * FROM test WHERE id = 1 ;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Bitmap Heap Scan on test (cost=3.23..794.23 rows=1 width=14)
Recheck Cond: (id = 1)
-> Bitmap Index Scan on <20032106>brin_test_id (cost=0.00..3.23 rows=20000 width=0)
Index Cond: (id = 1)
(4 rows)
可见,还支持 Brin索引。通过调用hypopg_reset可以清除所有假设索引。
postgres=# select hypopg_reset();
hypopg_reset
--------------
(1 row)
最后我们要测试假设分区功能,但可能我安装的版本有问题,没有找到官方文档中介绍的函数hypopg_partition_table
postgres=# \df hypopg_partition_table
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+------+------------------+---------------------+------
(0 rows)
SELECT n.nspname as "Schema",
p.proname as "Name",
pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(p.proowner) as "Owner",
pg_catalog.array_to_string(p.proacl, E'\n') AS "Access privileges",
l.lanname as "Language",
p.prosrc as "Source code",
pg_catalog.obj_description(p.oid, 'pg_proc') as "Description"
FROM pg_catalog.pg_proc p
LEFT JOIN pg_catalog.pg_namespace n ON n.oid = p.pronamespace
LEFT JOIN pg_catalog.pg_language l ON l.oid = p.prolang
WHERE p.proname OPERATOR(pg_catalog.~) '^(hypopg.*)$' COLLATE pg_catalog.default
AND pg_catalog.pg_function_is_visible(p.oid)
ORDER BY 1, 2, 3;
Schema | Name | Owner | Source code
--------+----------------------+----------+-----------------------------------------------------------------------
public | hypopg | postgres | hypopg
public | hypopg_create_index | postgres | hypopg_create_index
public | hypopg_drop_index | postgres | hypopg_drop_index
public | hypopg_get_indexdef | postgres | hypopg_get_indexdef
public | hypopg_list_indexes | postgres | +
| | | SELECT h.indexrelid, h.indexname, n.nspname, c.relname, am.amname+
| | | FROM hypopg() h +
| | | JOIN pg_class c ON c.oid = h.indrelid +
| | | JOIN pg_namespace n ON n.oid = c.relnamespace +
| | | JOIN pg_am am ON am.oid = h.amid +
| | |
public | hypopg_relation_size | postgres | hypopg_relation_size
public | hypopg_reset | postgres | hypopg_reset
public | hypopg_reset_index | postgres | hypopg_reset_index
(8 rows)
经过测试,发现1.1.4没有这个功能,看了一下2.0.0 beta版才有这个功能。
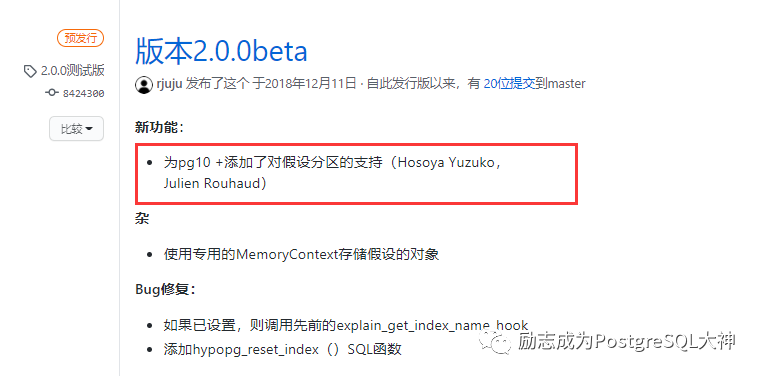
而且这一版本有点老,还在2018年12月发布的。我下载后结果编译了半天也没办法成功,也有可能是我的环境安装了1.1.4版本没有铲干净,看来只能等新版本了,暂时这个功能还不能在最新的 PostgreSQL12.5中使用,我调整了一些代码也没办法编译。
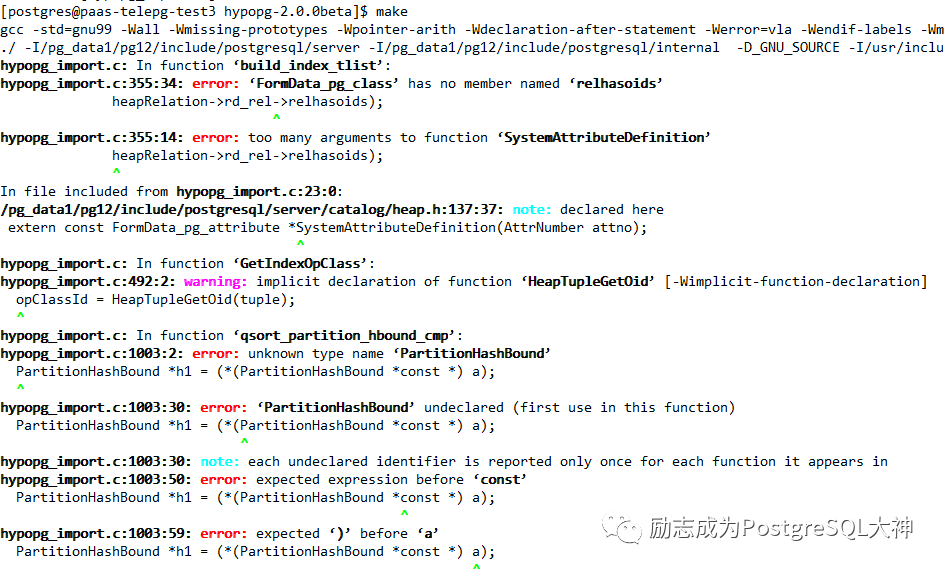
只能等2.0的稳定版出现了。
后记
现在我们了解了 HypoPG插件的使用,它与 Oracle的虚拟索引功能相似,这个插件可以帮助我们进行SQL优化。






