之前我们讨论了表级锁,今天我们要讨论的是行级锁。
行级锁
除了表级锁外, PostgreSQL还有行级锁。其四种形式分别是:
FOR UPDATE FOR NO KEY UPDATE FOR SHARE FOR KEY SHARE
实际上,在此之前,我对 insert, update, delete这些不是行级锁有些惊讶。我认为行锁实际上与这些有关,但在 PostgreSQL上却并非如此。我们将研究这四种行级锁定的行为。
FOR UPDATE
它其实是一种悲观的锁定方式,也是开发最喜欢使用的方法。只要修改了一些符合条件的数据,我就会先锁定那些符合条件的数据,不让别人修改,等修改完后,再把释放给其他人。其他人在此期间只能查询数据。
它与update、delete、select fot update、select for no key update、select for share、select for key share互斥。
--会话1
postgres=# begin;
BEGIN
postgres=*# select * from testlock for update;
id | name
----+------
2 | bbb
5 | sss
1 | ddd
(3 rows)
--会话2
postgres=# begin;
BEGIN
postgres=*# update testlock set name='aaa' where id=1;
这时会话2将被阻塞,此时可以通过前面的查锁脚本找到阻塞源。
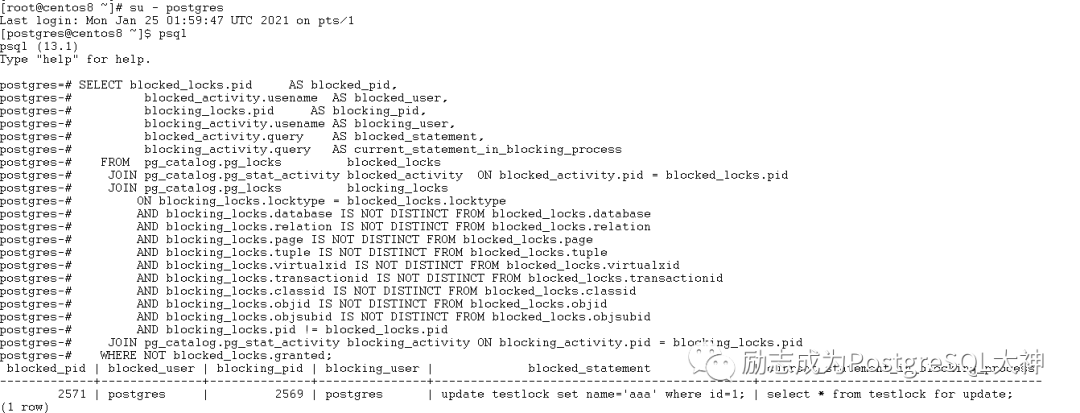
当然这里还可以以其他方式进行查询,即 pgrowlocks扩展,该扩展只能用于行级锁定,如果在表级锁定问题上进行查询,则将卡住无法得到任何结果。
postgres=# \dx
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Schema | Description
--------------------+---------+------------+------------------------------------------------------------------------
pg_cron | 1.3 | public | Job scheduler for PostgreSQL
pg_stat_statements | 1.8 | public | track planning and execution statistics of all SQL statements executed
pgrowlocks | 1.2 | public | show row-level locking information
plpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language
(4 rows)
postgres=#
postgres=# select * from pgrowlocks('testlock');
locked_row | locker | multi | xids | modes | pids
------------+--------+-------+-------+----------------+--------
(0,2) | 768 | f | {768} | {"For Update"} | {2569}
(0,6) | 768 | f | {768} | {"For Update"} | {2569}
(0,7) | 768 | f | {768} | {"For Update"} | {2569}
locked_row显示Tuple ID, modes表示持有者使用的锁定模式,在这里可以清楚地看到是for update。
FOR NO KEY UPDATE
for no key updates类似于for update锁定,但该锁定更弱。对于同一行,它不会阻止 select for key share锁定。任何不获取for update锁的update也会获得这种锁模式。
但是这个锁通常是用于带有主外键的表。让我们看一下它与 for update的区别。分别创建A和B表,设置B的id列是表A的id列的外键。
create table a (id int primary key);
create table b (bid int primary key, id int references a (id) on update cascade on delete cascade, name varchar);
insert into a(id) values (1);
insert into a(id) values (2);
insert into b(bid,id,name) values (1,1,'xxx');
insert into b(bid,id,name) values (2,2,'yyy');
「问:现在我使用for update锁定表 A。那么B表还可以插入或更新数据吗?」
--会话1
postgres=# begin;
BEGIN
postgres=*# select * from a for update;
id
----
1
2
(2 rows)
--会话2
postgres=# insert into b values(3,1,'aaa');
此时会话2会卡住,「无法插入和更新数据」。
postgres=# select * from pgrowlocks('a');
locked_row | locker | multi | xids | modes | pids
------------+--------+-------+-------+----------------+--------
(0,1) | 834 | f | {834} | {"For Update"} | {3361}
(0,2) | 834 | f | {834} | {"For Update"} | {3361}
(2 rows)
postgres=# select * from pgrowlocks('b');
locked_row | locker | multi | xids | modes | pids
------------+--------+-------+------+-------+------
(0 rows)
要解决这种问题,您可以使用for no key update,以便 b表能够插入数据。
--会话1
postgres=# begin;
BEGIN
postgres=*# select * from a for no key update;
id
----
1
2
(2 rows)
--会话2
postgres=# insert into b values(3,1,'aaa');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# insert into b values(4,2,'aaa');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# select * from pgrowlocks('a');
locked_row | locker | multi | xids | modes | pids
------------+--------+-------+-----------+-----------------------------------+----------
(0,1) | 5 | t | {872,873} | {"For No Key Update","Key Share"} | {3527,0}
(0,2) | 6 | t | {872,874} | {"For No Key Update","Key Share"} | {3527,0}
FOR SHARE
这种和for no key updates类似,区别在于所检索的每一行都是共享锁,而非互斥锁。它与update、delete、select fot update、select for no key update互斥,但它可以与select for share、select for key share共享。
这个锁的主要作用就是我们正在读的那一行,我不想有人去改变它。但我不会阻止其他人使用 for share来读取它。
--会话1
postgres=# begin;
BEGIN
postgres=*# select * from a for share;
id
----
1
2
(2 rows)
--会话2
postgres=# begin;
BEGIN
postgres=*# select * from a for share;
id
----
1
2
(2 rows)
postgres=# select * from pgrowlocks('a');
locked_row | locker | multi | xids | modes | pids
------------+--------+-------+-----------+---------------+-------------
(0,1) | 4 | t | {870,871} | {Share,Share} | {3512,3492}
(0,2) | 4 | t | {870,871} | {Share,Share} | {3512,3492}
(2 rows)
FOR KEY SHARE
这与for share相似,但是锁定比较弱。执行select for update会被阻塞。该锁还可以防止其他事务对键值进行update和 delete操作,但是不会阻止非键值列的更新,也不会阻止select for no key update、select for share或者select for key share。该锁主要使用场景还是与主外键约束相关。
介绍了行级锁定模式。通过一个图表,我们可以看到所有锁定互斥现象。

深入理论部分
对表级锁和行级锁进行了研究,得出以下结论::
「表级锁和行级锁在PostgreSQL是各自独立的,但是这两者之间又有着微妙的关系。」
为了搞清楚细节,我搜集了一些资料,资料主要来源于PostgreSQL源代码的readme。
https://github.com/postgres/postgres/blob/322548a8abe225f2cfd6a48e07b99e2711d28ef7/src/backend/storage/lmgr/README
https://github.com/postgres/postgres/blob/c62a0a49f33a0d45a97aa1d3a5bc6ddc83f10d82/src/backend/access/heap/README.tuplock
后记
有兴趣的可以先看看,我已经准备好慢慢啃了。






