与我们平台的所有部分一样,我们不断提高标准并添加新功能,以增强开发人员构建应用程序的能力,从而使他们的 Lakehouse 成为现实。在 Databricks 上构建实时应用程序也不例外。异步检查点、会话窗口和Delta Live Tables等功能允许组织使用 Delta Lake 作为流经 Lakehouse 的所有数据的基础,在 Databricks 上构建更强大的实时管道。
但是,对于利用 Flink 进行实时转换的组织来说,他们似乎无法利用一些出色的 Delta Lake 和 Databricks 功能,但事实并非如此。在这篇博客中,我们将探讨 Flink 开发人员如何构建管道以将他们的 Flink 应用程序集成到更广泛的 Lakehouse 架构中。
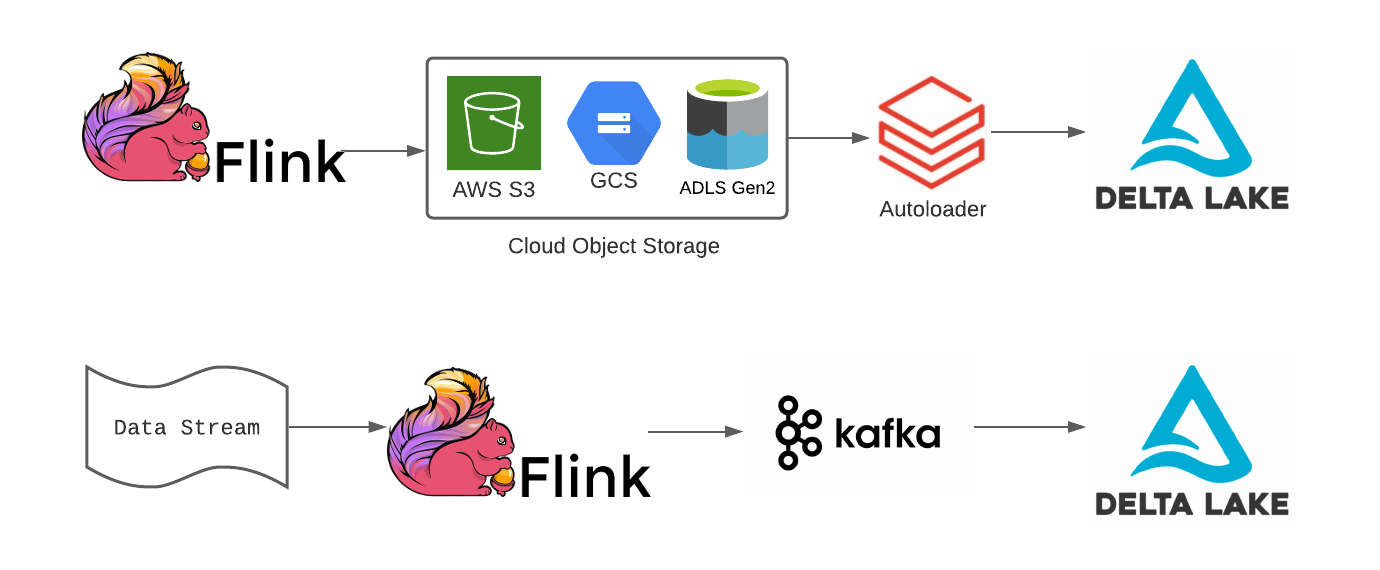
一个有状态的 Flink 应用
让我们使用一家信用卡公司来探索我们如何做到这一点。
对于信用卡公司来说,防止欺诈交易是成功企业的关键。信用卡欺诈会给金融机构带来声誉和收入风险,因此,信用卡公司必须建立适当的系统,以时刻保持警惕,防止欺诈交易。这些组织可以使用 Apache Flink 来实施监控系统,Apache Flink 是一种分布式的一次事件处理引擎,可以对流应用程序状态和时间进行细粒度控制。
下面是 Flink 中的欺诈检测应用程序的一个简单示例。它随着时间的推移监控交易金额,并在任何给定的信用卡账户在一分钟内立即进行一笔小额交易时发送警报。通过结合使用 Flink 的ValueState 数据类型和KeyedProcessFunction,开发人员可以实现他们的业务逻辑,根据事件和时间状态触发下游警报。
import org.apache.flink.api.common.state.{ValueState, ValueStateDescriptor}
import org.apache.flink.api.scala.typeutils.Types
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.KeyedProcessFunction
import org.apache.flink.util.Collector
import org.apache.flink.walkthrough.common.entity.Alert
import org.apache.flink.walkthrough.common.entity.Transaction
object FraudDetector {
val SMALL_AMOUNT: Double = 1.00
val LARGE_AMOUNT: Double = 500.00
val ONE_MINUTE: Long = 60 * 1000L
}
@SerialVersionUID(1L)
class FraudDetector extends KeyedProcessFunction[Long, Transaction, Alert] {
@transient private var flagState: ValueState[java.lang.Boolean] = _
@transient private var timerState: ValueState[java.lang.Long] = _
@throws[Exception]
override def open(parameters: Configuration): Unit = {
val flagDescriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor("flag", Types.BOOLEAN)
flagState = getRuntimeContext.getState(flagDescriptor)
val timerDescriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor("timer-state", Types.LONG)
timerState = getRuntimeContext.getState(timerDescriptor)
}
override def processElement(
transaction: Transaction,
context: KeyedProcessFunction[Long, Transaction, Alert]#Context,
collector: Collector[Alert]): Unit = {
// Get the current state for the current key
val lastTransactionWasSmall = flagState.value
// Check if the flag is set
if (lastTransactionWasSmall != null) {
if (transaction.getAmount > FraudDetector.LARGE_AMOUNT) {
// Output an alert downstream
val alert = new Alert
alert.setId(transaction.getAccountId)
collector.collect(alert)
}
// Clean up our state
cleanUp(context)
}
if (transaction.getAmount
In addition to sending alerts, most organizations will want the ability to perform analytics on all the transactions they process. Fraudsters are constantly evolving the techniques they use in the hopes of remaining undetected, so it is quite likely that a simple heuristic-based fraud detection application, such as the above, will not be sufficient for preventing all fraudulent activity. Organizations leveraging Flink for alerting will also need to combine disparate data sets to create advanced fraud detection models that analyze more than just transactional data, but include data points such as demographic information of the account holder, previous purchasing history, time and location of transactions, and more.
「喜欢这篇文章,您的关注和赞赏是给作者最好的鼓励」
关注作者
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文章的来源(墨天轮),文章链接,文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






