spark物理执行计划Aggregate策略
0 前言
上一篇概述了物理执行计划节点生成策略集,本文以具体的SQL为例,探索聚合(Aggregate)物理执行计划节点生成逻辑。
1 整体流程
Aggregate物理执行计划生成逻辑是在org.apache.spark.sql.execution.SparkStrategies.Aggregation#apply
方法中。
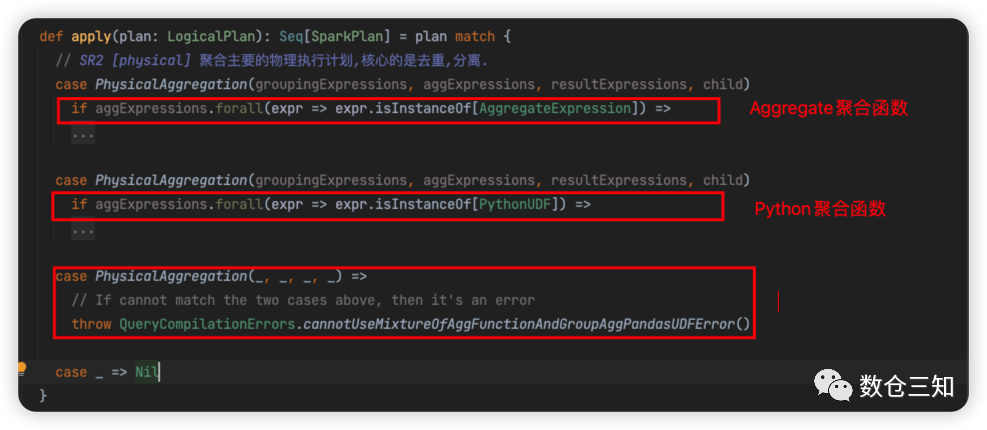
最外层根据聚合表达式(聚合表达式提取下文详述)类型分为2个分支,AggregateExpression
聚合分支和PythonUDF
聚合分支。PythonUDF聚合分支生成AggregateInPandasExec
;AggregateExpression
聚合分支生成HashAggregateExec
、ObjectHashAggregateExec
、SortAggregateExec
中一个。
这里单独分析AggregateExpression
分支,分支流程:
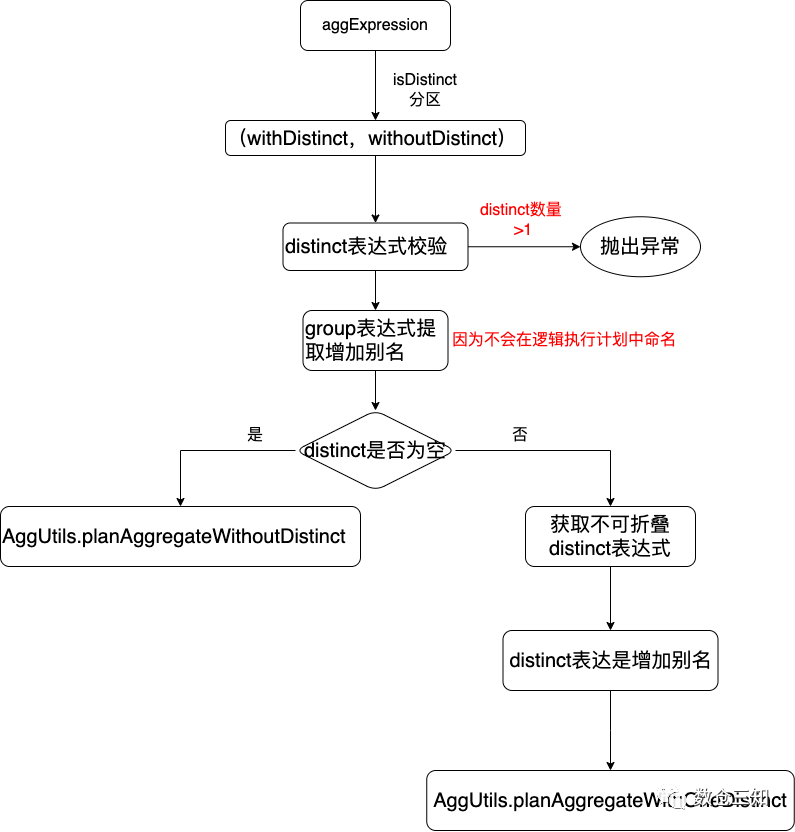
从流程上来看有3个重要的步骤:
1. 聚合元素提取,如聚合表达式`aggExpressions`、分组表达式`groupingExpressions`、聚合输出表达式`resultExpressions`;
1. 无distinct表达式的聚合函数生成;
1. 有一个distinct表达式的聚合函数生成;
下一节逐一进行拆分。
2 聚合元素提取
聚合元素提取方法是在 org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.planning.PhysicalAggregation#unapply
。主要包含聚合表达式、分组表达式、聚合输出结果三个元素:
1. 提取聚合表达式
aggExpressions
val equivalentAggregateExpressions = new EquivalentExpressions
val aggregateExpressions = resultExpressions.flatMap { expr =>
expr.collect {
// addExpr() always returns false for non-deterministic expressions and do not add them.
case a
if AggregateExpression.isAggregate(a) && !equivalentAggregateExpressions.addExpr(a) =>
a
}
}
对logical.Aggregate
逻辑执行计划中的输出结果resultExpressions
中的是聚合表达式(AggregateExpression
)进行提取。其中equivalentAggregateExpressions
的作用是对语义相同(具体判断逻辑挖个坑)的表达式进行去重,如sum(a + b)
和sum(b + a)
去重后只有sum(a + b)
,避免同一语义聚合表达式多次计算,增加计算成本。
1. 提取分组表达式
groupingExpressions
val namedGroupingExpressions = groupingExpressions.map {
case ne: NamedExpression => ne -> ne
// If the expression is not a NamedExpressions, we add an alias.
// So, when we generate the result of the operator, the Aggregate Operator
// can directly get the Seq of attributes representing the grouping expressions.
case other =>
val withAlias = Alias(other, other.toString)()
other -> withAlias
}
groupingExpressions = namedGroupingExpressions.map(_._2),
logical.Aggregate
逻辑执行计划中的分组表达提取,如果是NameExpression
返回本身,对于其他增加别名,便于在后续确定字段的唯一性,方便引用。
1. 提取聚合输出表达式
resultExpressions
val rewrittenResultExpressions = resultExpressions.map { expr =>
expr.transformDown {
case ae: AggregateExpression =>
// The final aggregation buffer's attributes will be `finalAggregationAttributes`,
// so replace each aggregate expression by its corresponding attribute in the set:
equivalentAggregateExpressions.getExprState(ae).map(_.expr)
.getOrElse(ae).asInstanceOf[AggregateExpression].resultAttribute
// Similar to AggregateExpression
case ue: PythonUDF if PythonUDF.isGroupedAggPandasUDF(ue) =>
equivalentAggregateExpressions.getExprState(ue).map(_.expr)
.getOrElse(ue).asInstanceOf[PythonUDF].resultAttribute
case expression if !expression.foldable =>
// Since we're using `namedGroupingAttributes` to extract the grouping key
// columns, we need to replace grouping key expressions with their corresponding
// attributes. We do not rely on the equality check at here since attributes may
// differ cosmetically. Instead, we use semanticEquals.
groupExpressionMap.collectFirst {
case (expr, ne) if expr semanticEquals expression => ne.toAttribute
}.getOrElse(expression)
}.asInstanceOf[NamedExpression]
}
提取逻辑是对logical.Aggregate
逻辑执行计划中的输出表达式遍历,如果AggregateExpression
从去重后的聚合表达式集合中获取到对应表达式,取其resultAttribute
属性;如果是其他表达式从上面增加别名后的分组元素列表groupExpressionMap
中取attribute
。
3 聚合物理计划生成
3.1 前置知识
1. 聚合模式
spark是分布式计算框架,定义了4中集合模式,Partial
局部聚合、PartialMerge
局部合并、Final
最终聚合及Complete
完全聚合。
• Partial:局部数据聚合。发生在读取原始数据所在的执行节点,对输入的数据进行聚合,返回局部聚合结果。
• PartialMerge:对前面Partial返回的聚合缓冲区进行合并。
• Final:将局部聚合的结果进行数据合并,返回最终聚合结果。
• Complete:用于直接从原始输入数据进行聚合,应用在不支持Partial模式的聚合函数上(比如求百分位percentile_approx)。
2. 聚合实现类
spark的聚合实现有HashAggregateExec
、ObjectHashAggregateExec
、SortAggregateExec
。这三种实现的效率依次降低,是根据聚合表达式的属性进行选择。
• HashAggregateExec满足以下条件:聚合表达式的类型都(
forall
)属于NullType
、BooleanType
、ByteType
、ShortType
、IntegerType
、LongType
、FloatType
、DoubleType
、DateType
、TimestampType
、TimestampNTZType$.MODULE$
、DecimalType
、CalendarIntervalType
、DayTimeIntervalType
、YearMonthIntervalType
中。• ObjectHashAggregateExec需要同时满足以下条件:
a. spark.sql.execution.useObjectHashAggregateExec
参数为true,默认是true。
b. 聚合表达式是TypedImperativeAggregate
子类。
def supportsObjectHashAggregate(aggregateExpressions: Seq[AggregateExpression]): Boolean = {
aggregateExpressions.map(_.aggregateFunction).exists {
case _: TypedImperativeAggregate[_] => true
case _ => false
}
}
• SortAggregateExec:当不符合上述两个聚合方式时,选择该聚合方式。
3.2 without distinct聚合
without distinct的聚合是由AggUtils.planAggregateWithoutDistinct
生成。以下面的SQL为例:
select a, sum(b) from `testdata2` as t1 group by a
优化后的逻辑执行计划是:
Aggregate [a#3], [a#3, sum(b#4) AS sum(b)#11L]
+- SerializeFromObject [a#3, b#4]
+- ExternalRDD [obj#2]
经过Aggregate策略后生成的物理执行计划是:
HashAggregate(keys=[a#3], functions=[sum(b#4)], output=[a#3, sum(b)#11L]) // ①
+- HashAggregate(keys=[a#3], functions=[partial_sum(b#4)], output=[a#3, sum#15L]) // ②
+- SerializeFromObject[a#3, b#4]
+- Scan[obj#2]
AggUtils.planAggregateWithoutDistinct
执行生成流程:
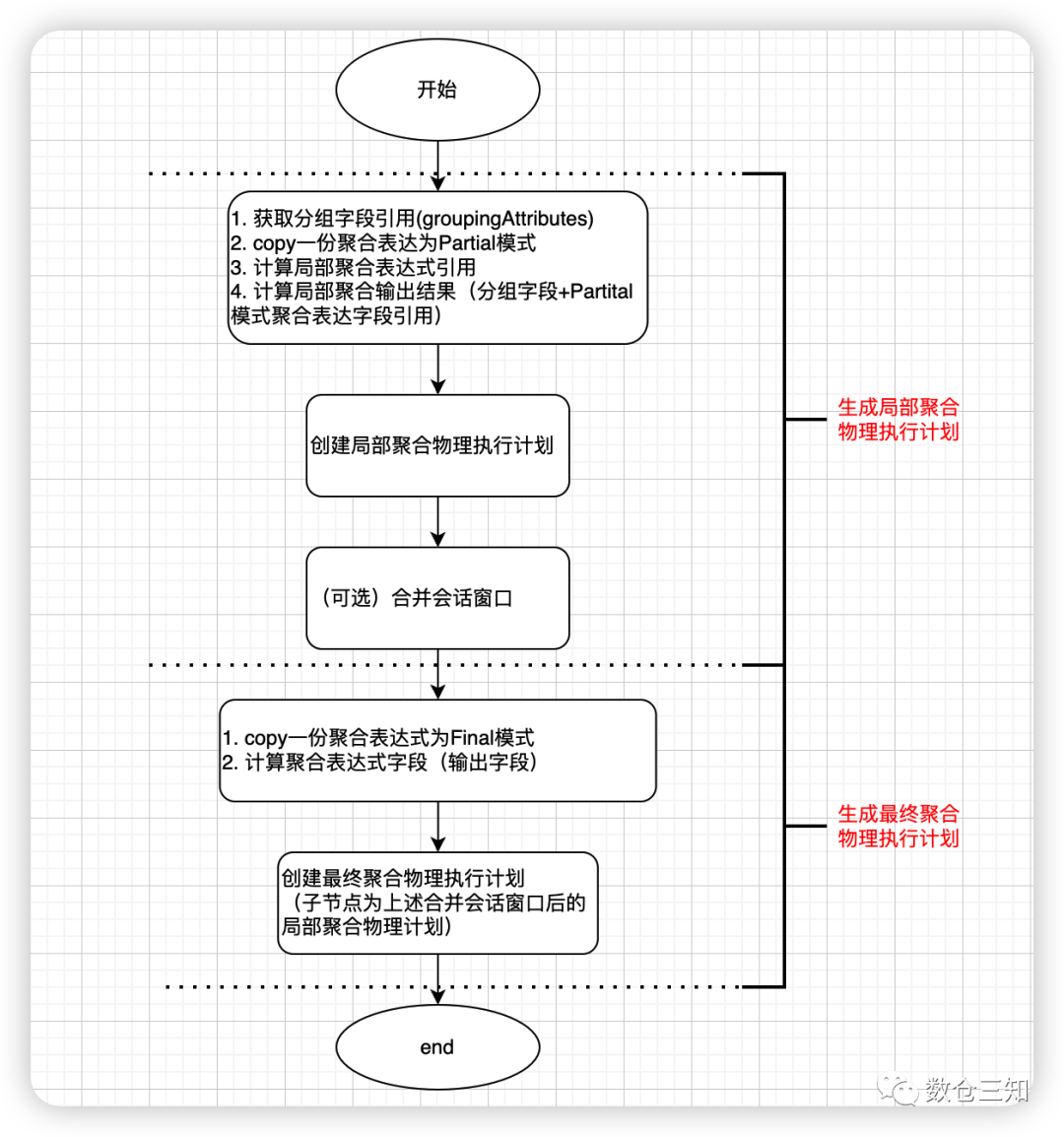
主要分2个步骤生成局部聚合和最终聚合,用下面真实的聚合计算流程更容易理解:
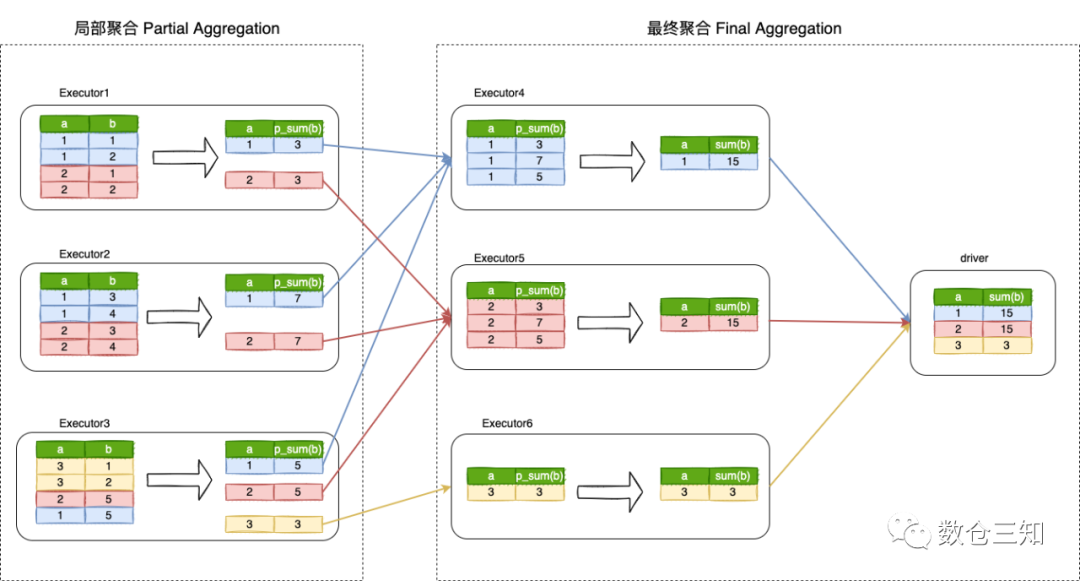
第一Partial聚合,每个分区按照a列进行分组,输出该分区的p_sum值。然后,将Partial聚合阶段的数据结果按照a列进行shuffle重分区,以便具有相同a列的行将被置于同一分区并在同一Spark executor中执行。最后执行Final聚合,将每个分区的所有p_sum数量加起来,并将最终结果返回给driver端。
3.3 one distinct聚合
one distinct的聚合是由AggUtils.planAggregateWithOneDistinct
生成。以下面的SQL为例:
select a, count(distinct b), sum(b) from `testdata2` as t1 group by a
优化后的逻辑执行计划是:
Aggregate [a#3], [a#3, count(distinct b#4) AS count(DISTINCT b)#12L, sum(b#4) AS sum(b)#13L]
+- SerializeFromObject [a#3, b#4]
+- ExternalRDD [obj#2]
经过Aggregate策略后生成的物理执行计划是:
HashAggregate(keys=[a#3], functions=[sum(b#4), count(distinct b#4)], output=[a#3, count(DISTINCT b)#12L, sum(b)#13L])
+- HashAggregate(keys=[a#3], functions=[merge_sum(b#4), partial_count(distinct b#4)], output=[a#3, sum#18L, count#21L])
+- HashAggregate(keys=[a#3, b#4], functions=[merge_sum(b#4)], output=[a#3, b#4, sum#18L])
+- HashAggregate(keys=[a#3, b#4], functions=[partial_sum(b#4)], output=[a#3, b#4, sum#18L])
+- SerializeFromObject [a#3, b#4]
+- Scan[obj#2]
含distinct的聚合物理计划生成比较复杂,先分析下AggUtils.planAggregateWithOneDistinct
方法的参数:
1.
groupingExpressions
归一化后的分组表达式;2. 聚合计算表达式有
functionsWithDistinct
和functionsWithoutDistinct
两个,这两个的计算位置在不同的聚合阶段;3.
distinctExpressions
去重表达式,在PartialMerge
阶段去重使用;4.
normalizedNamedDistinctExpressions
归一化后去重字段名称,用于在Partial
聚合阶段与分组表达联合生成分组字段;5.
resultExpressions
聚合输出结果表达式。
上述参数在例子中分别对应值分别是:
groupingExpressions = ArrayBuffer(a#3);
functionsWithDistinct = List(count(distinct b#4));
functionsWithoutDistinct = List(sum(b#4));
distinctExpressions = ArrayBuffer(b#4);
normalizedNamedDistinctExpressions = ArrayBuffer(b#4);
resultExpressions = List(a#3, count(b#4)#10L AS count(DISTINCT b)#12L, sum(b#4)#11L AS sum(b)#13L)
熟悉了函数参数后,来分析具体的算法逻辑:
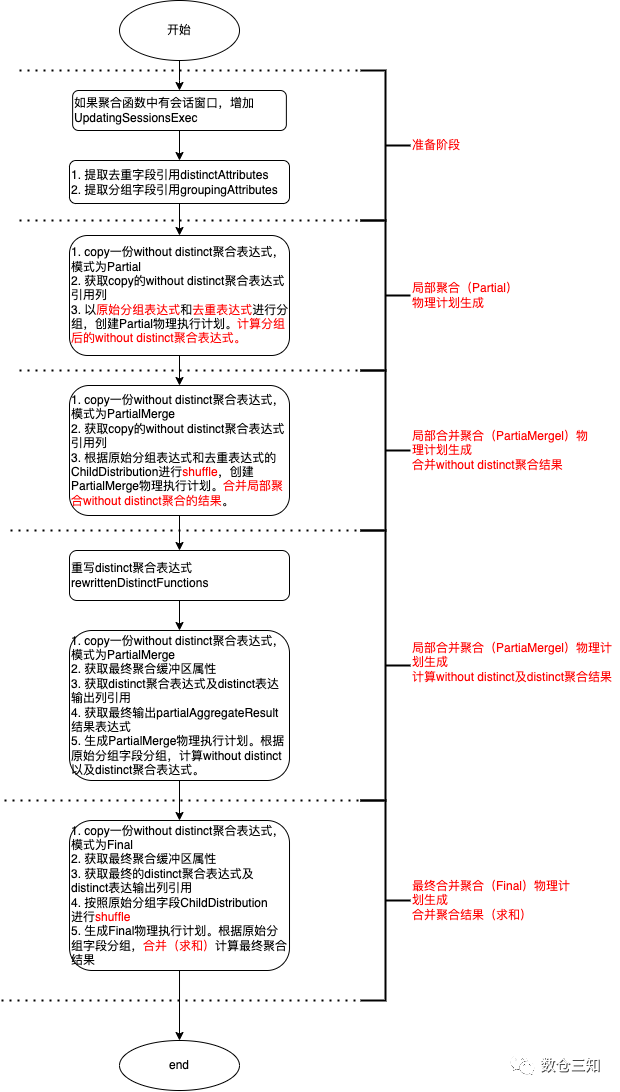
one distinct的聚合物理执行计划生成步骤比较复杂,看流程图不是很容易理解,我们用实际例子来描述:
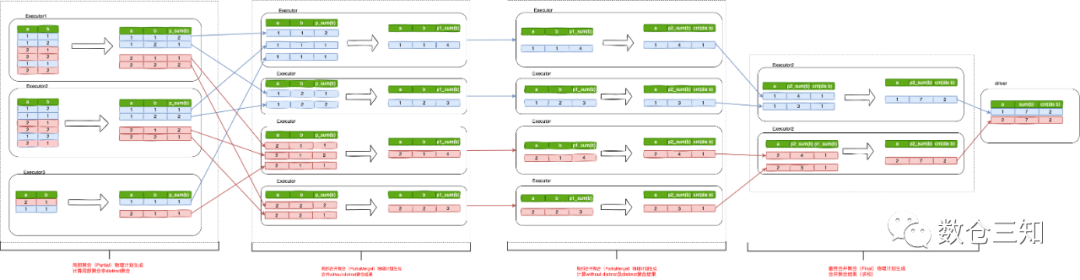
由图可以看出,distinct聚合计算发生2次shuffle。
3.4 多个distinct聚合
多个distinct列的聚合,spark在逻辑执行计划优化阶段进行了重写,通过对数据Expand后,转换成一个distinct的聚合,具体的转换逻辑在RewriteDistinctAggregates
规则中。生成物理执行计划同上。以具体实例为例:
select
course,
count(distinct year) as year_cnt,
count(distinct earnings) earnings_cnt
from courseSales group by course
优化前的逻辑执行计划:
Aggregate [course#24], [course#24, count(distinct year#25) AS year_cnt#34L, count(distinct earnings#26) AS earnings_cnt#35L]
+- SubqueryAlias coursesales
+- View (`courseSales`, [course#24,year#25,earnings#26])
+- SerializeFromObject [ course#24, year#25, earnings#26]
+- ExternalRDD [obj#23]
优化后的逻辑执行计划:
Aggregate [course#24], [course#24, count(coursesales.year#42) FILTER (WHERE (gid#41 = 1)) AS year_cnt#34L, count(coursesales.earnings#43) FILTER (WHERE (gid#41 = 2)) AS earnings_cnt#35L]
+- Aggregate [course#24, coursesales.year#42, coursesales.earnings#43, gid#41], [course#24, coursesales.year#42, coursesales.earnings#43, gid#41]
+-Expand [[course#24, year#25, null, 1], [course#24, null, earnings#26, 2]], [course#24, coursesales.year#42, coursesales.earnings#43, gid#41]
+- SerializeFromObject [ course#24, year#25, earnings#26]
+- ExternalRDD [obj#23]
思考:这样做的收益是什么呢?
4 小结
本文以具体SQL探索了Aggregate
物理执行计划的生成过程,个人觉得逻辑的核心是如何在分布式环境下进行聚合计算,重在理解局部聚合、局部合并、局部合并(for distinct)及最终聚合4个过程。
有人一定也发现了通过Aggregate
策略生成的物理执行计划中缺少shuffle算子,其实shuffle算子的生成是在QueryExecution#executedPlan
中生成,放在下一篇进行探索。
lazy val executedPlan: SparkPlan = {
// We need to materialize the optimizedPlan here, before tracking the planning phase, to ensure
// that the optimization time is not counted as part of the planning phase.
assertOptimized()
executePhase(QueryPlanningTracker.PLANNING) {
// clone the plan to avoid sharing the plan instance between different stages like analyzing,
// optimizing and planning.
QueryExecution.prepareForExecution(preparations, sparkPlan.clone())
}
}






