点击上方蓝字【囧囧妹】一起学习,一起成长!
一、开篇
最近两年一直在学习密码安全,感谢我的职场老师带我入门,我才非常快速的进入这个行业。最近整理了之前做的一套网络链路层加密的软件。这里主要涉及netfilter、skb、linux内核的一些东西。
我将我总结的资料整理成pdf版本放在了百度云盘上,感兴趣的可以关注囧囧妹公众号,回复“密码学常识”来获取。
二、sk_buff
我们先从sk_buff说起,关于它的简介就不多说了,直接从linux内核源码开始来。
我用的linux内核版本4.4.266。关于skb的定义在sk_buff结构体定义在文件/linux-4.4.266/include/linux/skbuff.h
/*** struct sk_buff - socket buffer* @next: Next buffer in list* @prev: Previous buffer in list* @tstamp: Time we arrived/left* @rbnode: RB tree node, alternative to next/prev for netem/tcp* @sk: Socket we are owned by* @dev: Device we arrived on/are leaving by* @cb: Control buffer. Free for use by every layer. Put private vars here* @_skb_refdst: destination entry (with norefcount bit)* @sp: the security path, used for xfrm* @len: Length of actual data* @data_len: Data length* @mac_len: Length of link layer header* @hdr_len: writable header length of cloned skb* @csum: Checksum (must include start/offset pair)* @csum_start: Offset from skb->head where checksumming should start* @csum_offset: Offset from csum_start where checksum should be stored* @priority: Packet queueing priority* @ignore_df: allow local fragmentation* @cloned: Head may be cloned (check refcnt to be sure)* @ip_summed: Driver fed us an IP checksum* @nohdr: Payload reference only, must not modify header* @nfctinfo: Relationship of this skb to the connection* @pkt_type: Packet class* @fclone: skbuff clone status* @ipvs_property: skbuff is owned by ipvs* @peeked: this packet has been seen already, so stats have been* done for it, don't do them again* @nf_trace: netfilter packet trace flag* @protocol: Packet protocol from driver* @destructor: Destruct function* @nfct: Associated connection, if any* @nf_bridge: Saved data about a bridged frame - see br_netfilter.c* @skb_iif: ifindex of device we arrived on* @tc_index: Traffic control index* @tc_verd: traffic control verdict* @hash: the packet hash* @queue_mapping: Queue mapping for multiqueue devices* @xmit_more: More SKBs are pending for this queue* @pfmemalloc: skbuff was allocated from PFMEMALLOC reserves* @ndisc_nodetype: router type (from link layer)* @ooo_okay: allow the mapping of a socket to a queue to be changed* @l4_hash: indicate hash is a canonical 4-tuple hash over transport* ports.* @sw_hash: indicates hash was computed in software stack* @wifi_acked_valid: wifi_acked was set* @wifi_acked: whether frame was acked on wifi or not* @no_fcs: Request NIC to treat last 4 bytes as Ethernet FCS* @napi_id: id of the NAPI struct this skb came from* @secmark: security marking* @offload_fwd_mark: fwding offload mark* @mark: Generic packet mark* @vlan_proto: vlan encapsulation protocol* @vlan_tci: vlan tag control information* @inner_protocol: Protocol (encapsulation)* @inner_transport_header: Inner transport layer header (encapsulation)* @inner_network_header: Network layer header (encapsulation)* @inner_mac_header: Link layer header (encapsulation)* @transport_header: Transport layer header* @network_header: Network layer header* @mac_header: Link layer header* @tail: Tail pointer* @end: End pointer* @head: Head of buffer* @data: Data head pointer* @truesize: Buffer size* @users: User count - see {datagram,tcp}.c*/struct sk_buff {union {struct {/* These two members must be first. */struct sk_buff *next;struct sk_buff *prev;union {ktime_t tstamp;struct skb_mstamp skb_mstamp;};};struct rb_node rbnode; /* used in netem, ip4 defrag, and tcp stack */};union {struct sock *sk;int ip_defrag_offset;};struct net_device *dev;/** This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every* layer. Please put your private variables there. If you* want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone()* first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM.*/char cb[48] __aligned(8);unsigned long _skb_refdst;void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb);#ifdef CONFIG_XFRMstruct sec_path *sp;#endif#if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE)struct nf_conntrack *nfct;#endif#if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER)struct nf_bridge_info *nf_bridge;#endifunsigned int len,data_len;__u16 mac_len,hdr_len;/* Following fields are _not_ copied in __copy_skb_header()* Note that queue_mapping is here mostly to fill a hole.*/kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags1);__u16 queue_mapping;__u8 cloned:1,nohdr:1,fclone:2,peeked:1,head_frag:1,xmit_more:1,pfmemalloc:1;kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags1);/* fields enclosed in headers_start/headers_end are copied* using a single memcpy() in __copy_skb_header()*//* private: */__u32 headers_start[0];/* public: *//* if you move pkt_type around you also must adapt those constants */#ifdef __BIG_ENDIAN_BITFIELD#define PKT_TYPE_MAX (7 << 5)#else#define PKT_TYPE_MAX 7#endif#define PKT_TYPE_OFFSET() offsetof(struct sk_buff, __pkt_type_offset)__u8 __pkt_type_offset[0];__u8 pkt_type:3;__u8 ignore_df:1;__u8 nfctinfo:3;__u8 nf_trace:1;__u8 ip_summed:2;__u8 ooo_okay:1;__u8 l4_hash:1;__u8 sw_hash:1;__u8 wifi_acked_valid:1;__u8 wifi_acked:1;__u8 no_fcs:1;/* Indicates the inner headers are valid in the skbuff. */__u8 encapsulation:1;__u8 encap_hdr_csum:1;__u8 csum_valid:1;__u8 csum_complete_sw:1;__u8 csum_level:2;__u8 csum_bad:1;#ifdef CONFIG_IPV6_NDISC_NODETYPE__u8 ndisc_nodetype:2;#endif__u8 ipvs_property:1;__u8 inner_protocol_type:1;__u8 remcsum_offload:1;/* 3 or 5 bit hole */#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED__u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */#ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT__u16 tc_verd; /* traffic control verdict */#endif#endifunion {__wsum csum;struct {__u16 csum_start;__u16 csum_offset;};};__u32 priority;int skb_iif;__u32 hash;__be16 vlan_proto;__u16 vlan_tci;#if defined(CONFIG_NET_RX_BUSY_POLL) || defined(CONFIG_XPS)union {unsigned int napi_id;unsigned int sender_cpu;};#endifunion {#ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK__u32 secmark;#endif#ifdef CONFIG_NET_SWITCHDEV__u32 offload_fwd_mark;#endif};union {__u32 mark;__u32 reserved_tailroom;};union {__be16 inner_protocol;__u8 inner_ipproto;};__u16 inner_transport_header;__u16 inner_network_header;__u16 inner_mac_header;__be16 protocol;__u16 transport_header;__u16 network_header;__u16 mac_header;/* private: */__u32 headers_end[0];/* public: *//* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */sk_buff_data_t tail;sk_buff_data_t end;unsigned char *head,*data;unsigned int truesize;atomic_t users;};
struct sk_buff_head {/* These two members must be first. */struct sk_buff*next;struct sk_buff*prev;__u32qlen;//skb链表中的节点数,队列长度spinlock_tlock;//用于控制对skb链表并发操作的自旋锁};
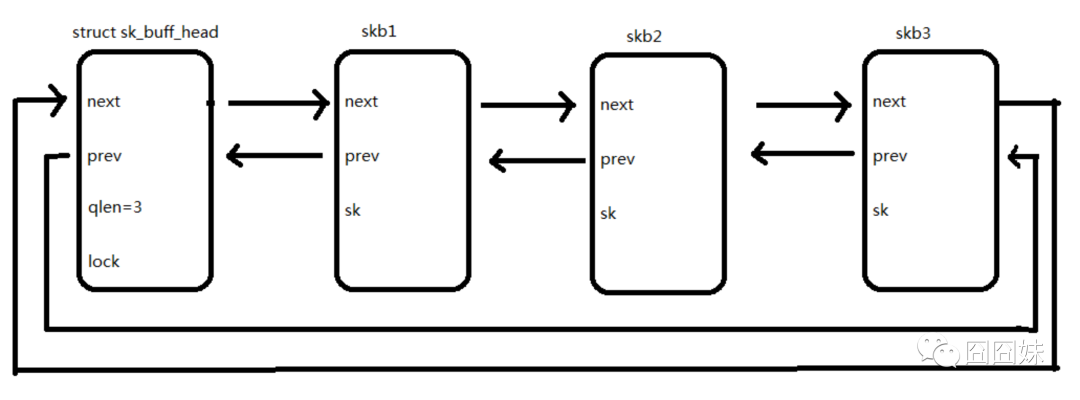
【skb数据存储相关变量】
struct sock *sk skb的宿主传输控制块在网络数据报文由本地发出或由本地接收时才有效,使传输控制块与套接口及用户应用程序相关。当一个skb仅在二层或者三层被转发时,即源IP和目的IP都不是本机地址时该指针值为NULL。
unsigned int len skb中数据部分长度。该字段值随着skb从一个协议层向另一个协议层传递而改变,向上传递时下层首部就不再需要了,而向下层传递时需添加本层首部,因此len也包含了协议首部的长度。(len=线性缓冲区数据长度+SG类型的聚合分散IO数据长度+FRAGLIST类型的聚合分散IO数据长度)
unsigned int data_lenSG类型和FRAGLIST类型聚合分散IO存储区中的数据长度
__u16 mac_len二层首部长度
void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb);skb析构函数指针,释放skb时被调用。在转发时如果skb没有宿主传输控制块则该指针为NULL。
unsigned char *data指向数据的头
sk_buff_data_t tail指向数据的尾(typedef unsigned char *sk_buff_data_t;)
sk_buff_data_t end指向缓冲区的尾
unsigned char *head指向缓冲区的头
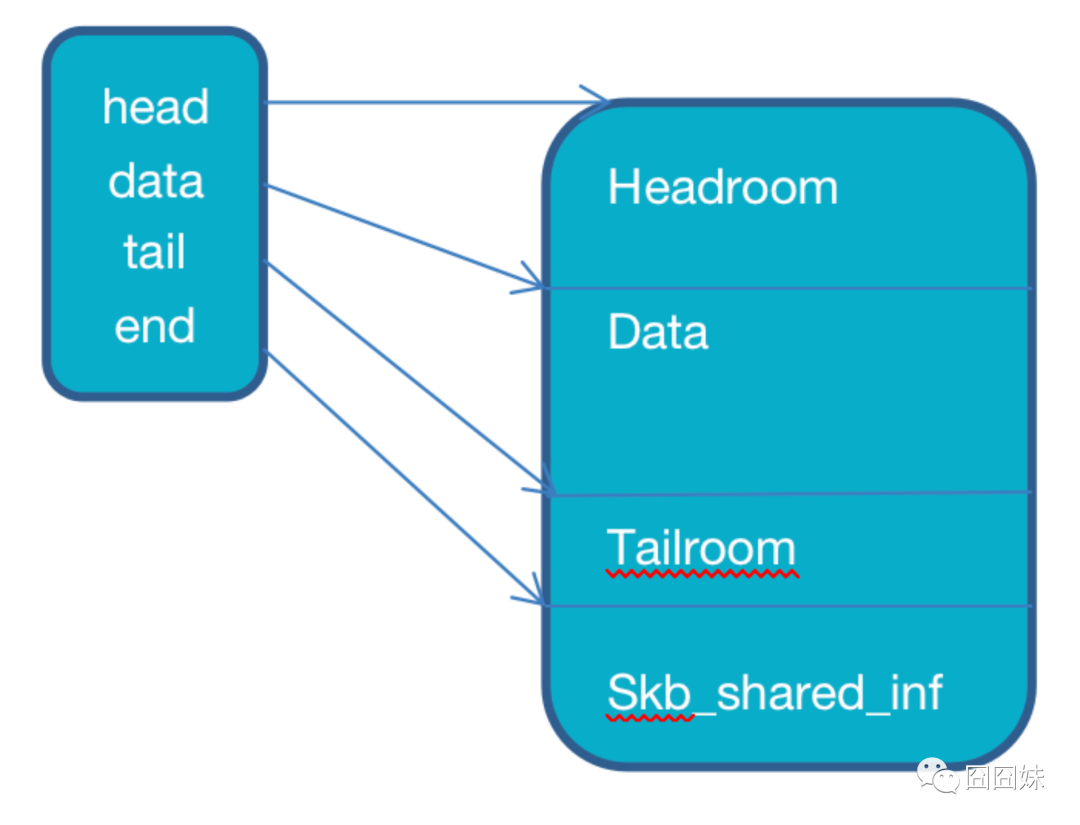
unsigned int truesize整个数据缓存区的总长度,alloc_skb()会将truesize初始化成len+sizeof(sk_buff)
atomic_t users引用计数,用来标识有多少实体引用了该skb。其主要作用是确定释放所属skb的时机,当计数器为零时,skb才能被释放。因此,每个引用该skb的实体都必须在适当的时候递增和递减引用计数,该计数器只保护skb描述符,而skb数据缓存区也有类似的计数器(skb_shared_info结构中的dataref),通常使用skb_get()和kfree_skb()操作skb描述符引用计数。skb_get()在返回前先执行atomic_inc()操作,而kfree_skb则先执行atomic_dec_and_test(),当引用计数为0时就会释放skb,否则只是简单递减计数。
【skb通用成员变量】
union {ktime_ttstamp;struct skb_mstamp skb_mstamp;};
接收或发送时间戳,在网络设备收到一个数据包后通过netif_receive_skb()和netif_rx调用net_timestamp()来设置。
struct net_device*dev;网络设备指针,接收数据包时该指针指向收到数据包的网络设备,发送数据包时该指针指向输出数据包的网络设备。
Linux支持多种形式的虚拟网络设备并由一个虚拟网络设备驱动管理,当这个虚拟设备被使用时,dev指着指向该虚拟设备的net_device结构,在输出时虚拟设备驱动会在一组设备中选择其中的某个合适的设备,并将dev指针修改为指向这个设备的net_device,而在输入时,当原始网络设备接收到报文后,根据某种算法选择某个合适的虚拟网络设备,并将dev指针修改为指向这个虚拟设备的net_device结构。
charcb[48] __aligned(8);skb信息控制块,由每层协议自己维护并使用,只在本层有效。
__u8ip_summed:2;标记传输层校验和的状态
ip_summed取下述值:
#define CHECKSUM_NONE 0//硬件不支持,完全由软件来执行校验和
#define CHECKSUM_UNNECESSARY 1//没有必要执行校验和
#define CHECKSUM_COMPLETE 2//已经完成执行校验和
#define CHECKSUM_PARTIAL 3//由硬件来执行校验和
union {__wsumcsum;struct {__u16csum_start;__u16csum_offset;};};
csum在校验状态为CHECKSUM_NONE时用于存放负载数据报的数据部分的校验和;csum_offset在校验状态为CHECKSUM_PARTIAL时记录传输层首部中的校验和字段的偏移.
__u8cloned:1,标记skb是否已克隆
__u8pkt_type:3;帧类型,分类由二层目的地址来决定.
pkt_type取值如下:
#define PACKET_HOST 0 /* To us */
#define PACKET_BROADCAST 1 /* To all */
#define PACKET_MULTICAST 2 /* To group */
#define PACKET_OTHERHOST 3 /* To someone else */
#define PACKET_OUTGOING 4 /* Outgoing of any type */
#define PACKET_LOOPBACK 5 /* MC/BRD frame looped back */
#define PACKET_USER 6 /* To user space */
#define PACKET_KERNEL 7 /* To kernel space */
__u32priority;发送或转发数据包QoS类别。
__be16protocol;从二层设备角度看到的上层协议。
【标志性变量】
__u8nohdr:1,标识payload是否被单独引用,不存在协议首部。
__u8fclone:2,当前克隆状态
fclone取值如下:
enum {SKB_FCLONE_UNAVAILABLE, /* skb has no fclone (from head_cache) 未被克隆*/SKB_FCLONE_ORIG, /* orig skb (from fclone_cache) 分配的父skb,可以被克隆*/SKB_FCLONE_CLONE, /* companion fclone skb (from fclone_cache) 分配的子skb,从父skb克隆得到的*/};
SKB_FCLONE_UNAVAILABLE 表示未被克隆
SKB_FCLONE_ORIG 表示分配的父skb,可以被克隆
SKB_FCLONE_CLONE 表示分配的子skb,从父skb克隆得到的
总结一下,这里只是介绍了下skb的定义,以及其内部的数据描述,结构比较复杂,下一节我们来着重看关于skb的操作。明白数据描述和操作后我们就可以通过skb来做一套网络链路层加密软件,应用层无需改变任何代码只需加载一套内核ko驱动即可完成网络数据在物理线路上的密文传输。
如果有不对的或者问题大家可以后台私信我们一起学习!一起进步!






