蓝字 关注我吧

阅读本文大概需要18分钟
MyBatis常用注解
这几年来注解开发越来越流行,Mybatis也可以使用注解开发方式,这样我们就可以减少编写Mapper映射文件了。我们先了解一些基本的CRUD,再看一下复杂映射多表操作。
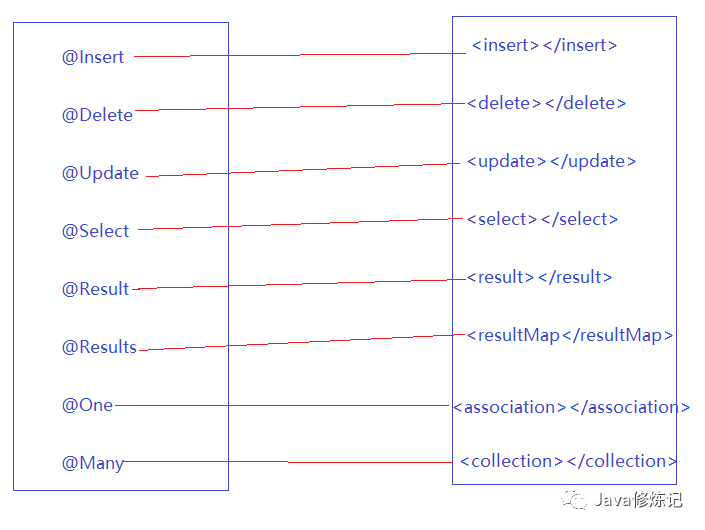
* @Insert:实现新增,代替了<insert></insert>
* @Delete:实现删除,代替了<delete></delete>
* @Update:实现更新,代替了<update></update>
* @Select:实现查询,代替了<select></select>
* @Result:实现结果集封装,代替了<result></result>
* @Results:可以与@Result一起使用,封装多个结果集,代替了<resultMap></resultMap>
* @One:实现一对一结果集封装,代替了<association></association>
* @Many:实现一对多结果集封装,代替了<collection></collection>
MyBatis注解的增删改查【重点】
1. 创建UserMapper接口
public interface UserMapper {
/*
查询用户
*/
@Select("select * from user")
public List<User> findAll();
/*
添加用户
*/
@Insert("insert into user(username,birthday,sex,address)
values(#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})")
public void save(User user);
/*
更新用户
*/
@Update("update user set username = #{username},birthday=#{birthday}
where id = #{id}")
public void update(User user);
/*
删除用户
*/
@Delete("delete from user where id = #{id}")
public void delete(Integer id);
}
2. 编写核心配置文件
sqlMapConfig.xml
<!-- xml文件方式,引入映射文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="com/zwt/mapper/UserMapper.xml"></mapper>
</mappers>
<!-- 注解方式,引入映射文件 -->
<mappers>
<!-- 方式一:这里使用了注解替代的映射文件,
所以我们只需要加载使用了注解的Mapper接口即可-->
<!-- <mapper class="com.zwt.mapper.UserMapper"></mapper>-->
<!-- 方式二:扫描使用注解的Mapper类所在的包,批量加载映射-->
<package name="com.zwt.mapper"/>
</mappers>
3. 测试代码
public class MybatisTest {
private SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory;
private SqlSession sqlSession;
// 在 @Test方法标注的方法执行之前来执行
@Before
public void before() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("sqlMapConfig.xml");
sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
}
// 在 @Test方法标注的方法执行之后来执行
@After
public void after(){
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
}
// 查询
@Test
public void testSelect() throws IOException {
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> all = mapper.findAll();
for (User user : all) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
// 添加
@Test
public void testInsert(){
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("汤唯");
user.setSex("女");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setAddress("北京");
mapper.save(user);
}
// 更新
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = new User();
user.setUsername("柳岩真美");
user.setBirthday(new Date());
user.setId(9);
mapper.update(user);
}
// 删除
@Test
public void testDelete(){
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
mapper.delete(9);
}
}
使用注解实现复杂映射开发
之前我们在映射文件中通过配置 <resultMap>、<association>、<collection> 来实现复杂关系映射。
使用注解开发后,我们可以使用 @Results、@Result,@One、@Many 注解组合完成复杂关系的配置。

一对一查询
1. 介绍
需求:查询一个订单,与此同时查询出该订单所属的用户
一对一查询语句
SELECT * FROM orders;
SELECT * FROM `user` WHERE id = #{订单的uid};
2. 代码实现
a)OrderMapper接口
OrderMapper.java
/*
查询所有订单,同时查询订单所属的用户信息
*/
@Select("select * from orders")
@Results({ // 代替的就是resultMap标签 id标签 result标签
@Result(property = "id",column = "id",id = true),
@Result(property = "ordertime",column = "ordertime"),
@Result(property = "total",column = "total"),
@Result(property = "uid",column = "uid"),
@Result(property = "user",javaType = User.class,column = "uid",
one = @One(select = "com.zwt.mapper.UserMapper.findById"))
})
public List<Orders> findAllWithUser();
对应 xml 写法如下:
OrderMapper.xml
<resultMap id="orderMap" type="com.zwt.domain.Orders">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="ordertime" column="ordertime"/>
<result property="total" column="total"/>
<result property="uid" column="uid"/>
<!--
根据订单中uid外键,查询用户表
property:属性名
javaType:属性类型
select:子查询语句的statementId
column: 子查询参数 所对应的列名
-->
<association property="user" javaType="com.zwt.domain.User"
select="com.zwt.mapper.UserMapper.findById"
column="uid" />
</resultMap>
<!--一对一嵌套查询-->
<select id="findAllWithUser" resultMap="orderMap">
SELECT * FROM orders
</select>
b)UserMapper接口
public interface UserMapper {
/*
子查询:根据id查询用户
*/
@Select("SELECT * FROM `user` WHERE id = #{id}")
public User findById(Integer id);
}
c)测试代码
/*
一对一查询(注解方式)
*/
@Test
public void testOneToOne(){
OrderMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(OrderMapper.class);
List<Orders> allWithUser = mapper.findAllWithUser();
for (Orders orders : allWithUser) {
System.out.println(orders);
}
}
一对多查询
1. 介绍
需求:查询一个用户,与此同时查询出该用户具有的订单
一对多查询语句
SELECT * FROM `user`;
SELECT * FROM orders where uid = #{用户id};
2. 代码实现
a)UserMapper接口
userMapper.java
/*
查询所有用户,及关联的订单信息
*/
@Select("select * from user")
@Results({
@Result(property = "id",column = "id",id = true),
@Result(property = "username",column = "username"),
@Result(property = "birthday",column = "birthday"),
@Result(property = "sex",column = "sex"),
@Result(property = "address",column = "address"),
@Result(property = "ordersList",javaType = List.class,column = "id",
many = @Many(select = "com.zwt.mapper.OrderMapper.findOrderByUid"))
})
public List<User> findAllWithOrder();
对应 xml 写法如下:
userMapper.xml
<!-- 一对多嵌套查询:
查询所有的用户,同时还要查询出每个用户所关联的订单信息 -->
<resultMap id="userOrderMap" type="com.zwt.domain.User">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="birthday" column="birthday"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="address" column="address"></result>
<!--根据用户id,查询订单表-->
<collection property="ordersList" ofType="com.zwt.domain.Orders"
column="id" select="com.zwt.mapper.OrderMapper.findOrderByUid" >
</collection>
</resultMap>
<select id="findAllWithOrder" resultMap="userOrderMap">
SELECT * FROM USER
</select>
b)OrderMapper接口
public interface OrderMapper {
/*
根据传递过来的用户id,查询该用户所具有的订单信息
*/
@Select("select * from orders where uid = #{uid}")
public List<Orders> findOrderByUid(Integer uid);
}
c)测试代码
/*
一对多查询(注解方式)
*/
@Test
public void testOneToMany(){
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> allWithOrder = mapper.findAllWithOrder();
for (User user : allWithOrder) {
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(user.getOrdersList());
}
}
多对多查询
1. 介绍
需求:查询所有用户,同时查询出该用户的所有角色
多对多查询语句
SELECT * FROM `user`;
SELECT * FROM role r INNER JOIN user_role ur ON r.`id` = ur.`rid`
WHERE ur.`uid` = #{用户id};
2. 代码实现
a)UserMapper接口
userMapper.java
/*
查询所有用户及关联的角色信息
*/
@Select("select * from user")
@Results({
@Result(property = "id",column = "id",id = true),
@Result(property = "username",column = "username"),
@Result(property = "birthday",column = "birthday"),
@Result(property = "sex",column = "sex"),
@Result(property = "address",column = "address"),
@Result(property = "roleList",javaType = List.class,column = "id",
many = @Many(select = "com.zwt.mapper.RoleMapper.findAllByUid")),
})
public List<User> findAllWithRole();
对应 xml 写法如下:
userMapper.xml
<resultMap id="userRoleMap" type="com.zwt.domain.User">
<id property="id" column="id"/>
<result property="username" column="username"></result>
<result property="birthday" column="birthday"></result>
<result property="sex" column="sex"></result>
<result property="address" column="address"></result>
<!--根据用户id,查询角色列表-->
<collection property="roleList" ofType="com.zwt.domain.Role"
column="id" select="com.zwt.mapper.RoleMapper.findByUid">
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!--
多对多嵌套查询:
查询所有的用户,同时还要查询出每个用户所关联的角色信息
-->
<select id="findAllWithRole" resultMap="userRoleMap">
SELECT * FROM USER
</select>
b)RoleMapper接口
public interface RoleMapper {
/*
子查询:根据传递过来的用户id,查询该用户所具有的角色信息
*/
@Select("SELECT * FROM sys_role r INNER JOIN sys_user_role ur
ON ur.roleid = r.id WHERE ur.userid = #{uid}")
public List<Role> findAllByUid(Integer uid);
}
c)测试代码
/*
多对多查询(注解方式)
*/
@Test
public void testManyToMany(){
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> allWithRole = mapper.findAllWithRole();
for (User user : allWithRole) {
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(user.getRoleList());
}
}
基于注解的二级缓存
1. 配置SqlMapConfig.xml文件开启二级缓存的支持
sqlMapConfig.xml
<settings>
<!--
因为cacheEnabled的取值默认就为true,所以这一步可以省略不配置。
为true代表开启二级缓存;为false代表不开启二级缓存。
-->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
2. 在Mapper接口中使用注解配置二级缓存
@CacheNamespace
public interface UserMapper {...}
注解延迟加载
不管是一对一还是一对多 ,在注解配置中都有fetchType的属性
fetchType = FetchType.LAZY 表示懒加载
fetchType = FetchType.EAGER 表示立即加载
fetchType = FetchType.DEFAULT 表示使用全局配置
举个栗子
在如下一对一查询中,设置 fetchType 属性为:FetchType.EAGER,表示立即加载
/*
查询所有订单,同时查询订单所属的用户信息
*/
@Select("select * from orders")
@Results({ // 代替的就是resultMap标签 id标签 result标签
@Result(property = "id",column = "id",id = true),
@Result(property = "ordertime",column = "ordertime"),
@Result(property = "total",column = "total"),
@Result(property = "uid",column = "uid"),
@Result(property = "user",javaType = User.class,column = "uid",
one = @One(select = "com.zwt.mapper.UserMapper.findById",
fetchType = FetchType.EAGER))
})
public List<Orders> findAllWithUser();
在如下一对多查询中,设置 fetchType 属性为:FetchType.LAZY,表示延迟加载
/*
查询所有用户,及关联的订单信息
*/
@Select("select * from user")
@Results({ // 代替的就是resultMap标签 id标签 result标签
@Result(property = "id",column = "id",id = true),
@Result(property = "username",column = "username"),
@Result(property = "birthday",column = "birthday"),
@Result(property = "sex",column = "sex"),
@Result(property = "address",column = "address"),
@Result(property = "ordersList",javaType = List.class,column = "id",
many = @Many(select = "com.zwt.mapper.OrderMapper.findOrderByUid",
fetchType = FetchType.LAZY))
})
public List<User> findAllWithOrder();
* 注解开发和xml配置优劣分析
1.注解开发和xml配置相比,从开发效率来说,注解编写更简单,效率更高。
2.从可维护性来说,注解如果要修改,必须修改源码,会导致维护成本增加。xml维护性更强。
至此,mybatis系列就完结啦~
长按二维码
识别关注
共同成长








