
文章转载自公众号:君子黎
作者:黎小刚
1. postgresql.auto.conf文件
对于PostgreSQL 9.4或之后的版本,当使用initdb程序命令初始化数据库集簇之后,会在PG_DATA目录下同时存在两个与PostgreSQL服务相关的配置文件。它们分别是postgresql.auto.conf和postgresql.conf。对于postgresql.conf文件,我们比较熟悉,该文件中存储着与PostgreSQL服务相关的所有默认参数。在PostgreSQL 9.4版本之前,如果需要对PostgreSQL服务的某些功能进行优化、或是调整默认配置参数,则修改postgresql.conf配置文件,然后重启PostgreSQL(对于大多数配置参数的修改,均需要重启以生效)服务。
但是从PostgreSQL 9.4版本开始,新引入了postgresql.auto.conf配置文件,它作为postgresql.conf文件的补充,在参数配置格式上,它和postgresql.conf保持一致。即:
configuration_parameter = value 或 configuration_parameter = 'value'
附:postgresql.auto.conf是在PostgreSQL 9.4版本中引入。
但是两个文件之间仍然有着许多的区别,下面将分别一一详细介绍说明。
2. postgresql.auto.conf与postgresql.conf之间的差异
2.1 文件默认内容不同
postgresql.conf文件创建成功之后,里面有PostgreSQL依赖的默认配置文件参数,比如“最大连接数、共享缓冲区、时区等等”,如下:
/* defaults */
static int n_connections = 10;
static int n_buffers = 50;
static const char *dynamic_shared_memory_type = NULL;
static const char *default_timezone = NULL;
. . . . . . //省略若干配置参数
而对于postgresql.auto.conf配置文件,一开始除了两行文本注释说明之外,没有其他的配置参数。如下图所示:
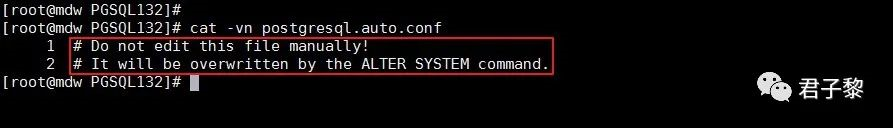
2.1.1 postgresql.auto.conf创建原理
对于postgresql.conf、postgresql.auto.conf两个配置文件,它们均由位于src/bin/initdb/initdb.c文件中的setup_config()函数内部完成。首先创建postgres.conf文件,创建成功之后,再创建postgresql.auto.conf文件。对于postgresql.auto.conf文件的创建过程,整体流程图如下所示:
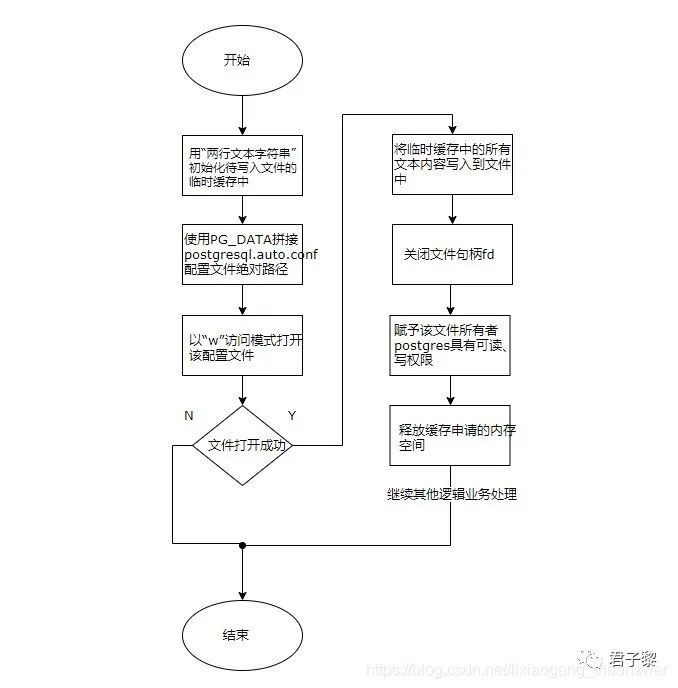
首先,使用默认的两行文本字符串初始化缓存变量。然后根据PG_DATA数据蔟目录路径来构建postgresql.auto.conf配置文件的绝对路径名,然后以"w(若文件已存在,则删除已有文件内容,文件被视为一个空文件)"访问模式打开该文件。之后将换取变量中的所有文本内容写入该文件中。接下来关闭该文件描述符,同时赋予该文件的所有者(postgres)具有可读写的权限,最后释放临时缓存变量申请的内存空间。
对于postgresql.auto.conf文件的创建过程,其完整代码如下:
static void
writefile(char *path, char **lines)
{
FILE *out_file;
char **line;
if ((out_file = fopen(path, "w")) == NULL)
{
pg_log_error("could not open file \"%s\" for writing: %m", path);
exit(1);
}
for (line = lines; *line != NULL; line++)
{
if (fputs(*line, out_file) < 0)
{
pg_log_error("could not write file \"%s\": %m", path);
exit(1);
}
free(*line);
}
if (fclose(out_file))
{
pg_log_error("could not write file \"%s\": %m", path);
exit(1);
}
}
static void
setup_config(void)
{
. . . . . . //省略若干代码
char *autoconflines[3];
autoconflines[0] = pg_strdup("# Do not edit this file manually!\n");
autoconflines[1] = pg_strdup("# It will be overwritten by the ALTER SYSTEM command.\n");
autoconflines[2] = NULL;
sprintf(path, "%s/postgresql.auto.conf", pg_data);
writefile(path, autoconflines);
if (chmod(path, pg_file_create_mode) != 0)
{
pg_log_error("could not change permissions of \"%s\": %m", path);
exit(1);
}
free(conflines);
. . . . . . //省略若干代码
}
附:strdup()函数底层实现采用了malloc(), 必须和free()搭配使用。
2.2 文件修改方式不同
正如postgresql.auto.conf配置文件中初始化时的文本字符串提示一样:
不要手动修改此文件, 因为它会被ALTER SYSTEM命令给覆盖。
该文件主要用于存储有ALTER SYSTEM命令设置的参数值。所以它不需要像postgresql.conf文件一样,每当调整配置参数时,都手动去打开修改、保存。
2.2.1 ALTER SYSTEM语句
ALTER SYSTEM语句是PostgreSQL数据库的一个扩展,它用于在PostgreSQL数据库集群中修改服务器的配置参数。然后修改后的参数将保存在postgresql.auto.conf配置文件中。
ALTER SYSTEM的使用格式如下:
ALTER SYSTEM SET configuration_parameter { TO | = } { value | ‘value’ | DEFAULT }
ALTER SYSTEM RESET configuration_parameter
ALTER SYSTEM RESET ALL
当使用ALTER SYSTEM语句修改了某配置参数之后,该文件中存在的这个参数将覆盖解析该文件之前存在的参数值。通俗点说,就是该文件中的这个参数将覆盖掉postgresql.conf文件中的该参数(但是postgresql.conf文件中这个参数值不会被修改,只是对于PostgreSQL服务,postgresql.auto.conf文件中的该参数具有更高的优先级)。
2.2.1.1 ALTER SYSTEM使用方法
对于ALTER SYSTEM语句的语法格式,已经在2.2.1节中进行了介绍,这里使用修改端口“port”参数进行示例说明。
(1) show命令查看当前该配置参数的值。
test=# show port;
port
------
5566
(1 row)
(2) 执行alter system命令修改该port端口为6789。如果待修改的参数值是字符串,则使用单引号将其括起来。
test=# alter system set port = 6789;
ALTER SYSTEM
(3) 通过pg_settings视图查看当前修改的值。
test=# select *from pg_settings where name like 'port';
name | setting | unit | category | short_desc | extra_desc | context | vartype | source | min_val | max_val | enumvals |
boot_val | reset_val | sourcefile | sourceline | pending_restart
------+---------+------+------------------------------------------------------+------------------------------------------+------------+------------+---------+--------------------+---------+---------+----------+
----------+-----------+------------------------------------+------------+-----------------
port | 5566 | | Connections and Authentication / Connection Settings | Sets the TCP port the server listens on. | | postmaster | integer | configuration file | 1 | 65535 | |
5432 | 5566 | /home/ssd/PGSQL132/postgresql.conf | 63 | f
(1 row)
从终端的显示结果看到,当前的port端口值仍然为postgresql.conf配置文件中的5566,并没有生效。
(4) 尝试使用pg_reload_conf()函数来使服务器进程重新装载它们的配置文件。
test=# select pg_reload_conf();
pg_reload_conf
----------------
t
(1 row)
(5) 通过pg_settings视图查看当前修改的值。
test=# select *from pg_settings where name like 'port';
name | setting | unit | category | short_desc | extra_desc | context | vartype | source | min_val | max_val | enumvals |
boot_val | reset_val | sourcefile | sourceline | pending_restart
------+---------+------+------------------------------------------------------+------------------------------------------+------------+------------+---------+--------------------+---------+---------+----------+
----------+-----------+------------------------------------+------------+-----------------
port | 5566 | | Connections and Authentication / Connection Settings | Sets the TCP port the server listens on. | | postmaster | integer | configuration file | 1 | 65535 | |
5432 | 5566 | /home/ssd/PGSQL132/postgresql.conf | 63 | t
(1 row)
可看到修改的端口配置参数,仍然没有生效。它和postgresql.conf的规则相同,某些参数修改之后必须重启才会生效。postgresql.conf文件中对端口配置参数有明确指示说明,必须重启生效。
port = 5566 # (change requires restart)
因此,重启PostgreSQL服务,然后再次通过pg_settings试图参考修改的端口参数情况。可看到,已经生效了。
test=# select *from pg_settings where name like 'port';
name | setting | unit | category | short_desc | extra_desc | context | vartype | source | min_val | max_val | enumvals |
boot_val | reset_val | sourcefile | sourceline | pending_restart
------+---------+------+------------------------------------------------------+------------------------------------------+------------+------------+---------+--------------------+---------+---------+----------+
----------+-----------+-----------------------------------------+------------+-----------------
port | 6789 | | Connections and Authentication / Connection Settings | Sets the TCP port the server listens on. | | postmaster | integer | configuration file | 1 | 65535 | |
5432 | 6789 | /home/ssd/PGSQL132/postgresql.auto.conf | 3 | f
(1 row)
test=#
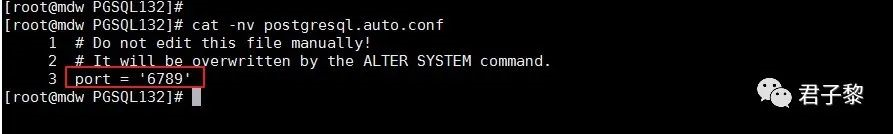
同时,postgresql.auto.conf配置文件中也新增了一行文本内容。如下图所示:
2.2.1.2 ALTER SYSTEM并非所有参数都能修改
并非所有postgresql.conf文件中的配置选项参数都能够使用ALTER SYSTEM命令进行修改,比如data_directory相关系列的配置参数就不能使用该命令进行修改。如:config_file、hba_file、ident_file、external_pid_file等,更多关于data_directory的配置参数请阅读GUC-DATA-DIRECTORY。此外,一些预配置选项也不能使用此命令修改。比如:block_size、data_checksums、lc_collate等,更多关于预配置选项的配置参数请阅读Options preconfigurees。
3. 总结
本文详细讲解了postgresql.auto.conf、postgresql.conf两个配置文件之间的区别与联系,同时对postgresql.auto.conf配置文件的创建过程做了详细的介绍。然后接着讲解了ALTER SYSTEM命令的语法,通过一个示例,图文并茂地对其使用方法进行了充分的补充说明,并且还附加了该命令的使用局限等等。





新闻|Babelfish使PostgreSQL直接兼容SQL Server应用程序

更多新闻资讯,行业动态,技术热点,请关注中国PostgreSQL分会官方网站
https://www.postgresqlchina.com
中国PostgreSQL分会生态产品
https://www.pgfans.cn
中国PostgreSQL分会资源下载站
https://www.postgreshub.cn


点击此处阅读原文
↓↓↓






