0. 目录
1.场景
2. 原理分析
3. 代码简析
1. 场景
常见的在线判题大概流程如图:
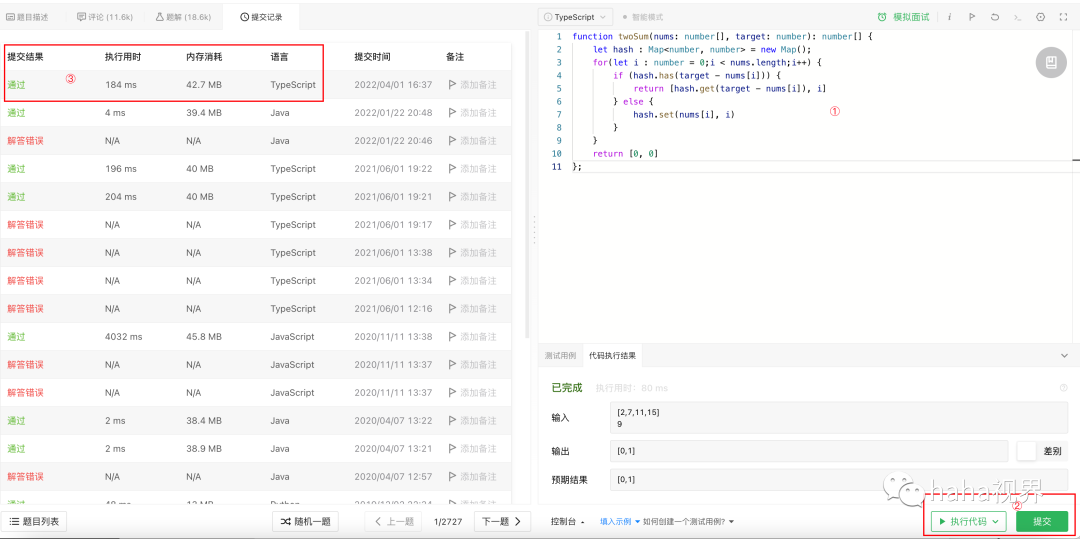
①:选择语言,编写代码
②:提交代码判题
③:返回判题结果
后台通过多个维度进行判断:
编译通过与否
测试用例通过情况
cpu耗时
内存消耗
2. 原理分析
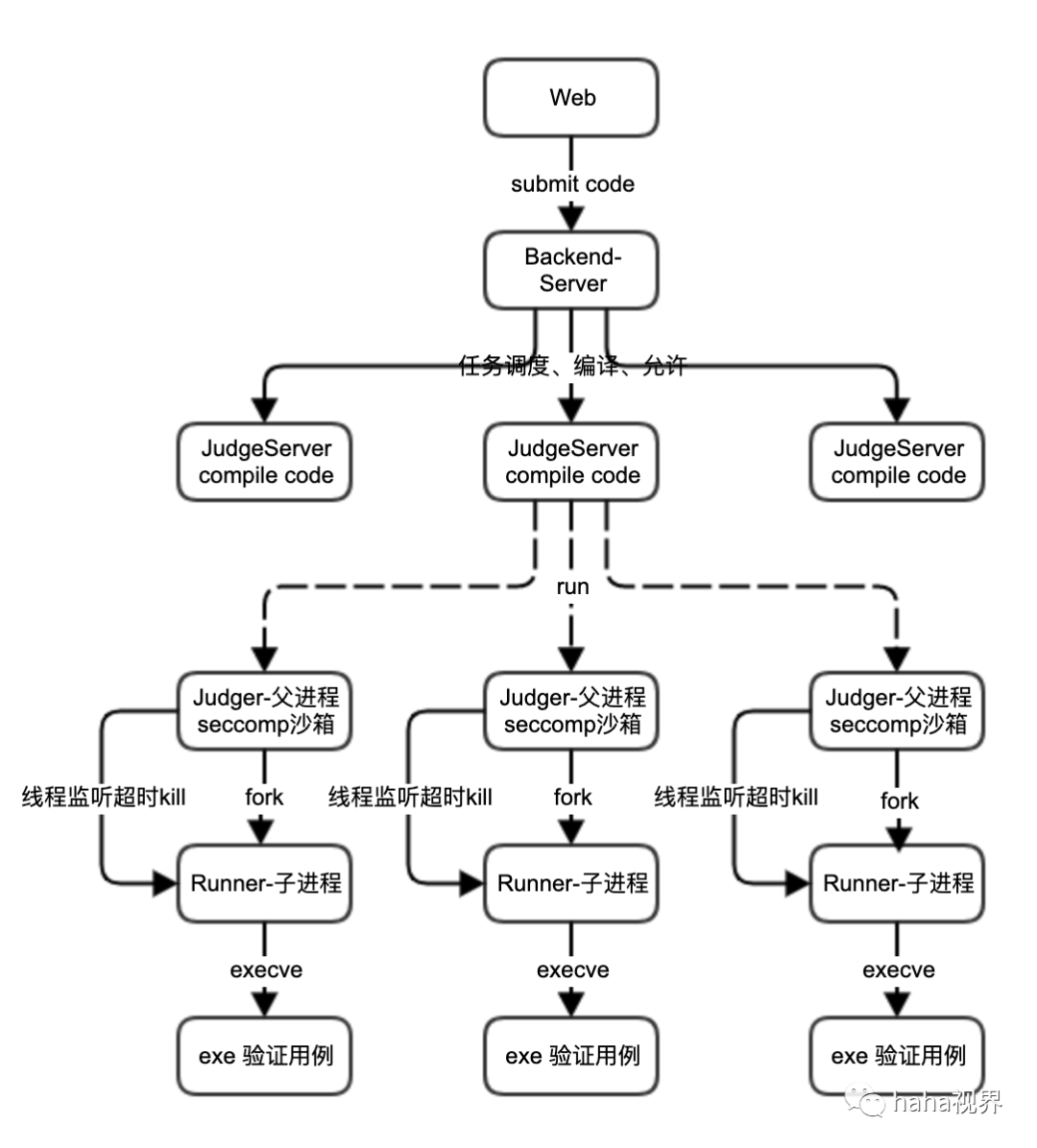
如上图,
用户提交代码后,后端服务器进行任务调度,选择空闲的判题服务器,发送编译请求。
判题服务器首先根据选择的语言,把提交的代码嵌入代码模板,进行编译,编译文件放入exe_dir可执行文件目录返回编译结果。
后端服务器根据编译结果判断是否进行运行请求。
判题服务器收到运行请求后,启动Judger(父)进程。
Judger进程fork子进程后,启动超时监听线程,超时杀死子进程,并wait子进程退出状态。
子进程根据题目要求,配置cpu、memory等资源限制。
子进程进行测试用例验证,完成后退出。
父进程统计子进程实际运行时间,退出状态、cpu耗时、内存消耗等,返回给后端服务器。
后端服务器获取结果后存入数据库,并返回给客户端呈现结果。
通过seccomp限制恶意代码。
seccomp是Linux内核中的计算机安全性工具。seccomp允许进程单向转换到“安全”状态,在该状态下,除了exit,sigreturn,读取和写入已打开的文件描述符之外,该进程无法进行任何系统调用。如果尝试任何其他系统调用,内核将仅记录事件或使用SIGKILL或SIGSYS终止进程。
3. 代码简析
1. 启动父进程
void run(struct config *_config, struct result *_result) {// record current timestruct timeval start, end;gettimeofday(&start, NULL);pid_t child_pid = fork();if (child_pid == 0) {child_process(log_fp, _config);}else if (child_pid > 0){// create new thread to monitor process running timepthread_t tid = 0;if (_config->max_real_time != UNLIMITED) {struct timeout_killer_args killer_args;killer_args.timeout = _config->max_real_time;killer_args.pid = child_pid;if (pthread_create(&tid, NULL, timeout_killer, (void *) (&killer_args)) != 0) {kill_pid(child_pid);ERROR_EXIT(PTHREAD_FAILED);}}int status;struct rusage resource_usage;// wait for child process to terminate// on success, returns the process ID of the child whose state has changed;// On error, -1 is returned.if (wait4(child_pid, &status, WSTOPPED, &resource_usage) == -1) {kill_pid(child_pid);ERROR_EXIT(WAIT_FAILED);}// 真实运行时间gettimeofday(&end, NULL);_result->real_time = (int) (end.tv_sec * 1000 + end.tv_usec 1000 - start.tv_sec * 1000 - start.tv_usec 1000);// 子进程退出,killer线程也退出if (_config->max_real_time != UNLIMITED) {if (pthread_cancel(tid) != 0) {// todo logging};}{// 获得:子进程退出原因,cpu耗时、内存使用_result->exit_code = WEXITSTATUS(status);_result->cpu_time = (int) (resource_usage.ru_utime.tv_sec * 1000 +resource_usage.ru_utime.tv_usec 1000);_result->memory = resource_usage.ru_maxrss * 1024;}}}
2. 超时看门狗
void *timeout_killer(void *timeout_killer_args) {pid_t pid = ((struct timeout_killer_args *)timeout_killer_args)->pid;int timeout = ((struct timeout_killer_args *)timeout_killer_args)->timeout;// 超时看门狗if (sleep((unsigned int)((timeout + 1000) 1000)) != 0) {kill_pid(pid);return NULL;}if (kill_pid(pid) != 0) {return NULL;}return NULL;}
3. 子进程
void child_process(FILE *log_fp, struct config *_config){FILE *input_file = NULL, *output_file = NULL, *error_file = NULL;setrlimit(RLIMIT_STACK, &max_stack);setrlimit(RLIMIT_AS, &max_memory);setrlimit(RLIMIT_CPU, &max_cpu_time);setrlimit(RLIMIT_NPROC, &max_process_number);setrlimit(RLIMIT_FSIZE, &max_output_size);// redirect file -> stdindup2(fileno(input_file), fileno(stdin);// redirect stdout -> filedup2(fileno(output_file), fileno(stdout);// redirect stderr -> filedup2(fileno(error_file), fileno(stderr);// set gid_config->gid != -1 && (setgid(_config->gid) == -1 || setgroups(sizeof(group_list) / sizeof(gid_t), group_list) == -1);// set uid_config->uid != -1 && setuid(_config->uid);//执行代码测试子进程execve(_config->exe_path, _config->args, _config->env);}
文章转载自haha视界,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






