记得去年 12 月份墨天轮就发起了“openGauss 每日一练”的打卡活动,有很多墨友积极参与与响应。当然,我也参与到其中,并坚持了 21 天的打卡活动,输出了【我和 openGauss 的故事】之 21 天学习总结。今年墨天轮社区继续联合 openGauss 社区、Gauss 松鼠会、鲲鹏社区再次举办每日一练学习打卡活动,时间是 11 月 24 日----12 月 14 日,21 天的时间,学习新的知识,让我们再次出发!
学习目标
学习从操作系统层面和使用 openGauss 工具查看数据库的状态、版本和数据文件目录。
课程学习
gs_ctl 是 openGauss 提供的数据库服务控制工具,可以用来启停数据库服务和查询数据库状态。主要供 openGauss 管理模块调用。
gs_ctl 工具由操作系统用户 omm 执行。可以执行:
启动、停止、重启 openGauss 节点。
在不停止数据库的情况下,重新加载配置文件(postgresql.conf,pg_hba.conf)。
主备切换、主备状态查询、重建和重建状态查询。
更加详细的参数可参考官方文档:工具参考–》系统内部使用的工具
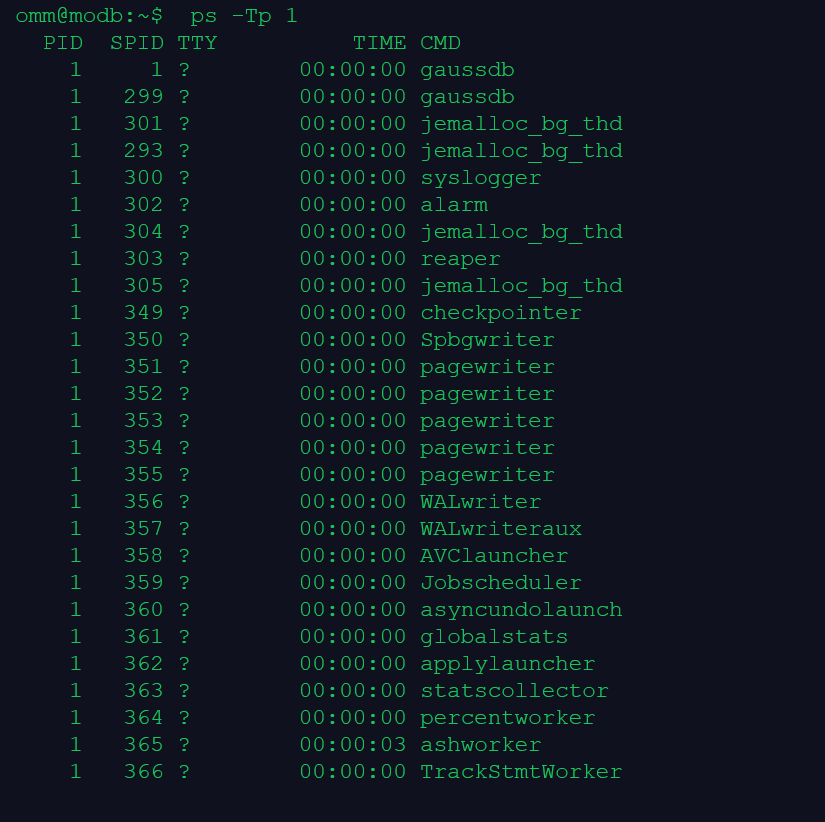
1.操作系统层面查看数据库进程和线程。如果数据库启动,则有相应的进程和线程。
ps -ef|grep gauss
ps -Tp 1
omm@modb:~$ ps -ef|grep gauss
omm 1 0 0 23:06 ? 00:00:07 gaussdb
omm 500 379 0 23:34 pts/0 00:00:00 grep gauss
omm@modb:~$ ps -Tp 1
PID SPID TTY TIME CMD
1 1 ? 00:00:00 gaussdb
1 299 ? 00:00:00 gaussdb
1 301 ? 00:00:00 jemalloc_bg_thd
1 293 ? 00:00:00 jemalloc_bg_thd
1 300 ? 00:00:00 syslogger
1 302 ? 00:00:00 alarm
1 304 ? 00:00:00 jemalloc_bg_thd
1 303 ? 00:00:00 reaper
1 305 ? 00:00:00 jemalloc_bg_thd
1 349 ? 00:00:00 checkpointer
1 350 ? 00:00:00 Spbgwriter
1 351 ? 00:00:00 pagewriter
1 352 ? 00:00:00 pagewriter
1 353 ? 00:00:00 pagewriter
1 354 ? 00:00:00 pagewriter
1 355 ? 00:00:00 pagewriter
1 356 ? 00:00:00 WALwriter
1 357 ? 00:00:00 WALwriteraux
1 358 ? 00:00:00 AVClauncher
1 359 ? 00:00:00 Jobscheduler
1 360 ? 00:00:00 asyncundolaunch
1 361 ? 00:00:00 globalstats
1 362 ? 00:00:00 applylauncher
1 363 ? 00:00:00 statscollector
1 364 ? 00:00:00 percentworker
1 365 ? 00:00:03 ashworker
1 366 ? 00:00:00 TrackStmtWorker
1 367 ? 00:00:00 auditor
1 368 ? 00:00:00 2pccleaner
1 369 ? 00:00:00 faultmonitor
1 370 ? 00:00:00 WLMworker
1 371 ? 00:00:00 WLMmonitor
1 372 ? 00:00:00 WLMarbiter
1 373 ? 00:00:00 undorecycler
2.使用 gs_ctl 工具查看数据库状态,如果数据库启动,显示 gs_ctl: server is running (PID: 1)
omm@modb:~$ gs_ctl status
[2022-11-24 23:37:32.007][515][][gs_ctl]: gs_ctl status,datadir is /var/lib/opengauss/data
gs_ctl: server is running (PID: 1)
/usr/local/opengauss/bin/gaussdb
3.使用 gs_ctl 查看数据文件的目录
官方文档参数释义 notify:启动后再指定主备机。
omm@modb:~$ gs_ctl notify
[2022-11-24 23:38:29.754][523][][gs_ctl]: gs_ctl notify ,datadir is /var/lib/opengauss/data
[2022-11-24 23:38:29.754][523][][gs_ctl]: the parameter of notify must be specified
4.查看 omm 用户的环境变量
omm@modb:~$ cat .bashrc | grep -v '^#' | grep -v '^$'
case $- in
*i*) ;;
*) return;;
esac
HISTCONTROL=ignoreboth
shopt -s histappend
HISTSIZE=1000
HISTFILESIZE=2000
shopt -s checkwinsize
if [ -z "${debian_chroot:-}" ] && [ -r /etc/debian_chroot ]; then
debian_chroot=$(cat /etc/debian_chroot)
fi
case "$TERM" in
xterm-color|*-256color) color_prompt=yes;;
esac
if [ -n "$force_color_prompt" ]; then
if [ -x /usr/bin/tput ] && tput setaf 1 >&/dev/null; then
# We have color support; assume it's compliant with Ecma-48
# (ISO/IEC-6429). (Lack of such support is extremely rare, and such
# a case would tend to support setf rather than setaf.)
color_prompt=yes
else
color_prompt=
fi
fi
if [ "$color_prompt" = yes ]; then
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\[\033[01;32m\]\u@\h\[\033[00m\]:\[\033[01;34m\]\w\[\033[00m\]\$ '
else
PS1='${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h:\w\$ '
fi
unset color_prompt force_color_prompt
case "$TERM" in
xterm*|rxvt*)
PS1="\[\e]0;${debian_chroot:+($debian_chroot)}\u@\h: \w\a\]$PS1"
;;
*)
;;
esac
if [ -x /usr/bin/dircolors ]; then
test -r ~/.dircolors && eval "$(dircolors -b ~/.dircolors)" || eval "$(dircolors -b)"
alias ls='ls --color=auto'
#alias dir='dir --color=auto'
#alias vdir='vdir --color=auto'
#alias grep='grep --color=auto'
#alias fgrep='fgrep --color=auto'
#alias egrep='egrep --color=auto'
fi
if [ -f ~/.bash_aliases ]; then
. ~/.bash_aliases
fi
if ! shopt -oq posix; then
if [ -f /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion ]; then
. /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion
elif [ -f /etc/bash_completion ]; then
. /etc/bash_completion
fi
fi
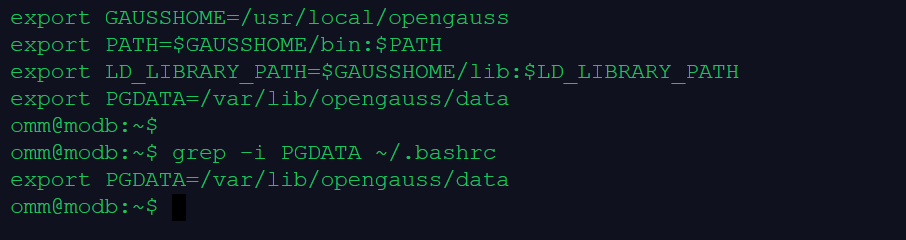
export GAUSSHOME=/usr/local/opengauss
export PATH=$GAUSSHOME/bin:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$GAUSSHOME/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
export PGDATA=/var/lib/opengauss/data
5.从环境变量查看数据文件的目录
omm@modb:~$ grep -i PGDATA ~/.bashrc
export PGDATA=/var/lib/opengauss/data
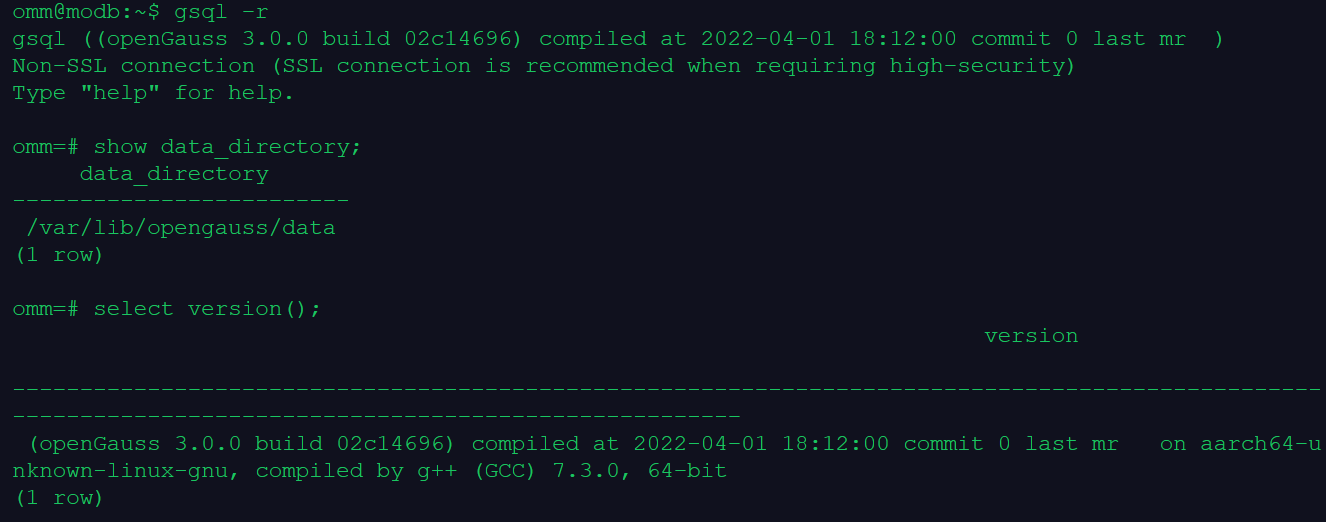
6.在 gsql 中查看数据文件的目录、数据库版本
gsql -r
show data_directory ;
select version();
课程作业
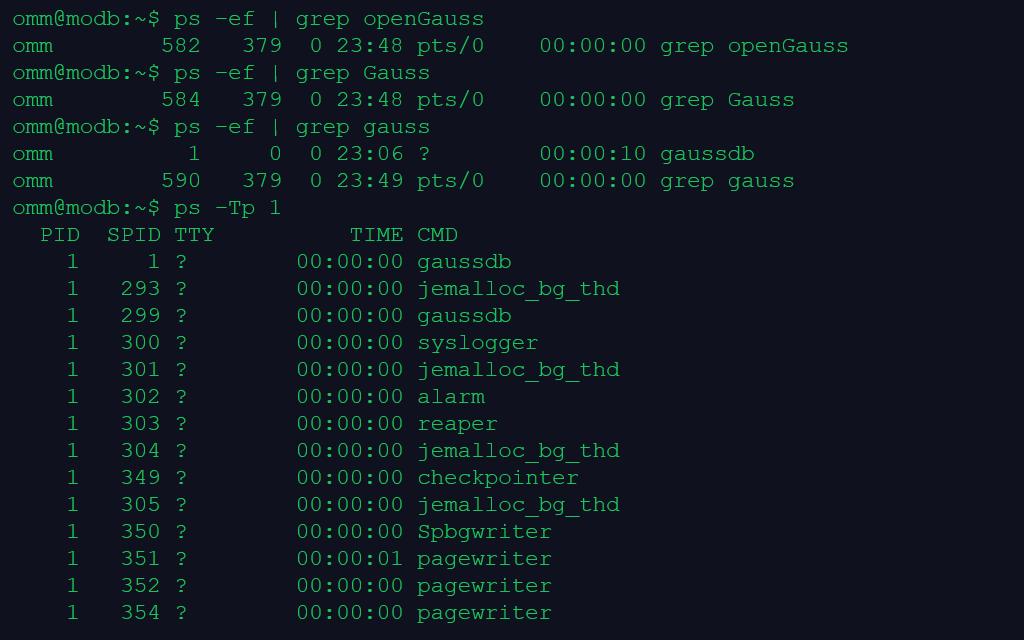
1.从操作系统层面查看数据库进程和线程,判断数据库是否启动。
使用 ps -ef | grep gauss 查看进程是否存在,使用 ps -Tp 1 查看进程 PID 为 1 时的线程有哪些。
2.使用 gs_ctl 工具查看数据库状态,判断数据库是否启动。
使用 gs_ctl --help 查看帮助命令,gs_ctl status 查看数据库状态是否为 running 。
omm@modb:~$ gs_ctl status
[2022-11-24 23:53:08.855][612][][gs_ctl]: gs_ctl status,datadir is /var/lib/opengauss/data
gs_ctl: server is running (PID: 1)
/usr/local/opengauss/bin/gaussdb
3.使用 gs_ctl 查看数据文件的目录
使用 gs_ctl notify 查看数据文件存放目录。
omm@modb:~$ gs_ctl notify
[2022-11-24 23:55:20.582][625][][gs_ctl]: gs_ctl notify ,datadir is /var/lib/opengauss/data
[2022-11-24 23:55:20.582][625][][gs_ctl]: the parameter of notify must be specified
4.从环境变量查看数据文件的目录
环境变量中参数 PGDATA 指定了数据文件存放路径。
omm@modb:~$ grep -i PGDATA ~/.bashrc
export PGDATA=/var/lib/opengauss/data
5.在 gsql 中查看数据文件目录、数据库版本
通过 gsql -r 连接到数据库,然后参数 data_directory 指定了数据文件的存放路径,通过 version() 函数来查看 openGauss 的数据库版本为 3.0.0。
omm@modb:~$ gsql -r
gsql ((openGauss 3.0.0 build 02c14696) compiled at 2022-04-01 18:12:00 commit 0 last mr )
Non-SSL connection (SSL connection is recommended when requiring high-security)
Type "help" for help.
omm=# show data_directory;
data_directory
-------------------------
/var/lib/opengauss/data
(1 row)
omm=# select version();
version
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------
(openGauss 3.0.0 build 02c14696) compiled at 2022-04-01 18:12:00 commit 0 last mr on aarch64-u
nknown-linux-gnu, compiled by g++ (GCC) 7.3.0, 64-bit
(1 row)
最后,\q 或者 Ctrl + d 退出数据库。






