第十七课
笔记本: 我的第一个笔记本
创建时间: 2022/12/10 10:27 更新时间: 2022/12/10 11:43 作者: 177zkcft091
URL: https://www.modb.pro/terminal/1179274
第十七课
17.1 第17天 | ope…
学习目标
掌握openGauss DBMS索引的管理: 创建索引、删除索引、查询索引的信息、修改索引的信息。
课程学习
索引是一个指向表中数据的指针。一个数据库中的索引与一本书的索引目录是非常相似的。
索引可以用来提高数据库查询性能, 但是不恰当的使用将导致数据库性能下降。
- 创建索引
--为表test的testnum列创建一个索引
su - omm gsql -r
drop table if exists test;
create table test(id serial primary key,testnum serial);
create index idx_test_testnum on test(testnum);
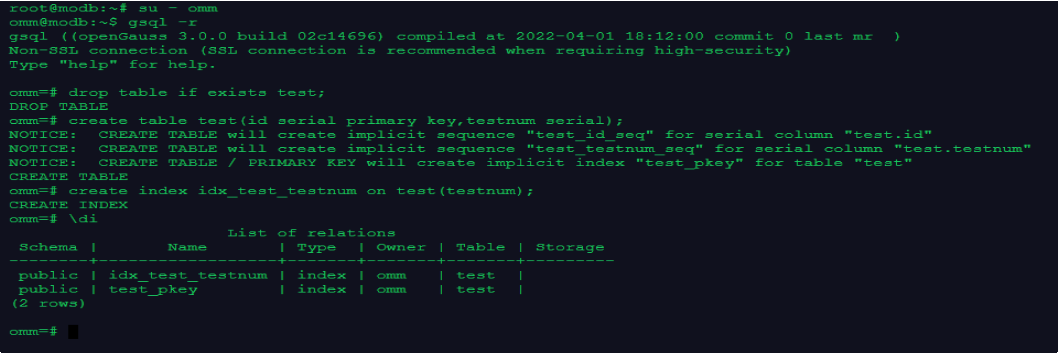
--查看索引
\di
- 通过hint使用索引
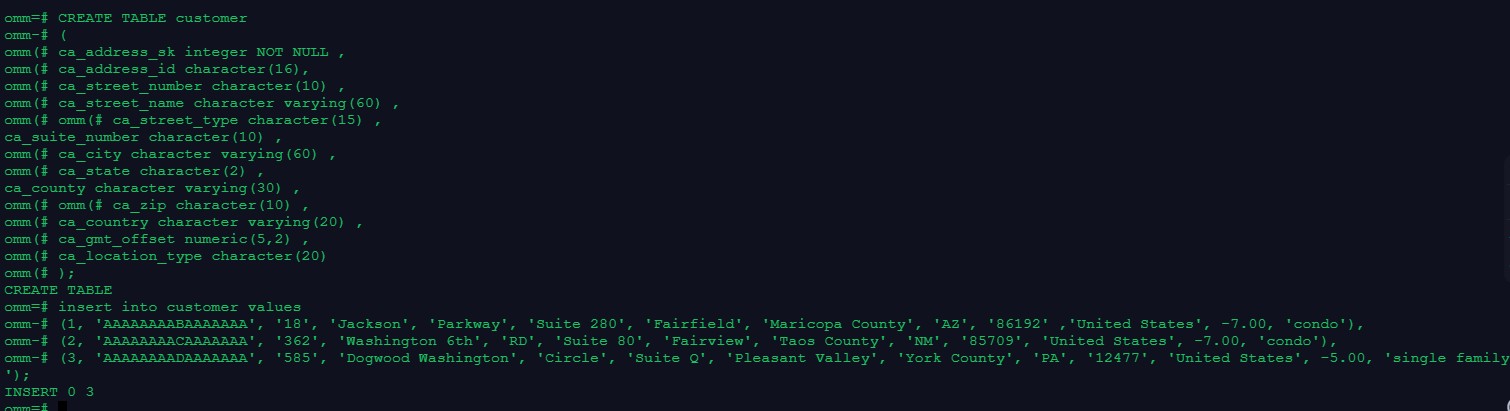
--测试准备,创建表customer,并插入数据CREATE TABLE customer
(
ca_address_sk integer NOT NULL , ca_address_id character(16), ca_street_number character(10) , ca_street_name character varying(60) , ca_street_type character(15) , ca_suite_number character(10) , ca_city character varying(60) , ca_county character varying(30) , ca_state character(2) ,
ca_zip character(10) ,
ca_country character varying(20) , ca_gmt_offset numeric(5,2) , ca_location_type character(20)
);
insert into customer values
(1, 'AAAAAAAABAAAAAAA', '18', 'Jackson', 'Parkway', 'Suite 28 (2, 'AAAAAAAACAAAAAAA', '362', 'Washington 6th', 'RD', 'Suite
(3, 'AAAAAAAADAAAAAAA', '585', 'Dogwood Washington', 'Circle'

--创建索引
create index customer_idx on customer(ca_address_sk);
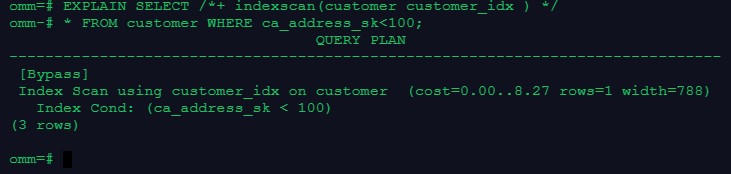
--通过hint强制使用索引,查看执行计划
EXPLAIN SELECT /*+ indexscan(customer customer_idx ) */
* FROM customer WHERE ca_address_sk<100;
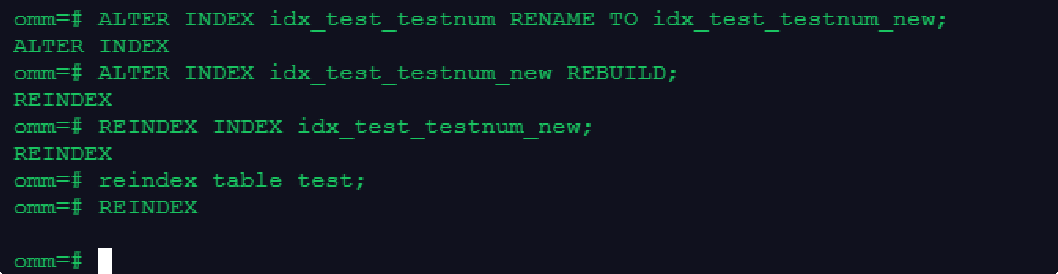
- rename索引

ALTER INDEX idx_test_testnum RENAME TO idx_test_testnum_new;
- 重建索引
--重建一个单独索引
ALTER INDEX idx_test_testnum_new REBUILD;
REINDEX INDEX idx_test_testnum_new;
--重建所有索引reindex table test;
- 移动索引到其他表空间
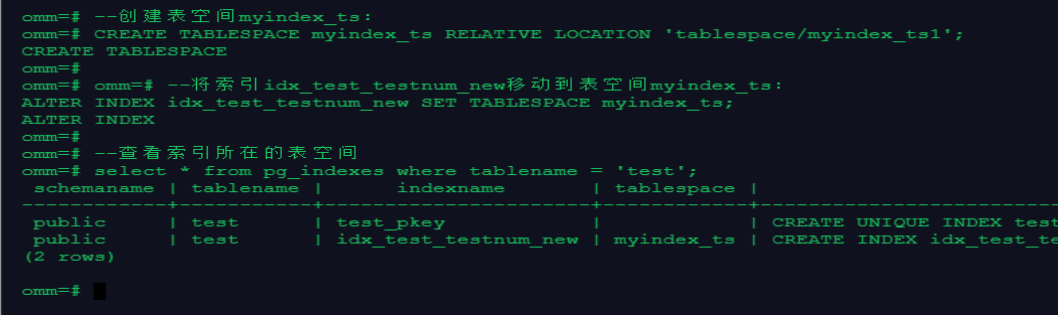
--创建表空间myindex_ts:
CREATE TABLESPACE myindex_ts RELATIVE LOCATION 'tablespace/my
--将索引idx_test_testnum_new移动到表空间myindex_ts:
ALTER INDEX idx_test_testnum_new SET TABLESPACE myindex_ts;
--查看索引所在的表空间
select * from pg_indexes where tablename = 'test';
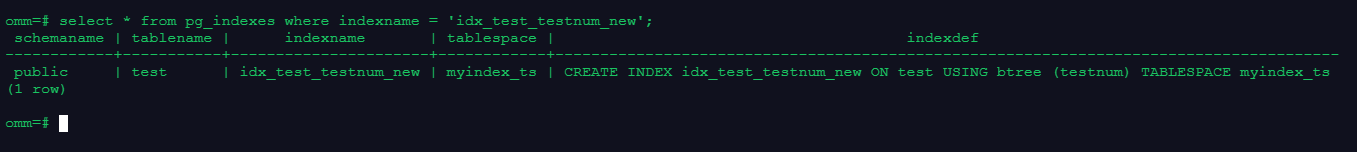
--或
select * from pg_indexes where indexname = 'idx_test_testnum_
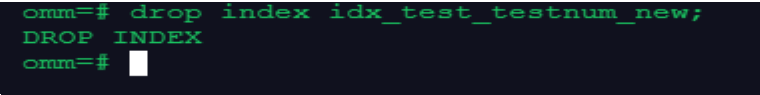
- 删除索引

--执行下面的命令,删除表test上的索引idx_test_testnum_new:
drop index idx_test_testnum_new;
总结:
- 创建表,在表中创建索引
drop table if exists 表名; create table 表名(表结构);
create index 索引名 on 表名(列名);
- 通过hint使用索引3.rename索引
ALTER INDEX (旧索引名) RENAME TO (新索引名);
- 重建索引
- 重建一个单独索引
ALTER INDEX (新索引名) REBUILD;
REINDEX INDEX (新索引名);
- 重建所有索引
reindex table test;
- 移动索引到其他表空间
- 创建表空间myindex_ts:
CREATE TABLESPACE ( 新表空间名) RELATIVE LOCATION ' 文件路
径信息';
ALTER INDEX (索引名) SET TABLESPACE 表空间名;
- 查看索引所在的表空间
select * from pg_indexes where tablename = '表名'; 或
select * from pg_indexes where indexname = '索引名';
- 删除索引
drop index (索引名);
难点:
openGauss之简单使用Plan hint进行SQL调优
一、Plan Hint调优概述
Plan Hint为用户提供了直接影响执行计划生成的手段,用户可以通过指定join顺序、join、scan方法、指定结果行数等多个手段来进行执行计划的调优,以提升查询的性能。
Plan Hint支持在SELECT关键字后通过如下形式指定:
/*+ <plan hint>*/
可以同时指定多个hint, 之间使用空格分隔。hint只能hint当前层的计划, 对于子查
询
计划的hint,需要在子查询的select关键字后指定hint。支持范围:
指定Join顺序的Hint - leading hint
指定Join方式的Hint,仅支持除semi/anti join、unique plan之外的常用hint。指定结果集行数的Hint
指定Scan方式的Hint,仅支持常用的tablescan、indexscan和indexonlyscan的hi
nt。
指定子链接块名的Hint
不支持:
不支持Agg、Sort、Setop和Subplan的hint。
二、华为openGauss Scan方式的Hint
plan功能描述
指明scan 使用的方法, 可以是tablescan 、indexscan 和indexonlysca n。
语法格式
[no] tablescan|indexscan|indexonlyscan(table [index]) 参数说明
- no表示hint的scan方式不使用。
- table表示hint指定的表, 只能指定一个表, 如果表存在别名应优先使用别名进行hint。
- index表示使用indexscan或indexonlyscan的hint时, 指定的索引名称,当前只能指定一个。
说明:
对于indexscan或indexonlyscan,只有hint的索引属于hint的表时,才能使用该hint。scan hint支持在行列存表、obs表、子查询表上指定。
结论:当表中数据比较少时,全表扫描的查询性能高于使用索引扫描, 当不指定scan类型时, 系统会自动选择seq scan, 因为这种扫描方式代价小。当数据量很大时,为条件列建立索引可以大幅提升查询性能。
示例:
为了hint使用索引扫描, 需要首先在表item的i_item_sk列上创建索引, 名称为i。
create index i on item(i_item_sk);
对示例中原语句使用如下hint:

explain select /*+ indexscan(item i) */ i_product_name product_n ame
EXPLAIN SELECT /*+ indexscan(item i) */ *
FROM item WHERE i_item_sk<100;






