EJB教程 - EJB
企业Java Beans(EJB)是一个集开发构建高度可扩展性和强大的企业级应用程序的架构上部署符合J2EE规范的应用服务器,如JBOSS,网站逻辑等。 EJB3.0从EJB2.0是一个伟大的转变,使得基于EJB应用的开发变得更容易。本教程讲述EJB概念和理解,在这一个过程中需要创建和部署企业级应用程序启动和运行。 读者对象: 本教程是专为软件专业人员学习EJB编程简单入门。本教程将介绍EJB编程概念和理解,在完成本教程后,希望你能够对EJB有一个初级的认识和应用。
前置技术知识要求: 在继续本教程之前,您应该对Java编程语言有一定的了解,文本编辑器和执行程序这些也必不可少,因为我们要开发企业应用程序使用EJB,如果你已经了解其他技术,如数据库服务器,应用服务器,那么你可以跳过上面技术知识的学习,直接进入下一章节。
EJB概述 - EJB
EJB其实就是企业Java Beans。 EJB是J2EE平台的重要组成部分。 J2EE平台基于组件的企业级应用架构,提供多层次,分布式和高事务的功能特点。 EJB提供了一个架构,充分考虑健壮性,高可扩展性和高性能的基于组件的企业应用程序开发和部署。一个EJB应用程序可以部署在任何符合J2EE1.3标准规范的应用程序服务器上。我们将在本教程中讨论EJB3.0。
优点
- 简化开发大型企业级应用。
- 应用服务器/ EJB容器提供了系统级服务,如事务处理,日志,负载均衡,持久性机制,异常处理等。开发者只专注于业务逻辑的应用程序。
- EJB容器管理EJB实例的生命周期,因此,开发人员并不需要担心何时创建/删除EJB对象。
类型 EJB主要有三种类型,下面简要介绍:
类型 | 描述 |
Session Bean | 会话bean将特定用户的数据存储为一个单一的会话。它可以是状态或无状态。它占用更少资源,相比于实体Bean。只要终止用户会话,会话bean被销毁。 |
Entity Bean | 实体bean代表持久性数据存储。可将用户数据保存到数据库中,通过实体bean,后来就可以检索从数据库中的实体bean。 |
Message Driven Bean | 使用消息驱动bean上下文中的JMS(Java消息服务)。消息驱动Bean可以从外部实体消耗JMS消息,并采取相应的动作。 |
EJB创建应用 - EJB
要创建一个简单的EJB模块,我们这里使用NetBeans“New project”向导。在下面的例子中,我们将创建一个名为“Component”的EJB模块项目。
创建项目
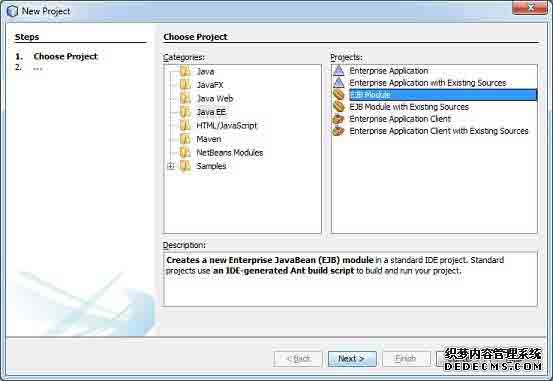
在NetBeans IDE中,选择File > New Project >. 可以看到如下图.
在类别中选择项目类型,Java EE的EJB模块项目类型。点击Next>按钮,你会看到以下的画面。
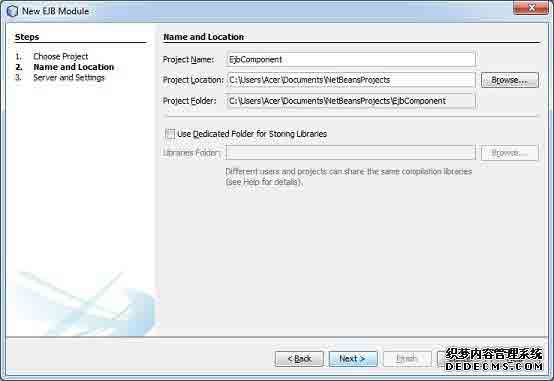
输入项目的名称和位置。点击Next>按钮。你会看到以下的画面。
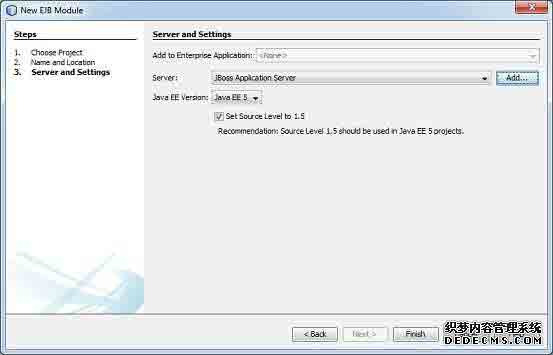
选择服务器为JBoss应用服务器。单击“Finish”按钮。你会看到以下由NetBeans创建的项目。
创建一个简单的EJB
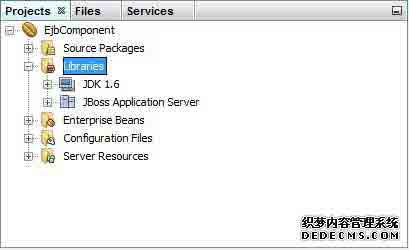
要创建一个简单的EJB,我们将使用NetBeans“New”向导。在下面的例子中,我们将在EjbComponent项目下创建一个无状态EJB类名为librarySessionBean。
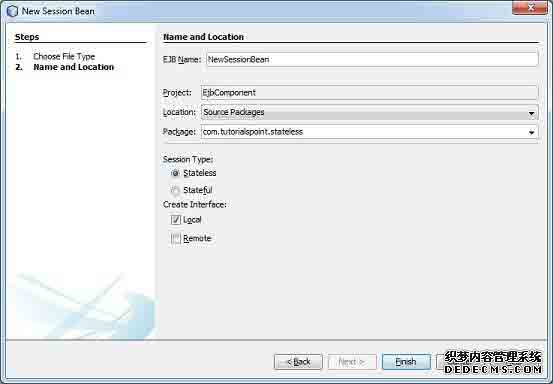
在项目资源管理器窗口中选择项目EjbComponent,右键单击它。选择New > Session Bean。您将看到新的会话Bean向导。
输入会话bean的名称和包名。单击“Finish ”按钮。你会看到以下由NetBeans创建的EJB类。
- LibrarySessionBean - 无状态会话bean
- LibrarySessionBeanLocal - 本地接口的会话bean
要改变本地接口,我们要一个基于控制台的应用程序访问我们的EJB远程接口。远程/本地接口用于公开一个EJB的业务方法实现。
LibrarySessionBeanLocal更名为LibrarySessionBeanRemote和LibrarySessionBean实现LibrarySessionBeanRemote接口。
LibrarySessionBeanRemote
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibrarySessionBeanRemote {
void addBook(String bookName);
List getBooks();
}
LibrarySessionBean
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
@Stateless
public class LibrarySessionBean implements LibrarySessionBeanRemote {
List<String> bookShelf;
public LibrarySessionBean(){
bookShelf = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public void addBook(String bookName) {
bookShelf.add(bookName);
}
public List<String> getBooks() {
return bookShelf;
}
}
构建项目
- 在Project Explorer窗口中选择EjbComponent项目。
- 右键点击它来打开上下文菜单。
- 选择 clean and build。
在NetBeans控制台输出,你会看到以下的输出。
ant -f C:\EJB\EjbComponent clean dist
init:
undeploy-clean:
deps-clean:
Deleting directory C:EJBEjbComponentuild
Deleting directory C:EJBEjbComponentdist
clean:
init:
deps-jar:
Created dir: C:EJBEjbComponentuildclasses
Copying 3 files to C:EJBEjbComponentuildclassesMETA-INF
Created dir: C:EJBEjbComponentuildempty
Created dir: C:EJBEjbComponentuildgenerated-sourcesap-source-output
Compiling 2 source files to C:EJBEjbComponentuildclasses
warning: [options] bootstrap class path not set in conjunction with -source 1.6
Note: C:EJBEjbComponentsrcjavacom utorialspointstateless
LibraryPersistentBean.java uses unchecked or unsafe operations.
Note: Recompile with -Xlint:unchecked for details.
1 warning
compile:
library-inclusion-in-archive:
Created dir: C:EJBEjbComponentdist
Building jar: C:EJBEjbComponentdistEjbComponent.jar
dist:
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 3 seconds)
启动应用程序服务器
- 服务器在服务窗口下选择JBoss应用服务器。
- 右键点击它来打开上下文菜单。
- 选择start。
你会看到下面的输出在NetBeans中JBoss应用服务器下的输出。
Calling C:jboss-5.1.0.GAin
un.conf.bat
=========================================================================
JBoss Bootstrap Environment
JBOSS_HOME: C:jboss-5.1.0.GA
JAVA: C:Program Files (x86)Javajdk1.6.0_21injava
JAVA_OPTS: -Dprogram.name=run.bat -Xms128m -Xmx512m -server
CLASSPATH: C:jboss-5.1.0.GAin
un.jar
=========================================================================
16:25:50,062 INFO [ServerImpl] Starting JBoss (Microcontainer)...
16:25:50,062 INFO [ServerImpl] Release ID: JBoss [The Oracle] 5.1.0.GA (build: SVNTag=JBoss_5_1_0_GA date=200905221634)
...
16:26:40,420 INFO [TomcatDeployment] deploy, ctxPath=/admin-console
16:26:40,485 INFO [config] Initializing Mojarra (1.2_12-b01-FCS) for context '/admin-console'
16:26:42,362 INFO [TomcatDeployment] deploy, ctxPath=/
16:26:42,406 INFO [TomcatDeployment] deploy, ctxPath=/jmx-console
16:26:42,471 INFO [Http11Protocol] Starting Coyote HTTP/1.1 on http-127.0.0.1-8080
16:26:42,487 INFO [AjpProtocol] Starting Coyote AJP/1.3 on ajp-127.0.0.1-8009
16:26:42,493 INFO [ServerImpl] JBoss (Microcontainer) [5.1.0.GA (build: SVNTag=JBoss_5_1_0_GA date=200905221634)] Started in 52s:427ms
部署项目
- 在Project Explorer窗口中选择EjbComponent项目。
- 右击它,打开上下文菜单。
- 选择 Deploy.
在NetBeans控制台输出,你会看到下面的输出。
ant -f C:\EJB\EjbComponent -DforceRedeploy=true -Ddirectory.deployment.supported=false -Dnb.wait.for.caches=true run
init:
deps-jar:
compile:
library-inclusion-in-archive:
Building jar: C:EJBEjbComponentdistEjbComponent.jar
dist-directory-deploy:
pre-run-deploy:
Checking data source definitions for missing JDBC drivers...
Distributing C:EJBEjbComponentdistEjbComponent.jar to [org.jboss.deployment.spi.LocalhostTarget@1e4f84ee]
Deploying C:EJBEjbComponentdistEjbComponent.jar
Applicaton Deployed
Operation start started
Operation start completed
post-run-deploy:
run-deploy:
run:
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 2 seconds)
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
16:30:00,963 INFO [DeployHandler] Begin start, [EjbComponent.jar]
...
16:30:01,233 INFO [Ejb3DependenciesDeployer] Encountered deployment AbstractVFSDeploymentContext@12038795{vfszip:/C:/jboss-5.1.0.GA/server/default/deploy/EjbComponent.jar/}
...
16:30:01,281 INFO [JBossASKernel] jndi:LibrarySessionBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanRemote
16:30:01,281 INFO [JBossASKernel] Class:com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanRemote
16:30:01,281 INFO [JBossASKernel] jndi:LibrarySessionBean/remote
16:30:01,281 INFO [JBossASKernel] Added bean(jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=
LibrarySessionBean,service=EJB3) to KernelDeployment of: EjbComponent.jar
16:30:01,282 INFO [JBossASKernel] installing bean: jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=BookMessageHandler,service=EJB3
16:30:01,282 INFO [JBossASKernel] with dependencies:
16:30:01,282 INFO [JBossASKernel] and demands:
16:30:01,282 INFO [JBossASKernel] jboss.ejb:service=EJBTimerService
...
16:30:01,283 INFO [EJB3EndpointDeployer] Deploy AbstractBeanMetaData@5497cb{name=jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar, name=LibrarySessionBean, service=EJB3_endpoint bean=org.jboss.ejb3.endpoint.deployers.impl.EndpointImpl properties=[container] constructor=null autowireCandidate=true}
...
16:30:01,394 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibrarySessionBean,service=EJB3
16:30:01,395 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBean ejbName: LibrarySessionBean
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibrarySessionBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibrarySessionBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibrarySessionBean,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBean ejbName: LibrarySessionBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibrarySessionBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibrarySessionBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
创建客户端访问EJB
- 在NetBeans IDE中选择 File > New Project >.
- 类别下选择项目类型为Java,项目类型为Java应用程序的Java。点击Next>按钮。
- 输入项目的名称和位置。单击“Finish >“按钮。我们选择名为EjbTester。
- 右键点击项目名称(在Project explore窗口中)。选择属性properties。
- 添加EJB组件项目的库使用“Add Project ”按钮,在compile选项卡下创建的。
- 添加JBoss库使用添加Add jar/folder按钮,在compile选项卡。 Jboss的库可以位于<JBOSS安装文件夹>客户端文件夹。
在工程中创建 jndi.properties说一个句话 EjbTester.
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
创建包com.tutorialspoint.test和EJBTester.java类在下面。
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testStatelessEjb();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testStatelessEjb(){
try {
int choice = 1;
LibrarySessionBeanRemote libraryBean =
(LibrarySessionBeanRemote)ctx.lookup("LibrarySessionBean/remote");
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
libraryBean.addBook(bookName);
}else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<String> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
for (int i = 0; i < booksList.size(); ++i) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + booksList.get(i));
}
LibrarySessionBeanRemote libraryBean1 =
(LibrarySessionBeanRemote)ctx.lookup("LibrarySessionBean/remote");
List<String> booksList1 = libraryBean1.getBooks();
System.out.println(
"***Using second lookup to get library stateless object***");
System.out.println(
"Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList1.size());
for (int i = 0; i < booksList1.size(); ++i) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + booksList1.get(i));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
运行客户端访问EJB
在project explorer中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择“run file”。
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: Learn Java
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. Learn Java
***Using second lookup to get library stateless object***
Book(s) entered so far: 0
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 13 seconds)
在下面的章节中,我们将讨论这个完整的EJB的多个层面应用程序。
EJB无状态Bean - EJB
无状态会话bean是一种企业bean,通常是用于执行独立操作。正如它的名字一样,无状态会话bean不具有任何关联的客户端的状态,但它可能会保持其实例的状态。 EJB容器通常创建一个容器池和几无状态的bean的对象,并使用这些对象来处理客户端的请求。由于有容器池,实例变量的值不能保证跨查找/方法调用同一个。
下面是创建一个无状态的EJB所需的步骤。
- 创建一个远程/本地接口暴露的业务方法。
- 此接口将用于EJB客户端应用程序。
- 使用@ Local注释如果EJB客户端是在相同的环境中部署EJB会话Bean。
- 使用@ Remote批注如果EJB客户端是在不同的环境中部署EJB会话Bean。
- 创建一个无状态会话bean实现上述接口。
- 使用@ Stateless注释,以表示它一个无状态的bean。 EJB容器会自动创建通过读取这个注解,在部署过程中的相关配置或接口。
Remote Interface
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibrarySessionBeanRemote {
//add business method declarations
}
Stateless EJB
@Stateless
public class LibrarySessionBean implements LibrarySessionBeanRemote {
//implement business method
}
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试测试无状态EJB的EJB应用程序。
步骤 | 描述 |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.stateless as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. You can also use the project created in EJB - Create Application chapter as such for this chapter to understand stateless ejb concepts. |
2 | Create LibrarySessionBean.java and LibrarySessionBeanRemote as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
3 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
4 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
5 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. |
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
LibrarySessionBeanRemote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibrarySessionBeanRemote {
void addBook(String bookName);
List getBooks();
}
LibrarySessionBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
@Stateless
public class LibrarySessionBean implements LibrarySessionBeanRemote {
List<String> bookShelf;
public LibrarySessionBean(){
bookShelf = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public void addBook(String bookName) {
bookShelf.add(bookName);
}
public List<String> getBooks() {
return bookShelf;
}
}
- As soon as you deploy the EjbComponent project on JBOSS, notice the jboss log.
- JBoss has automatically created a JNDI entry for our session bean -LibrarySessionBean/remote.
- We'll using this lookup string to get remote business object of type -com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanRemote
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
...
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibrarySessionBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibrarySessionBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibrarySessionBean,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanRemote ejbName: LibrarySessionBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibrarySessionBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibrarySessionBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
...
EJBTester (EJB Client)
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
- These properties are used to initialize the InitialContext object of java naming service
- InitialContext object will be used to lookup stateless session bean
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateful.LibrarySessionBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testStatelessEjb();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testStatelessEjb(){
try {
int choice = 1;
LibrarySessionBeanRemote libraryBean =
LibrarySessionBeanRemote)ctx.lookup("LibrarySessionBean/remote");
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
i++;
}
LibrarySessionBeanRemote libraryBean1 =
(LibrarySessionBeanRemote)ctx.lookup("LibrarySessionBean/remote");
List<String> booksList1 = libraryBean1.getBooks();
System.out.println(
"***Using second lookup to get library stateless object***");
System.out.println(
"Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList1.size());
for (int i = 0; i < booksList1.size(); ++i) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + booksList1.get(i));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester在执行以下任务。
- Load properties from jndi.properties and initialize the InitialContext object.
- In testStatelessEjb() method, jndi lookup is done with name - "LibrarySessionBean/remote" to obtain the remote business object (stateless ejb).
- Then user is shown a library store User Interface and he/she is asked to enter choice.
- If user enters 1, system asks for book name and saves the book using stateless session bean addBook() method. Session Bean is storing the book in its instance variable.
- If user enters 2, system retrieves books using stateless session bean getBooks() method and exits.
- Then another jndi lookup is done with name - "LibrarySessionBean/remote" to obtain the remote business object (stateless ejb) again and listing of books is done.
运行客户端访问EJB
Locate EJBTester.java in project explorer. Right click on EJBTester class and select run file.
Verify the following output in Netbeans console.
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: Learn Java
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. Learn Java
***Using second lookup to get library stateless object***
Book(s) entered so far: 0
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 13 seconds)
再次运行客户端访问EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 0
***Using second lookup to get library stateless object***
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. Learn Java
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 12 seconds)
- 如上图所示的输出可能会有所不同,这取决于许多无状态JBoss的EJB对象保持。
- 万一单一的无状态EJB对象得以维持,每次查找后,你可能会看到相同书籍列表。
- EJB容器可以为每个查询返回相同的无状态EJB对象。
无状态EJB的bean实例变量的值是直到重新启动服务器才失效的。
EJB有状态Bean - EJB
有状态会话Bean是一种企业bean保存客户端的会话状态类型。有状态会话bean作为每它的名字相关的客户端状态保持在它的实例变量。 EJB容器创建一个单独的有状态会话bean来处理客户端的每个请求。只要请求范围过,有状态会话bean被销毁。
以下是创建一个有状态的EJB所需的步骤:
- Create a remote/local interface exposing the business methods.
- This interface will be used by the ejb client application.
- Use @Local annotation if ejb client is in same environment where ejb session bean is to be deployed.
- Use @Remote annotation if ejb client is in different environment where ejb session bean is to be deployed.
- Create a stateful session bean implementing the above interface.
- Use @Stateful annotation to signify it a stateful bean. EJB Container automatically creates the relevant configurations or interfaces required by reading this annotation during deployment.
远程接口
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote {
//add business method declarations
}
Stateful EJB
@Stateful
public class LibraryStatefulSessionBean implements LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote {
//implement business method
}
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试测试状态EJB的EJB应用程序。
Step | 描述 |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.stateful as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. You can also use the project created in EJB - Create Application chapter as such for this chapter to understand stateful ejb concepts. |
2 | Create LibraryStatefulSessionBean.java and LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
3 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
4 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
5 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. |
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateful;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote {
void addBook(String bookName);
List getBooks();
}
LibraryStatefulSessionBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateful;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateful;
@Stateful
public class LibraryStatefulSessionBean implements LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote {
List<String> bookShelf;
public LibraryStatefulSessionBean(){
bookShelf = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public void addBook(String bookName) {
bookShelf.add(bookName);
}
public List<String> getBooks() {
return bookShelf;
}
}
- 只要你部署在JBoss EjbComponent项目发现jboss的日志。
- JBoss已经自动创建一个JNDI条目会话bean-LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote。
- 我们将使用这个查询字符串来获得远程类型的业务对象-com.tutorialspoint.stateful.LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
...
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateful.LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibraryStatefulSessionBean,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.stateful.LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote ejbName: LibraryStatefulSessionBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateful.LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
...
EJBTester (EJB Client)
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
- These properties are used to initialize the InitialContext object of java naming service
- InitialContext object will be used to lookup stateful session bean
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateful.LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testStatelessEjb();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testStatelessEjb(){
try {
int choice = 1;
LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote libraryBean =
LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote)ctx.lookup("LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote");
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
i++;
}
LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote libraryBean1 =
(LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote)ctx.lookup("LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote");
List<String> booksList1 = libraryBean1.getBooks();
System.out.println(
"***Using second lookup to get library stateful object***");
System.out.println(
"Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList1.size());
for (int i = 0; i < booksList1.size(); ++i) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + booksList1.get(i));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester is doing the following tasks.
- Load properties from jndi.properties and initialize the InitialContext object.
- In testStatefulEjb() method, jndi lookup is done with name - "LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote" to obtain the remote business object (stateful ejb).
- Then user is shown a library store User Interface and he/she is asked to enter choice.
- If user enters 1, system asks for book name and saves the book using stateful session bean addBook() method. Session Bean is storing the book in its instance variable.
- If user enters 2, system retrieves books using stateful session bean getBooks() method and exits.
- Then another jndi lookup is done with name - "LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote" to obtain the remote business object (stateful ejb) again and listing of books is done.
运行客户端访问EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键单击类EJBTester并选择run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: Learn Java
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. Learn Java
***Using second lookup to get library stateful object***
Book(s) entered so far: 0
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 13 seconds)
再次运行客户端访问EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键单击类EJBTester选择run file.
在NetBeans控制台验证以下输出.
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 0
***Using second lookup to get library stateful object***
Book(s) entered so far: 0
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 12 seconds)
- 输出上面显示的状态,对于每个查询不同状态的EJB实例将被返回.
- 只适用于单个会话状态EJB对象值。在第二次运行时,我们没有得到任何值.
EJB持久性 - EJB
EJB2.0中使用的实体bean持久化机制在很大程度上被EJB3.0取代。现在实体bean是一个简单的POJO映射表。
以下是持久性API的关键角色
- Entity - 持久对象代表数据存储记录。这也是可序列化的。
- EntityManager - 持久性接口做数据操作,如添加/删除/更新/找到持久化对象(实体)。它还有助于执行查询使用query接口
- Persistence unit (persistence.xml) - 持久性单元介绍了持久性机制的属性。
- Data Source (*ds.xml) - 数据源描述了数据存储相关的属性,如连接URL。用户名,密码等。
为了证明EJB的持久化机制,我们要做好以下几项工作。
- Step 1. 在数据库中创建表.
- Step 2. 创建实体类对应的表.
- Step 3. 创建数据源和持久性单元
- Step 4. 创建一个无状态EJB EntityManager实例.
- Step 5. 更新无状态EJB。添加添加记录并获得通过实体管理器从数据库中记录的方法。
- Step 6. 一个基于控制台应用程序客户端将访问无状态EJB的持久化数据库中的数据。
创建表
创建一个表 books 在默认的数据库 postgres.
CREATE TABLE books (
id integer PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar(50)
);
创建实体类
//mark it entity using Entity annotation
//map table name using Table annoation
@Entity
@Table(name="books")
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
public Book(){
}
//mark id as primary key with autogenerated value
//map database column id with id field
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="id")
public int getId() {
return id;
}
...
}
创建数据源和持久性单元
DataSource (jboss-ds.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<datasources>
<local-tx-datasource>
<jndi-name>PostgresDS</jndi-name>
<connection-url>jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/postgres</connection-url>
<driver-class>org.postgresql.driver</driver-class>
<user-name>sa</user-name>
<password>sa</password>
<min-pool-size>5</min-pool-size>
<max-pool-size>20</max-pool-size>
<idle-timeout-minutes>5</idle-timeout-minutes>
</local-tx-datasource>
</datasources>
Persistence Unit (persistence.xml)
<persistence version="1.0" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/persistence/persistence_1_0.xsd">
<persistence-unit name="EjbComponentPU" transaction-type="JTA">
<jta-data-source>java:/PostgresDS</jta-data-source>
<exclude-unlisted-classes>false</exclude-unlisted-classes>
<properties/>
</persistence-unit>
<persistence-unit name="EjbComponentPU2" transaction-type="JTA">
<provider>org.hibernate.ejb.HibernatePersistence</provider>
<jta-data-source>java:/PostgresDS</jta-data-source>
<exclude-unlisted-classes>false</exclude-unlisted-classes>
<properties>
<property name="hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto" value="update"/>
</properties>
</persistence-unit>
</persistence>
Create Stateless EJB having EntityManager instance
@Stateless
public class LibraryPersistentBean implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
//pass persistence unit to entityManager.
@PersistenceContext(unitName="EjbComponentPU")
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void addBook(Book book) {
entityManager.persist(book);
}
public List<Book> getBooks() {
return entityManager.createQuery("From Books").getResultList();
}
...
}
构建EJB模块后,我们需要一个无状态的bean,我们将在下一节要创建客户端来访问。
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试EJB应用程序来测试EJB的持久化机制。
Step | 描述 |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.entity as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. You can also use the project created in EJB - Create Application chapter as such for this chapter to understand ejb persistence concepts. |
2 | Create Book.java under package com.tutorialspoint.entity and modify it as shown below. |
3 | Create LibraryPersistentBean.java and LibraryPersistentBeanRemote as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter and modify them as shown below. |
4 | Create jboss-ds.xml in EjbComponent > setup folder and persistence.xml in EjbComponent > src > conf folder. These folder can be seen in files tab in Netbeans. Modify these files as shown above. |
5 | 清理并生成应用程序以确保业务逻辑是按要求工作。 |
6 | 最后,将应用程序部署在JBoss应用服务器上的jar文件的形式。 JBoss应用服务器将自动开始浏览网页,如果它尚未启动。 |
7 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. Modify it as shown below. |
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
Book.java
package com.tutorialspoint.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.EntityListeners;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="books")
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
public Book(){
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="id")
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
void addBook(Book bookName);
List<Book> getBooks();
}
LibraryPersistentBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
@Stateless
public class LibraryPersistentBean implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
public LibraryPersistentBean(){
}
@PersistenceContext(unitName="EjbComponentPU")
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void addBook(Book book) {
entityManager.persist(book);
}
public List<Book> getBooks() {
return entityManager.createQuery("From Book").getResultList();
}
}
- As soon as you deploy the EjbComponent project on JBOSS, notice the jboss log.
- JBoss has automatically created a JNDI entry for our session bean -LibraryPersistentBean/remote.
- We'll using this lookup string to get remote business object of type -com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
...
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibraryPersistentBeanRemote,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote ejbName: LibraryPersistentBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
...
EJBTester (EJB Client)
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
- These properties are used to initialize the InitialContext object of java naming service
- InitialContext object will be used to lookup stateless session bean
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testEntityEjb();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testEntityEjb(){
try {
int choice = 1;
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean =
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote)ctx.lookup("LibraryPersistentBean/remote");
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester is doing the following tasks.
- Load properties from jndi.properties and initialize the InitialContext object.
- In testStatefulEjb() method, jndi lookup is done with name - "LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote" to obtain the remote business object (stateful ejb).
- Then user is shown a library store User Interface and he/she is asked to enter choice.
- If user enters 1, system asks for book name and saves the book using stateless session bean addBook() method. Session Bean is persisting the book in database via EntityManager call.
- If user enters 2, system retrieves books using stateful session bean getBooks() method and exits.
- Then another jndi lookup is done with name - "LibraryStatelessSessionBean/remote" to obtain the remote business object (stateless ejb) again and listing of books is done.
运行客户端访问EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择 run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: Learn Java
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. learn java
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 15 seconds)
再次运行客户端来访问EJB。
访问EJB之前重新启动JBoss。
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择 run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: Learn Spring
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 2
1\. learn java
2\. Learn Spring
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 15 seconds)
- 上面显示的输出状态书存储在持久性存储,并从数据库中检索。
EJB消息驱动Bean - EJB
一个消息驱动bean是一种类型的企业Bean,这是由EJB容器调用,当它接收到一个消息队列或主题。消息驱动bean是一个无状态的bean是用来做异步任务。
为了演示如何使用消息驱动bean,我们将利用EJB持久章节的内容,我们要做好以下几项工作。
- Step 1. 在数据库中创建表(请参阅EJB持久章节)。
- Step 2. 创建实体类对应的表 (请参阅EJB持久章节).
- Step 3. 创建数据源和持久性单元 (请参阅EJB持久章节).
- Step 4. 创建一个无状态EJB EntityManager实例 (请参阅EJB持久章节).
- Step 5. 更新无状态EJB。添加添加记录的方法,并通过实体管理器,从数据库中获取记录 (请参阅EJB持久章节).
- Step 6. 创建队列名为 BookQueue 在JBoss default 应用目录.
- Step 7. 一个基于控制台应用程序客户端发送消息到这个队列
- Step 8. 创建消息驱动bean将使用无状态的bean持久化客户数据。
- Step 9. JBoss的EJB容器将调用上面的消息驱动bean,并把它传递的消息将要发送给客户端。
创建队列
创建一个文件名为jbossmq目的地service.xml中,如果不存在 <JBoss Installation Folder> > server > default > deploy 目录.
在这里,我们创建名为BookQueue一个队列
jbossmq-destinations-service.xml
<mbean code="org.jboss.mq.server.jmx.Queue"
name="jboss.mq.destination:service=Queue,name=BookQueue">
<depends optional-attribute-name="DestinationManager">
jboss.mq:service=DestinationManager
</depends>
</mbean>
当你启动JBoss,你会看到类似的内容在JBoss日志
...
10:37:06,167 INFO [QueueService] Queue[/queue/BookQueue] started, fullSize=200000, pageSize=2000, downCacheSize=2000
...
创建消息驱动bean
@MessageDriven(
name = "BookMessageHandler",
activationConfig = {
@ActivationConfigProperty( propertyName = "destinationType",
propertyValue = "javax.jms.Queue"),
@ActivationConfigProperty( propertyName = "destination",
propertyValue ="/queue/BookQueue")
}
)
public class LibraryMessageBean implements MessageListener {
@Resource
private MessageDrivenContext mdctx;
@EJB
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean;
public LibraryMessageBean(){
}
public void onMessage(Message message) {
}
}
- LibraryMessageBean annoatated@MessageDriven注解,把它标记为消息驱动bean。
- Its properties are defined as destinationType - Queue and destination - /queue/BookQueue.
- It implements MessageListener interface which exposes onMessage method.
- It has MessgeDrivenContext as resource.
- LibraryPersistentBeanRemote stateless bean is injected in this bean for persistence purpose.
构建EjbComponent项目,并将其部署在JBoss上。构建和部署EJB模块后,我们需要一个客户端发送一个消息到JBoss队列。
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试EJB应用程序来测试消息驱动bean。
Step | Description |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.entity as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. You can also use the project created in EJB - Create Application chapter as such for this chapter to understand ejb persistence concepts. |
2 | Create Book.java under package com.tutorialspoint.entity as created in _EJB-Persistence_chapter |
3 | Create LibraryPersistentBean.java and LibraryPersistentBeanRemote as created in EJB-Persistence chapter |
4 | Create jboss-ds.xml in EjbComponent > setup folder and persistence.xml in EjbComponent > src > conf folder. These folder can be seen in files tab in Netbeans as created in EJB-Persistence chapter |
5 | Create LibraryMessageBean.java under a package com.tutorialspoint.messagebean and modify it as shown below. |
6 | Create BookQueue queue in Jboss as described above. |
7 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
8 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
9 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. Modify it as shown below. |
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
LibraryMessageBean.java
package com.tuturialspoint.messagebean;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.ejb.ActivationConfigProperty;
import javax.ejb.EJB;
import javax.ejb.MessageDriven;
import javax.ejb.MessageDrivenContext;
import javax.jms.JMSException;
import javax.jms.Message;
import javax.jms.MessageListener;
import javax.jms.ObjectMessage;
@MessageDriven(
name = "BookMessageHandler",
activationConfig = {
@ActivationConfigProperty( propertyName = "destinationType",
propertyValue = "javax.jms.Queue"),
@ActivationConfigProperty( propertyName = "destination",
propertyValue ="/queue/BookQueue")
}
)
public class LibraryMessageBean implements MessageListener {
@Resource
private MessageDrivenContext mdctx;
@EJB
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean;
public LibraryMessageBean(){
}
public void onMessage(Message message) {
ObjectMessage objectMessage = null;
try {
objectMessage = (ObjectMessage) message;
Book book = (Book) objectMessage.getObject();
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} catch (JMSException ex) {
mdctx.setRollbackOnly();
}
}
}
EJBTester (EJB Client)
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.jms.ObjectMessage;
import javax.jms.Queue;
import javax.jms.QueueConnection;
import javax.jms.QueueConnectionFactory;
import javax.jms.QueueSender;
import javax.jms.QueueSession;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testMessageBeanEjb();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testMessageBeanEjb(){
try {
int choice = 1;
Queue queue = (Queue) ctx.lookup("/queue/BookQueue");
QueueConnectionFactory factory =
(QueueConnectionFactory) ctx.lookup("ConnectionFactory");
QueueConnection connection = factory.createQueueConnection();
QueueSession session =
connection.createQueueSession(false, QueueSession.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
QueueSender sender = session.createSender(queue);
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
ObjectMessage objectMessage =
session.createObjectMessage(book);
sender.send(objectMessage);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean =
(LibraryPersistentBeanRemote)
ctx.lookup("LibraryPersistentBean/remote");
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester做以下任务。
- jndi.properties中加载和初始化的InitialContext对象。
- In testStatefulEjb() method, jndi lookup is done with name - "/queue/BookQueue" to obtain treference of queue available in Jboss. Then sender is created using queue session.
- Then user is shown a library store User Interface and he/she is asked to enter choice.
- If user enters 1, system asks for book name and sender sends the book name to queue. When JBoss container receives this message in queue, it calls our message driven bean's onMessage method. Our message driven bean then saves book using stateful session bean addBook() method. Session Bean is persisting the book in database via EntityManager call.
- If user enters 2, then another jndi lookup is done with name - "LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote" to obtain the remote business object (stateful ejb) again and listing of books is done.
运行客户端访问EJB
Locate EJBTester.java in project explorer. Right click on EJBTester class and select run file.
Verify the following output in Netbeans console.
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: Learn EJB
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 2
1\. learn java
1\. learn EJB
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 15 seconds)
上面显示的输出状态,我们的消息驱动bean接收消息和存储在持久性存储的书和书籍通过数据库检索。
EJB注解/注释 - EJB
在Java 5.0中引入的注解。注释的目的是要重视在类中更多的信息或元数据在其源代码内类。在EJB 3.0中,注释是用来描述配置元数据在ejb类。通过这种方式,EJB3.0消除了需要描述在XML配置文件中的配置数据。
EJB容器使用的编译器工具来生成所需的工件,如接口,部署描述符,通过阅读这些注释。下面列出的常用的注解。
Sr. No. | 名称 | 描述 |
1 | javax.ejb.Stateless | 指定一个给定的EJB类是一个无状态会话bean. 属性 name - 用于指定会话bean的名称。 mappedName - 用于指定的会话bean的JNDI名称。 description - 用于提供会话bean的描述。 |
2 | javax.ejb.Stateful | 指定一个给定的EJB类是有状态会话bean。属性 name - 用于指定会话bean的名称。 mappedName - 用于指定的会话bean的JNDI名称。 description - 用于提供会话bean的描述。 |
3 | javax.ejb.MessageDrivenBean | 指定一个给定的EJB类是消息驱动的Bean。属性 name - 用于指定消息驱动bean的名称。 messageListenerInterface - 消息驱动bean用于指定消息监听器接口。 activationConfig - 用于指定的配置细节,消息驱动Bean消息驱动bean的经营环境。 mappedName - 用于指定的会话bean的JNDI名称。 description - 用于提供会话bean的描述。 |
4 | javax.ejb.EJB | 用于指定或注入到另一个EJB的EJB实例的依赖。属性 name - 用来指定将被使用的环境中找到引用的bean的名称。 beanInterface - 用于指定的接口类型引用的bean。 beanName - 用来提供引用的bean的名称。 mappedName - 用于引用bean指定的JNDI名称。 description - 用来提供引用的bean的描述。 |
5 | javax.ejb.Local | 用于指定一个会话bean的本地接口(次)。这个本地接口状态会话bean的业务方法(可以是无状态或有状态)。这个接口是用来以暴露本地客户端都运行在相同的部署/应用EJB的业务方法。 属性 value - 用于指定的本地接口列表接口数组。 |
6 | javax.ejb.Remote | 用于指定一个会话bean的远程接口(次)。这个远程接口状态会话bean的业务方法(可以是无状态或有状态)。这个接口是用来揭露远程客户端运行在不同的部署/应用EJB的业务方法。属性 value - 用于指定远程接口接口数组列表。 |
7 | javax.ejb.ActivationConfigProperty | 用于指定需要消息驱动的Bean的属性。例如终止点,目的地,消息选择等。这个注解通过作为参数,activationConfig属性javax.ejb.MessageDrivenBean注释。属性 propertyName - 属性名称. propertyValue - 属性值. |
8 | javax.ejb.PostActivate | 用于指定EJB的生命周期的回调方法。这种方法时,将调用EJB容器刚刚激活/激活bean实例。这个接口是用来以暴露本地客户端都运行在相同的部署/应用EJB的业务方法。 |
EJB回调 - EJB
回调是一种机制,可以截获企业Bean的生命周期。 EJB 3.0规范指定的回调,回调处理方法是要创建。 EJB容器调用这些回调。 EJB类本身或在一个单独的类,我们可以定义回调方法。 EJB3.0提供了许多回调的注解
以下是无状态的bean回调的注解。
Annotation | 描述 |
@PostConstruct | method is invoked when a bean is created for the first time |
--- | --- |
@PreDestroy | method is invoked when a bean is removed from the bean pool or is destroyed. |
--- | --- |
Following is the list of callback annotations for stateful bean.
Annotation | 描述 |
@PostConstruct | method is invoked when a bean is created for the first time |
--- | --- |
@PreDestroy | method is invoked when a bean is removed from the bean pool or is destroyed. |
--- | --- |
@PostActivate | method is invoked when a bean is loaded to be used. |
--- | --- |
@PrePassivate | method is invoked when a bean is put back to bean pool. |
--- | --- |
Following is the list of callback annotations for message driven bean.
Annotation | 描述 |
@PostConstruct | method is invoked when a bean is created for the first time |
--- | --- |
@PreDestroy | method is invoked when a bean is removed from the bean pool or is destroyed. |
--- | --- |
Following is the list of callback annotations for entity bean.
Annotation | Description |
@PrePersist | method is invoked when an entity is created in database. |
--- | --- |
@PostPersist | method is invoked after an entity is created in database. |
--- | --- |
@PreRemove | method is invoked when an entity is deleted from the database. |
--- | --- |
@PostRemove | method is invoked after an entity is deleted from the database. |
--- | --- |
@PreUpdate | method is invoked before an entity is to be updated in the database. |
--- | --- |
@PostLoad | method is invoked when a record is fetched from database and loaded into the entity. |
--- | --- |
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试EJB应用程序来测试各种回调EJB。
Step | 描述 |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.stateless as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. You can also use the project created in EJB - Persistence chapter as such for this chapter to add various callbacks to ejbs. |
2 | Create LibrarySessionBean.java and LibrarySessionBeanRemote as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
3 | Use Beans created in the EJB - Persistence chapter. Add callback methods as shown below. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
4 | Create a java class BookCallbackListener under package com.tutorialspoint.callback. This class will demonstrates the seperation of callback methods. |
5 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
6 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
7 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. |
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
BookCallbackListener.java
package com.tutorialspoint.callback;
import javax.persistence.PrePersist;
import javax.persistence.PostLoad;
import javax.persistence.PostPersist;
import javax.persistence.PostRemove;
import javax.persistence.PostUpdate;
import javax.persistence.PreRemove;
import javax.persistence.PreUpdate;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
public class BookCallbackListener {
@PrePersist
public void prePersist(Book book){
System.out.println("BookCallbackListener.prePersist:"
+ "Book to be created with book id: "+book.getId());
}
@PostPersist
public void postPersist(Object book){
System.out.println("BookCallbackListener.postPersist::"
+ "Book created with book id: "+((Book)book).getId());
}
@PreRemove
public void preRemove(Book book)
{
System.out.println("BookCallbackListener.preRemove:"
+ " About to delete Book: " + book.getId());
}
@PostRemove
public void postRemove(Book book)
{
System.out.println("BookCallbackListener.postRemove::"
+ " Deleted Book: " + book.getId());
}
@PreUpdate
public void preUpdate(Book book)
{
System.out.println("BookCallbackListener.preUpdate::"
+ " About to update Book: " + book.getId());
}
@PostUpdate
public void postUpdate(Book book)
{
System.out.println("BookCallbackListener.postUpdate::"
+ " Updated Book: " + book.getId());
}
@PostLoad
public void postLoad(Book book)
{
System.out.println("BookCallbackListener.postLoad::"
+ " Loaded Book: " + book.getId());
}
}
Book.java
package com.tutorialspoint.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.EntityListeners;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="books")
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
public Book(){
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="id")
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
LibraryStatefulSessionBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateful;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import javax.ejb.PostActivate;
import javax.ejb.PrePassivate;
import javax.ejb.Stateful;
@Stateful
public class LibraryStatefulSessionBean
implements LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote {
List<String> bookShelf;
public LibraryStatefulSessionBean(){
bookShelf = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public void addBook(String bookName) {
bookShelf.add(bookName);
}
public List<String> getBooks() {
return bookShelf;
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct(){
System.out.println("LibraryStatefulSessionBean.postConstruct::"
+ " bean created.");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy(){
System.out.println("LibraryStatefulSessionBean.preDestroy:"
+ " bean removed.");
}
@PostActivate
public void postActivate(){
System.out.println("LibraryStatefulSessionBean.postActivate:"
+ " bean activated.");
}
@PrePassivate
public void prePassivate(){
System.out.println("LibraryStatefulSessionBean.prePassivate:"
+ " bean passivated.");
}
}
LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRempote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateful;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryStatefulSessionBeanRemote {
void addBook(String bookName);
List getBooks();
}
LibraryPersistentBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import javax.annotation.PreDestroy;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
@Stateless
public class LibraryPersistentBean
implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
public LibraryPersistentBean(){}
@PersistenceContext(unitName="EntityEjbPU")
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void addBook(Book book) {
entityManager.persist(book);
}
public List<Book> getBooks() {
return entityManager.createQuery("From Book")
.getResultList();
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct(){
System.out.println("postConstruct:: LibraryPersistentBean session bean"
+ " created with entity Manager object: ");
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy(){
System.out.println("preDestroy: LibraryPersistentBean session"
+ " bean is removed ");
}
}
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
void addBook(Book bookName);
List<Book> getBooks();
}
- 只要你部署在JBoss EjbComponent项目,就会发现jboss的日志。
- JBoss已经自动为我们的会话bean创建一个JNDI条目 -LibraryPersistentBean/remote.
- 我们将使用这个查询字符串来获得远程类型的业务对象 -com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
...
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibraryPersistentBean,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanRemote ejbName: LibraryPersistentBean
...
EJBTester (EJB Client)
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
- 这些属性是用来初始化InitialContext对象的Java命名服务
- InitialContext的对象将被用于查找无状态会话bean
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateful.LibrarySessionBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testEntityEjb();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testEntityEjb(){
try {
int choice = 1;
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean =
(LibraryPersistentBeanRemote)
ctx.lookup("LibraryPersistentBean/remote");
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester is doing the following tasks.
- Load properties from jndi.properties and initialize the InitialContext object.
- In testStatelessEjb() method, jndi lookup is done with name - "LibrarySessionBean/remote" to obtain the remote business object (stateless ejb).
- Then user is shown a library store User Interface and he/she is asked to enter choice.
- If user enters 1, system asks for book name and saves the book using stateless session bean addBook() method. Session Bean is storing the book in the database.
- If user enters 2, system retrieves books using stateless session bean getBooks() method and exits.
运行客户端访问EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择 run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: Learn Java
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. Learn Java
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 13 seconds)
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
你可以找到以下的回调在JBoss日志项
14:08:34,293 INFO [STDOUT] postConstruct:: LibraryPersistentBean session bean created with entity Manager object
...
16:39:09,484 INFO [STDOUT] BookCallbackListener.prePersist:: Book to be created with book id: 0
16:39:09,531 INFO [STDOUT] BookCallbackListener.postPersist:: Book created with book id: 1
16:39:09,900 INFO [STDOUT] BookCallbackListener.postLoad:: Loaded Book: 1
EJB定时器服务 - EJB
定时器服务使用计划应用程序可以建立一个机制。例如,每月1日的工资单生成。 EJB3.0规范指定超时注释,这有助于编程一个无状态或消息驱动Bean的EJB服务。 EJB容器调用的方法,这是注释@Timeout.
EJB计时器服务是有助于创造的定时器,并安排回调计时器到期时由EJB容器提供的服务。
创建定时器的步骤
使用@ Resource注解注入SessionContext的bean
@Stateless
public class TimerSessionBean {
@Resource
private SessionContext context;
...
}
使用SessionContext对象TimerService创造定时器的。传递时间(以毫秒为单位)和消息。
public void createTimer(long duration) {
context.getTimerService().createTimer(duration, "Hello World!");
}
使用定时器的步骤
使用@Timeout批注的方法。返回类型必须为void,并传递一个参数类型的定时器。我们取消计时器后第一次执行,否则将继续运行,修正后的时间间隔。
@Timeout
public void timeOutHandler(Timer timer){
System.out.println("timeoutHandler : " + timer.getInfo());
timer.cancel();
}
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试测试计时器服务在EJB的EJB应用程序中。
Step | 描述 |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.timer as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. |
2 | Create TimerSessionBean.java and TimerSessionBeanRemote as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
3 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
4 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
5 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. |
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
TimerSessionBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.timer;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.ejb.SessionContext;
import javax.ejb.Timer;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.ejb.Timeout;
@Stateless
public class TimerSessionBean implements TimerSessionBeanRemote {
@Resource
private SessionContext context;
public void createTimer(long duration) {
context.getTimerService().createTimer(duration, "Hello World!");
}
@Timeout
public void timeOutHandler(Timer timer){
System.out.println("timeoutHandler : " + timer.getInfo());
timer.cancel();
}
}
TimerSessionBeanRemote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.timer;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface TimerSessionBeanRemote {
public void createTimer(long milliseconds);
}
- 一旦你在Jboss应用服务器部署EjbComponent项目,发现jboss日志。
- JBoss已经自动为我们的会话bean创建一个JNDI条目 -TimerSessionBean/remote.
- 我们将使用这个查询字符串来获得远程类型的业务对象 -com.tutorialspoint.timer.TimerSessionBeanRemote
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
...
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
TimerSessionBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
TimerSessionBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.timer.TimerSessionBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=TimerSessionBean,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.timer.TimerSessionBeanRemote ejbName: TimerSessionBean
...
EJBTester (EJB Client)
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
- 这些属性是用来初始化InitialContext对象的Java命名服务
- InitialContext对象将被用于查找无状态会话bean
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateful.TimerSessionBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testTimerService();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testTimerService(){
try {
TimerSessionBeanRemote timerServiceBean = (TimerSessionBeanRemote)ctx.lookup("TimerSessionBean/remote");
System.out.println("["+(new Date()).toString()+ "]" + "timer created.");
timerServiceBean.createTimer(2000);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
EJBTester做以下任务。
- jndi.properties中加载和初始化的InitialContext对象。
- 在testTimerService()方法,名字完成JNDI查找 - “TimerSessionBean/remote”,以获得远程业务对象(定时器无状态EJB)。
- 然后的调用createTimer通过预定时间为2000毫秒。
- 2秒后EJB容器调用timeoutHandler,方法。
运行客户端访问EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
[Wed Jun 19 11:35:47 IST 2013]timer created.
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 0 seconds)
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
你可以找到以下的回调在JBoss日志项
...
11:35:49,555 INFO [STDOUT] timeoutHandler : Hello World!
...
EJB依赖注入 - EJB
EJB 3.0规范提供了注释字段或setter方法注入依赖可以应用。 EJB容器使用的全局JNDI注册表定位的依赖。以下注解在EJB 3.0中使用依赖注入。
- @EJB - 用来注入其他EJB引用。
- @Resource - 用于注入数据源或单例服务,如sessionContext,timerService等
@EJB使用步骤
@EJB 可以使用栏位或以下方式的方法。
public class LibraryMessageBean implements MessageListener {
//dependency injection on field.
@EJB
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean;
...
}
public class LibraryMessageBean implements MessageListener {
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean;
//dependency injection on method.
@EJB(beanName="com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBean")
public void setLibraryPersistentBean(
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean)
{
this.libraryBean = libraryBean;
}
...
}
@Resource 使用步骤
@Resource 通常用于注入EJB容器提供单例。
public class LibraryMessageBean implements MessageListener {
@Resource
private MessageDrivenContext mdctx;
...
}
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试EJB应用程序来测试EJB服务的依赖注入。
Step | Description |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.timer as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. |
3 | Use Beans created in the EJB - Message Driven Bean chapter. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
5 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
6 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
7 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. |
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
LibraryMessageBean.java
package com.tuturialspoint.messagebean;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.ejb.ActivationConfigProperty;
import javax.ejb.EJB;
import javax.ejb.MessageDriven;
import javax.ejb.MessageDrivenContext;
import javax.jms.JMSException;
import javax.jms.Message;
import javax.jms.MessageListener;
import javax.jms.ObjectMessage;
@MessageDriven(
name = "BookMessageHandler",
activationConfig = {
@ActivationConfigProperty( propertyName = "destinationType",
propertyValue = "javax.jms.Queue"),
@ActivationConfigProperty( propertyName = "destination",
propertyValue ="/queue/BookQueue")
}
)
public class LibraryMessageBean implements MessageListener {
@Resource
private MessageDrivenContext mdctx;
@EJB
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean;
public LibraryMessageBean(){
}
public void onMessage(Message message) {
ObjectMessage objectMessage = null;
try {
objectMessage = (ObjectMessage) message;
Book book = (Book) objectMessage.getObject();
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} catch (JMSException ex) {
mdctx.setRollbackOnly();
}
}
}
EJBTester (EJB Client)
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.jms.ObjectMessage;
import javax.jms.Queue;
import javax.jms.QueueConnection;
import javax.jms.QueueConnectionFactory;
import javax.jms.QueueSender;
import javax.jms.QueueSession;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testMessageBeanEjb();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testMessageBeanEjb(){
try {
int choice = 1;
Queue queue = (Queue) ctx.lookup("/queue/BookQueue");
QueueConnectionFactory factory =
(QueueConnectionFactory) ctx.lookup("ConnectionFactory");
QueueConnection connection = factory.createQueueConnection();
QueueSession session = connection.createQueueSession(
false, QueueSession.AUTO_ACKNOWLEDGE);
QueueSender sender = session.createSender(queue);
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
ObjectMessage objectMessage =
session.createObjectMessage(book);
sender.send(objectMessage);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean =
(LibraryPersistentBeanRemote)
ctx.lookup("LibraryPersistentBean/remote");
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: "
+ booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester做以下任务。
- jndi.properties中加载和初始化的InitialContext对象。
- JNDI查找testStatefulEjb()方法,完成了名字 - “/queue/BookQueue”在JBoss获得参考。发件人使用队列会话创建。
- 然后用户显示一个库存储的用户界面和他/她被要求输入选择。
- 如果用户输入1,系统要求输入书籍名称和发件人发送本书的名字来排队。当JBoss容器接收到这个消息队列,它会调用我们的消息驱动bean的onMessage方法。消息驱动bean保存使用状态会话bean addBook()方法的书。会话Bean持久化这本书中通过EntityManager调用数据库。
- 如果用户输入2,然后是另一个JNDI查找名字 - “LibraryStatefulSessionBean/remote”获取远程业务对象(状态EJB)再次上市的书籍完成。
运行客户端访问EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: Learn EJB
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 2
1\. learn java
1\. learn EJB
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 15 seconds)
- 输出上面显示说我们的消息驱动bean接收消息和持久性存储和书籍从数据库中检索存储本书。
- 我们的消息驱动bean被使用LibraryPersistentBean使用@ EJB注释注入的情况下例外MessageDrivenContext对象用于回滚事务。
EJB拦截 - EJB
EJB3.0提供了拦截业务方法的规范使用@ AroundInvoke注释注释的方法调用。一个拦截器方法被称为包含EJBContainer的业务方法调用前拦截。下面的例子是一个拦截器方法签名
@AroundInvoke
public Object methodInterceptor(InvocationContext ctx) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("*** Intercepting call to LibraryBean method: "
+ ctx.getMethod().getName());
return ctx.proceed();
}
拦截器方法可以应用在三个层面上的约束
- Default - 默认的拦截器被调用内deployment.Default拦截每个bean只能应用于通过XML(ejb-jar.xml)。
- Class - 类级别拦截所有的bean的方法被调用。类级别拦截器可以应用通过XML注释(ejb-jar.xml)。
- Method - 方法级别的拦截器是一个特定的bean的方法调用。方法级的拦截器可以应用通过XML注释(ejb-jar.xml)。
我们在这里讨论类级别拦截。
Interceptor class
package com.tutorialspoint.interceptor;
import javax.interceptor.AroundInvoke;
import javax.interceptor.InvocationContext;
public class BusinessInterceptor {
@AroundInvoke
public Object methodInterceptor(InvocationContext ctx) throws Exception
{
System.out.println("*** Intercepting call to LibraryBean method: "
+ ctx.getMethod().getName());
return ctx.proceed();
}
}
Remote Interface
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryBeanRemote {
//add business method declarations
}
Intercepted Stateless EJB
@Interceptors ({BusinessInterceptor.class})
@Stateless
public class LibraryBean implements LibraryBeanRemote {
//implement business method
}
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试测试截获的无状态EJB的EJB应用程序。
Step | 描述 |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.interceptor_as explained in the _EJB - Create Application chapter. You can also use the project created inEJB - Create Application chapter as such for this chapter to understand intercepted ejb concepts. |
2 | Create LibraryBean.java and LibraryBeanRemote under packagecom.tutorialspoint.interceptor as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
3 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
4 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
5 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. |
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
LibraryBeanRemote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.interceptor;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryBeanRemote {
void addBook(String bookName);
List getBooks();
}
LibraryBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.interceptor;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.interceptor.Interceptors;
@Interceptors ({BusinessInterceptor.class})
@Stateless
public class LibraryBean implements LibraryBeanRemote {
List<String> bookShelf;
public LibraryBean(){
bookShelf = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public void addBook(String bookName) {
bookShelf.add(bookName);
}
public List<String> getBooks() {
return bookShelf;
}
}
- 只要你部署在JBoss EjbComponent项目,会注意到jboss的日志。
- JBoss已经自动为我们的会话bean创建一个JNDI条目 - LibraryBean/remote.
- 我们将使用这个查询字符串来获得远程类型的业务对象 -com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryBeanRemote
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
...
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibraryBean,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryBeanRemote ejbName: LibraryBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
...
EJBTester (EJB Client)
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
- 这些属性是用来初始化InitialContext对象的Java命名服务
- InitialContext的对象将被用于查找无状态会话bean
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateful.LibraryBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testInterceptedEjb();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testInterceptedEjb(){
try {
int choice = 1;
LibraryBeanRemote libraryBean =
LibraryBeanRemote)ctx.lookup("LibraryBean/remote");
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester做以下任务。
- jndi.properties中加载和初始化的InitialContext对象。
- JNDI查找testInterceptedEjb()方法,完成了名称 - “LibraryBean/remote”获得远程业务对象(无状态EJB)。
- 如果用户输入1,系统要求输入书籍名称和节约使用无状态的会话bean addBook()方法的书。会话Bean存储在它的实例变量的书。
- 如果用户输入2,系统检索书使用状态会话Bean getBooks()方法和退出。
Run Client to access EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: Learn Java
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. Learn Java
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 13 seconds)
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
验证下面的输出在JBoss应用服务器的日志输出。
....
09:55:40,741 INFO [STDOUT] *** Intercepting call to LibraryBean method: addBook
09:55:43,661 INFO [STDOUT] *** Intercepting call to LibraryBean method: getBooks
EJB嵌入对象 - EJB
EJB 3.0中提供了选项嵌入到实体bean的Java POJO(普通Java对象)和嵌入式POJO类的方法允许列名映射。嵌入一个java的POJO必须定义了@ Embeddable注解。
@Embeddable
public class Publisher implements Serializable{
private String name;
private String address;
...
}
上面的类可以使用@ Embedded批注嵌入
@Entity
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
private Publisher publisher;
...
@Embedded
@AttributeOverrides({
@AttributeOverride(name = "name",
column = @Column(name = "PUBLISHER")),
@AttributeOverride(name = "address",
column = @Column(name = "PUBLISHER_ADDRESS"))
})
public Publisher getPublisher() {
return publisher;
}
...
}
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试EJB应用程序来测试EJB 3.0中的嵌入对象。
Step | 描述 |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.entity as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. Please use the project created in EJB - Persistence chapter as such for this chapter to understand embedded objects in ejb concepts. |
2 | Create Publisher.java under package com.tutorialspoint.entity as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
3 | Create Book.java under package com.tutorialspoint.entity. Use EJB - Persistence chapter as reference. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
4 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
5 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
6 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. |
Create/Alter book table
CREATE TABLE book (
id integer PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar(50)
);
Alter table book add publisher varchar(100);
Alter table book add publisher_address varchar(200);
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
Publisher.java
package com.tutorialspoint.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Embeddable;
@Embeddable
public class Publisher implements Serializable{
private String name;
private String address;
public Publisher(){}
public Publisher(String name, String address){
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String toString(){
return name + "," + address;
}
}
Book.java
package com.tutorialspoint.entity;
import com.tutorialspoint.callback.BookCallbackListener;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.AttributeOverride;
import javax.persistence.AttributeOverrides;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Embedded;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.EntityListeners;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="book")
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
private Publisher publisher;
public Book(){
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="id")
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Embedded
@AttributeOverrides({
@AttributeOverride(name = "name",
column = @Column(name = "PUBLISHER")),
@AttributeOverride(name = "address",
column = @Column(name = "PUBLISHER_ADDRESS"))
})
public Publisher getPublisher() {
return publisher;
}
public void setPublisher(Publisher publisher) {
this.publisher = publisher;
}
}
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
void addBook(Book bookName);
List<Book> getBooks();
}
LibraryPersistentBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
@Stateless
public class LibraryPersistentBean implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
public LibraryPersistentBean(){
}
@PersistenceContext(unitName="EjbComponentPU")
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void addBook(Book book) {
entityManager.persist(book);
}
public List<Book> getBooks() {
return entityManager.createQuery("From Book").getResultList();
}
}
- 一旦你部署EjbComponent项目在Jboss应用服务器 ,发现jboss的日志。
- JBoss已经自动为我们的会话bean创建一个JNDI入口 - LibraryPersistentBean/remote.
- 我们将使用这个查询字符串来获得远程类型的业务对象 -com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
...
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibraryPersistentBean,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote ejbName: LibraryPersistentBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
...
EJBTester (EJB Client)
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
- 这些属性是用来初始化InitialContext对象的Java命名服务
- InitialContext的对象将被用于查找无状态会话bean
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateful.LibraryBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testEmbeddedObjects();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testEmbeddedObjects(){
try {
int choice = 1;
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean =
(LibraryPersistentBeanRemote)
ctx.lookup("LibraryPersistentBean/remote");
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
String publisherName;
String publisherAddress;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
System.out.print("Enter publisher name: ");
publisherName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
System.out.print("Enter publisher address: ");
publisherAddress = brConsoleReader.readLine();
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
book.setPublisher
(new Publisher(publisherName,publisherAddress));
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
System.out.println("Publication: "+book.getPublisher());
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester做以下任务。
- jndi.properties中加载和初始化的InitialContext对象。
- In testInterceptedEjb() method, jndi lookup is done with name - "LibraryPersistenceBean/remote" to obtain the remote business object (stateless ejb).
- Then user is shown a library store User Interface and he/she is asked to enter choice.
- If user enters 1, system asks for book name and saves the book using stateless session bean addBook() method. Session Bean is storing the book in database.
- If user enters 2, system retrives books using stateless session bean getBooks() method and exits.
运行客户端访问EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择 run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: learn html5
Enter publisher name: SAMS
Enter publisher address: DELHI
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. learn html5
Publication: SAMS,DELHI
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 21 seconds)
EJB - Blobs/Clobs - EJB
EJB3.0提供支持BLOB和CLOB类型,使用@Lob注解。下面的Java类型可以映射使用@Lob注解。
- java.sql.Blob
- java.sql.Clob
- byte[]
- String
- Serializable Object
@Entity
@Table(name="books")
@EntityListeners(BookCallbackListener.class)
public class Book implements Serializable{
...
private byte[] image;
@Lob @Basic(fetch= FetchType.EAGER)
public byte[] getImage() {
return image;
}
...
}
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试EJB在EJB3.0应用程序来测试BLOB / CLOB支持。
Step | 描述 |
1 | 创建一个项目与一个名字EjbComponent包com.youcompany.entity下EJB中的解释 - 创建应用程序的章节。请作为的项目中创建EJB -阅读 持久性本章可了解CLOB/ BLOB对象EJB概念。 |
2 | 创建Book.java包com.youcompany.entity下。使用EJB - 持久性章作为参考。其余文件保持不变。 |
3 | 清理并生成应用程序以确保业务逻辑是按要求工作。 |
4 | 最后,将应用程序部署在JBoss应用服务器上的jar文件的形式。 JBoss应用服务器将自动开始浏览网页,如果它尚未启动。 |
5 | 现在创建EJB客户端,基于控制台的应用程序以同样的方式在EJB解释 - 下创建应用程序本章主题 Create Client to access EJB. |
Create/Alter book table
CREATE TABLE book (
id integer PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar(50)
);
Alter table book add image bytea;
Alter table book add xml text;
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
Book.java
package com.tutorialspoint.entity;
import com.tutorialspoint.callback.BookCallbackListener;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Basic;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.EntityListeners;
import javax.persistence.FetchType;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Lob;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="book")
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
private byte[] image;
private String xml;
public Book(){
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="id")
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Lob @Basic(fetch= FetchType.EAGER)
public byte[] getImage() {
return image;
}
public void setImage(byte[] image) {
this.image = image;
}
@Lob @Basic(fetch= FetchType.EAGER)
public String getXml() {
return xml;
}
public void setXml(String xml) {
this.xml = xml;
}
}
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
void addBook(Book bookName);
List<Book> getBooks();
}
LibraryPersistentBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
@Stateless
public class LibraryPersistentBean implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
public LibraryPersistentBean(){
}
@PersistenceContext(unitName="EjbComponentPU")
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void addBook(Book book) {
entityManager.persist(book);
}
public List<Book> getBooks() {
return entityManager.createQuery("From Book").getResultList();
}
}
- As soon as you deploy the EjbComponent project on JBOSS, notice the jboss log.
- JBoss has automatically created a JNDI entry for our session bean -LibraryPersistentBean/remote.
- We'll using this lookup string to get remote business object of type -com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote
JBoss Application server log output
...
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibraryPersistentBean,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote ejbName: LibraryPersistentBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
...
EJBTester (EJB Client)
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
- These properties are used to initialize the InitialContext object of java naming service
- InitialContext object will be used to lookup stateless session bean
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateful.LibraryBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testBlobClob();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testBlobClob(){
try {
int choice = 1;
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean =
(LibraryPersistentBeanRemote)
ctx.lookup("LibraryPersistentBean/remote");
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
String publisherName;
String publisherAddress;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
String xml = "<book><name>"+bookName+"</name></book>";
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
byte[] imageBytes = {0x32, 0x32,0x32, 0x32,0x32,
0x32,0x32, 0x32,
0x32, 0x32,0x32, 0x32,0x32, 0x32,0x32, 0x32,
0x32, 0x32,0x32, 0x32,0x32, 0x32,0x32, 0x32
};
book.setImage(imageBytes);
book.setXml(xml);
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
byte[] imageByts = book.getImage();
if(imageByts != null){
System.out.print("image bytes: [");
for(int j = 0; j < imageByts.length ; j++){
System.out.print("0x"
+ String.format("%x", imageByts[j]) +" ");
}
System.out.println("]");
}
System.out.println(book.getXml());
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester is doing the following tasks.
- Load properties from jndi.properties and initialize the InitialContext object.
- In testInterceptedEjb() method, jndi lookup is done with name - "LibraryPersistenceBean/remote" to obtain the remote business object (stateless ejb).
- Then user is shown a library store User Interface and he/she is asked to enter choice.
- If user enters 1, system asks for book name and saves the book using stateless session bean addBook() method. Session Bean is storing the book in database.
- If user enters 2, system retrieves books using stateless session bean getBooks() method and exits.
Run Client to access EJB
Locate EJBTester.java in project explorer. Right click on EJBTester class and select run file.
Verify the following output in Netbeans console.
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: learn testing
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. learn testing
image bytes: [
0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 0x32 ]
<book><name>learn testing</name></book>
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 20 seconds)
EJB事务 - EJB
事务是一个单元的工作项目遵循ACID特性。ACID代表原子性,一致性,独立性和持久性。
- 原子 -如果有任何的工作项失败,完整的单元被认为是失败。成功意味着所有项目的成功执行。
- 一致性- 事务必须保持系统处于一致状态。
- 独立性- 每个事务执行独立的任何其他的事务。
- 持久性 - 事务应该生存系统故障,如果已经执行或提交。
EJB容器/服务器,的事务服务器和处理事务上下文的传递和分布式事务。事务可以由容器管理或bean的代码自定义代码处理。
- Container Managed Transactions - 在这种类型中,容器管理的事务状态。
- Bean Managed Transactions - 在这种类型中,开发者管理事务状态的生命周期。
容器管理的事务
指定EJB3.0,EJB容器实现的事务特性。
- REQUIRED - 表示业务方法已被执行的范围内的事务,否则将开始一个新的事务方法。
- REQUIRES_NEW - 表示要开始一个新的事务,业务方法。
- SUPPORTS - 表示业务方法将执行作为的事务的一部分。
- NOT_SUPPORTED - 表示业务方法不应该被执行作为的事务的一部分。
- MANDATORY - 表示业务方法将执行作为的事务的一部分,否则将引发异常。
- NEVER - 表示如果业务方法执行作为的事务的一部分,那么会抛出一个异常。
例子
package com.tutorialspoint.txn.required;
import javax.ejb.*
@Stateless
@TransactionManagement(TransactionManagementType.CONTAINER)
public class UserDetailBean implements UserDetailRemote {
private UserDetail;
@TransactionAttribute(TransactionAttributeType.REQUIRED)
public void createUserDetail() {
//create user details object
}
}
createUserDetail()业务方法时,需要使用Required注解。
package com.tutorialspoint.txn.required;
import javax.ejb.*
@Stateless
public class UserSessionBean implements UserRemote {
private User;
@EJB
private UserDetailRemote userDetail;
public void createUser() {
//create user
//...
//create user details
userDetail.createUserDetail();
}
}
为createUser()业务方法的使用createUserDetail()。如果为createUser(期间发生的异常)调用和用户对象不会创建那么UserDetail对象也不会被创建。
Bean管理的事务
Bean管理的事务,事务处理应用水平的异常,可以管理。以下是要考虑的关键点
- Start - 当启动一个事务中的业务方法。
- Sucess - 确定成功的情况下,当一个事务被提交。
- Failed - 确定失败的情况下,事务回滚。
实例
package com.tutorialspoint.txn.bmt;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.ejb.TransactionManagement;
import javax.ejb.TransactionManagementType;
import javax.transaction.UserTransaction;
@Stateless
@TransactionManagement(value=TransactionManagementType.BEAN)
public class AccountBean implements AccountBeanLocal {
@Resource
private UserTransaction userTransaction;
public void transferFund(Account fromAccount, double fund ,
Account toAccount) throws Exception{
try{
userTransaction.begin();
confirmAccountDetail(fromAccount);
withdrawAmount(fromAccount,fund);
confirmAccountDetail(toAccount);
depositAmount(toAccount,fund);
userTransaction.commit();
}catch (InvalidAccountException exception){
userTransaction.rollback();
}catch (InsufficientFundException exception){
userTransaction.rollback();
}catch (PaymentException exception){
userTransaction.rollback();
}
}
private void confirmAccountDetail(Account account)
throws InvalidAccountException {
}
private void withdrawAmount() throws InsufficientFundException {
}
private void depositAmount() throws PaymentException{
}
}
在这个例子中,我们使用UserTransaction接口标记开始使用userTransaction.begin()方法调用事务处理。我们标记事务完成使用userTransaction.commit()方法,如果期间发生任何异常,那么我们完整的事务回滚使用userTransaction.rollback()方法调用。
EJB安全 - EJB
安全性是任何企业级应用关注的重大问题。它包括用户身份识别(S)或系统访问的应用程序,并允许或拒绝的访问应用程序内的资源。在EJB中,安全性可以声明的方式称为声明性安全EJB容器管理的安全问题,或者自定义代码可以在EJB处理安全问题的关注,通过自已声明。
安全的重要术语
- 认证 - 这是确保用户访问系统或应用程序被验证为是正品的方法。
- 授权 - 这是过程,确保用户有权访问系统资源的权限级别。
- 用户 - 用户表示访问该应用程序的客户端或系统。
- 用户组 - 用户可能具有一定部门例如管理员组的一部分。
- 用户角色 - 角色定义授权用户有权限访问系统资源的水平。
容器管理安全
EJB3.0指定下列属性/安全EJB容器实现的注解。
- DeclareRoles - 指示类将接受这些声明的的角色。注释在类级别应用。
- RolesAllowed -指示指定的角色的用户可以访问的方法。可以应用在一流水平,导致指定角色的用户可以访问的所有类方法。
- PermitAll - 表示该业务的方法是访问。可以应用在类以及方法级别。
- DenyAll - 表明业务方法不能访问任何用户指定的类或方法级别。
实例
package com.tutorialspoint.security.required;
import javax.ejb.*
@Stateless
@DeclareRoles({"student" "librarian"})
public class LibraryBean implements LibraryRemote {
@RolesAllowed({"librarian"})
public void delete(Book book){
//delete book
}
@PermitAll
public void viewBook(Book book){
//view book
}
@DenyAll
public void deleteAll(){
//delete all books
}
}
安全配置
在配置文件中的的映射角色和用户组。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE sun-ejb-jar PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Application Server 9.0 EJB 3.0//EN" "http://www.sun.com/software/appserver/dtds/sun-ejb-jar_3_0-0.dtd">
<ejb-jar>
<security-role-mapping>
<role-name>student</role-name>
<group-name>student-group</group-name>
</security-role-mapping>
<security-role-mapping>
<role-name>librarian</role-name>
<group-name>librarian-group</group-name>
</security-role-mapping>
<enterprise-beans/>
</ejb-jar>
EJBJNDI绑定 - EJB
JNDI代表Java命名和目录接口。它是一组API和服务接口。基于Java的应用程序使用JNDI命名和目录服务。在EJB的背景下,有两个方面。
- Binding - 这指的是以后可以使用一个EJB对象分配一个名称。
- Lookup - 这指的是寻找并获得EJB对象。
在JBoss中,会话bean绑定到JNDI,默认情况下有以下格式。
- local - ejb-name/local
- remote - ejb-name/remote
情况下,EJB捆绑在一起<application-name> ear文件默认格式如下。
- local - application-name/ejb-name/local
- remote - application-name/ejb-name/remote
默认绑定的例子
请参阅EJB - 创建应用本章的JBoss的控制台输出。
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
...
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibrarySessionBean,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBean ejbName: LibrarySessionBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibrarySessionBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibrarySessionBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
...
定制绑定
以下注释可以用来定制默认JNDI绑定。
- local - org.jboss.ejb3.LocalBinding
- remote - org.jboss.ejb3.RemoteBindings
更新LibrarySessionBean.java。请参阅EJB - 创建应用程序一章
LibrarySessionBean
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
@Stateless
@LocalBinding(jndiBinding="tutorialsPoint/librarySession")
public class LibrarySessionBean implements LibrarySessionBeanLocal {
List<String> bookShelf;
public LibrarySessionBean(){
bookShelf = new ArrayList<String>();
}
public void addBook(String bookName) {
bookShelf.add(bookName);
}
public List<String> getBooks() {
return bookShelf;
}
}
LibrarySessionBeanLocal
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Local;
@Local
public interface LibrarySessionBeanLocal {
void addBook(String bookName);
List getBooks();
}
构建项目。将应用程序部署在JBoss在JBoss控制台验证下面的输出。
...
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibrarySessionBean,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBean ejbName: LibrarySessionBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
tutorialsPoint/librarySession - EJB3.x Default Local Business Interface
tutorialsPoint/librarySession-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibrarySessionBeanLocal - EJB3.x Local Business Interface
...
重复上述步骤,为远程和检查结果。
EJB实体关系 - EJB
EJB 3.0中提供的选项来定义像一对一的数据库实体关系/映射,一对多,多对一和多对多关系。以下是相关的注释。
- OneToOne - 对象都具有一对一的关系。例如,乘客可以在时间旅行使用一张票。
- OneToMany - 对象是具有一对多的关系。例如,一个父亲可以有多个孩子。
- ManyToOne - 对象有多对一的关系。举例来说,多个孩子对一个母亲。
- ManyToMany - 对象是多对多的关系。举例来说,一本书可以多发作者,一个作者可以写多本书。
在这里,我们将演示如何使用多对多的映射。要代表多对多的关系,三表是必需的。
- Book - 书籍记录表
- Author - 作者Author表记录
- Book_Author - BOOK_AUTHOR上述Book和Author表的表具有关联。
创建表
创建表book author, book_author 在默认数据库 postgres.
CREATE TABLE book (
book_id integer,
name varchar(50)
);
CREATE TABLE author (
author_id integer,
name varchar(50)
);
CREATE TABLE book_author (
book_id integer,
author_id integer
);
创建实体类
@Entity
@Table(name="author")
public class Author implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
...
}
@Entity
@Table(name="book")
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String title;
private Set<Author> authors;
...
}
Use ManyToMany annotation in Book Entity
@Entity
public class Book implements Serializable{
...
@ManyToMany(cascade = {CascadeType.PERSIST, CascadeType.MERGE}
, fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinTable(table = @Table(name = "book_author"),
joinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "book_id")},
inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "author_id")})
public Set<Author> getAuthors()
{
return authors;
}
...
}
实例应用
让我们创建一个测试EJB应用程序来测试EJB3.0实体关系对象。
Step | 描述 |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.entity as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. Please use the project created in EJB - Persistence chapter as such for this chapter to understand embedded objects in ejb concepts. |
2 | Create Author.java under package com.tutorialspoint.entity as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
3 | Create Book.java under package com.tutorialspoint.entity. Use EJB - Persistence chapter as reference. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
4 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
5 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
6 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. |
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
Author.java
package com.tutorialspoint.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
@Entity
@Table(name="author")
public class Author implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
public Author(){}
public Author(int id, String name){
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="author_id")
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String toString(){
return id + "," + name;
}
}
Book.java
package com.tutorialspoint.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
@Entity
@Table(name="book")
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
private Set<Author> authors;
public Book(){
}
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy= GenerationType.IDENTITY)
@Column(name="book_id")
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAuthors(Set<Author> authors) {
this.authors = authors;
}
@ManyToMany(cascade = {CascadeType.PERSIST, CascadeType.MERGE}
, fetch = FetchType.EAGER)
@JoinTable(table = @Table(name = "book_author"),
joinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "book_id")},
inverseJoinColumns = {@JoinColumn(name = "author_id")})
public Set<Author> getAuthors()
{
return authors;
}
}
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
void addBook(Book bookName);
List<Book> getBooks();
}
LibraryPersistentBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
@Stateless
public class LibraryPersistentBean implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
public LibraryPersistentBean(){
}
@PersistenceContext(unitName="EjbComponentPU")
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void addBook(Book book) {
entityManager.persist(book);
}
public List<Book> getBooks() {
return entityManager.createQuery("From Book").getResultList();
}
}
- 只要你在JBoss部署 EjbComponent项目,会注意到jboss的日志。
- JBoss已经自动为我们的会话bean创建一个JNDI条目 -LibraryPersistentBean/remote.
- 我们将使用这个查询字符串来获得远程类型的业务对象 -com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
...
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibraryPersistentBean,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote ejbName: LibraryPersistentBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.interceptor.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
...
EJBTester (EJB Client)
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
- These properties are used to initialize the InitialContext object of java naming service
- InitialContext object will be used to lookup stateless session bean
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateful.LibraryBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testEmbeddedObjects();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testEmbeddedObjects(){
try {
int choice = 1;
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean =
(LibraryPersistentBeanRemote)
ctx.lookup("LibraryPersistentBean/remote");
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
String authorName;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
System.out.print("Enter author name: ");
authorName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
Author author = new Author();
author.setName(authorName);
Set<Author> authors = new HashSet<Author>();
authors.add(author);
book.setAuthors(authors);
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
System.out.print("Author: ");
Author[] authors = (Author[])books.getAuthors().toArray();
for(int j=0;j<authors.length;j++){
System.out.println(authors[j]);
}
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester做以下任务。
- jndi.properties中加载和初始化的InitialContext对象。
- 在testInterceptedEjb()方法,JNDI查找名称 - 的“LibraryPersistenceBean/远程”获得远程业务对象(无状态的EJB)。
- 然后用户显示一个库存储的用户界面和他/她被要求输入选择。
- 如果用户输入1,系统要求输入书籍名称和节约使用无状态的会话bean addBook()方法的书。会话Bean在数据库中存储的书。
- 如果用户输入2,系统检索书使用状态会话Bean getBooks()方法和退出。
运行客户端访问EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: learn html5
Enter Author name: Robert
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. learn html5
Author: Robert
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 21 seconds)
EJB访问数据库 - EJB
EJB 3.0持久性机制来访问容器管理的数据库中的数据库相关的操作。开发人员访问数据库可以直接使用JDBC API调用EJB的业务方法。
为了证明在ejb的数据库访问,我们要做好以下几项工作。
- 步骤 1. 在数据库中创建表.
- 步骤 2. 创建一个无状态EJB.
- 步骤 3. 更新无状态的EJB。添加添加记录并获得通过实体管理器从数据库中记录的方法。
- 步骤 4. 一个基于控制台应用程序客户端将访问无状态EJB的持久化数据库中的数据。
创建表
创建一张表 books 在默认的数据库 postgres.
CREATE TABLE books (
id integer PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar(50)
);
创建模型类
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
public Book(){
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
...
}
创建无状态EJB
@Stateless
public class LibraryPersistentBean implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
public void addBook(Book book) {
//persist book using jdbc calls - by yiibai.com
}
public List<Book> getBooks() {
//get books using jdbc calls
}
...
}
构建EJB模块后,我们需要一个无状态的bean,我们将在下一节要创建客户端来访问。
实例应用
让我们创建一个测试EJB应用程序来测试EJB的数据库访问机制。
Step | 描述 |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.entity as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. You can also use the project created in EJB - Create Application chapter as such for this chapter to understand ejb data access concepts. |
2 | Create Book.java under package com.tutorialspoint.entity and modify it as shown below. |
3 | Create LibraryPersistentBean.java and LibraryPersistentBeanRemote as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter and modify them as shown below. |
4 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
5 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
6 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. Modify it as shown below. |
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
Book.java
package com.tutorialspoint.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
public Book(){
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
void addBook(Book bookName);
List<Book> getBooks();
}
LibraryPersistentBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
@Stateless
public class LibraryPersistentBean implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
public LibraryPersistentBean(){
}
public void addBook(Book book) {
Connection con = null;
String url = "jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/postgres";
String driver = "org.postgresql.driver";
String userName = "sa";
String password = "sa";
List<Book> books = new ArrayList<Book>();
try {
Class.forName(driver).newInstance();
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url , userName, password);
PreparedStatement st =
con.prepareStatement("insert into book(name) values(?)");
st.setString(1,book.getName());
int result = st.executeUpdate();
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
public List<Book> getBooks() {
Connection con = null;
String url = "jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/postgres";
String driver = "org.postgresql.driver";
String userName = "sa";
String password = "sa";
List<Book> books = new ArrayList<Book>();
try {
Class.forName(driver).newInstance();
con = DriverManager.getConnection(url , userName, password);
Statement st = con.createStatement();
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery("select * from book");
Book book;
while (rs.next()) {
book = new Book();
book.setId(rs.getInt(1));
book.setName(rs.getString(2));
books.add(book);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
return books;
}
}
- 只要你在JBoss部署 EjbComponent项目,注意到jboss的日志。
- JBoss已经自动为我们的会话bean创建一个JNDI条目 -LibraryPersistentBean/remote.
- 我们将使用这个查询字符串来获得远程类型的业务对象 -com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
...
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibraryPersistentBeanRemote,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote ejbName: LibraryPersistentBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
...
EJBTester (EJB Client)
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
- 这些属性是用来初始化InitialContext对象的Java命名服务
- InitialContext的对象将被用于查找无状态会话bean
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testEntityEjb();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testEntityEjb(){
try {
int choice = 1;
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean =
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote)
ctx.lookup("LibraryPersistentBean/remote");
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester做以下任务。
- jndi.properties中加载和初始化的InitialContext对象。
- 在testStatefulEjb()方法,JNDI名称进行查找 - "LibraryStatelessSessionBean/remote"以获得远程业务对象(状态EJB)。
- 然后用户显示一个库存储的用户界面和他/她被要求输入选择。
- 如果用户输入1,系统要求输入书籍名称和可以节省使用无状态的会话bean addBook()方法。会话Bean坚持这本书中通过EntityManager的调用数据库。
- 如果用户输入2,系统检索书使用状态会话Bean getBooks()方法和退出。
- 然后另一个JNDI名称进行查找 - "LibraryStatelessSessionBean/remote" 获得远程业务对象(状态EJB)再次列出书籍。
运行客户端访问EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: Learn Java
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. learn java
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 15 seconds)
EJB查询语言 - EJB
EJB3.0,EJB查询语言编写自定义的查询非常方便,不用担心底层数据库的详细信息。这是很相似的HQL(Hibernate查询语言),通常被称为按名称EJBQL。
要理解熟悉ejb的EJBQL,要做好以下几项工作。
- 步骤 1. 在数据库中创建表.
- 步骤 2. 创建一个无状态EJB.
- 步骤 3. 更新无状态的EJB。添加添加记录并获得通过实体管理器从数据库中记录的方法。
- 步骤 4. 一个基于控制台应用程序客户端将访问无状态EJB的持久化数据库中的数据。
创建数据库表
创建表 books 在默认数据库 postgres.
CREATE TABLE books (
id integer PRIMARY KEY,
name varchar(50)
);
创建模型类
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
public Book(){
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
...
}
创建无状态EJB
@Stateless
public class LibraryPersistentBean implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
public void addBook(Book book) {
//persist book using entity manager
}
public List<Book> getBooks() {
//get books using entity manager
}
...
}
构建EJB模块后,我们需要一个无状态的bean,我们将在下一节要创建客户端来访问。
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试EJB应用程序来测试EJB的数据库访问机制。
Step | Description |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.entity as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. You can also use the project created in EJB - Create Application chapter as such for this chapter to understand ejb data access concepts. |
2 | Create Book.java under package com.tutorialspoint.entity and modify it as shown below. |
3 | Create LibraryPersistentBean.java and LibraryPersistentBeanRemote as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter and modify them as shown below. |
4 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
5 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
6 | Now create the ejb client, a console based application in the same way as explained in theEJB - Create Application chapter under topic Create Client to access EJB. Modify it as shown below. |
EJBComponent (EJB Module)
Book.java
package com.tutorialspoint.entity;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Book implements Serializable{
private int id;
private String name;
public Book(){
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
@Remote
public interface LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
void addBook(Book bookName);
List<Book> getBooks();
}
LibraryPersistentBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
import javax.persistence.Query;
@Stateless
public class LibraryPersistentBean implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
public LibraryPersistentBean(){
}
@PersistenceContext(unitName="EntityEjbPU")
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void addBook(Book book) {
entityManager.persist(book);
}
public List<Book> getBooks() {
//create an ejbql expression
String ejbQL = "From Book b where b.name like ?1";
//create query
Query query = entityManager.createQuery(ejbQL);
//substitute parameter.
query.setParameter(1, "%test%");
//execute the query
return query.getResultList();
}
}
- 只要在JBoss部署 EjbComponent项目,会注意到jboss的日志。
- JBoss已经自动为我们的会话bean创建一个JNDI条目 -LibraryPersistentBean/remote.
- 我们将使用这个查询字符串来获得远程类型的业务对象 -com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
...
16:30:01,401 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
16:30:02,723 INFO [SessionSpecContainer] Starting jboss.j2ee:jar=EjbComponent.jar,name=LibraryPersistentBeanRemote,service=EJB3
16:30:02,723 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote ejbName: LibraryPersistentBean
16:30:02,731 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
...
EJBTester (EJB Client)
jndi.properties
java.naming.factory.initial=org.jnp.interfaces.NamingContextFactory
java.naming.factory.url.pkgs=org.jboss.naming:org.jnp.interfaces
java.naming.provider.url=localhost
- 这些属性是用来初始化InitialContext对象的Java命名服务
- InitialContext的对象将被用于查找无状态会话bean
EJBTester.java
package com.tutorialspoint.test;
import com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class EJBTester {
BufferedReader brConsoleReader = null;
Properties props;
InitialContext ctx;
{
props = new Properties();
try {
props.load(new FileInputStream("jndi.properties"));
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
try {
ctx = new InitialContext(props);
} catch (NamingException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
brConsoleReader =
new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EJBTester ejbTester = new EJBTester();
ejbTester.testEntityEjb();
}
private void showGUI(){
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.println("Welcome to Book Store");
System.out.println("**********************");
System.out.print("Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: ");
}
private void testEntityEjb(){
try {
int choice = 1;
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote libraryBean =
LibraryPersistentBeanRemote)
ctx.lookup("LibraryPersistentBean/remote");
while (choice != 2) {
String bookName;
showGUI();
String strChoice = brConsoleReader.readLine();
choice = Integer.parseInt(strChoice);
if (choice == 1) {
System.out.print("Enter book name: ");
bookName = brConsoleReader.readLine();
Book book = new Book();
book.setName(bookName);
libraryBean.addBook(book);
} else if (choice == 2) {
break;
}
}
List<Book> booksList = libraryBean.getBooks();
System.out.println("Book(s) entered so far: " + booksList.size());
int i = 0;
for (Book book:booksList) {
System.out.println((i+1)+". " + book.getName());
i++;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(brConsoleReader !=null){
brConsoleReader.close();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
}
}
}
EJBTester做以下任务。
- jndi.properties中加载和初始化的InitialContext对象。
- 在testStatefulEjb()方法,JNDI名称进行查找 - "LibraryStatelessSessionBean/remote" 以获得远程业务对象(状态EJB)。
- 然后用户显示一个库存储的用户界面和他/她被要求输入选择。
- 如果用户输入1,系统要求输入书籍名称和节省了使用无状态的会话bean addBook()方法。会话Bean坚持这本书中通过EntityManager的调用数据库。
- 如果用户输入2,系统检索书使用状态会话Bean getBooks()方法和退出。
- 然后另一个JNDI名称进行查找 - "LibraryStatelessSessionBean/remote"获得远程业务对象(状态EJB)再次列出书籍。
运行客户端访问EJB
在项目资源管理器中找到EJBTester.java。右键点击上EJBTester类,并选择run file.
在Netbeans控制台验证以下输出。
run:
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 1
Enter book name: Learn Testing
**********************
Welcome to Book Store
**********************
Options
1\. Add Book
2\. Exit
Enter Choice: 2
Book(s) entered so far: 1
1\. learn Testing
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 15 seconds)
EJB Web Services - EJB
EJB3.0暴露会话EJB作为Web服务提供选项。@WebService注释是用来标记一类作为一个Web服务端点,并使用@WebMethod是用来作为客户端的Web方法的公开方法。
@Stateless
@WebService(serviceName="LibraryService")
public class LibraryPersistentBean implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
...
@WebMethod(operationName="getBooks")
public List<Book> getBooks() {
return entityManager.createQuery("From Books").getResultList();
}
...
}
示例应用程序
让我们创建一个测试EJB在EJB3.0应用程序来测试BLOB/CLOB支持。
Step | Description |
1 | Create a project with a name EjbComponent under a package com.tutorialspoint.entity as explained in the EJB - Create Application chapter. Please use the project created in EJB - Persistence chapter as such for this chapter to understand clob/blob objects in ejb concepts. |
2 | Create LibraryPersistentBean.java under package com.tutorialspoint.stateless. Use EJB - Persistence chapter as reference. Keep rest of the files unchanged. |
3 | Clean and Build the application to make sure business logic is working as per the requirements. |
4 | Finally, deploy the application in the form of jar file on JBoss Application Server. JBoss Application server will get started automatically if it is not started yet. |
LibraryPersistentBean.java
package com.tutorialspoint.stateless;
import com.tutorialspoint.entity.Book;
import java.util.List;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
import javax.jws.WebMethod;
import javax.jws.WebService;
import javax.persistence.EntityManager;
import javax.persistence.PersistenceContext;
@Stateless
@WebService(serviceName="LibraryService")
public class LibraryPersistentBean implements LibraryPersistentBeanRemote {
public LibraryPersistentBean(){
}
@PersistenceContext(unitName="EjbComponentPU")
private EntityManager entityManager;
public void addBook(Book book) {
entityManager.persist(book);
}
@WebMethod(operationName="getBooks")
public List<Book> getBooks() {
return entityManager.createQuery("From Book").getResultList();
}
}
JBoss应用服务器的日志输出
10:51:37,271 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBean ejbName: LibraryPersistentBean
10:51:37,287 INFO [JndiSessionRegistrarBase] Binding the following Entries in Global JNDI:
LibraryPersistentBean/remote - EJB3.x Default Remote Business Interface
LibraryPersistentBean/remote-com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBeanRemote - EJB3.x Remote Business Interface
10:51:37,349 INFO [EJBContainer] STARTED EJB: com.tuturialspoint.messagebean.LibraryMessageBean ejbName: BookMessageHandler
10:51:37,443 INFO [DefaultEndpointRegistry] register: jboss.ws:context=EjbComponent,endpoint=LibraryPersistentBean
10:51:38,191 INFO [WSDLFilePublisher] WSDL published to: file:/D:/Jboss-5.0.1/server/default/data/wsdl/EjbComponent.jar/
LibraryService3853081455302946642.wsdl
创建客户端访问EJB作为Web服务
在NetBeansIDE中,选择File>NewProject>类别下选择项目类型,Java项目类型为Java应用。点击Next>按钮。输入项目的名称和位置。单击“Next>“按钮。我们选择名为EJBWebServiceClient。
右键点击项目名称在项目exporer窗口中。选择 New > WebService Client .
添加EJB组件项目的LibraryPersistentBean早下创建WSDL和客户端位置使用在"编译"选项卡中添加项目“按钮。
单击“完成”按钮。在项目资源管理器验证以下结构。
Create EJBWebServiceClient.java
package ejbwebserviceclient;
public class EJBWebServiceClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
}
如下图所示,选择Web服务getBooks Web方法,将其拖动到代码窗口EJBWebServiceClient。
会看到类似的输出如下所示。
更新EJBWebServiceClient的代码使用此方法。
package ejbwebserviceclient;
public class EJBWebServiceClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(com.tutorialspoint.stateless.Book book:getBooks()){
System.out.println(book.getName());
}
}
private static java.util.List
<com.tutorialspoint.stateless.Book> getBooks() {
com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryService service =
new com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryService();
com.tutorialspoint.stateless.LibraryPersistentBean port =
service.getLibraryPersistentBeanPort();
return port.getBooks();
}
}
运行客户端
右键点击项目名称,项目资源管理器窗口。选择“Run”。 NetBeans将生成客户端并运行它。验证下面的输出。
ant -f D:\SVN\EJBWebServiceClient run
init:
Deleting: D:SVNEJBWebServiceClientuilduilt-jar.properties
deps-jar:
Updating property file: D:SVNEJBWebServiceClientuilduilt-jar.properties
wsimport-init:
wsimport-client-LibraryPersistentBean:
files are up to date
classLoader = java.net.URLClassLoader@4ce46c
SharedSecrets.getJavaNetAccess()=java.net.URLClassLoader$7@182cdac
wsimport-client-generate:
Compiling 1 source file to D:SVNEJBWebServiceClientuildclasses
compile:
run:
learn java
Learn Spring
learn JSF
Learn HTML
Learn JBoss
Learn EJB
Learn Hibernate
Learn IBatis
Times Now
learn html5
Learn images
Learn Testing
Forbes
test1
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 1 second)
EJB封装应用 - EJB
封装要求应用程序使用EJB 3.0是类似于J2EE平台。 EJB组件打包成jar文件的模块被打包成ear文件的应用企业归档。 主要的企业应用程序有三个组成部分。
- jar - Java应用程序归档,包含EJB模块,EJB客户端模块和实用模块。
- war - Web应用程序归档,包含Web模块。
- ear - 企业应用程序归档包括 jars 和 war 模块.
在NetBeans它是很容易的创建,开发,打包和部署J2EE应用程序。
在NetBeans IDE中,选择File>New Project>选择项目类型为企业应用程序的JavaEE项目类型。 点击Next>按钮。输入项目的名称和位置。单击“Finish >“按钮。我们选择名为EnterpriseApplicaton。
选择服务器和设置。保持创建EJB模块“和”创建Web应用程序模块检查提供的默认名称。单击“完成”按钮。 NetBeans将创建下列结构在项目窗口。
项目企业在项目资源管理器中的应用上点击右键并选择“生成”。
ant -f D:\SVN\EnterpriseApplication dist
pre-init:
init-private:
init-userdir:
init-user:
init-project:
do-init:
post-init:
init-check:
init:
deps-jar:
deps-j2ee-archive:
EnterpriseApplication-ejb.init:
EnterpriseApplication-ejb.deps-jar:
EnterpriseApplication-ejb.compile:
EnterpriseApplication-ejb.library-inclusion-in-manifest:
Building jar: D:SVNEnterpriseApplicationEnterpriseApplication-ejbdistEnterpriseApplication-ejb.jar
EnterpriseApplication-ejb.dist-ear:
EnterpriseApplication-war.init:
EnterpriseApplication-war.deps-module-jar:
EnterpriseApplication-war.deps-ear-jar:
EnterpriseApplication-ejb.init:
EnterpriseApplication-ejb.deps-jar:
EnterpriseApplication-ejb.compile:
EnterpriseApplication-ejb.library-inclusion-in-manifest:
EnterpriseApplication-ejb.dist-ear:
EnterpriseApplication-war.deps-jar:
EnterpriseApplication-war.library-inclusion-in-archive:
EnterpriseApplication-war.library-inclusion-in-manifest:
EnterpriseApplication-war.compile:
EnterpriseApplication-war.compile-jsps:
EnterpriseApplication-war.do-ear-dist:
Building jar: D:SVNEnterpriseApplicationEnterpriseApplication-wardistEnterpriseApplication-war.war
EnterpriseApplication-war.dist-ear:
pre-pre-compile:
pre-compile:
Copying 1 file to D:SVNEnterpriseApplicationuild
Copying 1 file to D:SVNEnterpriseApplicationuild
do-compile:
post-compile:
compile:
pre-dist:
do-dist-without-manifest:
do-dist-with-manifest:
Building jar: D:SVNEnterpriseApplicationdistEnterpriseApplication.ear
post-dist:
dist:
BUILD SUCCESSFUL (total time: 1 second)
在这里,你可以看到每个jar,war和ear文件带有一个META-INF文件夹,按照J2EE规范的元数据。