JavaMail API 教程
JavaMail API提供了一种与平台无关和协议独立的框架来构建邮件和消息应用程序。 JavaMail API提供了一组抽象类定义构成一个邮件系统的对象。它是阅读,撰写和发送电子信息的可选包(标准扩展)。
读者
本教程乃为初学者,帮助他们了解基本的JavaMail的编程。完成本教程后,在一定程度上提高了你自己的 JavaMail 的编程水平。
必备条件
JavaMail 编程是基于Java 编程语言,所以如果你对Java编程有基本的了解,那么在应用程序开发中使用JavaMail 会比较顺手。
JavaMail API 概述 - JavaMail
JavaMail API提供了一种与平台无关和协议独立的框架来构建邮件和消息应用程序。 JavaMail API提供了一组抽象类定义构成一个邮件系统的对象。它是阅读,撰写和发送电子信息的可选包(标准扩展)。
JavaMail 规定,用于构造一个接口,一个消息传送系统中的元素,包括系统的部件和接口。虽然本规范没有定义任何特定的实现,JavaMail是否包括实现RFC822和MIME Internet邮件标准几类。这些类都作为JavaMail的类包的一部分。
以下是一些在 JavaMail API 支持的协议:
- SMTP:缩写为简单邮件传输协议。它提供传送邮件的机制。
- POP: 缩写为邮局协议。 POP是大多数人在互联网上使用,以获得他们的邮件的机制。它定义了一个单个邮箱的支持为每个用户。 RFC 1939定义了该协议。
- IMAP: 缩写为Internet邮件访问协议。它是一种先进的协议,用于接收消息。它提供了多个邮箱的支持为每个用户,除了邮箱可以被多个用户共享。它是在RFC2060中定义。
- MIME: 缩写为多用途Internet邮件扩展。 。这不是一个邮件传输协议。相反,它定义了什么是传输的内容:邮件,附件,等等的格式。有许多不同的文档生效这里:RFC822,RFC2045,RFC2046和RFC2047。作为 JavaMail API 用户,您通常不需要担心这些格式。然而,这些格式确实存在,并且由程序使用。
- NNTP 其它: 有由第三方供应商提供的许多协议。其中有些是网络新闻传输协议(NNTP),安全多用途Internet邮件扩展(S / MIME)等。
这些细节将包括在后续章节。
体系结构
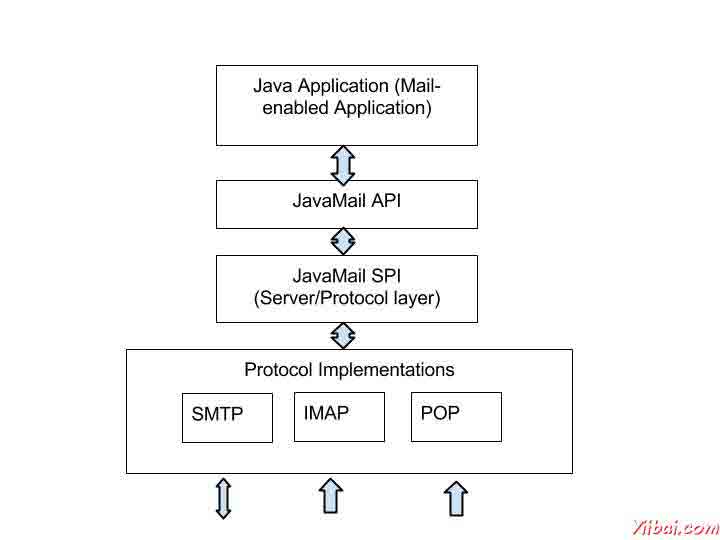
正如上面的 java 应用程序表示用户使用 JavaMail API 来编写,发送和接收电子邮件。下图说明了JavaMail 的体系结构:
JavaMail API 的抽象机制类似于其他的J2EE API,如JDBC,JNDI和JMS。如上面看到的体系结构图,JavaMail API 被分为两个主要部分:
- 与应用程序无关的部分:应用程序编程接口(API)是由应用程序使用的组件来发送和接收邮件,独立于底层的供应商或协议中使用的。
- 一个服务相关的部分:一个服务提供商接口(SPI)说,协议特定的语言,如SMTP,POP,IMAP和网络新闻传输协议(NNTP)。它是用来插在一封邮件服务到J2EE平台的供应商。
JavaMail API 环境设置 - JavaMail
要使用Java应用程序发送邮件是很简单的,但首先应该有安装 JavaMail API 和 Java 激活框架(JAF)。
> 您需要JavaBeans激活框架(JAF)的扩展,当你不使用Java SE6或更高版本提供了javax.activation中的包。
下载并解压缩这些文件,在新创建的顶层目录,你会发现一些jar文件同时为应用。需要添加 mail.jar 和 activation.jar 文件在CLASSPATH中。
SMPT 服务器
发送电子邮件,您必须有SMTP服务器,它负责发送邮件。您可以使用下列方法之一来获取SMTP服务器:
- 安装和使用任何SMTP服务器,如 Postfix 服务器(Ubuntu),James Apache服务器(Apache 的 Java 的企业邮件服务器)等。
- 使用由主机供应商如提供的SMTP服务器:免费 SMTP 通过JangoSMTP 网站提供的是 relay.jangosmtp.net。
- 使用由公司提供的SMTP服务器如Gmail,雅虎等。
> 在随后的章节中的例子中,我们使用了免费 JangoSMTP 服务器发送电子邮件。您可以通过访问这个网站上创建一个帐户,并配置您的电子邮件地址。
JavaMail API 核心类 - JavaMail
JavaMail API包含了一些接口,用于发送,读取和删除电子邮件消息的类。虽然有许多软件包在JavaMail API中,频繁用于Java邮件API主要有两个包:javax.mail和javax.mail.internet。这些软件包包含所有的JavaMail核心类。它们分别是:
类 | 描述 |
The key class of the API. A multithreaded object represents the connection factory. | |
An abstract class that models an e-mail message. Subclasses provide the actual implementations. | |
An abstract class that models the addresses (from and to addresses) in a message. Subclasses provide the specific implementations. | |
An abstract class used to protect mail resources on the mail server. | |
An abstract class that models a message transport mechanism for sending an e-mail message. | |
An abstract class that models a message store and its access protocol, for storing and retrieving messages. A Store is divided into Folders. | |
An abstract class that represents a folder of mail messages. It can contain subfolders. | |
javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage | Message is an abstract class, hence must work with a subclass; in most cases, you’ll use a MimeMessage. A MimeMessage is an e-mail message that understands MIME types and headers. |
javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress | This class represents an Internet email address using the syntax of RFC822. Typical address syntax is of the formuser@host.domain or Personal Name <user@host.domain>. |
让我们研究这些类的细节,并在随后的章节中,我们将使用所有这些研究的例子。
会话类
会话类是JavaMail API的主要类,它不创建子类。 Session 对象充当连接工厂的JavaMail API,它可以同时处理配置设置和身份验证。
Session 对象可以通过以下方式创建:
- 通过查找存储在JNDI服务的管理对象
InitialContext ctx = new InitialContext();
Session session = (Session) ctx.lookup("usersMailSession");
usersMailSession是用作Session 对象的管理对象的JNDI名称的对象。 usersMailSession 可以创建并配置必要的参数作为名称/值对,包括信息,如邮件服务器的主机名,用户帐户发送邮件,并通过 Session 对象所支持的协议。
- 创建Session对象的另一种方法是基于编程方法,可以在其中使用的java.util.Properties对象来覆盖一些默认信息,如邮件服务器名,用户名,密码,那可以是其他信息整个应用程序共享。
该构造Session类是私有的。因此,会话类提供了两个方法(如下所示),它获得了Session对象。
- getDefaultInstance(): 有两种方法使用getDefaultInstance()方法来获取会话对象。它返回默认的会话。
public static Session getDefaultInstance(Properties props)
public static Session getDefaultInstance(Properties props,Authenticator auth)
- getInstance(): 有两种方法使用getInstance()方法来获取会话对象。它返回新的会话。
public static Session getInstance(Properties props)
public static Session getInstance(Properties props,Authenticator auth)
消息类
与Session对象创建的,我们现在继续创建将要发送的消息。该消息类型将是javax.mail.Message。
- Message是一个抽象类。因此,它的子类javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage类大多使用。
- 创建消息,你需要传递会话对象中的MimeMessage类的构造函数。例如:
MimeMessage message=new MimeMessage(session);
- 一旦消息对象被创建,我们需要存储的信息在里面。消息类实现了javax.mail.Part接口,当使用javax.mail.internet。的MimeMessage实现javax.mail.internet.MimePart。您可以使用message.setContent()或mimeMessage.setText()来存储内容。
- MimeMessage类的常用的方法有
方法 | 描述 |
public void setFrom(Address address) | used to set the from header field. |
public void addRecipients(Message.RecipientType type, String addresses) | used to add the given address to the recipient type. |
public void setSubject(String subject) | used to set the subject header field. |
public void setText(String textmessage) | used to set the text as the message content using text/plain MIME type. |
地址类
现在,我们有一个会话和消息(存储在它里面的内容)的对象,我们需要使用地址对象,以解决这封邮件。
- Address 是一个抽象类。因此,它的子类javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress类大多被使用。
- Address 可以通过刚好路过的电子邮件地址来创建:
Address address = new InternetAddress("manisha@gmail.com");
- 创建地址的另一种方式是通过将名称与电子邮件地址:
Address address = new InternetAddress("manisha@gmail.com", Manisha);
- 您还可以设置收件人,发件人,抄送,密件抄送(To, From, CC, BCC)字段如下 fields as below
- message.setFrom(address)
- message.addRecipient(type, address)
- 三种预定义的地址类型是与这些值中的一个对象:
- Message.RecipientType.TO
- Message.RecipientType.CC
- Message.RecipientType.BCC
Authenticator类
Authenticator 类表示懂得如何获得认证的网络连接的对象。通常情况下,它会通过提示信息的用户这样做。
- 身份验证是一个抽象类。您可以创建一个子类PasswordAuthentication,通过用户名和密码给它的构造。
- 必须注册认证者与当您创建会话对象的会话。
以下是验证器使用的一个例子:
Properties props = new Properties();
//Override props with any customized data
PasswordAuthentication auth = new PasswordAuthentication("manisha", "pswrd")
Session session = Session.getDefaultInstance(props, auth);
Transport 类
Transport 类用来作为消息传输机制。这个类通常使用SMTP协议来发送消息。
- 它是一个抽象类。
- 你可以通过只调用静态的send()方法使用该类的默认版本:
Transport.send(message);
- 发送消息的另一种方法是通过从会话您的协议得到一个特定的实例,传递下去的用户名和密码(空白,如果不必要的),发送消息,并关闭连接:
message.saveChanges(); // implicit with send()
//Get transport for session
Transport transport = session.getTransport("smtp");
//Connect
transport.connect(host, username, password);
//repeat if necessary
transport.sendMessage(message, message.getAllRecipients());
//Done, close the connection
transport.close();
Store 类
一个抽象类,模型信息存储和访问协议,用于存储和检索信息。子类提供实际的实现。存储扩展服务类,它提供命名商店,连接到存储,并听取连接事件很多常见的方法。
客户获得通过获得它实现了数据库访问协议的Store对象访问消息存储。大多数邮件存储需要进行身份验证,才允许访问的用户。 connect方法进行身份验证。
Store store = session.getStore("pop3");
store.connect(host, username, password);
Folder 类
folder 是表示一个文件夹的邮件消息的抽象类。子类实现协议的具体文件夹。文件夹可以包含子文件夹,以及消息,从而提供了一种分层结构。
连接到存储后,您就可以得到一个文件夹,必须先打开,然后才能从中读取消息。
Folder folder = store.getFolder("INBOX");
folder.open(Folder.READ_ONLY);
Message message[] = folder.getMessages();
getFolder(字符串name)方法为一个Folder 对象返回指定的子文件夹。关闭一次读邮件完成两者的存储和文件夹的连接。
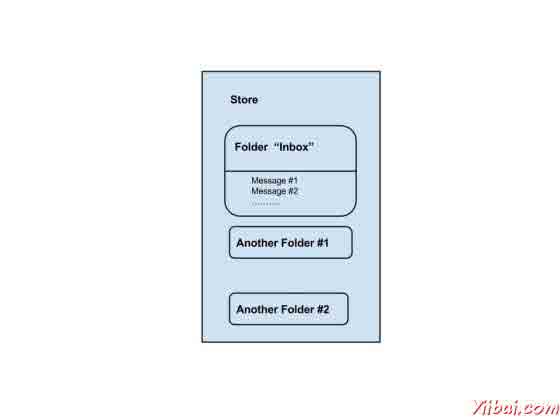
我们可以看到下面的图片的存储和文件夹的关系:
正如我们所看到的,每个用户帐户,该服务器有一个商店,这是用户的信息的存储。该存储分为文件夹,并在“收件箱”文件夹,其中包含电子邮件的主要文件夹。文件夹可以包含邮件和子文件夹。
JavaMail API 发送电子邮件 - JavaMail
现在,我们对JavaMail API及其核心类有一个清晰的概念,现在让我们写这将发送简单的电子邮件,邮件带有附件,电子邮件,HTML内容和电子邮件内嵌图像一个简单的程序。
接着在上述所有情况的基本步骤如下:
- 获取Session对象。
- 撰写邮件。
- 发送消息。
在下面的章节中,我们已经证明了简单的例子:
JavaMail 查询电子邮件 - JavaMail
分为两部分,需要在继续本章之前的理解。邮件检查和提取。
- 检查在JavaMail的电子邮件是我们在邮箱打开相应的文件夹,每个消息传递的过程。在这里,我们只检查每封邮件的标题即发件人,收件人,主题。内容不会被读取。
- 在获取JavaMail的电子邮件是我们在邮箱中打开相应的文件夹,每个消息传递的过程。非常久远的标题,我们也认识到内容类型阅读的内容。
为了使用JavaMail API 检查或提取电子邮件,我们需要 POP或IMAP服务器。要检查并获取邮件,需要文件夹和存储类。在这里,我们使用了Gmail 的 POP3服务器(pop.gmail.com)。在本章将学习如何使用JavaMail API 来检查电子邮件。提取应覆盖在随后的章节。要检查的电子邮件:
- 获得一个 Session
- 创建POP3 Store对象并连接pop服务器。
- 创建文件夹对象。在您的邮箱中打开相应的文件夹。
- 得到消息。
- 关闭存储和文件夹对象。
创建Java类
创建一个Java类文件CheckingMails,是其内容如下:
package com.yiibai;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Folder;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.MessagingException;
import javax.mail.NoSuchProviderException;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Store;
public class CheckingMails {
public static void check(String host, String storeType, String user,
String password)
{
try {
//create properties field
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("mail.pop3.host", host);
properties.put("mail.pop3.port", "995");
properties.put("mail.pop3.starttls.enable", "true");
Session emailSession = Session.getDefaultInstance(properties);
//create the POP3 store object and connect with the pop server
Store store = emailSession.getStore("pop3s");
store.connect(host, user, password);
//create the folder object and open it
Folder emailFolder = store.getFolder("INBOX");
emailFolder.open(Folder.READ_ONLY);
// retrieve the messages from the folder in an array and print it
Message[] messages = emailFolder.getMessages();
System.out.println("messages.length---" + messages.length);
for (int i = 0, n = messages.length; i < n; i++) {
Message message = messages[i];
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
System.out.println("Email Number " + (i + 1));
System.out.println("Subject: " + message.getSubject());
System.out.println("From: " + message.getFrom()[0]);
System.out.println("Text: " + message.getContent().toString());
}
//close the store and folder objects
emailFolder.close(false);
store.close();
} catch (NoSuchProviderException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (MessagingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "pop.gmail.com";// change accordingly
String mailStoreType = "pop3";
String username = "yourmail@gmail.com";// change accordingly
String password = "*****";// change accordingly
check(host, mailStoreType, username, password);
}
}
编译并运行
现在,我们班是准备好了,让我们编译上面的类。我已经保存了类CheckingMails.java目录: /home/manisha/JavaMailAPIExercise. 我们需要 javax.mail.jar andactivation.jar 在classpath中。执行下面的命令从命令提示符编译类(两个jar文件被放置在 /home/manisha/ 目录下):
javac -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: CheckingMails.java
现在,这个类被编译,执行下面的命令来运行:
java -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: CheckingMails
验证输出
你应该看到下面的消息命令控制台上:
messages.length---4
---------------------------------
Email Number 1
Subject: Test Mail--Fetch
From: <abcd@gmail.com>
Text: javax.mail.internet.MimeMultipart@327a5b7f
---------------------------------
Email Number 2
Subject: testing ----checking simple email
From: <abcd@gmail.com>
Text: javax.mail.internet.MimeMultipart@7f0d08bc
---------------------------------
Email Number 3
Subject: Email with attachment
From: <abcd@gmail.com>
Text: javax.mail.internet.MimeMultipart@30b8afce
---------------------------------
Email Number 4
Subject: Email with Inline image
From: <abcd@gmail.com>
Text: javax.mail.internet.MimeMultipart@2d1e165f
这里,我们已经打印的消息,其中是4在这种情况下,收件箱的数目。我们还印制主题,发件人地址和文本的每封电子邮件。
JavaMail 获取电子邮件 - JavaMail
在前面的章节中,我们学会了如何检查电子邮件。现在让我们来看看如何获取每封电子邮件和阅读其内容。让我们编写一个Java类FetchingEmail 读取以下类型的电子邮件:
- 简单的电子邮件
- 电子邮件与附件
- 电子邮件与内嵌图像
其次在代码的基本步骤如下:
- 获取Session对象。
- 创建POP3存储对象,并连接到存储。
- 创建文件夹对象,并在您的邮箱中打开相应的文件夹。
- 检索消息。
- 分别关闭文件夹和存储对象。
创建Java类
创建一个Java创建一个Java类文件FetchingEmail,内容都是如下:
package com.yiibai;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Address;
import javax.mail.Folder;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.MessagingException;
import javax.mail.Multipart;
import javax.mail.NoSuchProviderException;
import javax.mail.Part;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Store;
public class FetchingEmail {
public static void fetch(String pop3Host, String storeType, String user,
String password) {
try {
// create properties field
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("mail.store.protocol", "pop3");
properties.put("mail.pop3.host", pop3Host);
properties.put("mail.pop3.port", "995");
properties.put("mail.pop3.starttls.enable", "true");
Session emailSession = Session.getDefaultInstance(properties);
// emailSession.setDebug(true);
// create the POP3 store object and connect with the pop server
Store store = emailSession.getStore("pop3s");
store.connect(pop3Host, user, password);
// create the folder object and open it
Folder emailFolder = store.getFolder("INBOX");
emailFolder.open(Folder.READ_ONLY);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
System.in));
// retrieve the messages from the folder in an array and print it
Message[] messages = emailFolder.getMessages();
System.out.println("messages.length---" + messages.length);
for (int i = 0; i < messages.length; i++) {
Message message = messages[i];
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
writePart(message);
String line = reader.readLine();
if ("YES".equals(line)) {
message.writeTo(System.out);
} else if ("QUIT".equals(line)) {
break;
}
}
// close the store and folder objects
emailFolder.close(false);
store.close();
} catch (NoSuchProviderException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (MessagingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "pop.gmail.com";// change accordingly
String mailStoreType = "pop3";
String username =
"abc@gmail.com";// change accordingly
String password = "*****";// change accordingly
//Call method fetch
fetch(host, mailStoreType, username, password);
}
/*
* This method checks for content-type
* based on which, it processes and
* fetches the content of the message
*/
public static void writePart(Part p) throws Exception {
if (p instanceof Message)
//Call methos writeEnvelope
writeEnvelope((Message) p);
System.out.println("----------------------------");
System.out.println("CONTENT-TYPE: " + p.getContentType());
//check if the content is plain text
if (p.isMimeType("text/plain")) {
System.out.println("This is plain text");
System.out.println("---------------------------");
System.out.println((String) p.getContent());
}
//check if the content has attachment
else if (p.isMimeType("multipart/*")) {
System.out.println("This is a Multipart");
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Multipart mp = (Multipart) p.getContent();
int count = mp.getCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
writePart(mp.getBodyPart(i));
}
//check if the content is a nested message
else if (p.isMimeType("message/rfc822")) {
System.out.println("This is a Nested Message");
System.out.println("---------------------------");
writePart((Part) p.getContent());
}
//check if the content is an inline image
else if (p.isMimeType("image/jpeg")) {
System.out.println("--------> image/jpeg");
Object o = p.getContent();
InputStream x = (InputStream) o;
// Construct the required byte array
System.out.println("x.length = " + x.available());
int i = 0;
byte[] bArray = new byte[x.available()];
while ((i = (int) ((InputStream) x).available()) > 0) {
int result = (int) (((InputStream) x).read(bArray));
if (result == -1)
break;
}
FileOutputStream f2 = new FileOutputStream("/tmp/image.jpg");
f2.write(bArray);
}
else if (p.getContentType().contains("image/")) {
System.out.println("content type" + p.getContentType());
File f = new File("image" + new Date().getTime() + ".jpg");
DataOutputStream output = new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f)));
com.sun.mail.util.BASE64DecoderStream test =
(com.sun.mail.util.BASE64DecoderStream) p
.getContent();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int bytesRead;
while ((bytesRead = test.read(buffer)) != -1) {
output.write(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
}
}
else {
Object o = p.getContent();
if (o instanceof String) {
System.out.println("This is a string");
System.out.println("---------------------------");
System.out.println((String) o);
}
else if (o instanceof InputStream) {
System.out.println("This is just an input stream");
System.out.println("---------------------------");
InputStream is = (InputStream) o;
is = (InputStream) o;
int c;
while ((c = is.read()) != -1)
System.out.write(c);
}
else {
System.out.println("This is an unknown type");
System.out.println("---------------------------");
System.out.println(o.toString());
}
}
}
/*
* This method would print FROM,TO and SUBJECT of the message
*/
public static void writeEnvelope(Message m) throws Exception {
System.out.println("This is the message envelope");
System.out.println("---------------------------");
Address[] a;
// FROM
if ((a = m.getFrom()) != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++)
System.out.println("FROM: " + a[j].toString());
}
// TO
if ((a = m.getRecipients(Message.RecipientType.TO)) != null) {
for (int j = 0; j < a.length; j++)
System.out.println("TO: " + a[j].toString());
}
// SUBJECT
if (m.getSubject() != null)
System.out.println("SUBJECT: " + m.getSubject());
}
}
> 您可以通过取消注释语句上设置调试emailSession.setDebug(true);
编译并运行
现在,我们班是准备好了,让我们编译上面的类。我已经保存了类FetchingEmail.java目录: /home/manisha/JavaMailAPIExercise. 我们需要 javax.mail.jar andactivation.jar 在classpath中。执行下面的命令从命令提示符编译类(两个罐子被放置在 /home/manisha/目录下):
javac -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: FetchingEmail.java
现在,这个类被编译,执行下面的命令来运行:
java -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: FetchingEmail
验证输出
你应该看到下面的消息命令控制台上:
messages.length---3
---------------------------------
This is the message envelope
---------------------------
FROM: XYZ <xyz@gmail.com>
TO: ABC <abc@gmail.com>
SUBJECT: Simple Message
----------------------------
CONTENT-TYPE: multipart/alternative; boundary=047d7b343d6ad3e4ea04e8ec6579
This is a Multipart
---------------------------
----------------------------
CONTENT-TYPE: text/plain; charset=ISO-8859-1
This is plain text
---------------------------
Hi am a simple message string....
--
Regards
xyz
This is the message envelope
---------------------------
FROM: XYZ <xyz@gmail.com>
TO: ABC <abc@gmail.com>
SUBJECT: Attachement
----------------------------
CONTENT-TYPE: multipart/mixed; boundary=047d7b343d6a99180904e8ec6751
This is a Multipart
---------------------------
----------------------------
CONTENT-TYPE: text/plain; charset=ISO-8859-1
This is plain text
---------------------------
Hi I've an attachment.Please check
--
Regards
XYZ
----------------------------
CONTENT-TYPE: application/octet-stream; name=sample_attachement
This is just an input stream
---------------------------
Submit your Tutorials, White Papers and Articles into our Tutorials Directory. This is a tutorials database where we are keeping all the tutorials shared by the internet community for the benefit of others.
This is the message envelope
---------------------------
FROM: XYZ <xyz@gmail.com>
TO: ABC <abc@gmail.com>
SUBJECT: Inline Image
----------------------------
CONTENT-TYPE: multipart/related; boundary=f46d04182582be803504e8ece94b
This is a Multipart
---------------------------
----------------------------
CONTENT-TYPE: text/plain; charset=ISO-8859-1
This is plain text
---------------------------
Hi I've an inline image
[image: Inline image 3]
--
Regards
XYZ
----------------------------
CONTENT-TYPE: image/png; name="javamail-mini-logo.jpg"
content typeimage/png; name="javamail-mini-logo.jpg"
在这里,你可以看到有三封邮件在邮箱中。首先一个简单的邮件消息 "Hi am a simple message string...."。第二个邮件有附件。附件的内容也印如上所示。第三个邮件有一个内嵌图像。
JavaMail认证/验证 - JavaMail
在前面的章节查询电子邮件和读取电子邮件,我们通过授权凭证(用户名和密码)以及主机,连接到您的邮箱中存储时。相反,我们可以配置属性有主机,并告诉您的自定义的Authenticator实例的会话。这示于下面的例子:
创建Java类
我们将修改CheckingMails.java 请先阅读 章查询电子邮件 这章。其内容如下所述:
package com.yiibai;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Authenticator;
import javax.mail.Folder;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.MessagingException;
import javax.mail.NoSuchProviderException;
import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Store;
public class CheckingMails {
public static void check(String host, String storeType, String user,
String password)
{
try {
// create properties field
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("mail.pop3s.host", host);
properties.put("mail.pop3s.port", "995");
properties.put("mail.pop3s.starttls.enable", "true");
// Setup authentication, get session
Session emailSession = Session.getInstance(properties,
new javax.mail.Authenticator() {
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() {
return new PasswordAuthentication(
"manishapatil3may@gmail.com", "manisha123");
}
});
// emailSession.setDebug(true);
// create the POP3 store object and connect with the pop server
Store store = emailSession.getStore("pop3s");
store.connect();
// create the folder object and open it
Folder emailFolder = store.getFolder("INBOX");
emailFolder.open(Folder.READ_ONLY);
// retrieve the messages from the folder in an array and print it
Message[] messages = emailFolder.getMessages();
System.out.println("messages.length---" + messages.length);
for (int i = 0, n = messages.length; i < n; i++) {
Message message = messages[i];
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
System.out.println("Email Number " + (i + 1));
System.out.println("Subject: " + message.getSubject());
System.out.println("From: " + message.getFrom()[0]);
System.out.println("Text: " + message.getContent().toString());
}
// close the store and folder objects
emailFolder.close(false);
store.close();
} catch (NoSuchProviderException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (MessagingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "pop.gmail.com";// change accordingly
String mailStoreType = "pop3";
String username = "abc@gmail.com";// change accordingly
String password = "*****";// change accordingly
check(host, mailStoreType, username, password);
}
}
> 您可以通过取消注释语句上设置调试emailSession.setDebug(true);
编译并运行
现在,我们班是准备好了,让我们编译上面的类。我已经保存了类CheckingMails.java目录: /home/manisha/JavaMailAPIExercise. 我们需要 javax.mail.jar andactivation.jar 在classpath中。执行下面的命令从命令提示符编译类(两个罐子被放置在 /home/manisha/ 目录下):
javac -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: CheckingMails.java
现在,这个类被编译,执行下面的命令来运行:
java -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: CheckingMails
验证输出
你可以看到一个类似的消息,如下命令控制台上:
messages.length---3
---------------------------------
Email Number 1
Subject: Today is a nice day
From: XYZ <xyz@gmail.com>
Text: javax.mail.internet.MimeMultipart@45f676cb
---------------------------------
Email Number 2
Subject: hiiii....
From: XYZ <xyz@gmail.com>
Text: javax.mail.internet.MimeMultipart@37f12d4f
---------------------------------
Email Number 3
Subject: helloo
From: XYZ <xyz@gmail.com>
Text: javax.mail.internet.MimeMultipart@3ad5ba3a
JavaMail 电子邮件答复/回复 - JavaMail
在本章中,我们将看到如何使用JavaMail API来回复电子邮件。接着在下面的程序中的列出基本步骤:
- 获取Session对象与POP和SMTP 服务器的细节属性。我们需要 POP 细节来检索信息和SMPT详细信息发送邮件。
- 创建POP3存储对象,并连接到存储。
- 创建文件夹对象,并在您的邮箱中打开相应的文件夹。
- 检索消息。
- 遍历的消息,如果你想回复键入“Y”或“y”。
- 得到消息的所有信息(收件人,发件人,主题,内容)(To,From,Subject, Content) 。
- 建立应答消息,使用Message.reply()方法。这个方法配置一个新的消息与适当的收件人和主题。该方法接受一个布尔参数,指示是否只回复给发送者 (false)或回复给所有人(true)。
- 从设置,文本和回复到邮件中,并通过传输对象的实例发送。
- 关闭传输,文件夹和存储对象分别。
> 在这里,我们使用JangoSMPT服务器通过该电子邮件发送到我们的目标电子邮件地址。设置是在环境设置章节解释。
创建Java类
创建一个Java类文件ReplyToEmail,是其内容如下:
package com.yiibai;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Folder;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Store;
import javax.mail.Transport;
import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage;
public class ReplyToEmail {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Date date = null;
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("mail.store.protocol", "pop3");
properties.put("mail.pop3s.host", "pop.gmail.com");
properties.put("mail.pop3s.port", "995");
properties.put("mail.pop3.starttls.enable", "true");
properties.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true");
properties.put("mail.smtp.starttls.enable", "true");
properties.put("mail.smtp.host", "relay.jangosmtp.net");
properties.put("mail.smtp.port", "25");
Session session = Session.getDefaultInstance(properties);
// session.setDebug(true);
try
{
// Get a Store object and connect to the current host
Store store = session.getStore("pop3s");
store.connect("pop.gmail.com", "xyz@gmail.com",
"*****");//change the user and password accordingly
Folder folder = store.getFolder("inbox");
if (!folder.exists()) {
System.out.println("inbox not found");
System.exit(0);
}
folder.open(Folder.READ_ONLY);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
System.in));
Message[] messages = folder.getMessages();
if (messages.length != 0) {
for (int i = 0, n = messages.length; i < n; i++) {
Message message = messages[i];
date = message.getSentDate();
// Get all the information from the message
String from = InternetAddress.toString(message.getFrom());
if (from != null) {
System.out.println("From: " + from);
}
String replyTo = InternetAddress.toString(message
.getReplyTo());
if (replyTo != null) {
System.out.println("Reply-to: " + replyTo);
}
String to = InternetAddress.toString(message
.getRecipients(Message.RecipientType.TO));
if (to != null) {
System.out.println("To: " + to);
}
String subject = message.getSubject();
if (subject != null) {
System.out.println("Subject: " + subject);
}
Date sent = message.getSentDate();
if (sent != null) {
System.out.println("Sent: " + sent);
}
System.out.print("Do you want to reply [y/n] : ");
String ans = reader.readLine();
if ("Y".equals(ans) || "y".equals(ans)) {
Message replyMessage = new MimeMessage(session);
replyMessage = (MimeMessage) message.reply(false);
replyMessage.setFrom(new InternetAddress(to));
replyMessage.setText("Thanks");
replyMessage.setReplyTo(message.getReplyTo());
// Send the message by authenticating the SMTP server
// Create a Transport instance and call the sendMessage
Transport t = session.getTransport("smtp");
try {
//connect to the smpt server using transport instance
//change the user and password accordingly
t.connect("abc", "****");
t.sendMessage(replyMessage,
replyMessage.getAllRecipients());
} finally {
t.close();
}
System.out.println("message replied successfully ....");
// close the store and folder objects
folder.close(false);
store.close();
} else if ("n".equals(ans)) {
break;
}
}//end of for loop
} else {
System.out.println("There is no msg....");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
> 您可以通过取消注释语句上设置调试 session.setDebug(true);
编译并运行
现在,我们班是准备好了,让我们编译上面的类。我已经保存了类ReplyToEmail.java到目录: /home/manisha/JavaMailAPIExercise. 我们需要 javax.mail.jar andactivation.jar 在 classpath 中。执行下面的命令从命令提示符编译类(两个罐子被放置在 /home/manisha/ 目录下):
javac -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: ReplyToEmail.java
现在,这个类被编译,执行下面的命令来运行:
java -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: ReplyToEmail
验证输出
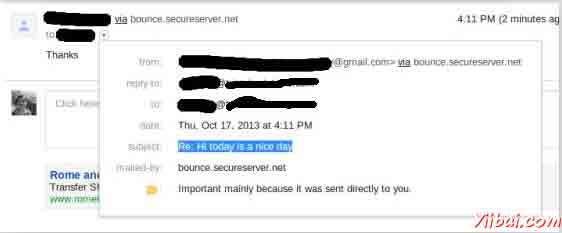
你应该看到下面的消息命令控制台上:
From: ABC <abc@gmail.com>
Reply-to: abc@trioteksolutions.com
To: XYZ <xyz@gmail.com>
Subject: Hi today is a nice day
Sent: Thu Oct 17 15:58:37 IST 2013
Do you want to reply [y/n] : y
message replied successfully ....
检查该邮件发送的收件箱。在我们的例子中收到的邮件看起来如下:
JavaMail 转发电子邮件 - JavaMail
在本章中,我们将看到如何使用JavaMail API来转发电子邮件。接着在下面的程序的基本步骤是:
- 获取Session对象与POP和SMTP服务器的细节的属性。我们需要的POP细节来检索信息和SMPT详细信息发送邮件。
- 创建POP3存储对象,并连接到存储。
- 创建文件夹对象,并在您的邮箱中打开相应的文件夹。
- 检索消息。
- 遍历的消息,如果你想转发键入“Y”或“y”。
- 得到消息的所有信息(收件人,发件人,主题,内容)。
- 通过与组成消息的各个部分的工作建立转发消息。第一部分将是消息的文本和第二部分将要转发的邮件。结合两成多部分。那么你多部分添加到妥善处理消息并发送它。
- 关闭传输,文件夹和存储对象分别。
> 在这里,我们使用JangoSMPT服务器通过该电子邮件被发送到我们的目标电子邮件地址。设置是在环境设置章节解释。
创建Java类
创建一个Java类文件ForwardEmail,是其内容如下:
package com.yiibai;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.BodyPart;
import javax.mail.Folder;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.Multipart;
import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Store;
import javax.mail.Transport;
import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeBodyPart;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMultipart;
public class ForwardEmail {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("mail.store.protocol", "pop3");
properties.put("mail.pop3s.host", "pop.gmail.com");
properties.put("mail.pop3s.port", "995");
properties.put("mail.pop3.starttls.enable", "true");
properties.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true");
properties.put("mail.smtp.host", "relay.jangosmtp.net");
properties.put("mail.smtp.port", "25");
Session session = Session.getDefaultInstance(properties);
try {
// session.setDebug(true);
// Get a Store object and connect to the current host
Store store = session.getStore("pop3s");
store.connect("pop.gmail.com", "xyz@gmail.com",
"*****");//change the user and password accordingly
// Create a Folder object and open the folder
Folder folder = store.getFolder("inbox");
folder.open(Folder.READ_ONLY);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
System.in));
Message[] messages = folder.getMessages();
if (messages.length != 0) {
for (int i = 0, n = messages.length; i < n; i++) {
Message message = messages[i];
// Get all the information from the message
String from = InternetAddress.toString(message.getFrom());
if (from != null) {
System.out.println("From: " + from);
}
String replyTo = InternetAddress.toString(message
.getReplyTo());
if (replyTo != null) {
System.out.println("Reply-to: " + replyTo);
}
String to = InternetAddress.toString(message
.getRecipients(Message.RecipientType.TO));
if (to != null) {
System.out.println("To: " + to);
}
String subject = message.getSubject();
if (subject != null) {
System.out.println("Subject: " + subject);
}
Date sent = message.getSentDate();
if (sent != null) {
System.out.println("Sent: " + sent);
}
System.out.print("Do you want to reply [y/n] : ");
String ans = reader.readLine();
if ("Y".equals(ans) || "y".equals(ans)) {
Message forward = new MimeMessage(session);
// Fill in header
forward.setRecipients(Message.RecipientType.TO,
InternetAddress.parse(from));
forward.setSubject("Fwd: " + message.getSubject());
forward.setFrom(new InternetAddress(to));
// Create the message part
MimeBodyPart messageBodyPart = new MimeBodyPart();
// Create a multipart message
Multipart multipart = new MimeMultipart();
// set content
messageBodyPart.setContent(message, "message/rfc822");
// Add part to multi part
multipart.addBodyPart(messageBodyPart);
// Associate multi-part with message
forward.setContent(multipart);
forward.saveChanges();
// Send the message by authenticating the SMTP server
// Create a Transport instance and call the sendMessage
Transport t = session.getTransport("smtp");
try {
//connect to the smpt server using transport instance
//change the user and password accordingly
t.connect("abc", "*****");
t.sendMessage(forward, forward.getAllRecipients());
} finally {
t.close();
}
System.out.println("message forwarded successfully....");
// close the store and folder objects
folder.close(false);
store.close();
}// end if
}// end for
}// end if
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
> 您可以通过取消注释语句上设置调试 session.setDebug(true);
编译并运行
现在类准备好了,编译上面的类。我已经保存了类ForwardEmail.java目录: /home/manisha/JavaMailAPIExercise. 我们需要javax.mail.jar 和 activation.jar 在 classpath中。执行下面的命令从命令提示符编译类(两个jar 放置在 /home/manisha/ 目录下):
javac -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: ForwardEmail.java
现在,这个类被编译,执行下面的命令来运行:
java -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: ForwardEmail
验证输出
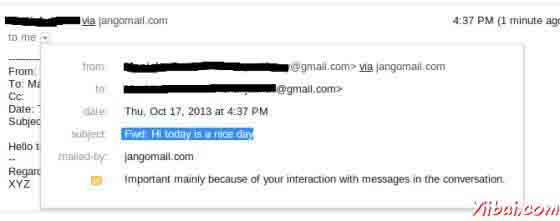
你应该看到下面的消息命令控制台上:
From: ABC <abc@gmail.com>
Reply-to: abc@trioteksolutions.com
To: XYZ <xyz@gmail.com>
Subject: Hi today is a nice day
Sent: Thu Oct 17 15:58:37 IST 2013
Do you want to reply [y/n] : y
message forwarded successfully....
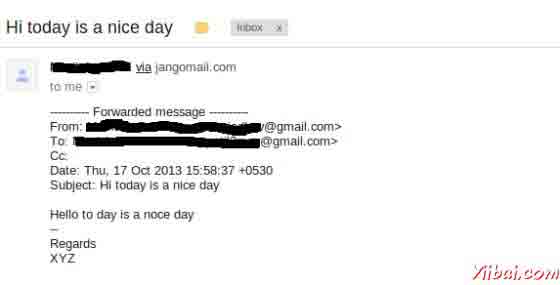
检查该邮件发送的收件箱。在我们的例子中转发的邮件看起来如下:
JavaMail 删除电子邮件 - JavaMail
在本章中,我们将看到如何使用JavaMail API来删除电子邮件。删除信息涉及与该消息相关联的标志工作。有不同的标志为不同的状态,一些系统定义和一些用户定义的。预定义的标志在内部类中定义的标志。标志如下所列:
- Flags.Flag.ANSWERED
- Flags.Flag.DELETED
- Flags.Flag.DRAFT
- Flags.Flag.FLAGGED
- Flags.Flag.RECENT
- Flags.Flag.SEEN
- Flags.Flag.USER
POP协议支持的消息的唯一删除。
其次在删除程序的基本步骤是:
- 获取Session对象与POP和SMTP伺服器的细节的属性。我们需要的POP细节来检索信息和SMPT详细信息发送邮件。
- 创建POP3存储对象,并连接到存储。
- 创建文件夹对象,并在READ_WRITE模式下邮箱打开相应的文件夹。
- 从收件箱文件夹中检索邮件。
- 遍历的消息,如果你想通过Message对象上调用方法setFlag(Flags.Flag.DELETED, true)以删除邮件中键入“Y”或“y”。
- 这些消息标记DELETED 实际上并没有删除,直到我们调用Folder对象上expunge() 方法,或expunge 设置为true,关闭文件夹。
- 关闭存储对象。
创建Java类
创建一个Java类文件ForwardEmail,是其内容如下:
package com.yiibai;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Flags;
import javax.mail.Folder;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.MessagingException;
import javax.mail.NoSuchProviderException;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Store;
public class DeleteEmail {
public static void delete(String pop3Host, String storeType, String user,
String password)
{
try
{
// get the session object
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("mail.store.protocol", "pop3");
properties.put("mail.pop3s.host", pop3Host);
properties.put("mail.pop3s.port", "995");
properties.put("mail.pop3.starttls.enable", "true");
Session emailSession = Session.getDefaultInstance(properties);
// emailSession.setDebug(true);
// create the POP3 store object and connect with the pop server
Store store = emailSession.getStore("pop3s");
store.connect(pop3Host, user, password);
// create the folder object and open it
Folder emailFolder = store.getFolder("INBOX");
emailFolder.open(Folder.READ_WRITE);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
System.in));
// retrieve the messages from the folder in an array and print it
Message[] messages = emailFolder.getMessages();
System.out.println("messages.length---" + messages.length);
for (int i = 0; i < messages.length; i++) {
Message message = messages[i];
System.out.println("---------------------------------");
System.out.println("Email Number " + (i + 1));
System.out.println("Subject: " + message.getSubject());
System.out.println("From: " + message.getFrom()[0]);
String subject = message.getSubject();
System.out.print("Do you want to delete this message [y/n] ? ");
String ans = reader.readLine();
if ("Y".equals(ans) || "y".equals(ans)) {
// set the DELETE flag to true
message.setFlag(Flags.Flag.DELETED, true);
System.out.println("Marked DELETE for message: " + subject);
} else if ("n".equals(ans)) {
break;
}
}
// expunges the folder to remove messages which are marked deleted
emailFolder.close(true);
store.close();
} catch (NoSuchProviderException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (MessagingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException io) {
io.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "pop.gmail.com";// change accordingly
String mailStoreType = "pop3";
String username = "abc@gmail.com";// change accordingly
String password = "*****";// change accordingly
delete(host, mailStoreType, username, password);
}
}
> 您可以通过取消注释语句上设置调试 emailSession.setDebug(true);
编译并运行
现在,我们的类是准备好了,让我们编译上面的类。我已经保存了类DeleteEmail.java目录: /home/manisha/JavaMailAPIExercise. 我们需要javax.mail.jar 和 activation.jar 在 classpath 中。执行下面的命令从命令提示符编译类(两个jar 放置在 /home/manisha/ 目录下):
javac -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: DeleteEmail.java
现在,这个类被编译,执行下面的命令来运行:
java -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: DeleteEmail
验证输出
你应该看到下面的消息命令控制台上:
messages.length---1
---------------------------------
Email Number 1
Subject: Testing
From: ABC <abc@gmail.com>
Do you want to delete this message [y/n] ? y
Marked DELETE for message: Testing
JavaMail Gmail SMTP服务器 - JavaMail
在所有前面的章节中,我们使用JangoSMPT服务器来发送电子邮件。在本章中,我们将了解通过Gmail时提供的SMTP伺服器。 Gmail的(等等)提供了使用他们的公共SMTP服务器的免费。
Gmail SMTP服务器的详细信息可以在这里找到。正如你可以在细节里看到的一样,我们可以使用TLS或SSL连接,以通过Gmail SMTP服务器发送邮件。
使用Gmail SMTP服务器发送邮件的过程类似的发送电子邮件的章节中描述说明,除了我们改变主机服务器。作为先决条件,发件人的电子邮件地址应该是一个活跃的Gmail帐户。让我们尝试一个例子。
创建Java类
创建一个Java类文件SendEmailUsingGMailSMTP,内容都是如下:
package com.yiibai;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.MessagingException;
import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Transport;
import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage;
public class SendEmailUsingGMailSMTP {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Recipient's email ID needs to be mentioned.
String to = "xyz@gmail.com";//change accordingly
// Sender's email ID needs to be mentioned
String from = "abc@gmail.com";//change accordingly
final String username = "abc";//change accordingly
final String password = "*****";//change accordingly
// Assuming you are sending email through relay.jangosmtp.net
String host = "smtp.gmail.com";
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true");
props.put("mail.smtp.starttls.enable", "true");
props.put("mail.smtp.host", host);
props.put("mail.smtp.port", "587");
// Get the Session object.
Session session = Session.getInstance(props,
new javax.mail.Authenticator() {
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() {
return new PasswordAuthentication(username, password);
}
});
try {
// Create a default MimeMessage object.
Message message = new MimeMessage(session);
// Set From: header field of the header.
message.setFrom(new InternetAddress(from));
// Set To: header field of the header.
message.setRecipients(Message.RecipientType.TO,
InternetAddress.parse(to));
// Set Subject: header field
message.setSubject("Testing Subject");
// Now set the actual message
message.setText("Hello, this is sample for to check send "
+ "email using JavaMailAPI ");
// Send message
Transport.send(message);
System.out.println("Sent message successfully....");
} catch (MessagingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
主机设置为smtp.gmail.com,端口设置为587。在这里,我们已经启用TLS连接。
编译并运行
现在,我们的类是准备好了,让我们编译上面的类。我已经保存了类SendEmailUsingGMailSMTP.java到目录: /home/manisha/JavaMailAPIExercise. 我们需要 javax.mail.jar 和 activation.jar 文件在classpath中。执行下面的命令从命令提示符编译类(jar文件放置在 /home/manisha/目录下):
javac -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: SendEmailUsingGMailSMTP.java
现在,这个类被编译,执行下面的命令来运行:
java -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: SendEmailUsingGMailSMTP
验证输出
你应该可以看到下面的消息命令控制台上:
Sent message successfully....
JavaMail 邮件文件夹管理 - JavaMail
到目前为止,我们已经在前面的章节主要介绍收件箱文件夹的工作。这是大多数邮件位于其中的默认文件夹。有些系统可能会调用它的收件箱和其他一些可能被其他一些名字来称呼它。但是,你总是可以从JavaMail API为使用该名称的收件箱访问它。
JavaMail API为代表文件夹的文件夹抽象类的实例:
public abstract class Folder extends Object
这个类声明请求命名文件夹从服务器,从文件夹中删除邮件,搜索文件夹中特定消息,列出文件夹中的邮件,等等方法。
打开文件夹
我们不能直接创建一个文件夹中 Folder 类唯一的构造函数是受保护的。我们可以得到一个文件夹从:
- Session
- Store
- 另外的Folder
上述所有的类都有一个类似的getFolder()方法类似签名:
public abstract Folder getFolder(String name) throws MessagingException
一些在其中获取Folder 对象帮助的方法有:
方法 | 描述 |
boolean exists() | Checks if the folder really exists. Use this method before getting the Folder object. |
abstract void open(int mode) | When you get a Folder, its closed. Use this method to open it. _mode _can be Folder.READ_ONLY or Folder.READ_WRITE. |
abstract boolean isOpen() | This method returns true if the folder is open, false if it’s closed |
abstract void close(boolean expunge) | Closes the folder. If the expunge argument is true, any deleted messages in the folder are deleted from the actual file on the server. Otherwise, they’re simply marked asdeleted, but the messages can still be undeleted. |
基本文件夹信息
以下是一些它返回有关一个文件夹的基本信息,文件夹类中的方法:
方法 | 描述 |
abstract String getName() | Returns the name of the folder, such as "TutorialsPoint Mail" |
abstract String getFullName() | Returns the complete hierarchical name from the root such as “books/Manisha/TutorialsPoint Mail”. |
URLName getURLName() | Return a URLName representing this folder. |
abstract Folder getParent() | Returns the name of the folder that contains this folder i.e the parent folder. E.g "Manisha" from the previous "TutorialsPoint Mail" example. |
abstract int getType() | Returns an int indicating whether the folder can contain messages and/or other folders. |
int getMode() | It returns one of the two named constants Folder.READ_ONLY or Folder.READ_WRITE or -1 when the mode is unknown. |
Store getStore() | Returns the Store object from which this folder was retrieved. |
abstract char getSeparator() | Return the delimiter character that separates this Folder's pathname from the names of immediate subfolders. |
管理文件夹
以下是一些有助于管理文件夹的方法:
方法 | 描述 |
abstract boolean create(int type) | This creates a new folder in this folder’s Store. Where type_would be:Folder.HOLDS_MESSAGES or Folder.HOLDS_FOLDERS. Returns _true if folder is successfully created else returns false. |
abstract boolean delete(boolean recurse) | This deletes the folder only if the folder is closed. Otherwise, it throws an IllegalStateException. If recurse istrue, then subfolders are deleted. |
abstract boolean renameTo(Folder f) | This changes the name of this folder. A folder must be closed to be renamed. Otherwise, an IllegalStateException is thrown. |
在文件夹管理邮件
以下是一些帮助文件夹管理邮件的方法:
方法 | 描述 |
abstract voidappendMessages(Message[] messages) | As the name implies, the messages in the array are placed at the end of this folder. |
void copyMessages(Message[] messages, Folder destination) | This copies messages from this folder into a specified folder given as an argument. |
abstract Message[] expunge() | To delete a message from a folder, set its Flags.Flag.DELETED flag to true. To physically remove deleted messages from a folder, you have to call this method. |
列出文件夹的内容
有四种方法可以列出一个文件夹中包含的文件夹:
方法 | 描述 |
Folder[] list() | This returns an array listing the folders that this folder contains. |
Folder[] listSubscribed() | This returns an array listing all the subscribed folders that this folder contains. |
abstract Folder[] list(String pattern) | This is similar to the list() method except that it allows you to specify a pattern. The pattern is a string giving the name of the folders that match. |
Folder[] listSubscribed(String pattern) | This is similar to the listSubscribed() method except that it allows you to specify a pattern. The pattern is a string giving the name of the folders that match. |
检查邮件
方法 | 描述 |
abstract int getMessageCount() | This method can be invoked on an open or closed folder. However, in the case of a closed folder, this method may (or may not) return -1 to indicate that the exact number of messages isn’t easily available. |
abstract boolean hasNewMessages() | This returns true if new messages have been added to the folder since it was last opened. |
int getNewMessageCount() | It returns the new message count by checking messages in the folder whose RECENT flag is set. |
int getUnreadMessageCount() | This can be invoked on either an open or a closed folder. However, in the case of a closed folder, it may return -1 to indicate that the real answer would be too expensive to obtain. |
获取信息的文件夹
Folder类提供了四种方法,用于检索从打开文件夹的邮件:
方法 | 描述 |
abstract Message getMessage(int messageNumber) | This returns the nth message in the folder. The first message in the folder is number 1. |
Message[] getMessages() | This returns an array of Message objects representing all the messages in this folder. |
Message[] getMessages(int start, int end) | This returns an array of Message objects from the folder, beginning with start and finishing with end, inclusive. |
Message[] getMessages(int[] messageNumbers) | This returns an array containing only those messages specifically identified by number in the _messageNumbers_array. |
void fetch(Message[] messages, FetchProfile fp) | Prefetch the items specified in the FetchProfile for the given Messages. The FetchProfile argument specifies which headers in the messages to prefetch. |
搜索文件夹
如果服务器支持搜索(许多IMAP服务器做最POP服务器没有),很容易搜索的文件夹,以满足某些条件的邮件。标准编码在搜索关键词的对象。以下是两种搜索方法:
方法 | 描述 |
Message[] search(SearchTerm term) | Search this Folder for messages matching the specified search criterion. Returns an array containing the matching messages. Returns an empty array if no matches were found. |
Message[] search(SearchTerm term, Message[] messages) | Search the given array of messages for those that match the specified search criterion. Returns an array containing the matching messages. Returns an empty array if no matches were found. The the specified Message objects must belong to this folder. |
Flags
当你需要改变标志的文件夹对整个消息集标志的修改是很有用的。以下是在文件夹类提供的方法:
方法 | 描述 |
void setFlags(Message[] messages, Flags flag, boolean value) | Sets the specified flags on the messages specified in the array. |
void setFlags(int start, int end, Flags flag, boolean value) | Sets the specified flags on the messages numbered from start through end, both start and end inclusive. |
void setFlags(int[] messageNumbers, Flags flag, boolean value) | Sets the specified flags on the messages whose message numbers are in the array. |
abstract Flags getPermanentFlags() | Returns the flags that this folder supports for all messages. |
JavaMail 限额管理 - JavaMail
JavaMail配额是限定或固定的号码或邮件的数量在电子邮件存储。JavaMail API为每个邮件服务请求调用计数配额。电子邮件服务可以适用下列配额标准:
- 外发邮件(包括附件)的最大大小。
- 邮件信息,包括附件的最大大小。
- 消息的最大大小时,管理员是一个收件人
对于配额管理的JavaMail有以下类别:
Class | 描述 |
public class Quota | This class represents a set of quotas for a given quota root. Each quota root has a set of resources, represented by the Quota.Resource class. Each resource has a name (for example, "STORAGE"), a current usage, and a usage limit. This has only one method setResourceLimit(String name, long limit). |
public static class Quota.Resource | Represents an individual resource in a quota root. |
public interface QuotaAwareStore | An interface implemented by Stores that support quotas. The getQuota and setQuota methods support the quota model defined by the IMAP QUOTA extension.GmailSSLStore, GmailStore, IMAPSSLStore, IMAPStore are the known implementing classes of this interface. |
让我们来看看和例子在下面的章节会检查邮件存储名称,并限制其使用。
创建Java类
创建一个Java类文件QuotaExample,是其内容如下:
package com.yiibai;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Quota;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Store;
import com.sun.mail.imap.IMAPStore;
public class QuotaExample
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
try
{
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.put("mail.store.protocol", "imaps");
properties.put("mail.imaps.port", "993");
properties.put("mail.imaps.starttls.enable", "true");
Session emailSession = Session.getDefaultInstance(properties);
// emailSession.setDebug(true);
// create the IMAP3 store object and connect with the pop server
Store store = emailSession.getStore("imaps");
//change the user and password accordingly
store.connect("imap.gmail.com", "abc@gmail.com", "*****");
IMAPStore imapStore = (IMAPStore) store;
System.out.println("imapStore ---" + imapStore);
//get quota
Quota[] quotas = imapStore.getQuota("INBOX");
//Iterate through the Quotas
for (Quota quota : quotas) {
System.out.println(String.format("quotaRoot:'%s'",
quota.quotaRoot));
//Iterate through the Quota Resource
for (Quota.Resource resource : quota.resources) {
System.out.println(String.format(
"name:'%s', limit:'%s', usage:'%s'", resource.name,
resource.limit, resource.usage));
}
}
} catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
这里是连接通过IMAP(imap.gmail.com)服务器的Gmail服务,为IMAPStore实现QuotaAwareStore。一旦你获得了存储对象,获取配额阵列和遍历并打印相关信息。
编译并运行
现在,我们的类是准备好了,让我们编译上面的类。我已经保存了类QuotaExample.java到目录 : /home/manisha/JavaMailAPIExercise. 我们需要javax.mail.jar 和 activation.jar在classpath中。执行下面的命令从命令提示符编译类(两个jar被放置在/home/manisha/ 目录下):
javac -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: QuotaExample.java
现在,这个类被编译,执行下面的命令来运行:
java -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: QuotaExample
验证输出
您应该看到类似的消息在命令控制台上:
imapStore ---imaps://abc%40gmail.com@imap.gmail.com
quotaRoot:''
name:'STORAGE', limit:'15728640', usage:'513'
JavaMail 退回邮件 - JavaMail
消息可以被退回的几个原因。这个问题是在rfc1211深度讨论。只有服务器可确定特定的邮箱或用户名的不存在。当服务器检测到错误,它会返回一个消息,指出失败的原邮件的发件人的原因。
有覆盖发送状态通知许多互联网标准,但大量的服务器不使用特殊技术来返还这些失败消息支持这些新的标准代替。因此,它变得非常难以关联与导致问题的原始邮件的退回邮件。
JavaMail 包括用于解析传递状态通知的支持。有许多技术和试探法来处理这个问题。其中一个是可变的信封返回路径的技术。可以设置的返回路径中的包封器,如下面的例子。这是在弹跳邮件被发送到的地址。您可能需要将其设置为一个通用的地址,而不同:头,这样你就可以处理远程退回。这可以通过设置mail.smtp.from属性在JavaMail中。
创建Java类
创建一个Java类文件SendEmail,是其内容如下:
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Transport;
import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage;
public class SendEmail {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String smtpServer = "smtp.gmail.com";
int port = 587;
final String userid = "youraddress";//change accordingly
final String password = "*****";//change accordingly
String contentType = "text/html";
String subject = "test: bounce an email to a different address " +
"from the sender";
String from = "youraddress@gmail.com";
String to = "bouncer@fauxmail.com";//some invalid address
String bounceAddr = "toaddress@gmail.com";//change accordingly
String body = "Test: get message to bounce to a separate email address";
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true");
props.put("mail.smtp.starttls.enable", "true");
props.put("mail.smtp.host", smtpServer);
props.put("mail.smtp.port", "587");
props.put("mail.transport.protocol", "smtp");
props.put("mail.smtp.from", bounceAddr);
Session mailSession = Session.getInstance(props,
new javax.mail.Authenticator() {
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() {
return new PasswordAuthentication(userid, password);
}
});
MimeMessage message = new MimeMessage(mailSession);
message.addFrom(InternetAddress.parse(from));
message.setRecipients(Message.RecipientType.TO, to);
message.setSubject(subject);
message.setContent(body, contentType);
Transport transport = mailSession.getTransport();
try {
System.out.println("Sending ....");
transport.connect(smtpServer, port, userid, password);
transport.sendMessage(message,
message.getRecipients(Message.RecipientType.TO));
System.out.println("Sending done ...");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.err.println("Error Sending: ");
e.printStackTrace();
}
transport.close();
}// end function main()
}
在这里,我们可以看到,该属性mail.smtp.from设距离来源地址不同。
编译并运行
现在,我们的类是准备好了,让我们编译上面的类。我已经保存了类SendEmail.java到目录 : /home/manisha/JavaMailAPIExercise. 我们需要 javax.mail.jar 和 activation.jar 在classpath中。执行下面的命令从命令提示符编译类(两个jar文件 被放置在/home/manisha/目录下):
javac -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: SendEmail.java
现在,这个类被编译,执行下面的命令来运行:
java -cp /home/manisha/activation.jar:/home/manisha/javax.mail.jar: SendEmail
验证输出
应该看到下面的消息命令控制台上:
Sending ....
Sending done ...
JavaMail SMTP服务器 - JavaMail
SMTP是一个缩写为简单邮件传输协议。它是跨越互联网协议(IP)网络电子邮件(电子邮件)传输的Internet标准。 SMTP使用TCP端口25。受SSL保护的SMTP连接通过缩写SMTPS称,虽然SMTPS不是一个协议在自己的权利。
JavaMail API 有包 com.sun.mail.smtp 它作为SMTP协议提供访问SMTP服务器。下表列出了包含在这个包中的类:
类 | 描述 |
SMTPMessage | This class is a specialization of the MimeMessage class that allows you to specify various SMTP options and parameters that will be used when this message is sent over SMTP. |
SMTPSSLTransport | This class implements the Transport abstract class using SMTP over SSL for message submission and transport. |
SMTPTransport | This class implements the Transport abstract class using SMTP for message submission and transport. |
下表列出抛出的异常:
异常 | 描述 |
SMTPAddressFailedException | This exception is thrown when the message cannot be sent. |
SMTPAddressSucceededException | This exception is chained off a SendFailedException when the mail.smtp.reportsuccess property is true. |
SMTPSenderFailedException | This exception is thrown when the message cannot be sent. |
SMTPSendFailedException | This exception is thrown when the message cannot be sent.The exception includes the sender's address, which the mail server rejected. |
com.sun.mail.smtp提供使用SMTP身份验证选择性。使用SMTP验证,您需要设置mail.smtp.auth属性或提供SMTP传输与连接到SMTP服务器的用户名和密码。您可以使用以下方法之一进行:
Transport.send(message);
- 创建您的邮件会话时提供一个Authenticator对象,并提供身份验证器回调过程中的用户名和密码信息。mail.smtp.user属性可以设置,以提供一个默认的用户名回调,但密码仍然需要显式提供。这种方法允许您使用静态传输send方法来发送消息。例如:
- 调用传输用户名和密码参数显式连接方法。例如:
Transport tr = session.getTransport("smtp");
tr.connect(smtphost, username, password);
msg.saveChanges();
tr.sendMessage(msg, msg.getAllRecipients());
tr.close();
SMTP协议提供程序支持以下属性,这些属性可以在JavaMail会话对象进行设置。该属性始终设置为字符串。例如:
props.put("mail.smtp.port", "587");
在这里,类型列描述字符串是如何解释的。
名称 | 类型 | 描述 |
mail.smtp.user | String | Default user name for SMTP. |
mail.smtp.host | String | The SMTP server to connect to. |
mail.smtp.port | int | The SMTP server port to connect to, if the connect() method doesn't explicitly specify one. Defaults to 25. |
mail.smtp.connectiontimeout | int | Socket connection timeout value in milliseconds. Default is infinite timeout. |
mail.smtp.timeout | int | Socket I/O timeout value in milliseconds. Default is infinite timeout. |
mail.smtp.from | String | Email address to use for SMTP MAIL command. This sets the envelope return address. Defaults to msg.getFrom() or InternetAddress.getLocalAddress(). |
mail.smtp.localhost | String | Local host name used in the SMTP HELO or EHLO command. Defaults to InetAddress.getLocalHost().getHostName(). Should not normally need to be set if your JDK and your name service are configured properly. |
mail.smtp.localaddress | String | Local address (host name) to bind to when creating the SMTP socket. Defaults to the address picked by the Socket class. Should not normally need to be set. |
mail.smtp.localport | int | Local port number to bind to when creating the SMTP socket. Defaults to the port number picked by the Socket class. |
mail.smtp.ehlo | boolean | If false, do not attempt to sign on with the EHLO command. Defaults to true. |
mail.smtp.auth | boolean | If true, attempt to authenticate the user using the AUTH command. Defaults to false. |
mail.smtp.auth.mechanisms | String | If set, lists the authentication mechanisms to consider. Only mechanisms supported by the server and supported by the current implementation will be used. The default is "LOGIN PLAIN DIGEST-MD5 NTLM", which includes all the authentication mechanisms supported by the current implementation. |
mail.smtp.auth.login.disable | boolean | If true, prevents use of the AUTH LOGIN command. Default is false. |
mail.smtp.auth.plain.disable | boolean | If true, prevents use of the AUTH PLAIN command. Default is false. |
mail.smtp.auth.digest-md5.disable | boolean | If true, prevents use of the AUTH DIGEST-MD5 command. Default is false. |
mail.smtp.auth.ntlm.disable | boolean | If true, prevents use of the AUTH NTLM command. Default is false. |
mail.smtp.auth.ntlm.domain | String | The NTLM authentication domain. |
mail.smtp.auth.ntlm.flags | int | NTLM protocol-specific flags. |
mail.smtp.submitter | String | The submitter to use in the AUTH tag in the MAIL FROM command. Typically used by a mail relay to pass along information about the original submitter of the message. |
mail.smtp.dsn.notify | String | The NOTIFY option to the RCPT command. Either NEVER, or some combination of SUCCESS, FAILURE, and DELAY (separated by commas). |
mail.smtp.dsn.ret | String | The RET option to the MAIL command. Either FULL or HDRS. |
mail.smtp.sendpartial | boolean | If set to true, and a message has some valid and some invalid addresses, send the message anyway, reporting the partial failure with a SendFailedException. If set to false (the default), the message is not sent to any of the recipients if there is an invalid recipient address. |
mail.smtp.sasl.enable | boolean | If set to true, attempt to use the javax.security.sasl package to choose an authentication mechanism for login. Defaults to false. |
mail.smtp.sasl.mechanisms | String | A space or comma separated list of SASL mechanism names to try to use. |
mail.smtp.sasl.authorizationid | String | The authorization ID to use in the SASL authentication. If not set, the authentication ID (user name) is used. |
mail.smtp.sasl.realm | String | The realm to use with DIGEST-MD5 authentication. |
mail.smtp.quitwait | boolean | If set to false, the QUIT command is sent and the connection is immediately closed. If set to true (the default), causes the transport to wait for the response to the QUIT command. |
mail.smtp.reportsuccess | boolean | If set to true, causes the transport to include an SMTPAddressSucceededException for each address that is successful. |
mail.smtp.socketFactory | SocketFactory | If set to a class that implements the javax.net.SocketFactory interface, this class will be used to create SMTP sockets. |
mail.smtp.socketFactory.class | String | If set, specifies the name of a class that implements the javax.net.SocketFactory interface. This class will be used to create SMTP sockets. |
mail.smtp.socketFactory.fallback | boolean | If set to true, failure to create a socket using the specified socket factory class will cause the socket to be created using the java.net.Socket class. Defaults to true. |
mail.smtp.socketFactory.port | int | Specifies the port to connect to when using the specified socket factory. If not set, the default port will be used. |
mail.smtp.ssl.enable | boolean | If set to true, use SSL to connect and use the SSL port by default. Defaults to false for the "smtp" protocol and true for the "smtps" protocol. |
mail.smtp.ssl.checkserveridentity | boolean | If set to true, checks the server identity as specified by RFC 2595. Defaults to false. |
mail.smtp.ssl.trust | String | If set, and a socket factory hasn't been specified, enables use of a MailSSLSocketFactory. If set to "*", all hosts are trusted. If set to a whitespace separated list of hosts, those hosts are trusted. Otherwise, trust depends on the certificate the server presents. |
mail.smtp.ssl.socketFactory | SSLSocketFactory | If set to a class that extends the javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory class, this class will be used to create SMTP SSL sockets. |
mail.smtp.ssl.socketFactory.class | String | If set, specifies the name of a class that extends the javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory class. This class will be used to create SMTP SSL sockets. |
mail.smtp.ssl.socketFactory.port | int | Specifies the port to connect to when using the specified socket factory. If not set, the default port will be used. |
mail.smtp.ssl.protocols | string | Specifies the SSL protocols that will be enabled for SSL connections. The property value is a whitespace separated list of tokens acceptable to the javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket.setEnabledProtocols method. |
mail.smtp.starttls.enable | boolean | If true, enables the use of the STARTTLS command (if supported by the server) to switch the connection to a TLS-protected connection before issuing any login commands. Defaults to false. |
mail.smtp.starttls.required | boolean | If true, requires the use of the STARTTLS command. If the server doesn't support the STARTTLS command, or the command fails, the connect method will fail. Defaults to false. |
mail.smtp.socks.host | string | Specifies the host name of a SOCKS5 proxy server that will be used for connections to the mail server. |
mail.smtp.socks.port | string | Specifies the port number for the SOCKS5 proxy server. This should only need to be used if the proxy server is not using the standard port number of 1080. |
mail.smtp.mailextension | String | Extension string to append to the MAIL command. |
mail.smtp.userset | boolean | If set to true, use the RSET command instead of the NOOP command in the isConnected method. In some cases sendmail will respond slowly after many NOOP commands; use of RSET avoids this sendmail issue. Defaults to false. |
一般情况下,应用程序应该不需要直接使用的类在这个包。相反,他们应该使用javax.mail的包定义的API(和子包)。例如说,应用程序不应该直接构造SMTPTransport的实例。相反,他们应该使用Session方法getTransport获得一个合适的Transport对象。
示例使用的SMTP服务器是体现在 发送邮件。
JavaMail IMAP服务器 - JavaMail
IMAP是缩写为Internet邮件访问协议。这是一个应用层互联网协议,它允许电子邮件客户端来访问邮件的远程服务器上的邮件。 IMAP服务器通常监听众所周知的端口143。 IMAP通过SSL(IMAPS)被分配为端口号993。
IMAP支持两种操作在线和离线模式。使用IMAP电子邮件客户端一般在服务器上保留邮件,直到用户显式删除它们。
包装com.sun.mail.imap是IMAP协议提供JavaMail API,它提供了访问一个IMAP邮件存储。下表列出了此提供程序的接口和类:
类/接口 | 描述 |
IMAPFolder.ProtocolCommand | This a simple interface for user-defined IMAP protocol commands. |
ACL | This is a class. An access control list entry for a particular authentication identifier (user or group). |
IMAPFolder | This class implements an IMAP folder. |
IMAPFolder.FetchProfileItem | This a class for fetching headers. |
IMAPMessage | This class implements an ReadableMime object. |
IMAPMessage.FetchProfileCondition | This class implements the test to be done on each message in the folder. |
IMAPSSLStore | This class provides access to an IMAP message store over SSL. |
IMAPStore | This class provides access to an IMAP message store. |
Rights | This class represents the set of rights for an authentication identifier (for instance, a user or a group). |
Rights.Right | This inner class represents an individual right. |
SortTerm | A particular sort criteria, as defined by RFC 5256. |
有几点要注意此提供以上:
- 提供同时支持IMAP4和的IMAP4rev1协议。
- 关连IMAPStore维护IMAP协议的对象池在与IMAP服务器进行通信的使用。为文件夹被打开,需要有新的IMAP协议的对象,如果没有可用,IMAPStore将为他们提供从连接池中,或者创建他们。当一个文件夹被关闭,其IMAP协议的对象被返回到连接池,如果池有创建过的对象。
- 该连接IMAPStore对象可能会或可能不会维持一个单独的IMAP协议的对象,它提供了存储专用连接到IMAP服务器。
IMAP协议提供程序支持以下属性,这些属性可以在JavaMail会话对象进行设置。该属性始终设置为字符串;类型列描述字符串是如何解释的。
名称 | 类型 | 描述 |
mail.imap.user | String | Default user name for IMAP. |
mail.imap.host | String | The IMAP server to connect to. |
mail.imap.port | int | The IMAP server port to connect to, if the connect() method doesn't explicitly specify one. Defaults to 143. |
mail.imap.partialfetch | boolean | Controls whether the IMAP partial-fetch capability should be used. Defaults to true. |
mail.imap.fetchsize | int | Partial fetch size in bytes. Defaults to 16K. |
mail.imap.ignorebodystructuresize | boolean | The IMAP BODYSTRUCTURE response includes the exact size of each body part. Normally, this size is used to determine how much data to fetch for each body part. Defaults to false. |
mail.imap.connectiontimeout | int | Socket connection timeout value in milliseconds. Default is infinite timeout. |
mail.imap.timeout | int | Socket I/O timeout value in milliseconds. Default is infinite timeout. |
mail.imap.statuscachetimeout | int | Timeout value in milliseconds for cache of STATUS command response. Default is 1000 (1 second). Zero disables cache. |
mail.imap.appendbuffersize | int | Maximum size of a message to buffer in memory when appending to an IMAP folder. |
mail.imap.connectionpoolsize | int | Maximum number of available connections in the connection pool. Default is 1. |
mail.imap.connectionpooltimeout | int | Timeout value in milliseconds for connection pool connections. Default is 45000 (45 seconds). |
mail.imap.separatestoreconnection | boolean | Flag to indicate whether to use a dedicated store connection for store commands. Default is false. |
mail.imap.auth.login.disable | boolean | If true, prevents use of the non-standard AUTHENTICATE LOGIN command, instead using the plain LOGIN command. Default is false. |
mail.imap.auth.plain.disable | boolean | If true, prevents use of the AUTHENTICATE PLAIN command. Default is false. |
mail.imap.auth.ntlm.disable | boolean | If true, prevents use of the AUTHENTICATE NTLM command. Default is false. |
mail.imap.proxyauth.user | String | If the server supports the PROXYAUTH extension, this property specifies the name of the user to act as. Authenticate to the server using the administrator's credentials. After authentication, the IMAP provider will issue the PROXYAUTH command with the user name specified in this property. |
mail.imap.localaddress | String | Local address (host name) to bind to when creating the IMAP socket. Defaults to the address picked by the Socket class. |
mail.imap.localport | int | Local port number to bind to when creating the IMAP socket. Defaults to the port number picked by the Socket class. |
mail.imap.sasl.enable | boolean | If set to true, attempt to use the javax.security.sasl package to choose an authentication mechanism for login. Defaults to false. |
mail.imap.sasl.mechanisms | String | A space or comma separated list of SASL mechanism names to try to use. |
mail.imap.sasl.authorizationid | String | The authorization ID to use in the SASL authentication. If not set, the authentication ID (user name) is used. |
mail.imap.sasl.realm | String | The realm to use with SASL authentication mechanisms that require a realm, such as DIGEST-MD5. |
mail.imap.auth.ntlm.domain | String | The NTLM authentication domain. |
mail.imap.auth.ntlm.flags | int | NTLM protocol-specific flags. |
mail.imap.socketFactory | SocketFactory | If set to a class that implements the javax.net.SocketFactory interface, this class will be used to create IMAP sockets. |
mail.imap.socketFactory.class | String | If set, specifies the name of a class that implements the javax.net.SocketFactory interface. This class will be used to create IMAP sockets. |
mail.imap.socketFactory.fallback | boolean | If set to true, failure to create a socket using the specified socket factory class will cause the socket to be created using the java.net.Socket class. Defaults to true. |
mail.imap.socketFactory.port | int | Specifies the port to connect to when using the specified socket factory. Default port is used when not set. |
mail.imap.ssl.enable | boolean | If set to true, use SSL to connect and use the SSL port by default. Defaults to false for the "imap" protocol and true for the "imaps" protocol. |
mail.imap.ssl.checkserveridentity | boolean | If set to true, check the server identity as specified by RFC 2595. Defaults to false. |
mail.imap.ssl.trust | String | If set, and a socket factory hasn't been specified, enables use of a MailSSLSocketFactory. If set to "*", all hosts are trusted. If set to a whitespace separated list of hosts, those hosts are trusted.Otherwise, trust depends on the certificate the server presents. |
mail.imap.ssl.socketFactory | SSLSocketFactory | If set to a class that extends the javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory class, this class will be used to create IMAP SSL sockets. |
mail.imap.ssl.socketFactory.class | String | If set, specifies the name of a class that extends the javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory class. This class will be used to create IMAP SSL sockets. |
mail.imap.ssl.socketFactory.port | int | Specifies the port to connect to when using the specified socket factory. If not set, the default port will be used. |
mail.imap.ssl.protocols | string | Specifies the SSL protocols that will be enabled for SSL connections. The property value is a whitespace separated list of tokens acceptable to the javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket.setEnabledProtocols method. |
mail.imap.starttls.enable | boolean | If true, enables the use of the STARTTLS command (if supported by the server) to switch the connection to a TLS-protected connection before issuing any login commands. Default is false. |
mail.imap.starttls.required | boolean | If true, requires the use of the STARTTLS command. If the server doesn't support the STARTTLS command, or the command fails, the connect method will fail. Defaults to false. |
mail.imap.socks.host | string | Specifies the host name of a SOCKS5 proxy server that will be used for connections to the mail server. |
mail.imap.socks.port | string | Specifies the port number for the SOCKS5 proxy server. This should only need to be used if the proxy server is not using the standard port number of 1080. |
mail.imap.minidletime | int | This property sets the delay in milliseconds. If not set, the default is 10 milliseconds. |
mail.imap.enableimapevents | boolean | Enable special IMAP-specific events to be delivered to the Store's ConnectionListener. If true, unsolicited responses received during the Store's idle method will be sent as ConnectionEvents with a type of IMAPStore.RESPONSE. The event's message will be the raw IMAP response string. By default, these events are not sent. |
mail.imap.folder.class | String | Class name of a subclass of com.sun.mail.imap.IMAPFolder. The subclass can be used to provide support for additional IMAP commands. The subclass must have public constructors of the form public MyIMAPFolder(String fullName, char separator, IMAPStore store, Boolean isNamespace) and public MyIMAPFolder(ListInfo li, IMAPStore store) |
一般情况下,应用程序应该不需要直接使用的类在这个包。相反,他们应该使用javax.mail包定义的API(和子包)。应用程序不应该兴建IMAPStore或IMAPFolder 的直接实例。相反,他们应该使用Session方法getStore获得适当的存储对象,并从获取文件夹对象。
示例使用IMAP服务器是体现在 限额管理.
JavaMail POP3服务器 - JavaMail
邮局协议(POP)是使用本地电子邮件客户端可以检索电子邮件从远程服务器通过TCP/ IP连接的应用层网络标准协议。 POP支持访问远程邮箱简单的下载和 - 删除要求。一个POP3服务器监听熟知端口110。
软件包com.sun.mail.pop3是POP3协议提供的JavaMail API,它提供了访问的POP3邮件存储。下表列出了类此包中:
名称 | 描述 |
POP3Folder | A POP3 Folder (can only be "INBOX"). |
POP3Message | A POP3 Message. |
POP3SSLStore | A POP3 Message Store using SSL. |
POP3Store | A POP3 Message Store. |
有几点要注意此提供以上:
- POP3提供程序只支持一个名为INBOX一个文件夹。由于POP3协议的限制,许多像事件通知,文件夹管理,标志管理等JavaMail的API的功能是不允许的。
- POP3提供通过的JavaMail API的使用协议名称POP3或以下形式的URL访问 pop3://user:password@host:port/INBOX".
- POP3支持没有永久的标志。例如,Flags.Flag.RECENT标志将永远不会被用于POP3邮件设置。它是由应用程序,以确定哪些是在一个POP3邮箱的新邮件。
- POP3不支持Folder.expunge()方法。删除并抹去消息,请将Flags.Flag.DELETED标志上的信息,并使用Folder.close(true)方法关闭文件夹。
- POP3不提供接收日期,所以getReceivedDate方法将返回null。
- 当被访问的POP3邮件的标题,在POP3提供程序使用top命令来获取所有标题,然后将其缓存。
- 当访问一个POP3邮件的内容时,POP3提供程序使用RETR命令来获取整个消息。
- POP3Message.invalidate方法可用于缓存的无效数据,但不关闭文件夹。
POP3协议提供程序支持以下属性,这些属性可以在JavaMail会话对象进行设置。该属性始终设置为字符串;类型列描述字符串是如何解释的。
名称 | 类型 | 描述 |
mail.pop3.user | String | Default user name for POP3. |
mail.pop3.host | String | The POP3 server to connect to. |
mail.pop3.port | int | The POP3 server port to connect to, if the connect() method doesn't explicitly specify one. Defaults to 110. |
mail.pop3.connectiontimeout | int | Socket connection timeout value in milliseconds. Default is infinite timeout. |
mail.pop3.timeout | int | Socket I/O timeout value in milliseconds. Default is infinite timeout. |
mail.pop3.rsetbeforequit | boolean | Send a POP3 RSET command when closing the folder, before sending the QUIT command. Default is false. |
mail.pop3.message.class | String | Class name of a subclass of com.sun.mail.pop3.POP3Message. The subclass can be used to handle (for example) non-standard Content-Type headers. The subclass must have a public constructor of the form MyPOP3Message(Folder f, int msgno) throws MessagingException. |
mail.pop3.localaddress | String | Local address (host name) to bind to when creating the POP3 socket. Defaults to the address picked by the Socket class. |
mail.pop3.localport | int | Local port number to bind to when creating the POP3 socket. Defaults to the port number picked by the Socket class. |
mail.pop3.apop.enable | boolean | If set to true, use APOP instead of USER/PASS to login to the POP3 server, if the POP3 server supports APOP. APOP sends a digest of the password rather than the clear text password. Defaults to false. |
mail.pop3.socketFactory | SocketFactory | If set to a class that implements the javax.net.SocketFactory interface, this class will be used to create POP3 sockets. |
mail.pop3.socketFactory.class | String | If set, specifies the name of a class that implements the javax.net.SocketFactory interface. This class will be used to create POP3 sockets. |
mail.pop3.socketFactory.fallback | boolean | If set to true, failure to create a socket using the specified socket factory class will cause the socket to be created using the java.net.Socket class. Defaults to true. |
mail.pop3.socketFactory.port | int | Specifies the port to connect to when using the specified socket factory. If not set, the default port will be used. |
mail.pop3.ssl.enable | boolean | If set to true, use SSL to connect and use the SSL port by default. Defaults to false for the "pop3" protocol and true for the "pop3s" protocol. |
mail.pop3.ssl.checkserveridentity | boolean | If set to true, check the server identity as specified by RFC 2595. Defaults to false. |
mail.pop3.ssl.trust | String | If set, and a socket factory hasn't been specified, enables use of a MailSSLSocketFactory. If set to "*", all hosts are trusted. If set to a whitespace separated list of hosts, those hosts are trusted. Otherwise, trust depends on the certificate the server presents. |
mail.pop3.ssl.socketFactory | SSLSocketFactory | If set to a class that extends the javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory class, this class will be used to create POP3 SSL sockets. |
mail.pop3.ssl.socketFactory.class | String | If set, specifies the name of a class that extends the javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory class. This class will be used to create POP3 SSL sockets. |
mail.pop3.ssl.socketFactory.port | int | Specifies the port to connect to when using the specified socket factory. If not set, the default port will be used. |
mail.pop3.ssl.protocols | string | Specifies the SSL protocols that will be enabled for SSL connections. The property value is a whitespace separated list of tokens acceptable to the javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket.setEnabledProtocols method. |
mail.pop3.starttls.enable | boolean | If true, enables the use of the STLS command (if supported by the server) to switch the connection to a TLS-protected connection before issuing any login commands. Defaults to false. |
mail.pop3.starttls.required | boolean | If true, requires the use of the STLS command. If the server doesn't support the STLS command, or the command fails, the connect method will fail. Defaults to false. |
mail.pop3.socks.host | string | Specifies the host name of a SOCKS5 proxy server that will be used for connections to the mail server. |
mail.pop3.socks.port | string | Specifies the port number for the SOCKS5 proxy server. |
mail.pop3.disabletop | boolean | If set to true, the POP3 TOP command will not be used to fetch message headers. Defaults to false. |
mail.pop3.forgettopheaders | boolean | If set to true, the headers that might have been retrieved using the POP3 TOP command will be forgotten and replaced by headers retrieved as part of the POP3 RETR command. Defaults to false. |
mail.pop3.filecache.enable | boolean | If set to true, the POP3 provider will cache message data in a temporary file rather than in memory. Messages are only added to the cache when accessing the message content. Message headers are always cached in memory (on demand). The file cache is removed when the folder is closed or the JVM terminates. Defaults to false. |
mail.pop3.filecache.dir | String | If the file cache is enabled, this property can be used to override the default directory used by the JDK for temporary files. |
mail.pop3.cachewriteto | boolean | Controls the behavior of the writeTo method on a POP3 message object. If set to true, and the message content hasn't yet been cached, and ignoreList is null, the message is cached before being written. Otherwise, the message is streamed directly to the output stream without being cached. Defaults to false. |
mail.pop3.keepmessagecontent | boolean | If this property is set to true, a hard reference to the cached content will be kept, preventing the memory from being reused until the folder is closed or the cached content is explicitly invalidated (using the invalidate method). Defaults to false. |
一般情况下,应用程序不应在此包中直接使用的类。相反,他们应该使用javax.mail的包定义的API(和子包)。应用程序不应该构建POP3Store或POP3Folder直接的实例。相反,他们应该使用Session方法getStore获得适当的存储对象,并从获取文件夹对象。
示例使用的POP3服务器是体现在 检查电子邮件.