导读:
Yogiyo 是韩国领先的移动和在线送餐平台,旨在为顾客提供更强大便捷的点餐服务。它是 Delivery Hero 的韩国分公司,直到 2021 年底被韩国十大上市公司之一的 GS Retail 以 6.84 亿美元收购。
本文来自 Yogiyo 研发中心从事 Orderyo(一种订购服务)的后端开发人员 Byungchul Kim,其团队最近为 Yogiyo 的订单服务使用了 Apache ShardingSphere。作者想通过本篇文章来分享来自 Yogiyo 的成功技术案例:如何用 Apache ShardingSphere 构建可扩展的订购服务?
订单服务数据库结构
为了解释背景,我想向你展示 Yogiyo 的订单服务的结构。下面是 Yogiyo 的订单服务的结构。
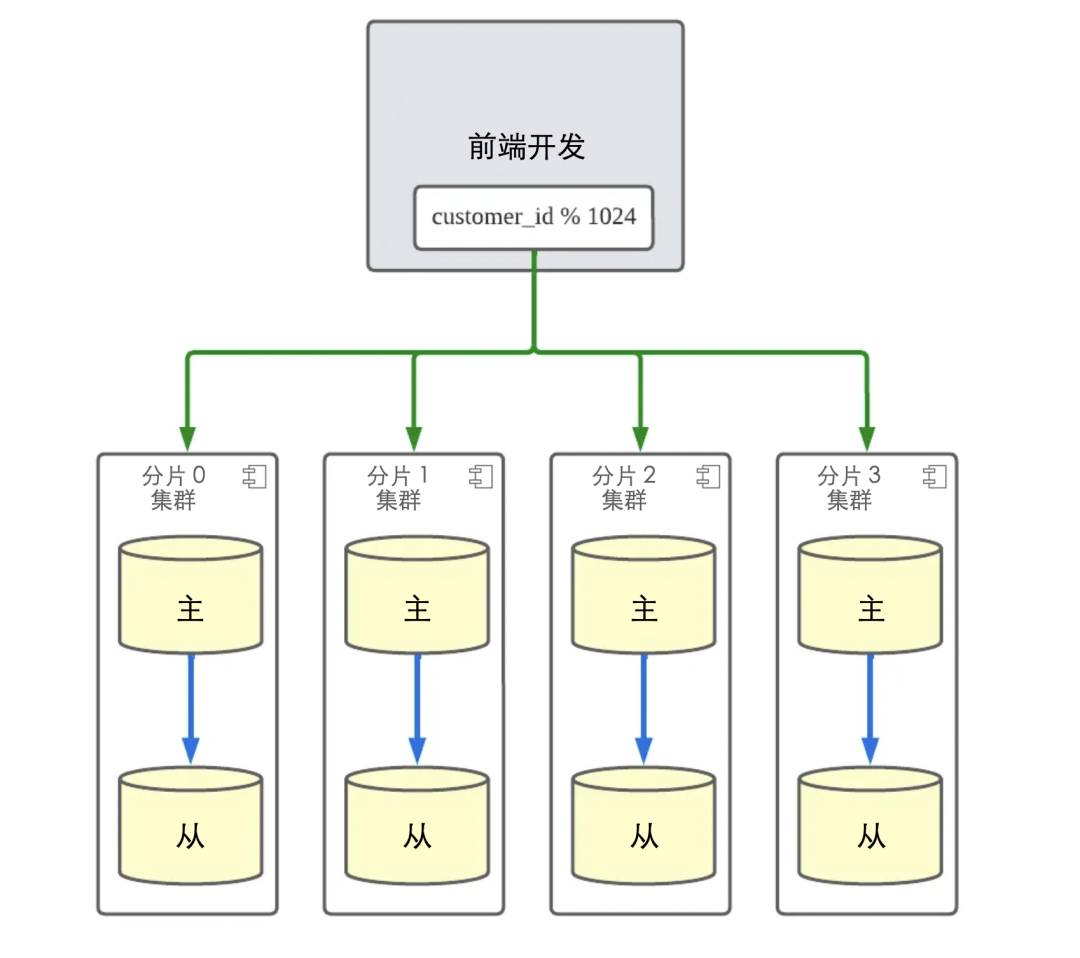
当订单创建/取消/更新流量发生时,Orderyo 应用程序代码通过基于客户 ID 的模块化操作将写入负载分配到四个分片集群。因此,应用程序只需要 customer_id 来找到它需要访问的分片集群并执行操作。
通过在订单服务中引入分片,基于 customer_id 的订单功能的整体响应时间得到了改善,并且通过分配 DB 负载,消除了数据库端的许多瓶颈问题。我们还可以将数据库扩展到适当的水平,以适应未来的流量增长。
然而,数据库分片并不全是好事。在过去一年为 Yogiyo 的订单服务实施和运行数据库分片的过程中,我们意识到有一个技术债务:DB 的结构要反映综合查询要求。订单服务功能的大部分流量都有 customer_id,所以我们使用分片 DB,但除此之外,我们还有订单的源数据,所以在面向运营和面向最高功能中,有一个没有分片键的综合查询要求。在过去的一年里,为了支持运营查询,我们通过从分片 DB 复制到一个单一的 DB(为了方便,我们称之为集成 DB)来收集数据,以实现查询。
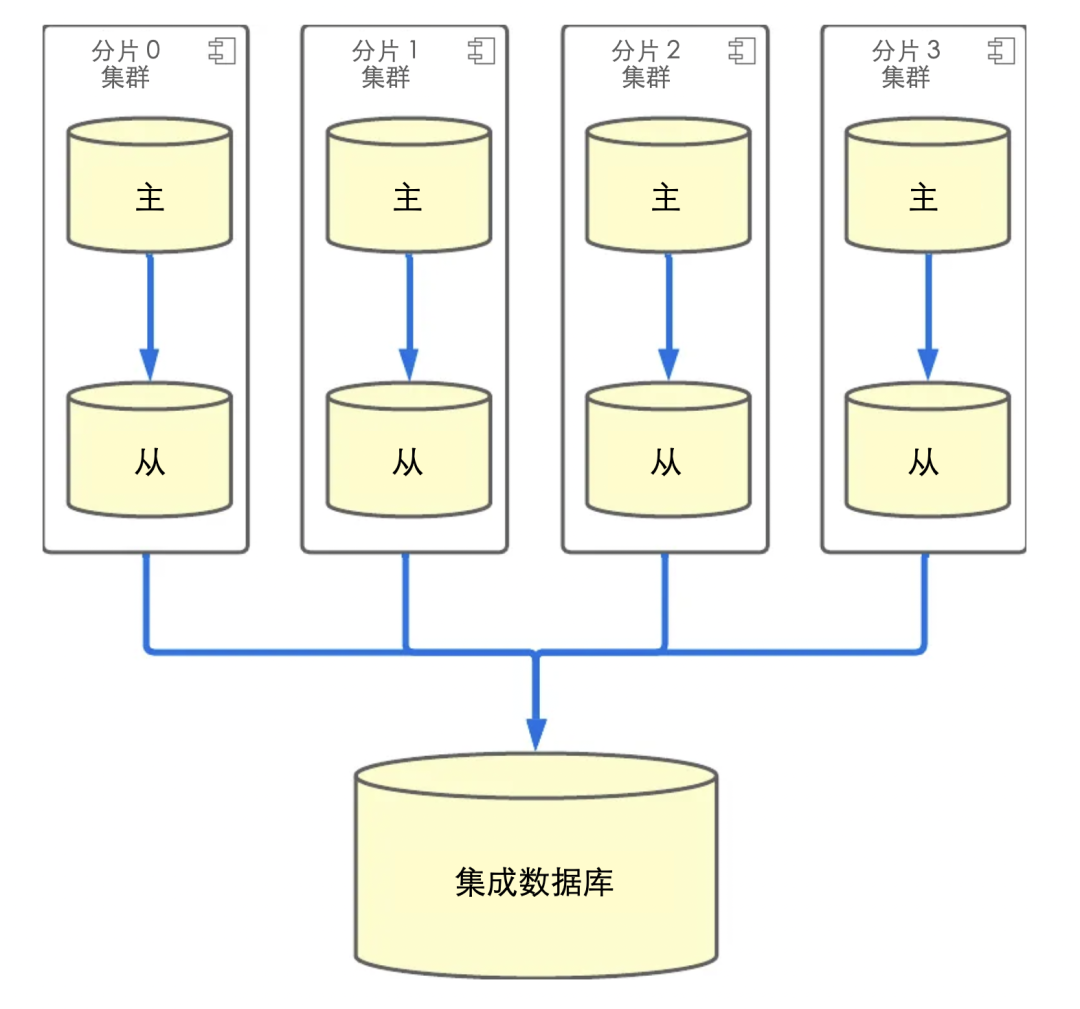
在这种结构中,随着分片的吞吐量增加,负载被放在单一的集成数据库上。因此,集成数据库成为一个瓶颈,而分片的优势之一--水平数据库扩展--就不复存在了。
支持面向商业侧功能的新要求
ShardingSphere-Proxy是如何被采用的
设置本地环境
[mysqld]
server_id=20
auto_increment_increment = 1024
auto_increment_offset = 1
[mysqld]
server_id=21
auto_increment_increment = 1024
auto_increment_offset = 2
######################################################################################################
#
# Here you can configure the rules for the proxy.
# This example is configuration of sharding rule.
#
# If you want to use sharding, please refer to this file;
# if you want to use master-slave, please refer to the config-master_slave.yaml.
#
######################################################################################################
databaseName: orderyo
dataSources:
ds_0:
url: jdbc:mysql://sharding-sphere-mysql-shard-0:3306/orderyo?serverTimezone=Asia/Seoul&useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: root
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
ds_1:
url: jdbc:mysql://sharding-sphere-mysql-shard-1:3306/orderyo?serverTimezone=Asia/Seoul&useSSL=false&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: root
connectionTimeoutMilliseconds: 30000
idleTimeoutMilliseconds: 60000
maxLifetimeMilliseconds: 1800000
maxPoolSize: 50
rules:
- !SHARDING
tables:
order_order:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.order_order
order_orderitem:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.order_orderitem
order_orderitemoption:
actualDataNodes: ds_${0..1}.order_orderitemoption
broadcastTables:
- django_admin_log,django_content_type,django_migrations,django_session
defaultShardingColumn: id
defaultDatabaseStrategy:
standard:
shardingColumn: id
shardingAlgorithmName: database-inline
defaultTableStrategy:
none:
shardingAlgorithms:
database-inline:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: ds_${id % 1024 - 1}
应用暂存环境
class IntegrationDatabaseWrapper:
def __call__(self, execute, sql, params, many, context):
db_alias = context["connection"].alias
if db_alias != settings.INTEGRATION_DB_READ_ONLY_NAME:
return execute(sql, params, many, context)
try:
integration_start = time.monotonic()
integration_result = execute(sql, params, many, context)
integration_execution_time = time.monotonic() - integration_start
except Exception as e:
raise e
else:
return integration_result
finally:
if config.INTEGRATION_DB_MODE == DatabaseMode.DUAL:
self._call_proxy_db(sql, params, integration_result, integration_execution_time)
def _call_proxy_db(self, sql, params, integration_result, integration_execution_time):
from django.db import connections
proxy_start = time.monotonic()
shardingsphere_cursor = connections[settings.SHARDINGSHPERE_PROXY_DB_READ_ONLY_NAME].cursor()
shardingsphere_result = shardingsphere_cursor.execute(sql, params)
shardingsphere_cursor.close()
proxy_execution_time = time.monotonic() - proxy_start
logger.info(....)
integration_db_wrapper = IntegrationDatabaseWrapper()
with connections[settings.INTEGRATION_DB_READ_ONLY_NAME].execute_wrapper(integration_db_wrapper):
do_queries()
1. 当数据库模式发生变化时,查询不工作。
2. 我们发现有些查询的结果与以前不同。
REFRESH TABLE METADATA;
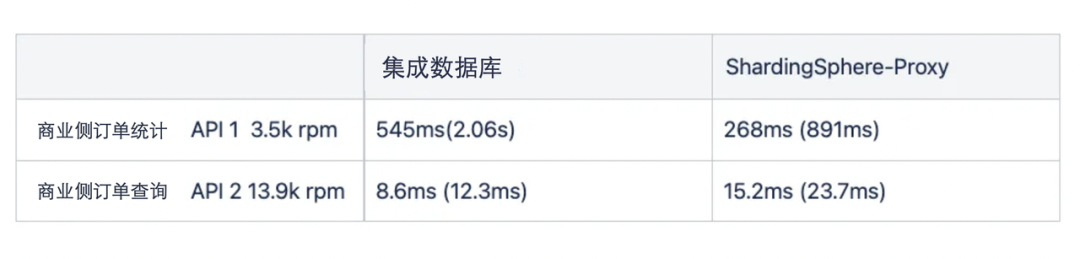
负载测试
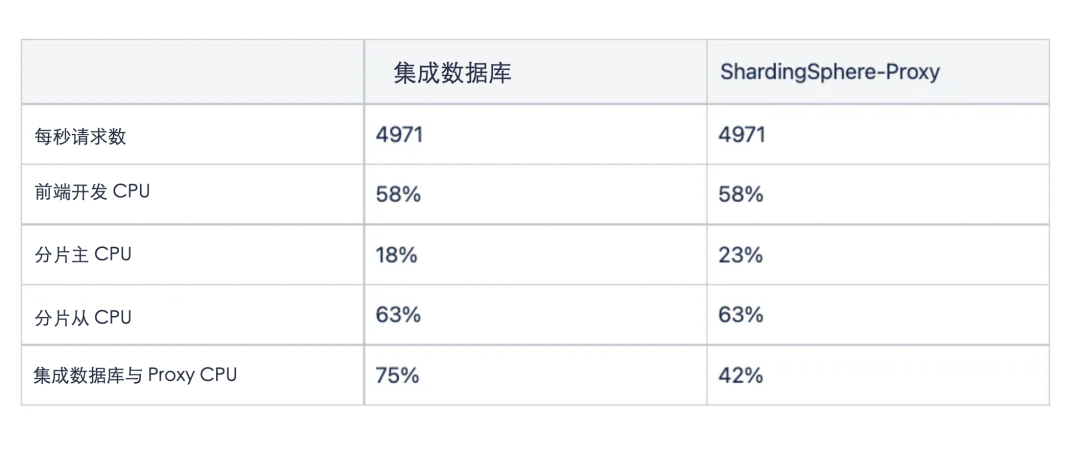
总结







